数据集:

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
print(data.head())

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.show() 
#数据预处理:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
#plt.show()
#预处理模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data['normAmount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1,1))
data=data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)#去掉这两列
print(data.head())
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
#plt.show()
#预处理模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data['normAmount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1,1))
data=data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)#去掉这两列
#print(data.head())
#数据切分
X=data.ix[:,data.columns!='Class']
y=data.ix[:,data.columns=='Class']
number_records_fraud=len(data[data.Class==1])
fraud_indices=np.array(data[data.Class==1].index)
normal_indices=data[data.Class==0].index
#通过索引进行随机选择
random_normal_indices=np.random.choice(normal_indices,number_records_fraud,replace=False)
random_normal_indices=np.array(random_normal_indices)
under_sample_indices=np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices])
#下采样
under_sample_data=data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:]
X_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns!='Class']
y_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns=="Class"]
print("Percentage of normal transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==0])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Percentage of fraud transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==1])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Total number of transactions in resampled data:",len(under_sample_data))

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
#plt.show()
#预处理模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data['normAmount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1,1))
data=data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)#去掉这两列
#print(data.head())
#数据切分
X=data.ix[:,data.columns!='Class']
y=data.ix[:,data.columns=='Class']
number_records_fraud=len(data[data.Class==1])
fraud_indices=np.array(data[data.Class==1].index)
normal_indices=data[data.Class==0].index
#通过索引进行随机选择
random_normal_indices=np.random.choice(normal_indices,number_records_fraud,replace=False)
random_normal_indices=np.array(random_normal_indices)
under_sample_indices=np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices])
#下采样
under_sample_data=data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:]
X_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns!='Class']
y_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns=="Class"]
print("Percentage of normal transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==0])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Percentage of fraud transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==1])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Total number of transactions in resampled data:",len(under_sample_data))
#交叉验证
#切分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#整体数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
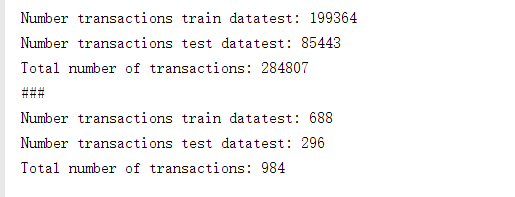
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train)+len(X_test))
#下采样数据集
X_train_undersample,X_test_undersample,y_train_undersample,y_test_undersample=train_test_split(X_undersample,y_undersample,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print("###")
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train_undersample))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test_undersample))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train_undersample)+len(X_test_undersample))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
#plt.show()
#预处理模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data['normAmount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1,1))
data=data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)#去掉这两列
#print(data.head())
#数据切分
X=data.ix[:,data.columns!='Class']
y=data.ix[:,data.columns=='Class']
number_records_fraud=len(data[data.Class==1])
fraud_indices=np.array(data[data.Class==1].index)
normal_indices=data[data.Class==0].index
#通过索引进行随机选择
random_normal_indices=np.random.choice(normal_indices,number_records_fraud,replace=False)
random_normal_indices=np.array(random_normal_indices)
under_sample_indices=np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices])
#下采样
under_sample_data=data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:]
X_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns!='Class']
y_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns=="Class"]
print("Percentage of normal transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==0])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Percentage of fraud transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==1])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Total number of transactions in resampled data:",len(under_sample_data))
#交叉验证
#切分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#整体数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train)+len(X_test))
#下采样数据集
X_train_undersample,X_test_undersample,y_train_undersample,y_test_undersample=train_test_split(X_undersample,y_undersample,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print("###")
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train_undersample))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test_undersample))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train_undersample)+len(X_test_undersample))
#recall召回率=TP/(TP+FN)
"""
true positivies(TP)正类判定为正类
false positivies(FP)负类判定为正类
false negatives(FN) 正类判定为负类
true negative(TN)负类判定为负类
例子:假如某个班级有男生80人,女生20人,共计100人,目标是
找出所有女生。现在某人挑选出50个人,其中20人是女生,另外还错误的
把30个男生也当作女生挑选出来了。
TP=20
FP=30
FN=0
TN=50
"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold,cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,classification_report
def printing_Kfold_scores(x_train_data,y_train_data):
fold = KFold(len(y_train_data),5,shuffle=False)
# Different C parameters
c_param_range = [0.01,0.1,1,10,100]
results_table = pd.DataFrame(index = range(len(c_param_range),2), columns = ['C_parameter','Mean recall score'])
results_table['C_parameter'] = c_param_range
# the k-fold will give 2 lists: train_indices = indices[0], test_indices = indices[1]
j = 0
for c_param in c_param_range:
print('-------------------------------------------')
print('C parameter: ', c_param)
print('-------------------------------------------')
print('')
recall_accs = []
for iteration, indices in enumerate(fold,start=1):
# Call the logistic regression model with a certain C parameter
lr = LogisticRegression(C = c_param, penalty = 'l1')
# Use the training data to fit the model. In this case, we use the portion of the fold to train the model
# with indices[0]. We then predict on the portion assigned as the 'test cross validation' with indices[1]
lr.fit(x_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:],y_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:].values.ravel())
# Predict values using the test indices in the training data
y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(x_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values)
# Calculate the recall score and append it to a list for recall scores representing the current c_parameter
recall_acc = recall_score(y_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values,y_pred_undersample)
recall_accs.append(recall_acc)
print('Iteration ', iteration,': recall score = ', recall_acc)
# The mean value of those recall scores is the metric we want to save and get hold of.
results_table.ix[j,'Mean recall score'] = np.mean(recall_accs)
j += 1
print('')
print('Mean recall score ', np.mean(recall_accs))
print('')
best_c = results_table.loc[results_table['Mean recall score'].idxmax()]['C_parameter']
# Finally, we can check which C parameter is the best amongst the chosen.
print('*********************************************************************************')
print('Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = ', best_c)
print('*********************************************************************************')
return best_c
best_c = printing_Kfold_scores(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample)
print(best_c)

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("creditcard.csv")
#print(data.head())
count_classes=pd.value_counts(data['Class'],sort=True).sort_index()
count_classes.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title("Fraud class histogram")
plt.xlabel("Class")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
#plt.show()
#预处理模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data['normAmount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1,1))
data=data.drop(['Time','Amount'],axis=1)#去掉这两列
#print(data.head())
#数据切分
X=data.ix[:,data.columns!='Class']
y=data.ix[:,data.columns=='Class']
number_records_fraud=len(data[data.Class==1])
fraud_indices=np.array(data[data.Class==1].index)
normal_indices=data[data.Class==0].index
#通过索引进行随机选择
random_normal_indices=np.random.choice(normal_indices,number_records_fraud,replace=False)
random_normal_indices=np.array(random_normal_indices)
under_sample_indices=np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices])
#下采样
under_sample_data=data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:]
X_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns!='Class']
y_undersample=under_sample_data.ix[:,under_sample_data.columns=="Class"]
print("Percentage of normal transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==0])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Percentage of fraud transactions:",len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class==1])/len(under_sample_data))
print("Total number of transactions in resampled data:",len(under_sample_data))
#交叉验证
#切分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#整体数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train)+len(X_test))
#下采样数据集
X_train_undersample,X_test_undersample,y_train_undersample,y_test_undersample=train_test_split(X_undersample,y_undersample,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print("###")
print("Number transactions train datatest:",len(X_train_undersample))
print("Number transactions test datatest:",len(X_test_undersample))
print("Total number of transactions:",len(X_train_undersample)+len(X_test_undersample))
#recall召回率=TP/(TP+FN)
"""
true positivies(TP)正类判定为正类
false positivies(FP)负类判定为正类
false negatives(FN) 正类判定为负类
true negative(TN)负类判定为负类
例子:假如某个班级有男生80人,女生20人,共计100人,目标是
找出所有女生。现在某人挑选出50个人,其中20人是女生,另外还错误的
把30个男生也当作女生挑选出来了。
TP=20
FP=30
FN=0
TN=50
"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold,cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,classification_report
def printing_Kfold_scores(x_train_data,y_train_data):
fold = KFold(len(y_train_data),5,shuffle=False)
# Different C parameters
c_param_range = [0.01,0.1,1,10,100]
results_table = pd.DataFrame(index = range(len(c_param_range),2), columns = ['C_parameter','Mean recall score'])
results_table['C_parameter'] = c_param_range
# the k-fold will give 2 lists: train_indices = indices[0], test_indices = indices[1]
j = 0
for c_param in c_param_range:
print('-------------------------------------------')
print('C parameter: ', c_param)
print('-------------------------------------------')
print('')
recall_accs = []
for iteration, indices in enumerate(fold,start=1):
# Call the logistic regression model with a certain C parameter
lr = LogisticRegression(C = c_param, penalty = 'l1')
# Use the training data to fit the model. In this case, we use the portion of the fold to train the model
# with indices[0]. We then predict on the portion assigned as the 'test cross validation' with indices[1]
lr.fit(x_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:],y_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:].values.ravel())
# Predict values using the test indices in the training data
y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(x_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values)
# Calculate the recall score and append it to a list for recall scores representing the current c_parameter
recall_acc = recall_score(y_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values,y_pred_undersample)
recall_accs.append(recall_acc)
print('Iteration ', iteration,': recall score = ', recall_acc)
# The mean value of those recall scores is the metric we want to save and get hold of.
results_table.ix[j,'Mean recall score'] = np.mean(recall_accs)
j += 1
print('')
print('Mean recall score ', np.mean(recall_accs))
print('')
best_c = results_table.loc[results_table['Mean recall score'].idxmax()]['C_parameter']
# Finally, we can check which C parameter is the best amongst the chosen.
print('*********************************************************************************')
print('Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = ', best_c)
print('*********************************************************************************')
return best_c
best_c = printing_Kfold_scores(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample)
#print(best_c)
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=0)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j],
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
import itertools
lr = LogisticRegression(C = best_c, penalty = 'l1')
lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel())
y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(X_test_undersample.values)
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test_undersample,y_pred_undersample)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1]))
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
class_names = [0,1]
plt.figure()
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix, classes=class_names, title='Confusion matrix')
plt.show()
lr = LogisticRegression(C = best_c, penalty = 'l1')
lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel())
y_pred = lr.predict(X_test.values)
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1]))
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
class_names = [0,1]
plt.figure()
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix
, classes=class_names
, title='Confusion matrix')
plt.show()
#用原始数据效果不如下采样
best_c = printing_Kfold_scores(X_train,y_train)
lr = LogisticRegression(C = best_c, penalty = 'l1')
lr.fit(X_train,y_train.values.ravel())
y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(X_test.values)
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred_undersample)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1]))
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
class_names = [0,1]
plt.figure()
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix
, classes=class_names
, title='Confusion matrix')
plt.show()
lr = LogisticRegression(C = 0.01, penalty = 'l1')
lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel())
y_pred_undersample_proba = lr.predict_proba(X_test_undersample.values)
thresholds = [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
j = 1
for i in thresholds:
y_test_predictions_high_recall = y_pred_undersample_proba[:,1] > i
plt.subplot(3,3,j)
j += 1
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test_undersample,y_test_predictions_high_recall)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1]))
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
class_names = [0,1]
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix
, classes=class_names
, title='Threshold >= %s'%i)
plt.show()



























 2069
2069











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










