集合技术在求解算法题中的应用
1 C# 和 Python 中的集合结构
集合技术在解题中主要用于处理有数据重复出现的问题。
HashSet<T>
C# 语言中 HashSet<T> 是包含不重复项的无序列表,称为“集合(set)”。由于set是一个保留字,所以用HashSet来表示。
源码:
HashSet的成员方法
-
public HashSet();-> 构造函数 -
public HashSet(IEnumerable<T> collection);-> 构造函数 -
public int Count { get; }-> 获取集合中包含的元素数。 -
public bool Add(T item);-> 将指定的元素添加到集合中。 -
public bool Remove(T item);-> 从集合中移除指定元素。 -
public void Clear();-> 从集合中移除所有元素。 -
public bool Contains(T item);-> 确定集合中是否包含指定的元素。 -
public void UnionWith(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 并集 -
public void IntersectWith(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 交集 -
public void ExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 差集 -
public bool IsSubsetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定当前集合是否为指定集合的子集。 -
public bool IsProperSubsetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定当前集合是否为指定集合的真子集。 -
public bool IsSupersetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定当前集合是否为指定集合的超集。 -
public bool IsProperSupersetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定当前集合是否为指定集合的真超集。 -
public bool Overlaps(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定是否当前集合和指定的集合共享通用元素。 -
public bool SetEquals(IEnumerable<T> other);-> 确定是否当前集合和指定集合包含相同的元素。
set
Python 中set与dict类似,也是一组key的集合,但不存储value。由于key不能重复,所以,在set中,没有重复的key。
注意,key为不可变类型,即可哈希的值。
num = {}
print(type(num)) # <class 'dict'>
num = {1, 2, 3, 4}
print(type(num)) # <class 'set'>
集合的创建
-
先创建对象再加入元素。
-
在创建空集合的时候只能使用
s = set(),因为s = {}创建的是空字典。
basket = set()
basket.add('apple')
basket.add('banana')
print(basket) # {'banana', 'apple'}
-
直接把一堆元素用花括号括起来
{元素1, 元素2, ..., 元素n}。 -
重复元素在
set中会被自动被过滤。
basket = {'apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange', 'banana'}
print(basket) # {'banana', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange'}
-
使用
set(value)工厂函数,把列表或元组转换成集合。
a = set('abracadabra')
print(a)
# {'r', 'b', 'd', 'c', 'a'}
b = set(("Google", "Lsgogroup", "Taobao", "Taobao"))
print(b)
# {'Taobao', 'Lsgogroup', 'Google'}
c = set(["Google", "Lsgogroup", "Taobao", "Google"])
print(c)
# {'Taobao', 'Lsgogroup', 'Google'}
-
去掉列表中重复的元素
lst = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 3, 1] temp = [] for item in lst: if item not in temp: temp.append(item) print(temp) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] a = set(lst) print(list(a)) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
从结果发现集合的两个特点:无序 (unordered) 和唯一 (unique)。
由于 set 存储的是无序集合,所以我们不可以为集合创建索引或执行切片(slice)操作,也没有键(keys)可用来获取集合中元素的值,但是可以判断一个元素是否在集合中。
访问集合中的值
-
可以使用
len()內建函数得到集合的大小。
thisset = set(['Google', 'Baidu', 'Taobao']) print(len(thisset)) # 3
-
可以使用
for把集合中的数据一个个读取出来。
thisset = set(['Google', 'Baidu', 'Taobao']) for item in thisset: print(item) # Baidu # Google # Taobao
-
可以通过
in或not in判断一个元素是否在集合中已经存在
thisset = set(['Google', 'Baidu', 'Taobao'])
print('Taobao' in thisset) # True
print('Facebook' not in thisset) # True
集合的内置方法
-
set.add(elmnt)-> 给集合添加元素,如果添加的元素在集合中已存在,则不执行任何操作。 -
set.update(set)-> 修改当前集合,可以添加新的元素或集合到当前集合中,如果添加的元素在集合中已存在,则该元素只会出现一次,重复的会忽略。 -
set.remove(item)-> 移除集合中的指定元素。如果元素不存在,则会发生错误。 -
set.discard(value)-> 移除指定的集合元素。remove()方法在移除一个不存在的元素时会发生错误,而discard()方法不会。 -
set.pop()-> 随机移除一个元素。 -
set.intersection(set1, set2 ...)-> 返回两个集合的交集。 -
set1 & set2返回两个集合的交集。 -
set.intersection_update(set1, set2 ...)-> 交集,在原始的集合上移除不重叠的元素。 -
set.union(set1, set2...)-> 返回两个集合的并集。 -
set1 | set2-> 返回两个集合的并集。 -
set.difference(set)-> 返回集合的差集。 -
set1 - set2-> 返回集合的差集。 -
set.difference_update(set)-> 集合的差集,直接在原来的集合中移除元素,没有返回值。 -
set.symmetric_difference(set)-> 返回集合的异或。 -
set1 ^ set2-> 返回集合的异或。 -
set.symmetric_difference_update(set)-> 移除当前集合中在另外一个指定集合相同的元素,并将另外一个指定集合中不同的元素插入到当前集合中。 -
set.issubset(set)-> 判断集合是不是被其他集合包含,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。 -
set1 <= set2-> 判断集合是不是被其他集合包含,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。 -
set.issuperset(set)-> 判断集合是不是包含其他集合,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。 -
set1 >= set2-> 判断集合是不是包含其他集合,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。 -
set.isdisjoint(set)-> 判断两个集合是不是不相交,如果是返回 True,否则返回 False。
frozenset
Python 提供了不能改变元素的集合的实现版本,即不能增加或删除元素,类型名叫frozenset。需要注意的是frozenset仍然可以进行集合操作,只是不能用带有update的方法。
-
frozenset([iterable])-> 返回一个冻结的集合,冻结后集合不能再添加或删除任何元素。
2 两个数组的交集
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2] 输出: [2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4] 输出: [9,4]
说明:
-
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
-
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
思路:直接利用集合这种结构
C# 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:276 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 96.33% 的用户
-
内存消耗:31.5 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
public class Solution
{
public int[] Intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2)
{
HashSet<int> h1 = new HashSet<int>(nums1);
HashSet<int> h2 = new HashSet<int>(nums2);
return h1.Intersect(h2).ToArray();
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:60 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 64.11% 的用户
-
内存消耗:13.8 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 20.00% 的用户
class Solution: def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]: h1 = set(nums1) h2 = set(nums2) return list(h1.intersection(h2))
3 存在重复元素
题号:217
难度:简单
给定一个整数数组,判断是否存在重复元素。
如果任何值在数组中出现至少两次,函数返回 true。如果数组中每个元素都不相同,则返回 false。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3,1] 输出: true
示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4] 输出: false
示例 3:
输入: [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2] 输出: true
思路:通过集合的方法
C# 语言
-
状态:通过
-
18 / 18 个通过测试用例
-
执行用时: 156 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 93.33% 的用户
-
内存消耗: 30.3 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.31% 的用户
public class Solution
{
public bool ContainsDuplicate(int[] nums)
{
if (nums.Length < 2)
return false;
HashSet<int> h = new HashSet<int>();
foreach (int num in nums)
{
if (h.Contains(num))
return true;
h.Add(num);
}
return false;
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 78.11% 的用户
-
内存消耗:18.9 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 24.00% 的用户
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
if len(nums) < 2:
return False
h = set()
for num in nums:
if num in h:
return True
h.add(num)
return False
4 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:

在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:

输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
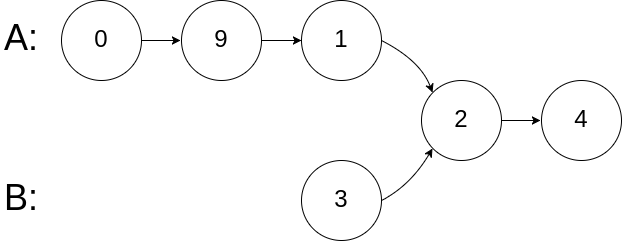
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Reference of the node with value = 2 输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:

输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。 由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
-
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
-
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
-
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
-
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
思路:通过集合的方法
C# 语言
-
状态:通过
-
45 / 45 个通过测试用例
-
执行用时: 172 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
-
内存消耗: 37.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.88% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public ListNode GetIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
HashSet<ListNode> hash = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null)
{
hash.Add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp != null)
{
if (hash.Contains(temp))
return temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:200 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 40.19% 的用户
-
内存消耗:29.4 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 5.00% 的用户
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> None: h = set() temp = headA while temp is not None: h.add(temp) temp = temp.next temp = headB while temp is not None: if temp in h: return temp temp = temp.next return None
5 环形链表
题号:141
难度:简单
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果pos是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
思路:通过集合的方法
通过检查一个结点此前是否被访问过来判断链表是否为环形链表。
C# 语言
-
状态:通过
-
执行用时:112 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 84.04% 的用户
-
内存消耗:26.5 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public bool HasCycle(ListNode head)
{
HashSet<ListNode> h = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
if (h.Contains(temp))
return true;
h.Add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
return false;
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:60 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 64.49% 的用户
-
内存消耗:17.3 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 9.52% 的用户
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
h = set()
temp = head
while temp is not None:
if temp in h:
return True
h.add(temp)
temp = temp.next
return False
6 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:tail connects to node index 1 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
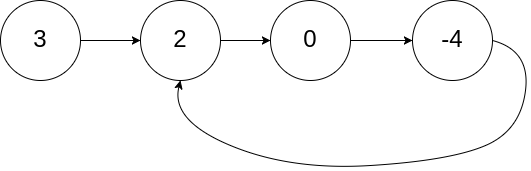
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:tail connects to node index 0 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。

示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:no cycle 解释:链表中没有环。

进阶:
你是否可以不用额外空间解决此题?
思路:通过集合的方法
C# 语言
-
状态:通过
-
16 / 16 个通过测试用例
-
执行用时: 140 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 82.93% 的用户
-
内存消耗: 26 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.00% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public ListNode DetectCycle(ListNode head)
{
HashSet<ListNode> h = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
if (h.Contains(temp))
return temp;
h.Add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:72 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 36.52% 的用户
-
内存消耗:17.2 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 7.69% 的用户
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: h = set() temp = head while temp is not None: if temp in h: return temp h.add(temp) temp = temp.next return None
7 快乐数
题号:202
难度:简单
编写一个算法来判断一个数是不是“快乐数”。
一个“快乐数”定义为:对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和,然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是无限循环但始终变不到 1。如果可以变为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
示例:
输入: 19 输出: true 解释: 1^2 + 9^2 = 82 8^2 + 2^2 = 68 6^2 + 8^2 = 100 1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1 输入:7 输出:true 输入: 20 输出: false 解释: 20 => 4 + 0 4 => 16 16 => 1 + 36 37 => 9 + 49 58 => 25 + 64 89 => 64 + 81 145 => 1 + 16 + 25 42 => 16 + 4 20 可以看到, 20再次重复出现了, 所以永远不可能等于1
思路:通过集合的方法
C# 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 80.74% 的用户
-
内存消耗:17 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
public class Solution
{
public bool IsHappy(int n)
{
HashSet<int> h = new HashSet<int>();
int m = 0;
while (true)
{
while (n != 0)
{
m += (int)Math.Pow(n % 10,2);
n /= 10;
}
if (m == 1)
{
return true;
}
if (h.Contains(m))
{
return false;
}
h.Add(m);
n = m;
m = 0;
}
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:40 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 79.79% 的用户
-
内存消耗:13.8 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 9.09% 的用户
class Solution: def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool: h = set() m = 0 while True: while n != 0: m += (n % 10) ** 2 n //= 10 if m == 1: return True if m in h: return False h.add(m) n = m m = 0
8 只出现一次的数字
题号:136
难度:简单
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1] 输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2] 输出: 4
思路:通过集合的方法
C# 语言
-
状态:通过
-
16 / 16 个通过测试用例
-
执行用时: 136 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 98.86% 的用户
-
内存消耗: 26.4 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.34% 的用户
public class Solution
{
public int SingleNumber(int[] nums)
{
HashSet<int> h = new HashSet<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
if (h.Contains(nums[i]))
{
h.Remove(nums[i]);
}
else
{
h.Add(nums[i]);
}
}
return h.ElementAt(0);
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:60 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 55.88% 的用户
-
内存消耗:15.6 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 5.26% 的用户
class Solution: def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: h = set() for num in nums: if num in h: h.remove(num) else: h.add(num) return list(h)[0]
9 不邻接植花
有 N 个花园,按从 1 到 N 标记。在每个花园中,你打算种下四种花之一。
paths[i] = [x, y] 描述了花园 x 到花园 y 的双向路径。
另外,没有花园有 3 条以上的路径可以进入或者离开。
你需要为每个花园选择一种花,使得通过边相连的任何两个花园中的花的种类互不相同。
以数组形式返回选择的方案作为答案 answer,其中 answer[i] 为在第 (i+1) 个花园中种植的花的种类。花的种类用 1, 2, 3, 4 表示。保证存在答案。
示例 1:
输入:N = 3, paths = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]] 输出:[1,2,3]
示例 2:
输入:N = 4, paths = [[1,2],[3,4]] 输出:[1,2,1,2]
示例 3:
输入:N = 4, paths = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,1],[1,3],[2,4]] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
思路:利用 字典 + 集合 构造图的邻接表。
C# 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:440 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
-
内存消耗:48.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
public class Solution
{
public int[] GardenNoAdj(int N, int[][] paths)
{
Dictionary<int, HashSet<int>> graph = new Dictionary<int, HashSet<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
graph.Add(i, new HashSet<int>());
}
foreach (int[] path in paths)
{
int i = path[0] - 1;
int j = path[1] - 1;
graph[i].Add(j);
graph[j].Add(i);
}
int[] result = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
bool[] visited = new bool[5];
foreach (int adj in graph[i])
{
visited[result[adj]] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
{
if (visited[j] == false)
{
result[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
Python 语言
-
执行结果:通过
-
执行用时:536 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 62.29% 的用户
-
内存消耗:20.6 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 33.33% 的用户
class Solution:
def gardenNoAdj(self, N: int, paths: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
graph = {i: set() for i in range(0, N)}
for path in paths:
i = path[0] - 1
j = path[1] - 1
graph[i].add(j)
graph[j].add(i)
result = [0] * N
for i in range(N):
visited = [False] * 5
for adj in graph[i]:
visited[result[adj]] = True
for j in range(1, 5):
if visited[j] is False:
result[i] = j
break
return result

























 761
761











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








