目录
一,题目描述
原题链接https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/
英文描述
Implement strStr().
Return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Clarification:
What should we return when needle is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when needle is an empty string. This is consistent to C's strstr() and Java's indexOf().
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
Output: 2Example 2:
Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
Output: -1Example 3:
Input: haystack = "", needle = ""
Output: 0
Constraints:
- 0 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 5 * 10^4
- haystack and needle consist of only lower-case English characters.
中文描述
实现 strStr() 函数。
给定一个 haystack 字符串和一个 needle 字符串,在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置 (从0开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1。
示例 1:
输入: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
输出: 2示例 2:
输入: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
输出: -1说明:
- 当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。
- 对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与C语言的 strstr() 以及 Java的 indexOf() 定义相符。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
二,解题思路
参考:
@Test【Sunday 解法】具体介绍了Sunday算法的实现;
@LoliconAutomaton【字符串匹配——Brute-Force、Sunday以及KMP算法】介绍了不同算法的区别,以及为什么有效;
@孤~影【(原创)详解KMP算法】详细介绍KMP算法原理;
1,Sunday算法
1.1 算法实现
图源@Test【Sunday 解法】。大佬讲解的十分清晰,就直接拿过来用了


1.2 算法原理
当模板字符串(pattern)与当前子串(curString)匹配失败后,需要考虑向右重新取出子串curString并与pattern进行比较;
普通的暴力解法是【老老实实的向右移一位】,再从当前位置取出新的子串;
Sunday算法就是计算出需要移动的最短距离,怎么理解最短呢?来举个栗子吧:
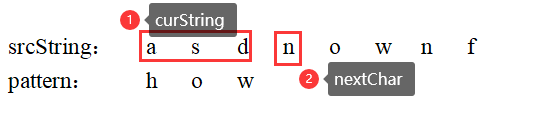
假设原字符串为srcString,当前字符串为curString,curString后一字符为nextChar,模式串为pattern;
例一:nextChar不在pattern中
当然可以跳过nextChar了,直接将指针锁定到nextChar的后一个位置,这里是4。
最短移动距离为pattern.size() + 1:
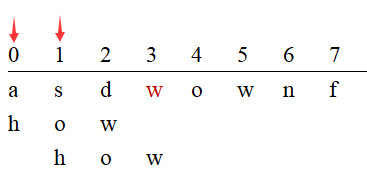
例二:nextChar为pattern最后一个字符
猜测最好的结果是,向右移动一位正好能完全匹配,所以最短移动距离为1;
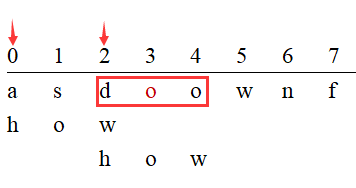
例三:nextChar为pattern倒数第二个字符
猜测最好的结果,红框中的字符串就是pattern,所以最短移动距离是2;
例四:pattern中有重复的字符
在算法实现中写道:【存储每一个在 模式串 中出现的字符,在 模式串 中出现的最右位置到尾部的距离 +1】。
所以这里最短距离为1,而不是3,这样就不会错过正确答案了。
2,KMP算法
参考@孤~影【(原创)详解KMP算法】,讲的非常详细!下面将关键部分摘抄下来,作为记录。

public static int[] getNext(String ps) {
char[] p = ps.toCharArray();
int[] next = new int[p.length];
next[0] = -1;
int j = 0;
int k = -1;
while (j < p.length - 1) {
if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) {
next[++j] = ++k;
} else {
k = next[k];
}
}
return next;
}



三,AC代码
Sunday算法
C++
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
unordered_map<char, int> shift;
int index = 0;
// 生成偏移表
for(int i = 0; i < needle.size(); i++) {
shift[needle[i]] = needle.size() - i;
}
while(index + needle.size() <= haystack.size()) {
// 匹配成功,返回下标
if(haystack.substr(index, needle.size()) == needle) return index;
// 当前子串后一个字符的位置
int nextCharIndex = index + needle.size();
// 超出原字符串范围,返回-1
if(nextCharIndex >= haystack.size()) return -1;
if(shift.find(haystack[nextCharIndex]) == shift.end()) {
index = index + needle.size() + 1;
} else {
index += shift[haystack[nextCharIndex]];
}
}
return -1;
}
};Java
字符串中字符的定位要用s.charAt(index);
字符串截取函数substring()的两个参数是左右边界,和C++的substr不同;
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
// 这里使用Integer代替int,否则会报错
Map<String, Integer> shift = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < needle.length(); i++) {
shift.put(String.valueOf(needle.charAt(i)), needle.length() - i);
}
while(index + needle.length() <= haystack.length()) {
// 匹配成功,返回下标.这里判断字符串内容是否相同,要用equals函数
// StringBuilder curString = new StringBuilder(haystack.substring(index, index + needle.length()));
// if(needle.equals(curString.toString())) return index;
if(needle.equals(haystack.substring(index, index + needle.length()))) return index;
// 当前子串后一个字符的位置
int nextCharIndex = index + needle.length();
// 超出原字符串范围,返回-1
if(nextCharIndex >= haystack.length()) return -1;
// 当前子串后一个字符的值
String key = String.valueOf(haystack.charAt(nextCharIndex));
if(shift.get(key) == null) {
index = index + needle.length() + 1;
} else {
index += shift.get(key);
}
}
return -1;
}
}KMP算法
C++
注意size()函数返回无符号数,与有符号数相比时,需要强制转化
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getNext(string ps) {
vector<int> next(ps.size(), -1); // 初始化next数组为-1
if(ps.size() == 0) return next; // 当字符串为空时 直接返回数组 避免在while中访问越界
int j = 0, k = -1;
while(j < ps.size() - 1) {
if(k == -1 || ps[j] == ps[k]) {
if(ps[++j] != ps[++k]) {
next[j] = k;
} else {
next[j] = next[k];
}
} else if(ps[j] != ps[k]) {
k = next[k]; // 第k个字符不匹配时将[需要偏移的位置]重新赋值给k next[k]小于k,所以看起来是在回溯
}
}
return next;
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;// i为主串指针 j为子串指针
vector<int> next = getNext(needle);
// C++中有符号数和无符号数比较时,默认先将有符号数转换为无符号数再比较
// 由于j可能为负,所以这里需要对needle.size()进行强制转换,确保条件正确
while(i < haystack.size() && j < int(needle.size())) {
if(j == -1 || haystack[i] == needle[j]) {
i++;
j++;
} else {
j = next[j];
}
}
if(j == needle.size()) {
return i - j;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
};Java
class Solution {
public static int[] getNext(String ps) {
char[] p = ps.toCharArray();
int[] next = new int[p.length];
if(p.length == 0) return next;
next[0] = -1;
int j = 0;
int k = -1;
while (j < p.length - 1) {
if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) {
if(p[++j] != p[++k]) {
next[j] = k;
} else {
next[j] = next[k];
}
} else {
k = next[k];
}
}
return next;
}
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
char[] t = haystack.toCharArray();
char[] p = needle.toCharArray();
int i = 0; // 主串的位置
int j = 0; // 模式串的位置
int[] next = getNext(needle);
while (i < t.length && j < p.length) {
if (j == -1 || t[i] == p[j]) { // 当j为-1时,要移动的是i,当然j也要归0
i++;
j++;
} else {
j = next[j]; // j回到指定位置
}
}
if (j == p.length) {
return i - j;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}四,解题过程
第一博
俺也一样ε(┬┬﹏┬┬)3
总之先老规矩,暴力一波
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
for(int i = 0; i + needle.size() <= haystack.size(); i++) {
if(haystack.substr(i, needle.size()) == needle) return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
你是否有很多问号?
别问,问就是不知道(⓿_⓿)
第二搏
使用sunday算法。。。

第三搏
使用KMP算法。。。

























 140
140











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








