堆是你见过的最有个性的树!它是用数组表示的树。
父节点:(i-1)/2
左子节点:2i+1
右子节点:2i+2
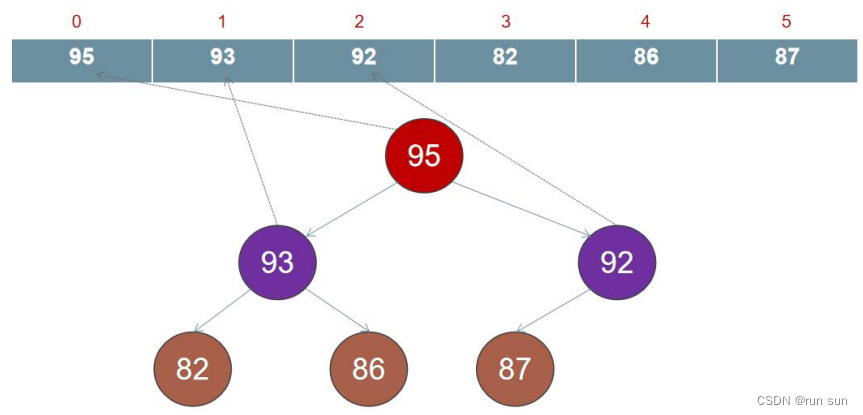
最大堆特点:
1.每个节点最多可以有两个节点。
2.根结点的键值是所有堆结点键值中最大者,且每个结点的值都比其孩子的值大。
2.除了根节点没有兄弟节点,最后一个左子节点可以没有兄弟节点,其他节点必须有兄弟节点。
最大堆
结构定义
#define DEFAULT_CAPACITY 128
typedef struct _Heap {
int* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}Heap;初始化
bool initHeap(Heap& heap, int* orginal, int size) {
int capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY > size ? DEFAULT_CAPACITY : size;
heap.arr = new int[capacity];
if (!heap.arr) return false;
heap.capacity = capacity;
heap.size = 0;
//如果存在原始数据则构建堆
if (size > 0) {
/*方式一: 直接调整所有元素
memcpy(heap.arr, orginal, size*sizeof(int));
heap.size = size;
//建堆
buildHeap(heap);
*/
//方式二: 一次插入一个
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
insert(heap, orginal[i]);
}
}
return true;
}建堆
/* 从最后一个父节点(size/2-1 的位置)逐个往前调整所有父节点(直到根节
点),确保每一个父节点都是一个最大堆,最后整体上形成一个最大堆*/
void buildHeap(Heap& heap) {
for (int i = heap.size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(heap, i);
}
}将当前节点和子节点调整成最大堆
void adjustDown(Heap& heap, int index)
{
int cur = heap.arr[index];//当前待调整的节点
int parent, child;
/*判断否存在大于当前节点子节点,如果不存在 ,则堆本身是平衡的,不
需要调整;
如果存在,则将最大的子节点与之交换,交换后,如果这个子节点还有子节
点,则要继续
按照同样的步骤对这个子节点进行调整
*/
for (parent = index; (parent * 2 + 1) < heap.size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2 + 1;
//取两个子节点中的最大的节点
if (((child + 1) < heap.size) && (heap.arr[child] < heap.arr[child +
1])) {
child++;
}
//判断最大的节点是否大于当前的父节点
if (cur >= heap.arr[child]) {//不大于,则不需要调整,跳出循环
break;
}
else {//大于当前的父节点,进行交换,然后从子节点位置继续向下调整
heap.arr[parent] = heap.arr[child];
heap.arr[child] = cur;
}
}
}将当前节点和父节点调整成最大堆
void adjustUp(Heap& heap, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= heap.size) {//大于堆的最大值直接 return
return;
}
while (index > 0) {
int temp = heap.arr[index];
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
if (parent >= 0) {//如果索引没有出界就执行想要的操作
if (temp > heap.arr[parent]) {
heap.arr[index] = heap.arr[parent];
heap.arr[parent] = temp;
index = parent;
}
else {//如果已经比父亲小 直接结束循环
break;
}
}
else {//越界结束循环
break;
}
}
}最大堆尾部插入节点
bool insert(Heap& heap, int value) {
if (heap.size == heap.capacity) {
fprintf(stderr, "栈空间耗尽!\n");
return false;
}
int index = heap.size;
heap.arr[heap.size++] = value;
adjustUp(heap, index);
return true;
}测试
int main(void) {
Heap hp;
int origVals[] = { 1, 2, 3, 87, 93, 82, 92, 86, 95 };
int i = 0;
if (!initHeap(hp, origVals, sizeof(origVals) / sizeof(origVals[0]))) {
fprintf(stderr, "初始化堆失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
for (i = 0; i < hp.size; i++) {
printf("the %dth element:%d\n", i, hp.arr[i]);
}
insert(hp, 99);
printf("在堆中插入新的元素 99,插入结果:\n");
for (i = 0; i < hp.size; i++) {
printf("the %dth element:%d\n", i, hp.arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}优先队列
如果最小键值元素拥有最高的优先级,那么这种优先队列叫作升序优先队列(即总是先删除最小 的元素),类似的,如果最大键值元素拥有最高的优先级,那么这种优先队列叫作降序优先队列 (即总是先删除最大的元素);由于这两种类型是完全对称的,所以只需要关注其中一种,如升 序优先队列。
#include <iostream>
#define DEFAULT_CAPCITY 128
typedef int DataType;
#define isLess(a,b) (a<b)
typedef struct _PriorityQueue {
DataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}PriorityQueue;
bool init(PriorityQueue& pq, int* orginal, int size);
bool push(PriorityQueue& pq, DataType value);
bool pop(PriorityQueue& pq, DataType& value);
bool isEmpty(PriorityQueue& pq);
bool isFull(PriorityQueue& pq);
void destroy(PriorityQueue& pq);
static void build(PriorityQueue& pq);
static void adjustDown(PriorityQueue& pq, int index);
static void adjustUp(PriorityQueue& pq, int index);
bool init(PriorityQueue& pq, DataType* orginal, int size) {
int capacity = DEFAULT_CAPCITY > size ? DEFAULT_CAPCITY : size;
pq.arr = new DataType[capacity];
if (!pq.arr) return false;
pq.capacity = capacity;
pq.size = 0;
if (size > 0) {
memcpy(pq.arr, orginal, size * sizeof(int));
pq.size = size;
build(pq);
}
return true;
}
void destroy(PriorityQueue& pq) {
if (pq.arr) delete[] pq.arr;
}
bool isEmpty(PriorityQueue& pq) {
if (pq.size < 1) return true;
return false;
}
bool isFull(PriorityQueue& pq) {
if (pq.size < pq.capacity) return false;
return true;
}
int size(PriorityQueue& pq) {
return pq.size;
}
void build(PriorityQueue& pq) {
int i;
for (i = pq.size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(pq, i);
}
}
/*将当前的节点和子节点调整成最大堆*/
void adjustDown(PriorityQueue& pq, int index)
{
DataType cur = pq.arr[index];//当前待调整的节点
int parent, child;
for (parent = index; (parent * 2 + 1) < pq.size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2 + 1;
//取两个子节点中的最大的节点
if (((child + 1) < pq.size) && isLess(pq.arr[child], pq.arr[child
+ 1])) {
child++;
}
//判断最大的节点是否大于当前的父节点
if (isLess(pq.arr[child], cur)) {//不大于,则不需要调整,跳出循环
break;
}
else {//大于当前的父节点,进行交换,然后从子节点位置继续向下调整
pq.arr[parent] = pq.arr[child];
pq.arr[child] = cur;
}
}
}
/*将当前的节点和父节点调整成最大堆*/
void adjustUp(PriorityQueue& pq, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= pq.size) {//大于堆的最大值直接 return
return;
}
while (index > 0) {
DataType temp = pq.arr[index];
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
if (parent >= 0) {//如果索引没有出界就执行想要的操作
if (isLess(pq.arr[parent], temp)) {
pq.arr[index] = pq.arr[parent];
pq.arr[parent] = temp;
index = parent;
}
else {//如果已经比父亲小 直接结束循环
break;
}
}
else {//越界结束循环
break;
}
}
}
/* 删除优先队列中最大的节点,并获得节点的值*/
bool pop(PriorityQueue& pq, DataType& value) {
if (isEmpty(pq)) return false;
value = pq.arr[0];
pq.arr[0] = pq.arr[--pq.size];
adjustDown(pq, 0);
return true;
}
/*优先队列中插入节点*/
bool push(PriorityQueue& pq, DataType value) {
if (isFull(pq)) {
fprintf(stderr, "优先队列空间耗尽!\n");
return false;
}
int index = pq.size;
pq.arr[pq.size++] = value;
adjustUp(pq, index);
return true;
}
int main(void) {
PriorityQueue pq;
int task[] = { 1, 2, 3, 87, 93, 82, 92, 86, 95 };
int i = 0;
if (!init(pq, task, sizeof(task) / sizeof(task[0]))) {
fprintf(stderr, "初始化优先队列失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
for (i = 0; i < pq.size; i++) {
printf("the %dth task:%d\n", i, pq.arr[i]);
}
//堆中插入优先级为 88 的任务
push(pq, 88);
//堆中元素出列
printf("按照优先级出列:\n");
DataType value;
while (pop(pq, value)) {
printf(" %d\n", value);
}
destroy(pq);
system("pause");
return 0;
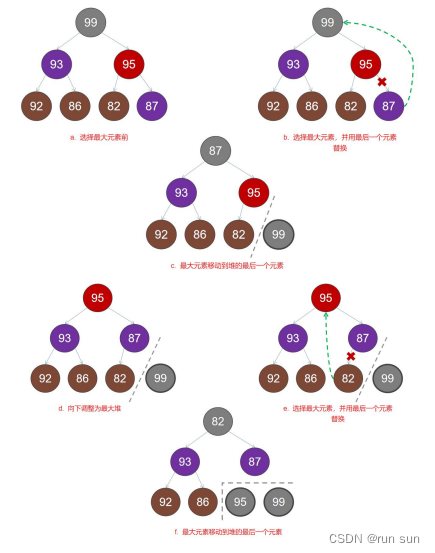
}堆排序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct _Heap {
int* arr; //存储堆元素的数组
int size; //当前已存储的元素个数
int capacity; //当前存储的容量
}Heap;
bool initHeap(Heap& heap, int* orginal, int size);
bool popMax(Heap& heap, int& value);
void heapSort(Heap& heap);
static void buildHeap(Heap& heap);
static void adjustDown(Heap& heap, int index);
/*初始化堆*/
bool initHeap(Heap& heap, int* orginal, int size) {
//heap.arr = new int[capacity];
heap.arr = orginal;
if (!heap.arr) return false;
heap.capacity = size;
heap.size = size;
//如果存在原始数据则构建堆
if (size > 0) {
//方式一: 直接调整所有元素
//建堆
buildHeap(heap);
}
return true;
}
/* 从最后一个父节点(size/2-1 的位置)逐个往前调整所有父节点(直到根节
点), 确保每一个父节点都是一个最大堆,最后整体上形成一个最大堆 */
void buildHeap(Heap& heap) {
int i;
for (i = heap.size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(heap, i);
}
}
/*将当前的节点和子节点调整成最大堆*/
void adjustDown(Heap & heap, int index)
{
int cur = heap.arr[index];//当前待调整的节点
int parent, child;
/*判断否存在大于当前节点子节点,如果不存在 ,则堆本身是平衡的,不
需要调整;
如果存在,则将最大的子节点与之交换,交换后,如果这个子节点还有子节
点,则要继续
按照同样的步骤对这个子节点进行调整
*/
for (parent = index; (parent * 2 + 1) < heap.size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2 + 1;
//取两个子节点中的最大的节点
if (((child + 1) < heap.size) && (heap.arr[child] < heap.arr[child + 1])) {
child++;
}
//判断最大的节点是否大于当前的父节点
if (cur >= heap.arr[child]) {//不大于,则不需要调整,跳出循环
break;
}
else {//大于当前的父节点,进行交换,然后从子节点位置继续向下调整
heap.arr[parent] = heap.arr[child];
heap.arr[child] = cur;
}
}
}
/* 实现堆排序 */
void heapSort(Heap& heap) {
if (heap.size < 1) return;
while (heap.size > 0) {
int tmp = heap.arr[0];
heap.arr[0] = heap.arr[heap.size - 1];
heap.arr[heap.size - 1] = tmp;
heap.size--;
adjustDown(heap, 0);// 向下执行堆调整
}
}
/* 删除最大的节点,并获得节点的值*/
bool popMax(Heap& heap, int& value) {
if (heap.size < 1) return false;
value = heap.arr[0];
heap.arr[0] = heap.arr[--heap.size];
//heap.arr[0] = heap.arr[heap.size-1];
//heap.size--;
adjustDown(heap, 0);// 向下执行堆调整
return true;
}
int main(void) {
Heap hp;
int origVals[] = { 1, 2, 3, 87, 93, 82, 92, 86, 95 };
int i = 0;
if (!initHeap(hp, origVals, sizeof(origVals) / sizeof(origVals[0]))) {
fprintf(stderr, "初始化堆失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
for (i = 0; i < hp.size; i++) {
printf("the %dth element:%d\n", i, hp.arr[i]);
}
//执行堆排序
heapSort(hp);
printf("堆排序后的结果:\n");
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(origVals) / sizeof(origVals[0]); i++) {
printf(" %d", origVals[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}






















 1511
1511











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










