

比较方式:
“==”
is
in
not in
id()
条件测试:
if 条件测试:
python中的真假
1.任何非零数字和非控对象都为真;
2.数字0、空对象和特殊对象None均为假
3.比较和相等测试会递归地应用于数据结构种;
4.返回值为True或False
组合条件测试:
X and Y :与运算
X or Y : 或运算
not X :非运算
if的语法结构

if x:
expression
elif :
expression
else:
expression

expression1 if boolean_expression else expression2
A=X if Y else Z
if Y:
A =X
else
A=Z

循环机制以及应用场景 
while 循环


while boolean_expression:
while boolean_expression:
expression
print()
else:
print()
break :调出最内层的循环
continue:跳到所处的最近层循环的开始处。跳过本次循环。```
pass:点位语句
else代码块:循环正常终止才能执行,如果循环终止是由break调出所导致的,则else代码块不会执行。
url=“xiaopanglikeyellowmangguo”
while url:
… print(url)
… url=url[:-1]
… else:
… print(“xiaopanglikexiaohe”)
…
xiaopanglikeyellowmangguo
xiaopanglikeyellowmanggu
xiaopanglikeyellowmangg
xiaopanglikeyellowmang
xiaopanglikeyellowman
xiaopanglikeyellowma
xiaopanglikeyellowm
xiaopanglikeyellow
xiaopanglikeyello
xiaopanglikeyell
xiaopanglikeyel
xiaopanglikeye
xiaopanglikey
xiaopanglike
xiaopanglik
xiaopangli
xiaopangl
xiaopang
xiaopan
xiaopa
xiaop
xiao
xia
xi
x
xiaopanglikexiaohe
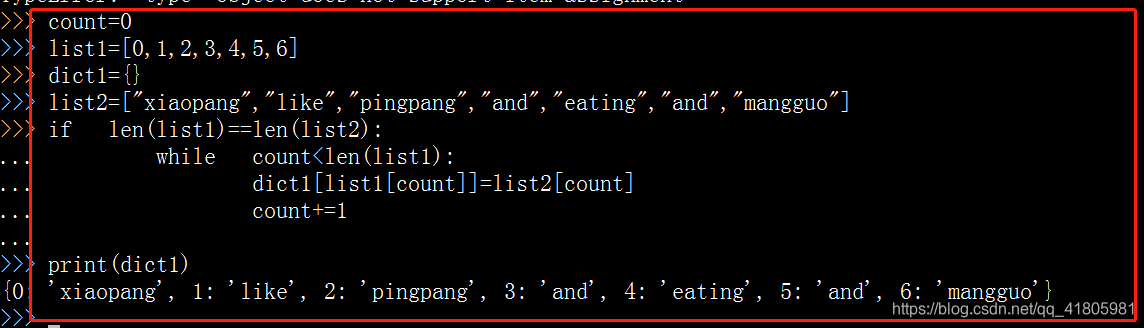
练习:l列表list1=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6] 列表list2=["xiaopang","like","pingpang","and","eating","and","mangguo"]
将两个列表合并成一一个字典,以第一个列表中的元素为键,第二个列表中的元素为值。
count=0
list1=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
dict1={}
list2=["xiaopang","like","pingpang","and","eating","and","mangguo"]
if len(list1)==len(list2):
while count<len(list1):
dict1[list1[count]]=list2[count]
count+=1
print(dict1)
# for循环
url=“xiaopanglikexiaoheandxiaohelikexiaopang”
for x in url:
… print(x)
…
for i in url:
… print(i)
’‘’
python2:

编写循环的技巧
>>> dict1={"z":1,"a":123,"c":1256}
>>> for (k,v) in dict1.items(): print(k,v)
...
z 1
a 123
c 1256



并行遍历

回顾
1.动态语言
sys.getrefcount()
增加对象的引用技术场景:
1.对象创建时
2.将对象添加到容器时:类似ist.append()
3.当对象被当作参数传递给函数时
4.为对象创建为另外的变量名
减少引用计数:
1.引用此对象的某变量名被显示销毁
2.给引用此对象的某变量名重新赋值
3.从容器中移除对象时候
4.容器本身被销毁
2.if
if boolean_expression:
…
elif boolean_expression:
…
else:
…
3.while
while boolean_expression:
while_suite
if boolean_expression2:continue
if boolean_expression3:break
else:
else_suite
4.for
for expression in object:
for_suite
if boolean_expression2:continue
if boolean_expression3:break
else:
else_suite






















 8987
8987











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








