模版
// 结果集合
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 路径集合
public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> model(int[] nums) {
// 根据是否需要指定开始位置进行传参
backtracking(nums,0);
return res;
}
public void show(int []nums,int index){
// 根据结果叶子节点还是节点进行结果收集
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
//根据 是否需要依赖上一位置进行遍历
for(int i=index;i<nums.length;i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums,i+1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
待选元素互不相同
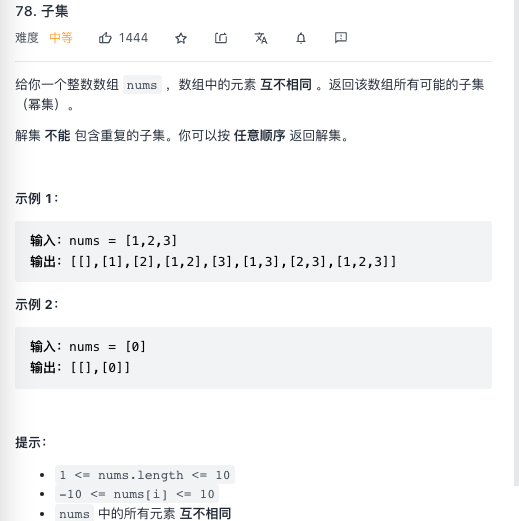
数组元素互不相同,所以不需要考虑去重的问题
收集的结果应该是递归树中的每一个节点,所以在进入回溯函数之后就直接收集结果
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
backtracking(nums,0);
return res;
}
public void show(int []nums,int index){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
for(int i=index;i<nums.length;i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums,i+1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
待选元素可能相同
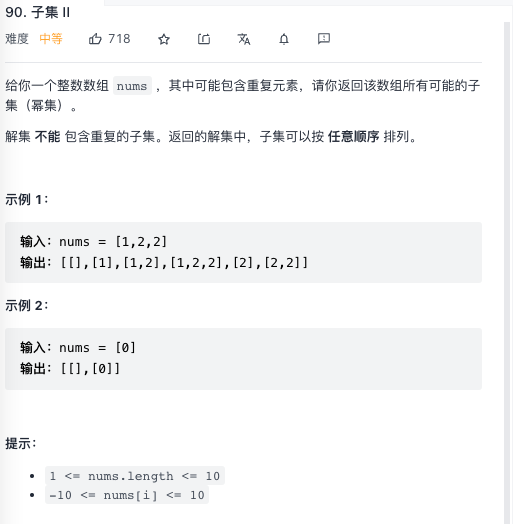
可能包含重复元素,需要进行去重处理
借助卡哥的图翻译翻译:
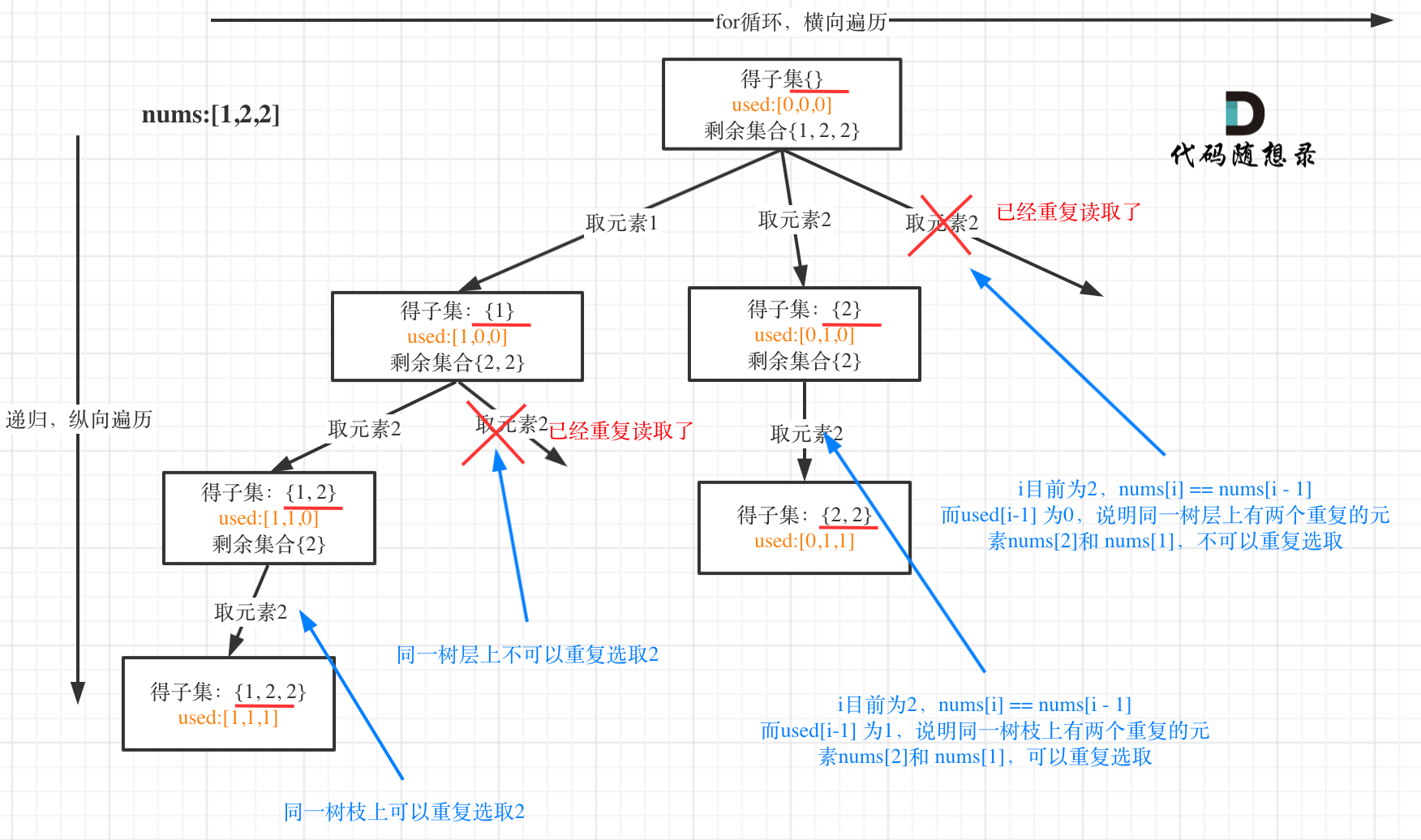
可以使用一个标记数组来判断待选集合中每个元素是否被使用过,
以【1,2,2】 为例子
最左边的遍历会产生【】、【1】、【1,2】、【1,2,2】 这四个集合
在【1,2,2】 产生之后会往上回溯,先回溯到集合为【1,2】,因为没有新的元素可以使用,再回溯到集合中只有【1】
此时第一个2已经使用过,而唯一可以选的元素的值也是2,需要跳过
对应下面代码中的
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1]==true)
continue;
它的意思是,如果当前待选元素与前一个元素相等,且前一个元素已经使用过了,那么这条分支就不应该继续往下走,因为前面已经走过了,所以continue,继续当前位置的 的 下一个元素的选择。
代码:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();// 用来存放符合条件结果
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0){
result.add(path);
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
used = new boolean[nums.length];
subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, 0);
return result;
}
private void subsetsWithDupHelper(int[] nums, int startIndex){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if (startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1]==true){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
优化:
如果当前选择的元素大于了开始选择的位置
且这个数字和它前面的数字一样,那就跳过
因为在选择这个元素之前,一定选择过了之前的和它相等的元素,(i>start)
if(i>start && nums[i-1]==nums[i])continue;
完整代码:
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsetsWithDupHelper(nums,0);
return res;
}
private void subsetsWithDupHelper( int[] nums, int start ) {
res.add( new ArrayList<>(path) );
for ( int i = start;i<nums.length;i++ ){
if(i>start && nums[i-1]==nums[i])continue;
path.add( nums[i] );
subsetsWithDupHelper( nums,i+1 );
path.removeLast();
}
}
待选元素可能相同–且有附加要求
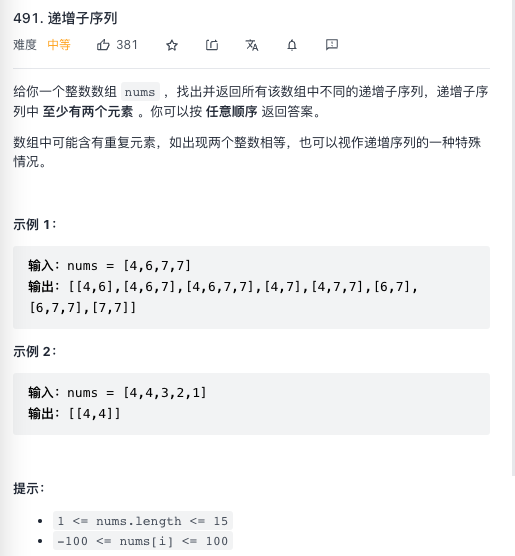
题目要求所有递增的子序列,且不能重复
🌰 【4,6,7(a),7(b)】 字母是为了标识相同元素
结果中可以有【4,7(a)】或 【4、7(b)】 但不能两个同时存在
借助卡哥的图分析分析:
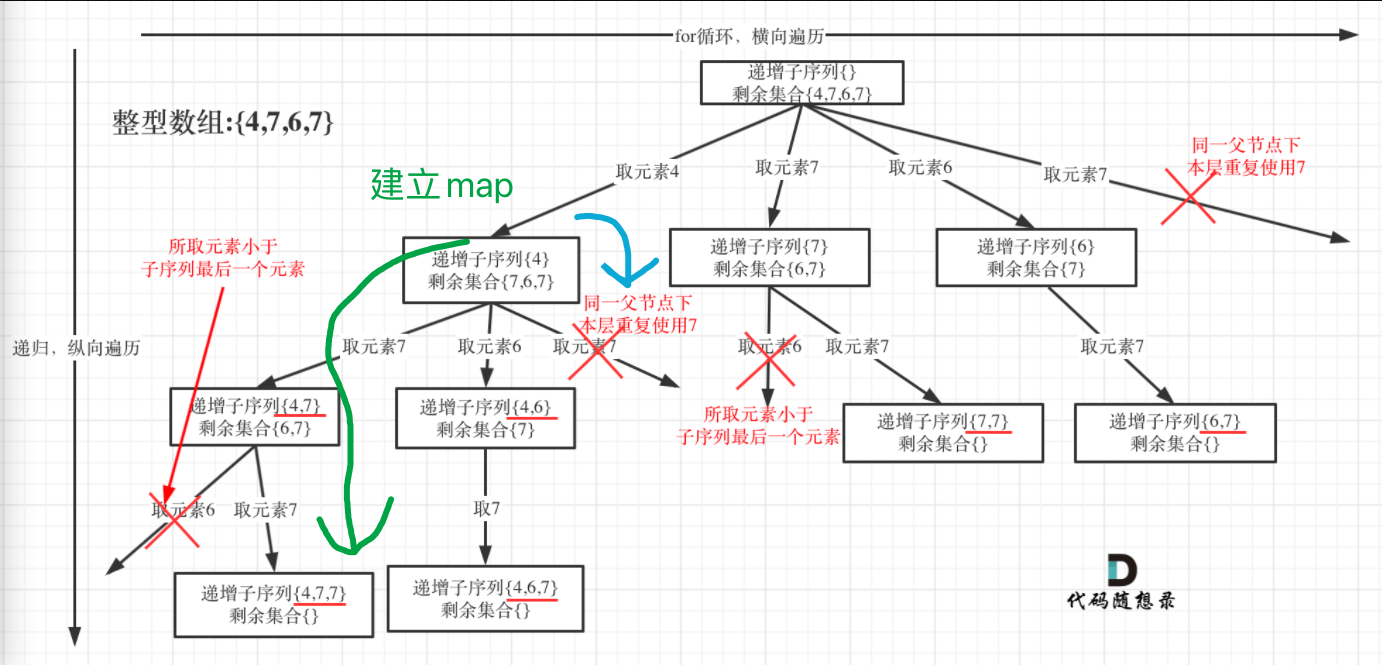
从绿色箭头往下递归前,建立map统计当前元素为开始时的使用情况,
最左边【4,7】 已经使用过一次 7
当蓝色箭头开始往下递归时,map中已经记录过7使用过,也就是以4开头,第二位置的元素使用过7,不能继续往下递归了,continue 之后继续选择下一个可以使用的元素。
无重复元素的排列问题
收集所有叶节点的结果集合
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return result;
backtrack(nums, path);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果path中已有,则跳过
if (path.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
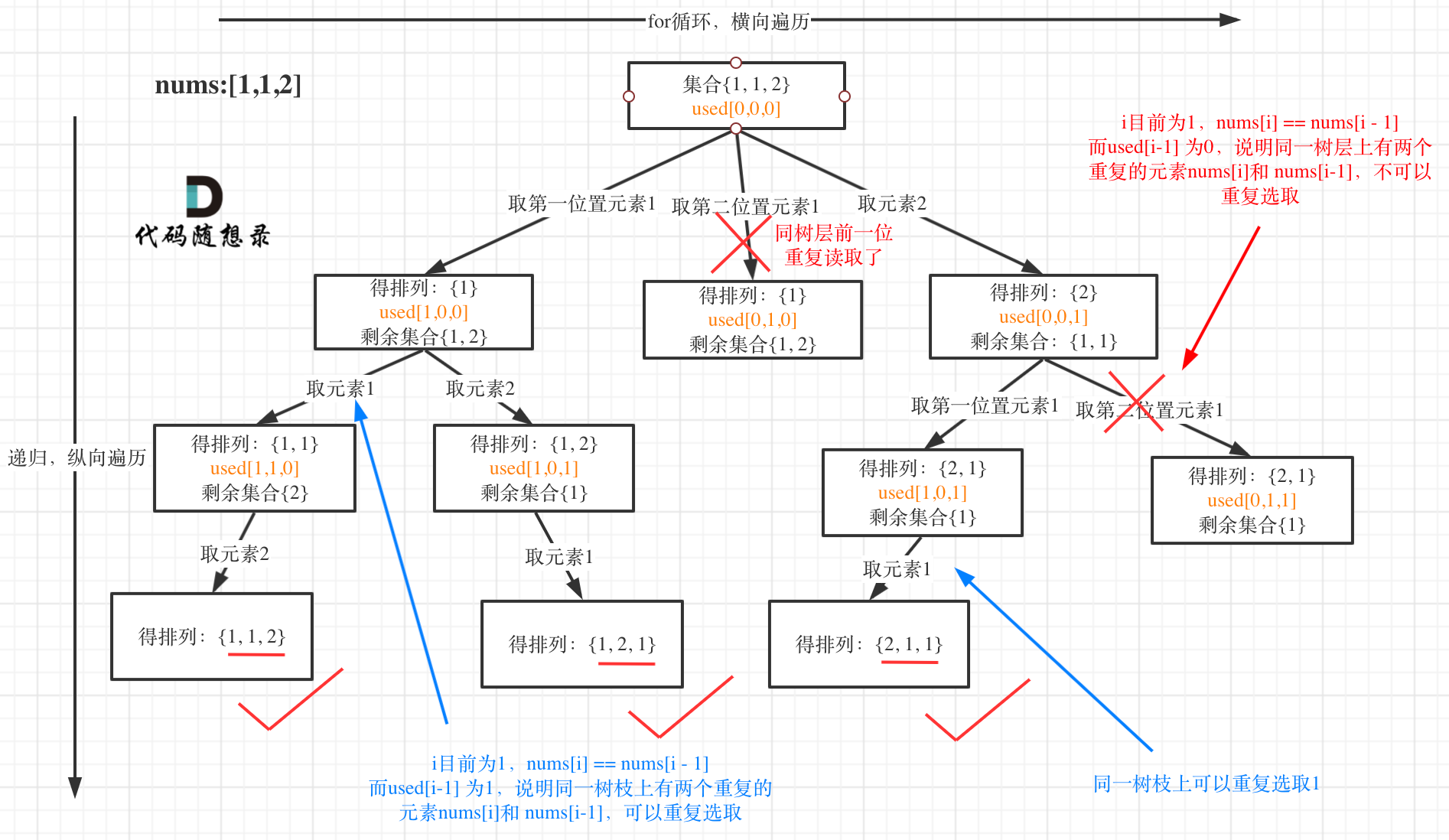
可能重复元素的排列问题
因为包含了重复元素,需要去重
【2,1(a),1(b)】或【2,1(b),1(a)】只能出现一个
交换律告诉我们,对于全排列,只要数组的元素一样,那么最后的全排列结果集合一定是一样的
为了方便判断元素是否使用过,所以先对数组排序。
和之前的去重一样,在同一层上,只允许相同值的元素使用一次
if ( i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false )
continue;
//结果集合
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//路径集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique( int[] nums ) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
getPermute( nums, used, 0 );
return res;
}
private void getPermute( int[] nums, boolean[] used, int start ) {
if ( path.size() == nums.length ) {
res.add( new ArrayList<>( path ) );
return;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++ ) {
// 当前元素与前一个元素相同,且前一个元素使用过
if ( i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false ) {
continue;
}
if ( used[i] == false ) {
used[i] = true;
path.add( nums[i] );
getPermute( nums, used, i + 1 );
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
这里不能直接使用 i>start的去重是因为之前是组合问题,需要从下一个元素开始,但全排列是要求所有元素都使用到。
关于数层去重与树枝去重,推荐看原文 :代码随想录-全排列























 2883
2883











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








