1. ESP32-S2简介
ESP32-S2 是一款安全可靠的低功耗、高集成 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi 系统级芯片 (SoC),支持 Wi-Fi HT40 和多达 43 个 GPIO。ESP32-S2 搭载 Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 单核处理器,工作时钟频率高达 240 MHz。
ESP32-S2 具有行业领先的低功耗管理与射频性能、IO 功能和安全性能,是物联网、移动设备、可穿戴电子设备、智能家居等各种应用的理想选择。ESP32-S2 集成了 240 MHz Xtensa® 单核处理器,无需外接任何 MCU 即可独立满足各种互联设备的需求。
ESP32-S2 仍然沿用了乐鑫已经非常成熟的软件开发框架 ESP-IDF,可以实现性能和成本的平衡,为市场带来更高速、更安全的物联网连接解决方案。
CPU 和存储
- Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 单核处理器
- 7 级流水线架构
- 时钟频率高达 240 MHz
- 超低功耗协处理器
- 320 KB SRAM,128 KB ROM,16 KB RTC 内存
- 最大可支持 1 GB 外部 flash and SRAM
- 独立的指令和数据 cache
Wi-Fi(连接)
- 支持 IEEE 802.11 b/g/n 协议
- 1x1 发送与接收
- 支持 HT40,数据速率高达 150 Mbps
- 支持 TCP/IP 联网、ESP-MESH 联网及 TLS 1.0、TLS 1.1、TLS1.2 等各种 - Wi-Fi 网络协议
- 支持正常 Wi-Fi 数据包的 TOF 测距
IO 外设
- 43 个 GPIO 口
- 14 个电容式传感 IO
- 支持 SPI、I2C、I2S、UART、ADC/DAC 和 PWM 等各种标准外设
- 支持 LCD 接口(8-bit 并口 RGB、8080、6800 接口)
- 支持 8-/16-bit DVP 图像传感器接口,最高时钟频率支持到 40 MHz
- 支持全速 USB OTG
安全
- 基于 RSA-3072 的可信应用程序引导
- 基于 AES256-XTS 的 flash 加密技术,保护静止的敏感数据
- 4096-bit eFuse 存储,其中 2048 bit 可用于应用程序
- 支持数字签名外设,可用于私钥的安全存储和 RSA 签名的生成
最优功耗
- ESP32-S2 通过选择时钟频率、占空比、Wi-Fi 操作模式和内部组件的单独电源控制,支持精细分辨率的电源控制。
当启用 Wi-Fi 时,芯片只在需要时自动开启或关闭射频收发器,从而降低系统的- 总功耗。 - 在 1% 占空比电流消耗下,超低功耗协处理器的空载模式为 5 μA ,空载模式为 7 μA。
- 改进了 Wi-Fi 连接和 MCU 空闲模式的功耗。
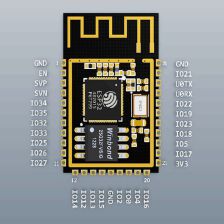
我选用的ESP32-S2板卡为下图,它将USB和TTL下载都用Type-C接口引出,用来调试ESP32-S2的USB功能也是非常的方便:

2.环境搭建
2.1 下载板卡包
从Github上下载 arduino-esp32 的 esp32s2 分支:【地址】,下载完成后进行解压。

2.2 更新板卡包中ESP32-S2的下载工具
进行解压后,打开文件夹,可以发现目录如下:

然后进入tools目录,目录如下:

双击get.exe文件会弹出命令窗口,等待上几分钟,下载完成后窗口会自动关闭。
2.3 将板卡支持包放入Arduino
再将板卡支持包放入Arduino之前,首先你之前安装过ESP32的开发环境, 如果没有安装过,请跟着流程走:
- 首先下载
ESP32的板卡包【地址】,解压后并按照下图目录放好,并且复制一份,并修改文件名为arduino-esp32-esp32s2,其中红色框出来的为你的Arduino软件的安装目录,如果不懂什么是安装目录,请自行搜索:

- 接下来进入
D:\Arduino\hardware\espressif\arduino-esp32-esp32s2目录,并将刚2.2步骤的文件夹下蓝色标记出来的文件拷贝到此目录中,如果弹出来 需要替换文件 ,点击全部替换即可,如果按照以上方式来的话,应该不会弹出。

3. 测试程序
我的板子上有一个2020封装的WS2812灯珠,根据板子原理图查到引脚为WS2812->IO18,现在使用【FastLED】库点亮板载灯试试,先查看IO口的宏定义,其文件在D:\Arduino\hardware\espressif\arduino-esp32-esp32s2\variants\esp32s2\pins_arduino.h:
#ifndef Pins_Arduino_h
#define Pins_Arduino_h
#include <stdint.h>
#define EXTERNAL_NUM_INTERRUPTS 46
#define NUM_DIGITAL_PINS 48
#define NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS 20
#define analogInputToDigitalPin(p) (((p)<20)?(esp32_adc2gpio[(p)]):-1)
#define digitalPinToInterrupt(p) (((p)<48)?(p):-1)
#define digitalPinHasPWM(p) (p < 46)
static const uint8_t TX = 43;
static const uint8_t RX = 44;
static const uint8_t SDA = 8;
static const uint8_t SCL = 9;
static const uint8_t SS = 34;
static const uint8_t MOSI = 35;
static const uint8_t MISO = 37;
static const uint8_t SCK = 36;
static const uint8_t A0 = 1;
static const uint8_t A1 = 2;
static const uint8_t A2 = 3;
static const uint8_t A3 = 4;
static const uint8_t A4 = 5;
static const uint8_t A5 = 6;
static const uint8_t A6 = 7;
static const uint8_t A7 = 8;
static const uint8_t A8 = 9;
static const uint8_t A9 = 10;
static const uint8_t A10 = 11;
static const uint8_t A11 = 12;
static const uint8_t A12 = 13;
static const uint8_t A13 = 14;
static const uint8_t A14 = 15;
static const uint8_t A15 = 16;
static const uint8_t A16 = 17;
static const uint8_t A17 = 18;
static const uint8_t A18 = 19;
static const uint8_t A19 = 20;
static const uint8_t T1 = 1;
static const uint8_t T2 = 2;
static const uint8_t T3 = 3;
static const uint8_t T4 = 4;
static const uint8_t T5 = 5;
static const uint8_t T6 = 6;
static const uint8_t T7 = 7;
static const uint8_t T8 = 8;
static const uint8_t T9 = 9;
static const uint8_t T10 = 10;
static const uint8_t T11 = 11;
static const uint8_t T12 = 12;
static const uint8_t T13 = 13;
static const uint8_t T14 = 14;
static const uint8_t DAC1 = 17;
static const uint8_t DAC2 = 18;
#endif /* Pins_Arduino_h */
然后打开Arduino软件,选择开发板:

从上表查到IO18的定义为:
static const uint8_t A17 = 18;
static const uint8_t DAC2 = 18;
因此我们需要在程序中使用A17或者DAC2来作为WS2812的输出口:
#include <FastLED.h>
FASTLED_USING_NAMESPACE
// FastLED "100-lines-of-code" demo reel, showing just a few
// of the kinds of animation patterns you can quickly and easily
// compose using FastLED.
//
// This example also shows one easy way to define multiple
// animations patterns and have them automatically rotate.
//
// -Mark Kriegsman, December 2014
#if defined(FASTLED_VERSION) && (FASTLED_VERSION < 3001000)
#warning "Requires FastLED 3.1 or later; check github for latest code."
#endif
//#define DATA_PIN A17 //IO口
#define DATA_PIN DAC2 //IO口
#define LED_TYPE WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
#define NUM_LEDS 1 //灯珠数目
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define BRIGHTNESS 96
#define FRAMES_PER_SECOND 120
void setup() {
delay(3000); // 3 second delay for recovery
// tell FastLED about the LED strip configuration
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
//FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,CLK_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
// set master brightness control
FastLED.setBrightness(BRIGHTNESS);
}
// List of patterns to cycle through. Each is defined as a separate function below.
typedef void (*SimplePatternList[])();
SimplePatternList gPatterns = { rainbow, rainbowWithGlitter, confetti, sinelon, juggle, bpm };
uint8_t gCurrentPatternNumber = 0; // Index number of which pattern is current
uint8_t gHue = 0; // rotating "base color" used by many of the patterns
void loop()
{
// Call the current pattern function once, updating the 'leds' array
gPatterns[gCurrentPatternNumber]();
// send the 'leds' array out to the actual LED strip
FastLED.show();
// insert a delay to keep the framerate modest
FastLED.delay(1000/FRAMES_PER_SECOND);
// do some periodic updates
EVERY_N_MILLISECONDS( 20 ) { gHue++; } // slowly cycle the "base color" through the rainbow
EVERY_N_SECONDS( 10 ) { nextPattern(); } // change patterns periodically
}
#define ARRAY_SIZE(A) (sizeof(A) / sizeof((A)[0]))
void nextPattern()
{
// add one to the current pattern number, and wrap around at the end
gCurrentPatternNumber = (gCurrentPatternNumber + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE( gPatterns);
}
void rainbow()
{
// FastLED's built-in rainbow generator
fill_rainbow( leds, NUM_LEDS, gHue, 7);
}
void rainbowWithGlitter()
{
// built-in FastLED rainbow, plus some random sparkly glitter
rainbow();
addGlitter(80);
}
void addGlitter( fract8 chanceOfGlitter)
{
if( random8() < chanceOfGlitter) {
leds[ random16(NUM_LEDS) ] += CRGB::White;
}
}
void confetti()
{
// random colored speckles that blink in and fade smoothly
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 10);
int pos = random16(NUM_LEDS);
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue + random8(64), 200, 255);
}
void sinelon()
{
// a colored dot sweeping back and forth, with fading trails
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
int pos = beatsin16( 13, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 );
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue, 255, 192);
}
void bpm()
{
// colored stripes pulsing at a defined Beats-Per-Minute (BPM)
uint8_t BeatsPerMinute = 62;
CRGBPalette16 palette = PartyColors_p;
uint8_t beat = beatsin8( BeatsPerMinute, 64, 255);
for( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { //9948
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette(palette, gHue+(i*2), beat-gHue+(i*10));
}
}
void juggle() {
// eight colored dots, weaving in and out of sync with each other
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
byte dothue = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
leds[beatsin16( i+7, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 )] |= CHSV(dothue, 200, 255);
dothue += 32;
}
}
点击上传程序,等待程序上传成功,即可发现LED布灵布灵的闪起来了呢:

4. 总结
到此我们的安装过程已经完成,可以进行ESP32-S2的开发了,但是现在很多库还没有对ESP32-S2进行适配,比如我尝试了下u8g2库去驱动OLED,就没有成功,因此还是有很多问题的哦,期待各开源库的完善~























 1035
1035

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








