自己从网上找了好久,都是各种错误,或者写的不清晰,忙活了两个小时,现在准备写到博客上,利人利己。
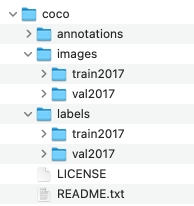
在coco数据集中,coco2017train或coco2017val数据集中标注的目标(类别)位置在 Annotations 文件中以 (x, y, width, height) 来进行表示,x,y表示bbox中心位置,width, height表示bbox的宽和高。而在YOLO训练或者进行验证的时候读取的标注格式是以 (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax) 来进行表示,xmin, ymin表示bbox左上角位置, xmax, ymax表示bbox右下角位置,并且要求保存为.txt文件格式(名字与image对应)。如下图所示:
运行环境,我是在pycharm中直接运行的,conda新建一个python3.6的环境,根据提示导入一些需要的包就行了。实现代码如下:
#COCO 格式的数据集转化为 YOLO 格式的数据集
#--json_path 输入的json文件路径
#--save_path 保存的文件夹名字,默认为当前目录下的labels。
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#这里根据自己的json文件位置,换成自己的就行
parser.add_argument('--json_path', default='D:/BaiduNetdiskDownload/COCO2017/annotations_train2017/annotations/instances_train2017.json',type=str, help="input: coco format(json)")
#这里设置.txt文件保存位置
parser.add_argument('--save_path', default='D:/BaiduNetdiskDownload/COCO2017/Lable/train2017', type=str, help="specify where to save the output dir of labels")
arg = parser.parse_args()
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = box[0] + box[2] / 2.0
y = box[1] + box[3] / 2.0
w = box[2]
h = box[3]
#round函数确定(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)的小数位数
x = round(x * dw, 6)
w = round(w * dw, 6)
y = round(y * dh, 6)
h = round(h * dh, 6)
return (x, y, w, h)
if __name__ == '__main__':
json_file = arg.json_path # COCO Object Instance 类型的标注
ana_txt_save_path = arg.save_path # 保存的路径
data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r'))
if not os.path.exists(ana_txt_save_path):
os.makedirs(ana_txt_save_path)
id_map = {} # coco数据集的id不连续!重新映射一下再输出!
with open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'classes.txt'), 'w') as f:
# 写入classes.txt
for i, category in enumerate(data['categories']):
f.write(f"{category['name']}\n")
id_map[category['id']] = i
# print(id_map)
#这里需要根据自己的需要,更改写入图像相对路径的文件位置。
list_file = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'train2017.txt'), 'w')
for img in tqdm(data['images']):
filename = img["file_name"]
img_width = img["width"]
img_height = img["height"]
img_id = img["id"]
head, tail = os.path.splitext(filename)
ana_txt_name = head + ".txt" # 对应的txt名字,与jpg一致
f_txt = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, ana_txt_name), 'w')
for ann in data['annotations']:
if ann['image_id'] == img_id:
box = convert((img_width, img_height), ann["bbox"])
f_txt.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (id_map[ann["category_id"]], box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]))
f_txt.close()
#将图片的相对路径写入train2017或val2017的路径
list_file.write('./images/train2017/%s.jpg\n' %(head))
list_file.close()
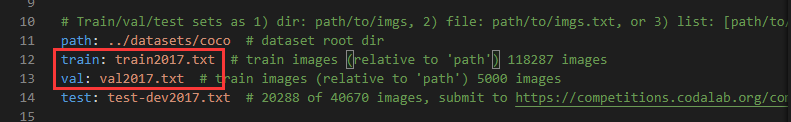
最后在–save_path会看到与图像对应的.txt文件,另外还会得到两个文件,其中一个class.txt(数据集的类别)和train2017.txt(val2017.txt)里面可以定义每个图像的相对位置,这个在“训练”和“评估”模型时会用到,具体可见yoloV5源码中data路径下的coco.yaml文件(如下图)。

如果不想自己重新生成,可以用我已经整理好的coco2017标准数据集,所有文件都已包含在压缩包中。链接为:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_42012888/22922136?spm=1001.2014.3001.5503(文件很多,上传不易,如果确实好用,请给好评)


纯属分享一下,愿你少走一些弯路,祝科研顺利,少掉头发,打工人,加油!





















 236
236











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








