Python3 爬虫教程
文章目录
学习网站:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av9784617?from=search&seid=3311514956616305524
BeautifulSoup
是用来解析HTML元素、形成标签树的库。
在HTML中,每个元素tag包含:标签名tag.name、属性域tag.attris、内容字符串tag.string。
HTML文档–>标签树–>BeautifulSoup类
BeautifulSoup 类的基本元素
| 基本元素 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Tag | 标签,最基本的信息组织单元,分别用<>和</>标明开头和结尾 |
| Name | 标签的名字, … 的名字’p’,格式:.name |
| Attributes | 标签的属性,字典形式组织,格式:.attrs |
| NavigableString | 标签内非属性字符串,<>…</>中字符串,格式:.string |
| Comment | 标签内的字符串的注释部分,一种特殊的Comment类型 |
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.a) #打印第一个a标签内容
print(soup.a.name) #打印a标签的名字
print(soup.a.parent.name)#打印a父亲标签的名字
print(soup.a.attrs)#打印a标签中的属性
print(soup.a.attrs["class"])#打印a标签中class属性的值
print(type(soup.a.attrs))#打印标签属性通过处理后的类型
print(type(soup.a))#标签的类型
print(soup.a.string)#打印标签内字符串信息
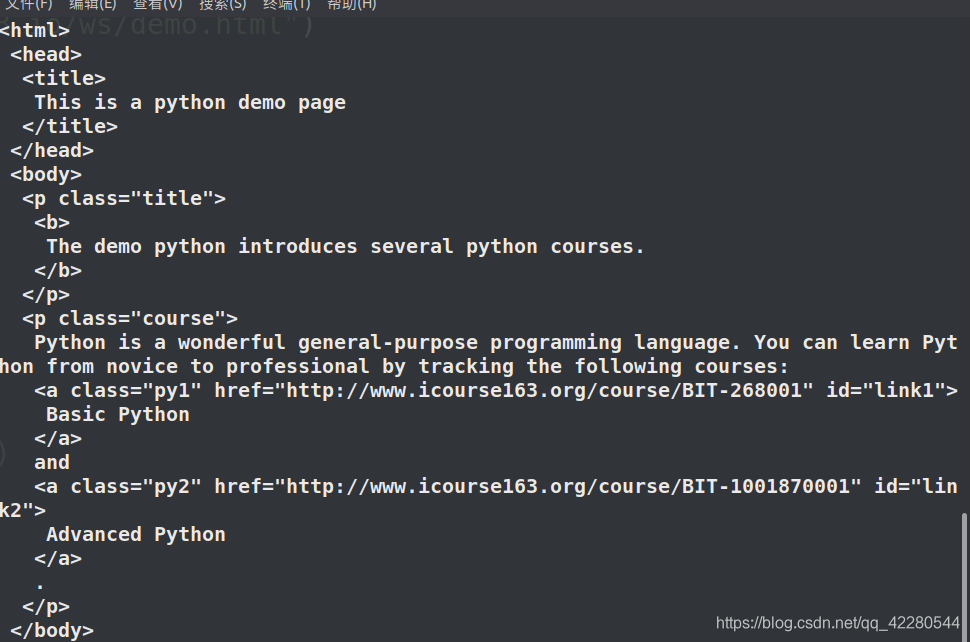
http://python123.io/ws/demo.html内容:
<html>
<head>
<title>This is a python demo page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>The demo python introduces several python courses.</b>
</p>
<p class="course">Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:
<a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" class="py1" id="link1">Basic Python</a>
and
<a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" class="py2" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
HTML标签的基本树形结构
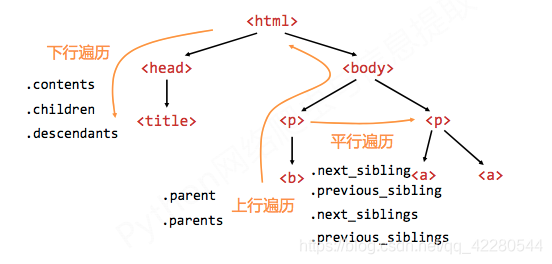
标签树的下行遍历
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .contents | 子节点的列表,将所有儿子节点存入列表 |
| .children | 子节点的迭代类型,与.contents类似,用于循环遍历儿子节点 |
| .descendants | 子孙节点的迭代类型,包含所有子孙节点,用于遍历循环 |
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.head.contents)#返回head标签子节点的列表
print(soup.body.contents)#返回body标签子节点的列表
print(len(soup.body.contents))#返回列表长度
print(soup.body.contents[1])#返回列表中的第二个元素
for child in soup.body.children:#遍历儿子节点
print(child)
for desc in soup.body.descendants:#遍历孙子节点
print(desc)
标签树的上行遍历
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .parent | 节点的父亲标签 |
| .parents | 节点先辈标签的迭代类型,用于循环遍历先辈节点 |
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.title.parent)#打印title的父标签
print(soup.html.parent)#打印html的父标签
for parent in soup.a.parents:#遍历a标签的所有父标签
if parent is None:
print(parent)
else:
print(parent.name)
标签树的平行遍历
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .next_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的下一个平行节点标签 |
| .previous_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的上一个平行节点标签 |
| .next_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照HTML文本顺序的后续所有平行节点标签 |
| .previous_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照HTML文本顺序的前续所有平行节点标签 |
平行遍历发生在同一个父节点下的各节点间
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.a.next_sibling)#返回a标签下一个平行节点标签
print(soup.a.next_sibling.next_sibling)#返回a标签下下一个平行节点标签
print(soup.a.previous_sibling)#返回a标签前一个平行节点标签
for sibling in soup.a.next_siblings:#平行遍历后续节点
print(sibling)
for sibling in soup.a.previous_siblings:#平行遍历前续节点
print(sibling)
基于bs4库的HTML格式和编码
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.prettify())#格式化输出
输出:
三种信息标记



基于bs4库的HTML内容查找方法
<>.find_all(name,attrs,recursive,string,**kwargs)
返回一个列表类型,存储查找结果
name:对标签名称的检索字符串
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all("a"))#返回所有a标签
print(soup.find_all(["a","b"]))#返回所有a标签和b标签
attrs:对标签属性值的检索字符串,可标注属性检索
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all("p","course"))#返回p标签属性值为'course'的标签
print(soup.find_all(id='link1'))#查找属性id='link1'的标签
recursive:是否对子孙全部检索,默认为True
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all('a', recursive=False) #该文档的第一层子标签没有a标签)
string:<>…</>中字符串区域的检索字符串
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r=requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all(string="Basic Python"))#精确查找相关字符串
扩展方法:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| <>.find() | 检索且只返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find_all()参数 |
| <>.find_parents() | 在先辈节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数 |
| <>.find_parent() | 在先辈节点中返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find()参数 |
| <>.find_next_siblings() | 在后续平行节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数 |
| <>.find_next_sibling() | 在后续平行节点中中返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find()参数 |
| <>.find_previous_siblings() | 在前续平行节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数 |
| <>.find_previous_sibling() | 在前续平行节点中中返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find()参数 |
中国大学排名实例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import bs4
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
# r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding
r.encoding = 'utf-8'
return r.text
except:
print("获得网站文本失败!")
def fillUniList(html, num, uInfo):
count = 1
s = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
for tr in s.find('tbody').children:
if isinstance(tr, bs4.element.Tag):
tds = tr('td')
uInfo.append([tds[0].string, tds[1].string, tds[3].string])
count += 1
if count>num:
break
def printUniList(uInfo):
tplt = "{0:^10}\t{1:^10}\t{2:^10}"
print(tplt.format("排名", "学校", "总分"))
for i in range(len(uInfo)):
u = uInfo[i]
print(tplt.format(u[0], u[1], u[2]))
def main():
url = 'http://www.zuihaodaxue.cn/zuihaodaxuepaiming2019.html'
num = 20
uInfo = []
html = getHTMLText(url)
fillUniList(html, num, uInfo)
printUniList(uInfo)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
正则表达式
| 操作符 | 说明 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| . | 表示任何单个字符 | |
| [] | 字符集,对单个字符给出取值范围 | [abc]表示a或b或c;[a-z]表示a到z单个字符 |
| [^ ] | 非字符集,对单个字符给出排除范围 | [^abc]表示非a或b或c的单个字符 |
| * | 前一个字符0次或无线次扩展 | abc*表示ab或abc或abcc等 |
| + | 前一个字符1次或无线次扩展 | abc+表示abc或abcc等 |
| ? | 前一个字符0次或1次扩展 | abc?表示ab或abc |
| | | 左右表达式任意一个 | abc|def 表示abd或def |
| {m} | 扩展前一个字符m次 | ab{2}c表示abbc |
| {m,n} | 扩展前一个字符m到n次(含n) | ab{1,2}c表示abc或abbc |
| ^ | 匹配字符串开头 | ^abc表示abc且在一个字符串的开头 |
| $ | 匹配字符串结尾 | abc$表示abc且在一个字符串的结尾 |
| () | 分组标记,内部只能使用|操作符 | (abc)表示abc,(abc,def)表示abc或def |
| \d | 数字,等价于[0-9] | |
| \w | 单词字符,等价于[A-Za-z0-9] |
1+$ : 由26个字母组成的字符串
^-?\d+$ : 整数形式的字符串
2+[0-9]*$:正整数形式的字符串
Re库
Re库主要功能函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| re.search() | 在一个字符串中搜索匹配正则表达式的附一个位置,返回match()对象 |
| re.match() | 从一个字符串的开始位置起匹配正则表达式,返回match对象 |
| re.findall() | 搜索字符串,以列表类型返回全部能匹配的子串 |
| re.split() | 将一个字符串按照正则表达式匹配结果进行分割,返回列表类型 |
| re.finditer() | 搜索字符串,返回一个匹配结果的迭代类型,每个迭代元素是match对象 |
| re.sub() | 在一个字符串中替换所有匹配正则表达式的子串,返回替换后的字符串 |
flags可选择值
| 常用标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| re.I re.IGNORECASE | 忽略正则表达式的大小写,[A-Z]能匹配小写字符 |
| re.M re.MULTILING | 正则表达式中的^操作符能够将给定字符串的每行当做匹配开始 |
| re.S re.DOTALL | 正则表达式中的 . 操作符能够匹配所有字符,默认匹配除换行符外的所有字符 |
re.search()
re.search(pattern,string,flags=0)
在一个字符串中搜索匹配正则表达式的第一个位置,返回match对象
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- string:待匹配字符串
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
match=re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
if match:
print(match.group(0))
re.match()
re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
从一个字符串的开始位置起匹配正则表达式,返回match对象
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- string:待匹配字符串
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
match=re.match(r'[1-9]\d{5}','100081 BIT')
if match:
print(match.group(0))
re.findall()
re.findall(pattern,string,flags=0)
搜索字符串,以列表类型返回全部能匹配的子串
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- string:待匹配字符串
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
f_all= re.findall(r"[1-9]\d{5}","BT100081 SH132132 FJ132431432")
print(f_all)
re.split()
re.split(pattern,string,maxsplit=0,flags=0)
将一个字符串按照正则表达式匹配结果进行分割,返回列表类型
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- string:待匹配字符串
- maxsplit:最大分割数,剩余部分作为最后一个元素输出
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
print(re.split(r'[1-9]\d{5}','dad100081 fsv100084'))
print(re.split(r'[1-9]\d{5}','dad100081 fsv100084',maxsplit=1))
re.finditer()
re.finditer(pattern,string,flags=0)
搜索字符串,返回一个匹配结果的迭代类型,每个迭代元素是match对象
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- string:待匹配字符串
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
for i in re.finditer(r'[1-9]\d{5}','dad100081 fsv100084'):
if i:
print(i.group(0))
re.sub()
re.sub(pattern,repl,string,count=0,flags=0)
在一个字符串中替换所有匹配正则表达式的子串,返回替换后的字符串
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- repl:替换匹配字符串的字符串
- string:待匹配字符串
- count:匹配的最大替换次数
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
import re
print(re.sub(r"[1-9]\d{5}",":world","BIT100081 SHS123123214345 SHDHKJ1231"))
RE库的另一种用法:
-
函数式:一次性操作
inport re match=re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081') -
面向对象:编译后的多次操作
import re regex=re.compile(r"[1-9]\d{5}") match=regex.search("BIT 100081")
regex=re.compile()
regex=re.compile(pattern,flags=0)
将正则表达式的字符串形式编译成正则表达式对象
- pattern:正则表达式的字符串或原生字符串表示
- flags:正则表达式使用时的控制标记
Re库的match对象
Match对象的属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .string | 待匹配的文本 |
| .re | 匹配时使用的pattern对象(正则表达式) |
| .pos | 正则表达式搜索文本的开始位置 |
| .endpos | 正则表达式搜索文本的结束位置 |
import re
match=re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081 HDJ23323213 JDK434382')
print(".string:",match.string)
print(".re:",match.re)
print(".pos:",match.pos)
print(".endpos:",match.endpos)
Match对象的方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .group() | 获得匹配后的字符串 |
| .start() | 匹配字符串在原始字符串的开始位置 |
| .end() | 匹配字符串在原始字符串的结束位置 |
| .span() | 返回(.start(),.end()) |
import re
match=re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
print(match)
if match:
print(match.group(0))
print(match.start())
print(match.end())
print(match.span())
Re库的贪婪匹配和最小匹配
贪婪匹配
Re库默认采用贪婪匹配,即输出匹配最长的子串
import re
match=re.search(r"PY.*N","PYANBNCNDN")
print(match.group(0))
最小匹配
import re
match =re.search(r"PY.*?N","PYANBNCNDN")
print(match.group(0))
最小匹配操作符
| 操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| *? | 前一个字符0次或无限次扩展,最小匹配 |
| +? | 前一个字符1次或无限次扩展,最小匹配 |
| ?? | 前一个字符0次或1一次扩展,最小匹配 |
| {m,n}? | 扩展前一个字符m至n次(含n),最小匹配 |
淘宝商品信息定向爬取实例
import requests
import re
headers={
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/78.0.3904.108 Safari/537.36",
"cookie": "登陆后访问页面的cookie"
}
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r=requests.get(url,headers=headers,timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding="utf-8"
return r.text
except:
print("网络获取失败!")
def parsePage(ilt,html):
try:
plt=re.findall(r'\"view_price\"\:\"[\d.]*\"',html)
tlt=re.findall(r'\"raw_title\"\:\".*?\"',html)
for i in range(len(plt)):
price=eval(plt[i].split(":")[1])
title=eval(tlt[i].split(":")[1])
ilt.append([price,title])
except:
print("网页获取失败!")
def printGoodsList(ilt):
tplt="{:4}\t{:8}\t{:16}"
print(tplt.format("序号","价格","商品名称"))
count=0
for g in ilt:
count=count+1
print(tplt.format(count,g[0],g[1]))
def main():
depth=2
start_url="https://s.taobao.com/list?spm=a217q.8031046.292818.2.3ab1789d9NSnuq&q=%E7%94%B7%E5%8C%85&cat=50072686&style=grid&seller_type=taobao&fs=1&auction_tag%5B%5D=12034"
infoList=[]
for i in range(depth):
try:
url=start_url+"&s="+str(44*i)
html=getHTMLText(url)
parsePage(infoList,html)
except:
continue
printGoodsList(infoList)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
股票定向爬虫 实例
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# import traceback
import re
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r=requests.get(url,timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding="utf-8"
return r.text
except:
# print("网站连接失败!")
return ""
def getStockList(lst,stockURL):
html=getHTMLText(stockURL)
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
a=soup.find_all('a')
for i in a:
try:
href=i.attrs["href"]
lst.append(re.findall(r"[s][hz]\d{6}",href)[0])
except:
continue
def getStockInfo(lst,stockURL,fpath):
count=0
for stock in lst:
url=stockURL+stock +".html"
html=getHTMLText(url)
try:
if html=="":
continue
infoDict={}
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
stockInfo=soup.find('div',attrs={'class','stock-bets'})
name=stockInfo.find_all(attrs={'class','bets-name'})[0]
infoDict.update({'股票名称':name.text.split()[0]})
keyList=stockInfo.find_all('dt')
valueList=stockInfo.find_all('dd')
for i in range(len(keyList)):
key=keyList[i].text
val=valueList[i].text
infoDict[key]=val
with open(fpath,'a',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(infoDict)+'\n')
count=count+1
print("\r当前速度:{:.2f}%".format(count*100/len(lst),end=''))
except:
count=count+1
print("\r当前速度:{:.2f}%".format(count*100/len(lst),end=''))
continue
return ""
def main():
stock_list_url="http://quote.eastmoney.com/stocklist.html"
stock_info_url="http://www.eastmoney.com/stock/"
output_file="./output_file.txt"
slist=[]
getStockList(slist,stock_list_url)
getStockInfo(slist,stock_info_url,output_file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
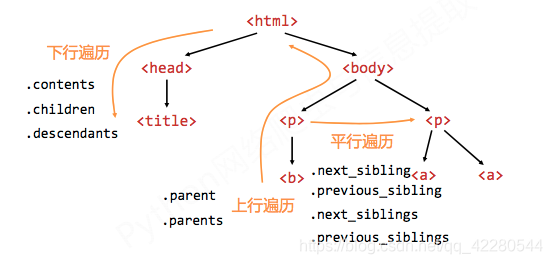
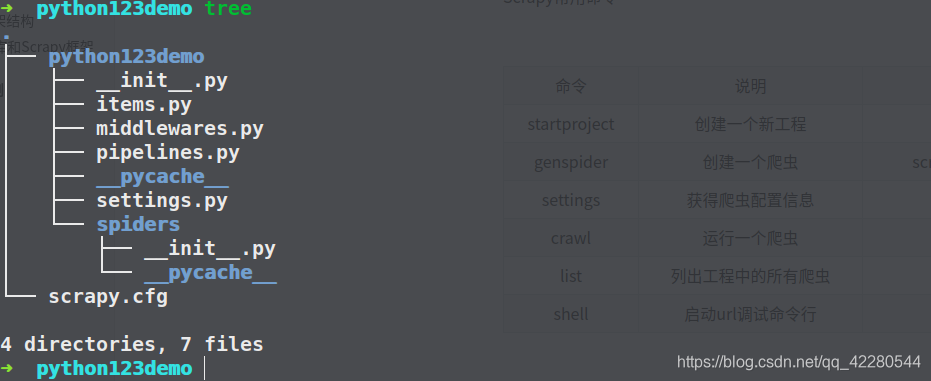
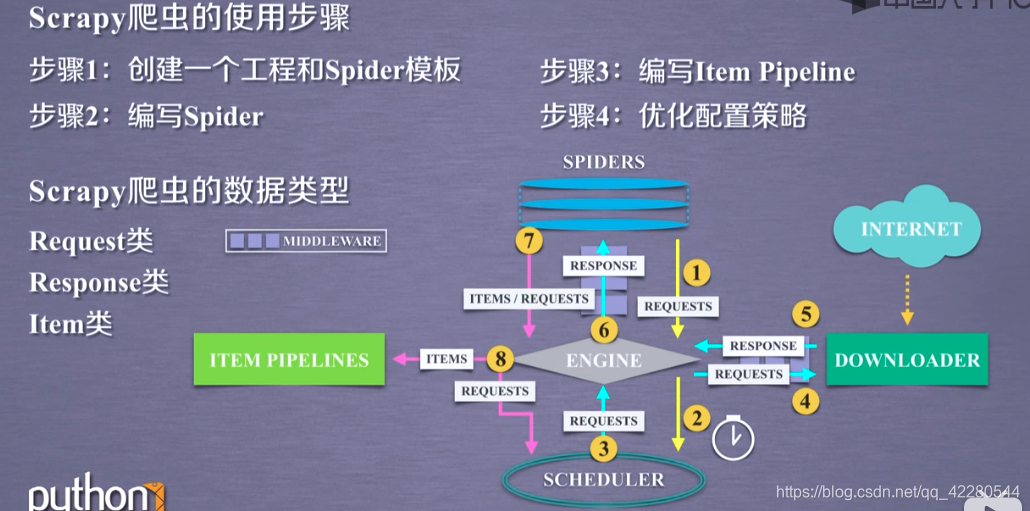
Scrapy爬虫框架结构
安装:pip install scrapy
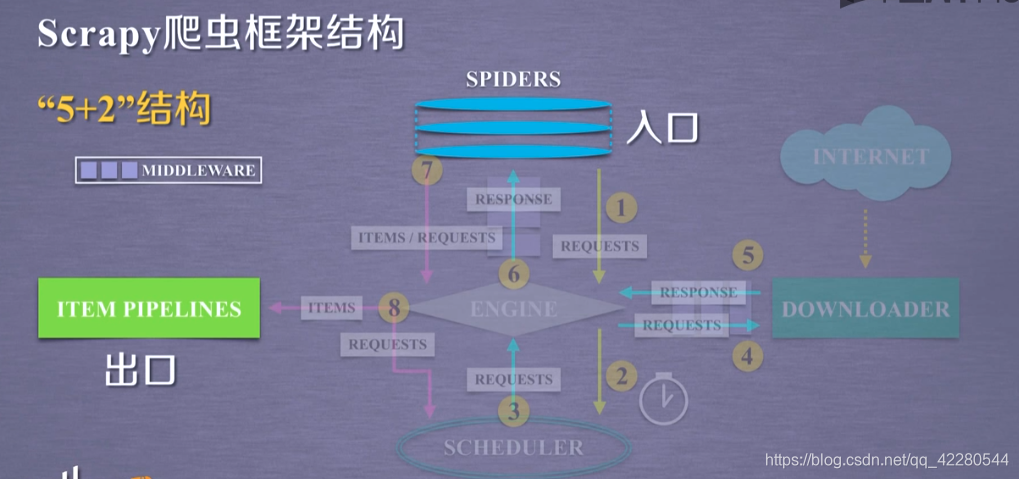
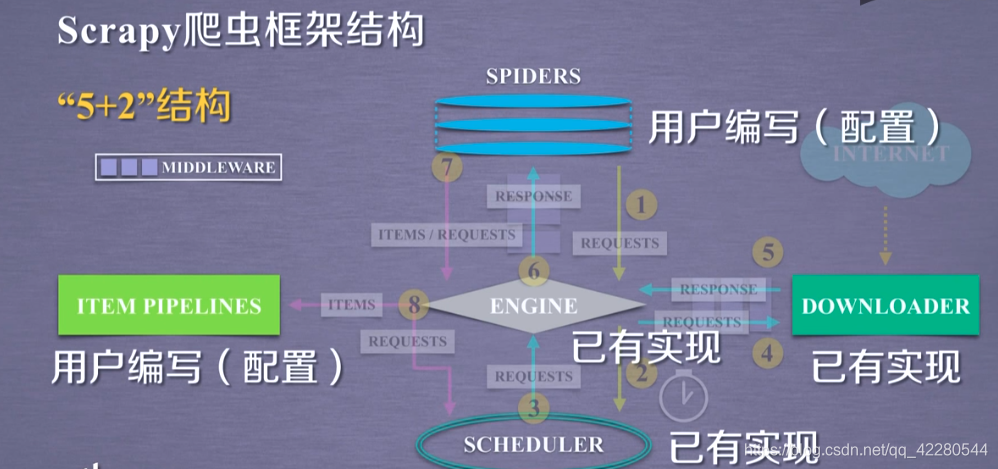
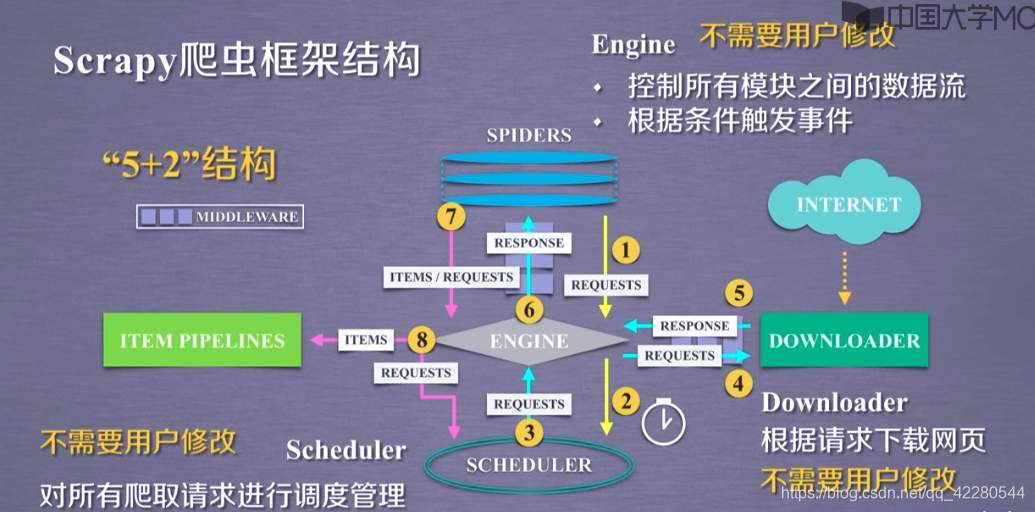
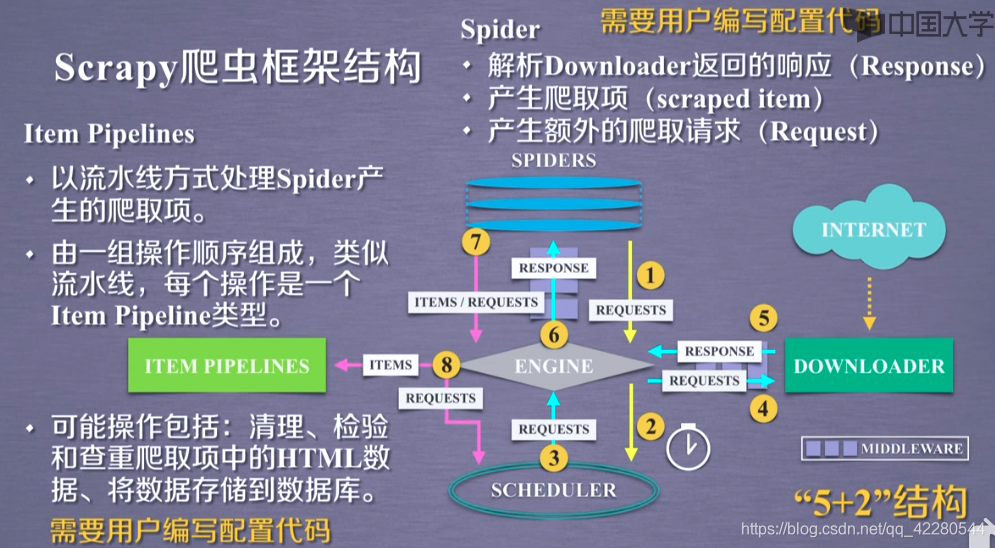


Requests库和Scrapy框架的比较
Requests VS Scrapy
| Requests | Scrapy |
|---|---|
| 页面级爬虫 | 网站级爬虫 |
| 功能库 | 框架 |
| 并发性考虑不足,性能差 | 并发性好,性能较高 |
| 重点在于网页下载 | 重点在于爬虫结构 |
| 定制灵活 | 一般定制灵活,深度定制困难 |
| 上手十分简单 | 入门稍难 |
Scrapy常用命令
| 命令 | 说明 | 格式 |
|---|---|---|
| startproject | 创建一个新工程 | scrapy startproject [dir] |
| genspider | 创建一个爬虫 | scrapy genspider [options] |
| settings | 获得爬虫配置信息 | scrapy settings [options] |
| crawl | 运行一个爬虫 | scrapy crawl |
| list | 列出工程中的所有爬虫 | scrapy list |
| shell | 启动url调试命令行 | scrapy shell [url] |
第一个实例
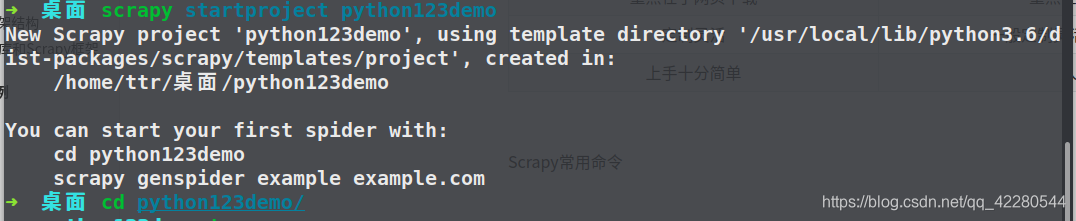


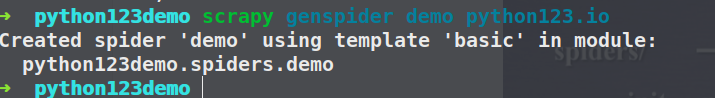
生成一个爬虫
scrapy genspider demo python123.io
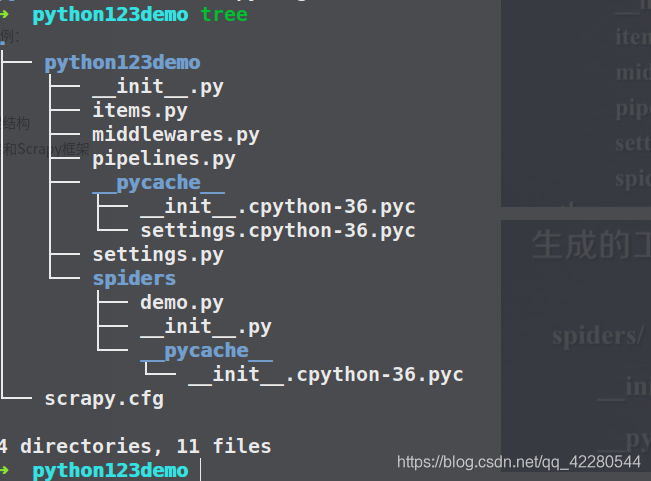
生成的demo.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
allowed_domains = ['python123.io']
start_urls = ['http://python123.io/']
def parse(self, response):
pass
parse()用于处理响应,解析内容形成字典,发现新的URL爬取请求
配置生成的spider爬虫:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
# allowed_domains = ['python123.io']
start_urls = ['http://python123.io/ws/demo.html']
def parse(self, response):
fname=response.url.split('/')[-1]
with open(fname,'wb') as f:
f.write(response.body)
self.log('Save file %s.' % fname)
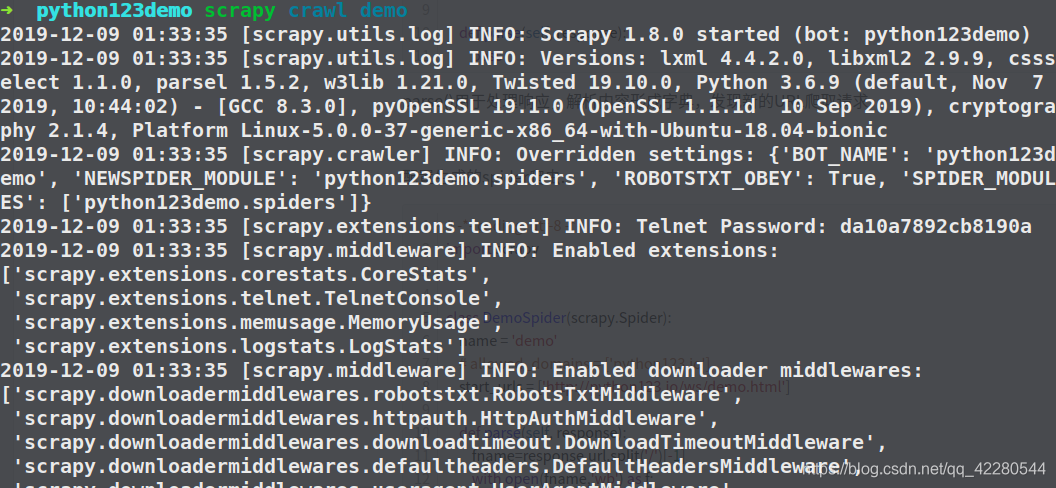
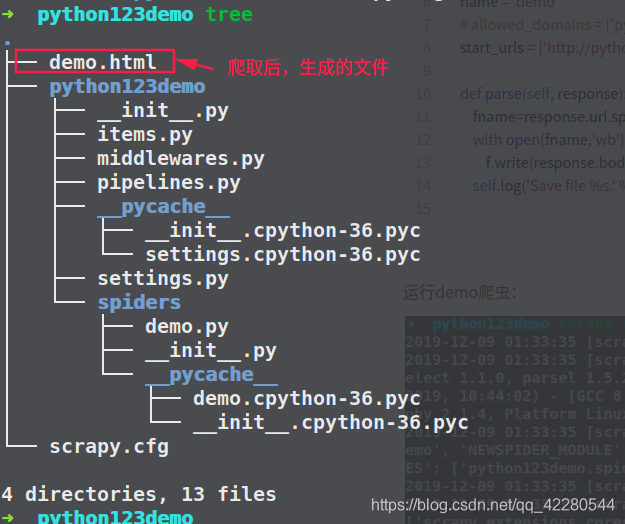
运行demo爬虫:
demo.py代码的完整版本:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
# allowed_domains = ['python123.io']
def start_requests(self):
urls = ['http://python123.io/ws/demo.html']
for url in urls:
yield scrapy.Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)
def parse(self, response):
fname=response.url.split('/')[-1]
with open(fname,'wb') as f:
f.write(response.body)
self.log('Save file %s.' % fname)
两者等价
yield关键字

例子:
#生成器写法
def gen(n):
for i in range(n):
yield i**2
for i in gen(5):
print(i," ",end="")
#普通写法
def square(n):
ls=[i**2 for i in range(n)]
return ls
for i in square(5):
print(i," ",end="")
生成器高效快捷,占用计算资源少,可以处理大数据
scrapy的基本使用
Request类
class scrapy.http.Request()
-
表示一个http请求
-
由Spider生成,由Downloader执行
Request类型
| 属性或方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .url | Request对应的请求URL地址 |
| .method | 对应的请求方法,“GET”,“POST”等 |
| .headers | 字典类型风格的请求头 |
| .body | 请求内容主体,字符串类型 |
| .meta | 用户添加的扩展信息,在Scrapy内部模块间传递信息使用 |
| .copy() | 复制该请求 |
Response类
class scrapy.http.Response()
-
Response对象表示一个http响应
-
由Downloader生成,由Spider处理
Response类型
| 属性或方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .url | Response对应的请求URL地址 |
| .status | HTTP状态码,默认是200 |
| .headers | Response对应的头部信息 |
| .body | Response对应的内容信息,字符串类型 |
| .flags | 一组标记 |
| .request | 产生Response类型对应的Request对象 |
| .copy() | 复制该响应 |
Item类
class scrapy.item.Item()
- Item对象表示一个从HTML页面中提取的信息内容
- 由Spider生成,由Item Pipeline处理
- Item类似字典型,可以按照字典类型操作
Scrapy爬虫提取信息的方法
scrapy爬虫框架支持多种HTML信息提取方法
- BeautifulSoup
- lxml
- re
- XPath Selector
- CSS Selector
股票数据scrapy爬取实例
步骤:
- scrapy startproject BaiduStocks
- cd BaiduStocks/
- scrapy genspider stocks baidu.com
- cd BaiduStocks/spiders
编写stocks.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
import re
class StocksSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'stocks'
start_urls = ['http://quote.eastmoney.com/stocklist.html']
def parse(self, response):
for href in response.css('a::attr(href)').extract():
try:
stock=re.findall(r"[s][hz]\d{6}",href)[0]
url='http://gupiao.baidu.com/stock/'+stock+'.html'
yield scrapy.Request(url,callback=self.parse_stock)
except:
continue
def parse_stock(self,response):
infoDict={}
stockInfo=response.css('.stock-bets')
name=stocklist.css('.bets-name').extract()[0]
keyList=stockInfo.css('dt').extract()
valueList=stockInfo.css('dd').extract()
for i in range(len(keyList)):
key=re.findall(r'>.*</dt>',keyList[i])[0][1:-5]
try:
val=re.findall(r'\d+\.?.*</dd>',valueList[i])[0][0:-5]
except:
val='--'
infoDict[key]=val
infoDict.update({'股票名称':re.findall(r'\s.*\(',name)[0].split()[0]+\
re.findall(r'\>.*\<',name)[0][1:-1]})
yield infoDict
编写pipeline.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
class BaidustocksPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
return item
#自写类
class BaidustocksInfoPipeline(object):
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.f=open('BaidustocksInfo.txt','w')
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.f.close()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
try:
line=str(dict(item))+'\n'
self.f.write(line)
except:
pass
return item
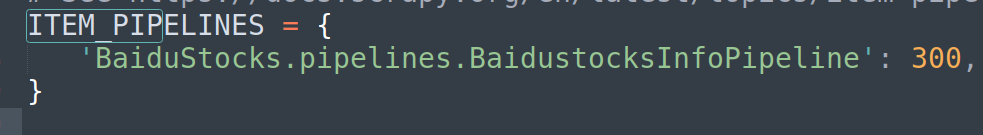
在settings.py中配置,来调用自写类,将ITEM_PIPELINES设置如下,然后保存:
配置并发连接选项
配置文件 settings.py
settings.py文件
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| CONCURRENT_REQUESTS | DOWnLoader最大并发请求下载数量,默认是32 |
| CONCURRENT_ITEMS | ItemPipeline最大并发ITEM处理数量,默认是100 |
| CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN | 每个目标域名的最大并发请求数量,默认是8 |
| CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP | 每个目标IP的最大并发请求数量,默认是0,非0有效 |





















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








