hash结构
- hash 结构的实现可以用数组实现,也可以用链表实现,redis是使用链表实现。也就是用的链地址法,大概形如:
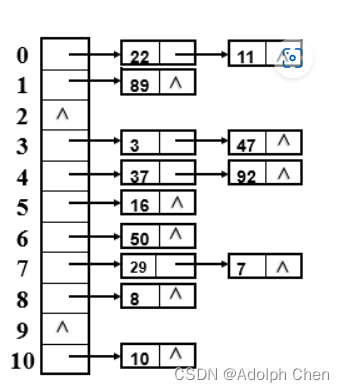
- 在redis-5.0中的代码:
// 一个键值对
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; // 键
union { // 值
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; // 下一个
} dictEntry;
// 一张表
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; // 二维数组
unsigned long size; // hash表的大小
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used; // 使用量
} dictht;
// 使用时的结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2]; // 两个表
long rehashidx; // 是否在进行rehash的标识,如果是-1 表示没
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
- 可能存在的问题
从上图可以看出,一个桶中可能放有多个元素,理论上可以一直链接下去。所以如果产生这种情况,会导致查询时在一个桶中耗费太多时间,从而降低性能。产生“一个桶元素太多”情况大多数都是因为键的元素太多,而hash的size又太小。所以我们需要对hash的size进行扩容。
redis的rehash实践
1. 触发rehash的条件
- _dictExpandIfNeeded
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
// 判断是否正在运行rehash
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
// 没被初始化
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
// 使用量大于hash表大小 并且
// 可以扩容 或者使用量大于hash表大小5倍(负载因子)
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
- updateDictResizePolicy : dict_can_resize 控制
void updateDictResizePolicy(void) {
// 没有执行 RDB 快照和没有进行 AOF 重写
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1)
dictEnableResize();
else
dictDisableResize();
}
void dictEnableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 1;
}
void dictDisableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 0;
}
- 调用
dictAdd:添加entry
dictRelace:添加或修改entry
dictAddorFind:
dictEntry *dictAddOrFind(dict *d, void *key) {
dictEntry *entry, *existing;
entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,&existing);
return entry ? entry : existing;
}
这三个函数都调用dictAddRaw,然后dictAddRaw调用_dictKeyIndex, _dictKeyIndex调用_dictExpandIfNeeded。
2. 扩容数量
// 目标值是当前的两倍
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
/* Expand or create the hash table */
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
// 计算扩容后实际大小
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Our hash table capability is a power of two */
static unsigned long _dictNextPower(unsigned long size)
{
// 设置初始值
unsigned long i = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
// 如果目标大小 超过最大值 直接加1
if (size >= LONG_MAX) return LONG_MAX + 1LU;
// 不断*2 直至大于等于
while(1) {
if (i >= size)
return i;
i *= 2;
}
}
3. 扩容实现
由于redis主线程需要处理其他请求,而rehash需要构造新的hash表,这时就需要把原来的内容拷贝到新地址,这会阻塞主线程。为了rehash减少对主线程的影响,redis提出了渐进式的方法,就是每次键的拷贝并不是所有的都一次性拷贝,而是分批一个一个桶的进行。
- dictRehash
// d需要操作的结构 n是每次拷贝桶的数量
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// 迁移了n个桶 或者 当前的hash表没有元素
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
// 如果桶是空的 下一个 但是会修改一下踏进空桶的次数
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
// rehashidx 表示当前操作的桶的序号
d->rehashidx++;
// 踏进空桶次数达到指定值 就终止
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
// 迁移当前桶到ht[1]
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
// ht[0]的迁移完成
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
// 释放一个ht[0]的
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
// 再把ht[1]的地址给ht[0] 这样操作的对象永远是ht[0]
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
// 复位ht[1]
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
// 设置标志 表示结束了rehash
d->rehashidx = -1;
// 返回0表示迁移完成了
return 0;
}
// 返回1 表示还没迁移完
return 1;
}
- _dictRehashStep
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
- 调用
dictAddRaw(增加),dictGenericDelete(删除),dictFind(查询),dictGetRandomKey(查询),dictGetSomeKeys(查询)调用_dictRehashStep,然后_dictRehashStep调用dictRehash
参考文献:
http://t.csdn.cn/NE9nM





















 498
498











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








