ㅤㅤㅤ
ㅤㅤㅤ
ㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤ(自我控制是最强的本能 - 萧伯纳)
ㅤㅤㅤ
ㅤㅤㅤ
ㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤ
问题
@albedo-auth-nestjs包(0.2.8版本之前)在安装到项目中后,在使用中无法抛出自定义的异常错误,而在以文件模块形式在项目中使用则能够正常鉴权和抛出异常错误。
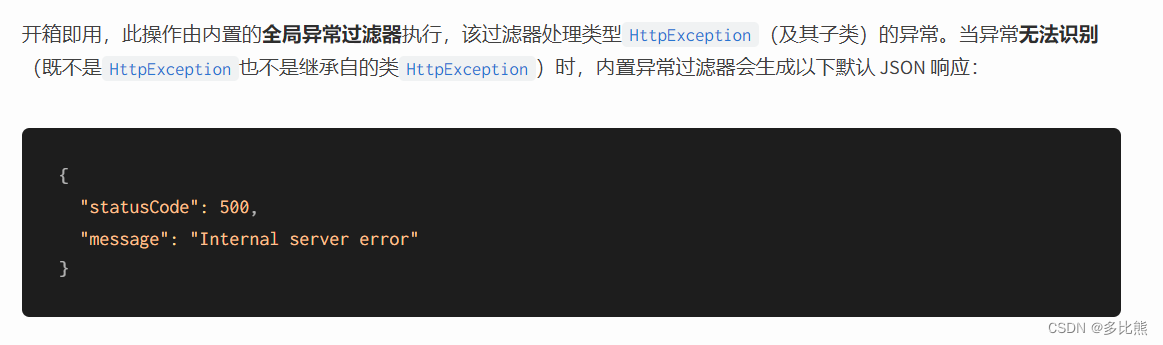
根据官方文档描述,默认会有一个全局异常过滤器,对于HttpException或者继承自HttpException类的异常,Nestjs默认会返回一个JSON 异常响应:
{"statusCode":500,"message":"Internal server error"}
而在鉴权守卫代码中使用的异常类是UnauthorizedException,该类继承了HttpException类。那么按照官方定义,是可以抛出UnauthorizedException异常的
throw new UnauthorizedException(this.verbose && 'Authorization header is required')
export class UnauthorizedException extends HttpException {
// .......
}
但经过测试,发现无论抛出什么异常,最终总是返回
{"statusCode":500,"message":"Internal server error"}
排查
于是开始调试源码,了解了Nestjs异常过滤器的处理流程
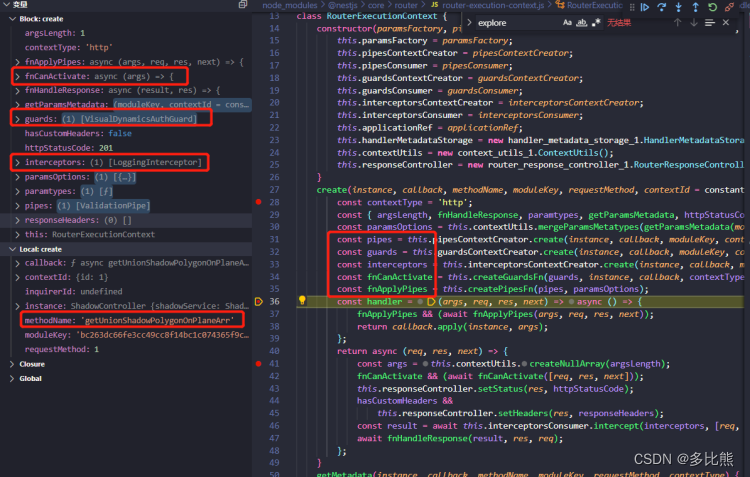
- Nestjs应用程序启动时会给Controller路由层的每一个方法绑定回调函数,该回调函数内包含了守卫,管道,拦截器等。用于后续每次请求执行
create(instance, callback, methodName, moduleKey, requestMethod, contextId = constants_3.STATIC_CONTEXT, inquirerId) {
const contextType = 'http';
const { argsLength, fnHandleResponse, paramtypes, getParamsMetadata, httpStatusCode, responseHeaders, hasCustomHeaders, } = this.getMetadata(instance, callback, methodName, moduleKey, requestMethod, contextType);
const paramsOptions = this.contextUtils.mergeParamsMetatypes(getParamsMetadata(moduleKey, contextId, inquirerId), paramtypes);
// 管道
const pipes = this.pipesContextCreator.create(instance, callback, moduleKey, contextId, inquirerId);
// 守卫
const guards = this.guardsContextCreator.create(instance, callback, moduleKey, contextId, inquirerId);
// 拦截器
const interceptors = this.interceptorsContextCreator.create(instance, callback, moduleKey, contextId, inquirerId);
const fnCanActivate = this.createGuardsFn(guards, instance, callback, contextType);
const fnApplyPipes = this.createPipesFn(pipes, paramsOptions);
const handler = (args, req, res, next) => async () => {
fnApplyPipes && (await fnApplyPipes(args, req, res, next));
return callback.apply(instance, args);
};
// 回调函数
return async (req, res, next) => {
const args = this.contextUtils.createNullArray(argsLength);
fnCanActivate && (await fnCanActivate([req, res, next]));
this.responseController.setStatus(res, httpStatusCode);
hasCustomHeaders &&
this.responseController.setHeaders(res, responseHeaders);
const result = await this.interceptorsConsumer.intercept(interceptors, [req, res, next], instance, callback, handler(args, req, res, next), contextType);
await fnHandleResponse(result, res, req);
};
}
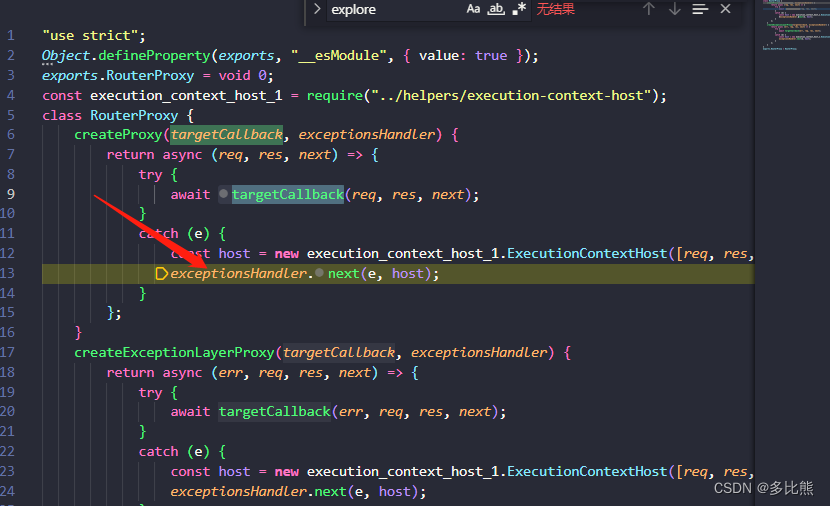
- 每一个回调函数都被包裹在try catch块中。用于处理全局异常,执行next函数
class RouterProxy {
createProxy(targetCallback, exceptionsHandler) {
return async (req, res, next) => {
try {
await targetCallback(req, res, next);
}
catch (e) {
const host = new execution_context_host_1.ExecutionContextHost([req, res, next]);
exceptionsHandler.next(e, host);
}
};
}
/// .....
}
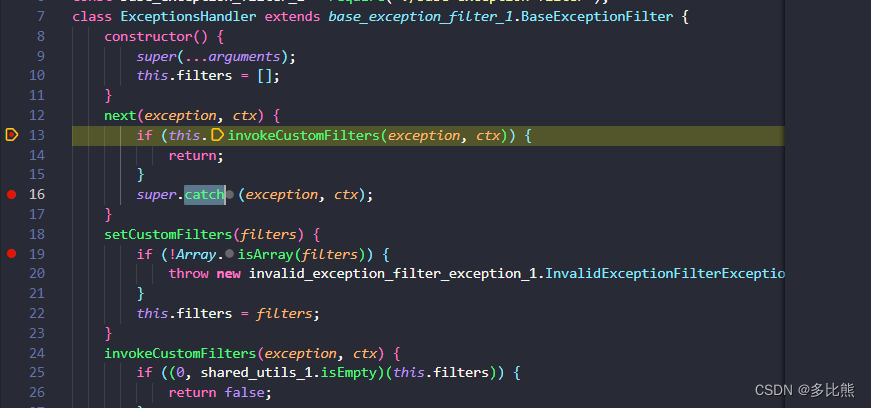
-
每次有异常被捕获时,都会判断是否有自定义过滤器,如果没有,则使用默认的异常过滤器
class ExceptionsHandler extends base_exception_filter_1.BaseExceptionFilter {
constructor() {
// …
}
next(exception, ctx) {
// 判断是否存在自定义过滤器
if (this.invokeCustomFilters(exception, ctx)) {
return;
}
// 执行全局异常过滤器的catch函数
super.catch(exception, ctx);
}
invokeCustomFilters(exception, ctx) {
// …
}
}
-
默认的异常过滤器会校验抛出的异常是否是HttpException类。如果不是,则按未知异常处理。否则返回自定义异常
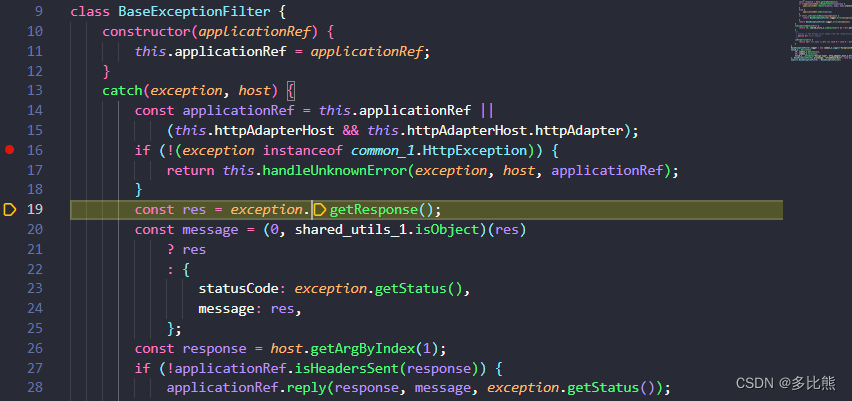
class BaseExceptionFilter {
constructor(applicationRef) {
this.applicationRef = applicationRef;
}
catch(exception, host) {
const applicationRef = this.applicationRef ||
(this.httpAdapterHost && this.httpAdapterHost.httpAdapter);
// 判断exception是否是HttpEception的实例
if (!(exception instanceof common_1.HttpException)) {
// 处理未知异常
return this.handleUnknownError(exception, host, applicationRef);
}
// 处理自定义异常
const res = exception.getResponse();
const message = (0, shared_utils_1.isObject)(res)
? res
: {
statusCode: exception.getStatus(),
message: res,
};
const response = host.getArgByIndex(1);
if (!applicationRef.isHeadersSent(response)) {
applicationRef.reply(response, message, exception.getStatus());
}
else {
applicationRef.end(response);
}
}
handleUnknownError(exception, host, applicationRef) {
// .....
}
}
经过反复debug,发现在执行!(exception instanceof common_1.HttpException)时永远都是false,导致每次都被当做未知异常处理,查看文件
可是守卫抛出的UnauthorizedException类是继承HttpException的。
在Nestjs的仓库中,找到了一例和我问题相似的issue
● https://github.com/nestjs/nest/issues/8617
原来是因为包版本嵌套依赖导致的,A服务依赖了@nestjs/common包,而A服务依赖的守卫组件又有自己的@nestjs/common包,虽然两个类名相同,但由于隶属于不同的文件,所以他们必然是没有关系的。
比如下面的例子:
为什么会有嵌套依赖?
因为下载npm包时,会同时将dependencies的依赖下载到当前的node_modules,这样就会导致每个npm包可能都有自己的依赖和版本。这样会造成两个问题
- 包版本可能不兼容
- 两个包实例不同,导致instansof永远为false
如何解决嵌套依赖导致的问题?
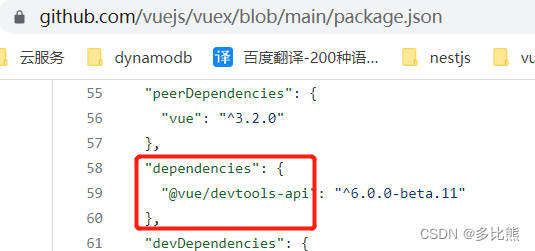
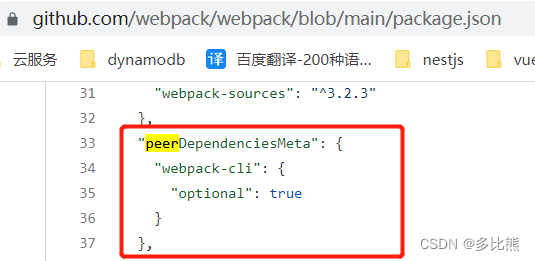
像vuex,webpack,@nestjs/core等包的package.json中都有peerDependencies和devDependencies。
-
vuex
-
webpack
-
@nestjs/core
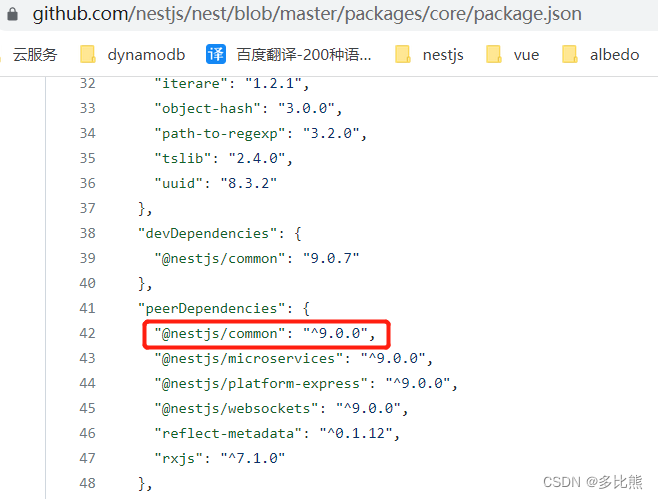
根据packge.json中的约定,定义在peerDependencies内的包在被安装时不会被下载,它直接指向了根目录下的依赖(如果根目录没有安装,则启动时会因为找不到依赖而提醒安装),这样就避免了因包嵌套导致的依赖版本,实例相等性问题
定义在devDependencies内的包在被安装时不会下载,仅用于开发阶段使用,这样就不用在安装阶段去下载这些依赖
解决
现在问题已经找到,于是调整了@albedo-inc/albedo-auth-nestjs服务的package.json
将@nestjs/common和@nestjs/core从dependencies中删除
然后复制到到devDependencies和peerDependencies,限制守卫组件和 Nestjs的项目使用同一个@nestjs/common和@nestjs/core模块包。
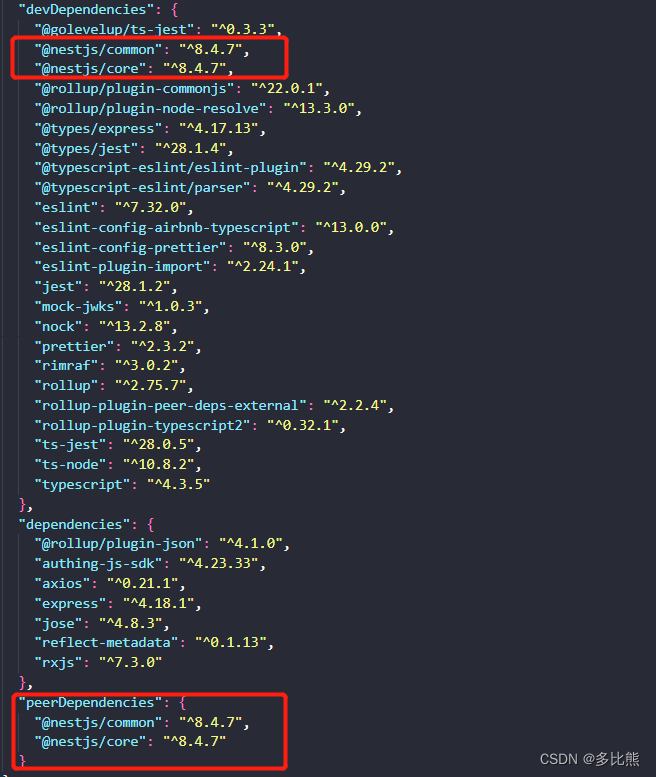
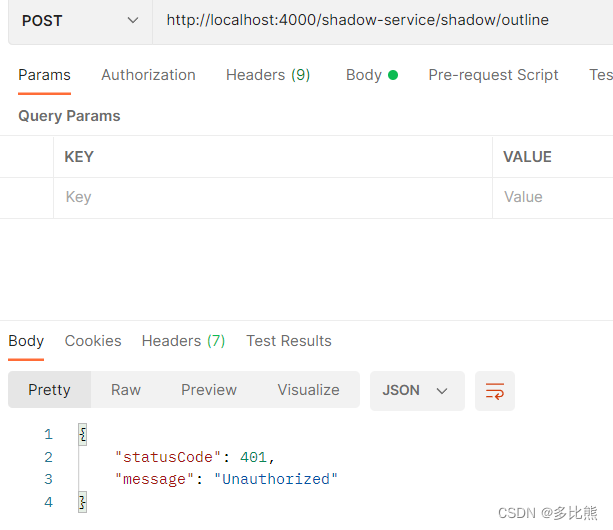
通过使用 Postman工具测试鉴权失败的接口,可见已正常抛出自定义的UnauthorizedException错误。





















 4588
4588











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








