小提示:
此系列文章属于个人学习笔记,如果其中有误,希望大家指正。
也希望大家能够提出一些游戏开发学习上的建议等等的~
谢谢大家!(๑•̀ㅂ•́)و✧
教程简介:
了解如何使用 LOVE 2D 和 Lua 创建游戏。LOVE 是一个框架,可用于在 Lua 中制作 2D 游戏。它是免费的,开源的,适用于Windows,Mac OS X,Linux,Android和iOS。
教程地址:
Game Development with LÖVE 2D and Lua – Full Course
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I549C6SmUnk(需科学上网)
辅助资料:
菜鸟教程:Lua教程
w3shcools:Lua教程
B站:Lua快速入门教程
B站:Lua进阶教程
本节目录
一、简介
1.什么是Lua?
Lua 是一种轻量小巧的脚本语言,用标准C语言编写并以源代码形式开放,其设计目的是为了嵌入应用程序中,从而为应用程序提供灵活的扩展和定制功能。现在Lua多用于游戏中。
2.哪些应用有使用到了Lua?
Adobe Photoshop Lightroom
Apache HTTP Server
Awesome WM
Roblox
Angry Birds
The Sims 2: Night life
Mafia Ⅱ
World of Warcraft
Fable 3
3.文本编辑器的选择?
VSCode
Vim
Sublime Text
Notepad
Notepad++
Notepadqq
Emacs
ZeroBrane Studio
IntelliJ IDEA
二、安装Lua (Windows)
可以选择按照如下步骤在本地安装和配置Lua,也可以使用LuatOS在线模拟器。
1.下载
https://luabinaries.sourceforge.net/download.html

2.添加路径
将下载后的压缩包解压缩,把Lua文件夹复制到Program Files下方。
并在环境变量 - 系统变量 - Path中添加路径:


打开命令指示符,可以输入 color 02,让自己看起来像黑客一样炫酷(๑•̀ㅂ•́)و✧:(误

3.运行
输入:lua53,返回如下信息则配置成功:

试试能否运行:

下面我们来尝试一下,任意位置新建lua文件和运行:

输入lua53 main.lua 成功运行:

三、运行Lua (VSCode)
1.安装VSCode
https://code.visualstudio.com/
2.打开文件夹
打开我们创建的lua文件所在的位置,记得是Open Folder...

3.运行文件
打开新终端,输入lua53 main.lua回车即可运行。

4.Lua官方文档查看(补充)
这部分是看了B站教程的补充:B站教程:查看官方接口文档。
中文版Lua5.3参考手册由云风翻译。

查找到函数后,参考对函数的介绍来进行使用:
print(math.abs(-10))
10
四、打印和注释 Printing and Comments
1.注释
(1)单行注释
-- 这是一条注释
(2)多行注释
--[[
这是多行注释
多行注释
]]
2.打印
print("Hello World!")
print("Hello","QingTail") --两个字符串中间出现一个tab
print("Hello".."QingTail") --两个字符串连接在一起
Hello World!
Hello QingTail
HelloQingTail
五、变量和数据类型 Variables & Data Types
1.数据类型
菜鸟教程:Lua 数据类型 这里贴了菜鸟教程对数据类型具体解释的链接。
(1)nil
表示一个无效值(在条件表达式中相当于false)。
(2)number
表示双精度类型的实浮点数。
(3)string
字符串用一对双引号或是单引号来表示。
(4)boolean
包含两个值:true false。
(5)tables
Lua 中的表(table)其实是一个"关联数组"(associative arrays),数组的索引可以是数字、字符串或表类型。在 Lua 里,table 的创建是通过"构造表达式"来完成,最简单构造表达式是{},用来创建一个空表。
2.变量
(1)局部变量
local a = 8
local b = 3.14
local c = "hello"
local d = [[
abcdefg
]]
print(a,b,c,d)
8 3.14 hello abcdefg
同时分配多个变量:
local one,two,three = "one",2,false
print(one,two,three)
one 2 false
(2)全局变量
GlobalVar = 10
print(_G["GlobalVar"])
10
(3)实例
local name = "QingTail"
print("Hello, my name is "..name)
name = "Steve"
print("This is a cool name, "..name)
Hello, my name is QingTail
This is a cool name, Steve
六、字符串 Strings
1.三种表示方式
单引号、双引号、[[ ]]
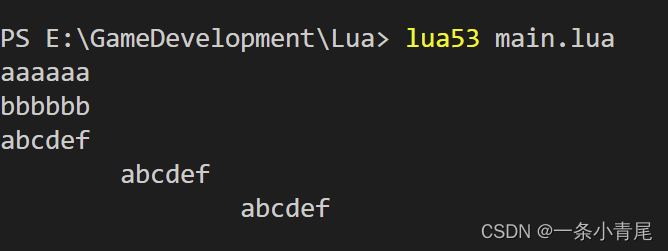
local a = 'aaaaaa'
local b = "bbbbbb"
local c = [[
abcdef
abcdef
abcdef
]]
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
输出:
2.输出字符串的长度
local x ="abcdef"
print(#x)
6
或是另一种写法:
local x =#"abcdef"
print(x)
6
3.数字转换为字符串
local num = 20
local str = tostring(num)
print(type(num),type(str))
number string
4.转义字符
\n 换行(LF) ,将当前位置移到下一行开头
\t 水平制表(HT) (跳到下一个TAB位置)
\v 垂直制表(VT)
\\ 代表一个反斜线字符’‘\’
\" 双引号
\’ 单引号
print("Hello\nWorld\tI am\valmost 19\\20 \"year\'")
输出:

5.字符大小写转换
local str = "Hello World!"
print(str)
print(str.lower(str)) --转换为全小写
print(str.upper(str)) --转换为全大写
print(str.len(str)) --输出字符串长度
print(#str) --输出字符串长度
Hello World!
hello world!
HELLO WORLD!
12
12
七、数学 Math
1.算术运算符
+、-、*、/、^、%
print(5 + 5)
print(5 - 5)
print(5 * 5)
print(17 / 5)
print(5 ^ 2)
print(17 % 5)
10
0
25
3.4
25.0
2
2.math库
w3school:Lua - Math数学库
(1)pi的值
print(math.pi)
3.1415926535898
(2)最小值、最大值
print(math.min(5,-5,10,100))
print(math.max(5,-5,10,100))
-5
100
(3)向上取整
print(math.ceil(20.1))
print(math.ceil(20.9))
21
21
(4)向下取整
print(math.floor(20.1))
print(math.floor(20.9))
20
20
(5)math.random ([m [, n]]) 随机数
math.random(),返回范围 [0,1) 内的统一伪随机实数。
math.random(m),math.random 返回范围 [1, m] 内的统一伪随机整数。
math.random(m,n),math.random 返回范围 [m, n] 内的统一伪随机整数。
print(math.random())
print(math.random(10))
print(math.random(10,50))
0.001251220703125
6
17
(6)随机数种子
math.randomseed (x)将 x 设置为伪随机生成器的"种子":相等的种子产生相等的数字序列。
math.randomseed(os.time())
print(math.random())
print(math.random())
PS E:\GameDevelopment\Lua> lua53 main.lua
0.79083251953125
0.89505004882812
PS E:\GameDevelopment\Lua> lua53 main.lua
0.44686889648438
0.98541259765625
PS E:\GameDevelopment\Lua> lua53 main.lua
0.75894165039062
0.16607666015625
八、条件语句 If Statements
1.逻辑运算符:and、or、not
if not false and true then
print("This is true.")
end
This is true.
2.关系运算符:>、<、>=、<=、~=、==
local x = 5
if x > 2 then
print("x is more than 2.")
end
x is more than 2.
3.实例
(1)条件语句1
local age = 17
if age >= 18 then
print("You may enter KTV.")
elseif age < 13 then
print("The water slides are down the road.")
else
print("You are not welcome, BEGONE!")
end
You are not welcome, BEGONE!
(2)条件语句2
local age = 18
local birthday = true
if age >= 18 then
print("You may enter.")
if birthday then
print("You get a free drink on us.")
end
elseif age < 13 then
print("The water slides are down the road.")
else
print("You are not welcome, BEGONE!")
end
You may enter.
You get a free drink on us.
(3)局部变量与全局变量
local age = 19
local name = age > 18 and "Mike" or "Jeff"
print(name)
if true then
name = "Luke"
end
print(name)
Mike
Luke
local age = 19
local name = age > 18 and "Mike" or "Jeff"
print(name)
if true then
local name = "Luke"
end
print(name)
Mike
Mike
九、循环 Loops
1.for 循环
for i = 1,10 do
print(i)
end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
for i = 1,10,2 do
print(i)
end
1
3
5
7
9
for i = 10,1,-2 do
print(i)
end
10
8
6
4
2
2.while 循环
while true do
print("mike")
end
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
……(无限输出)
while true do
print("mike")
break
end
mike
local count = 0
while true do
count = count + 1
print("mike")
if count > 10 then
break
end
end
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
local count = 0
while count < 10 do
count = count + 1
print("mike")
end
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
mike
3.repeat…until 循环
repeat…until 循环的条件语句在当前循环结束后判断。
local count = 10
repeat
count = count + 1
print("mike")
until count > 5
mike
十、用户输入 User Input
print("What is your name?")
local ans = io.read()
print("Name:",ans)
What is your name?
qingtail(输入)
Name: qingtail
io.write("Enter your name: ")
local ans = io.read()
print("Name:",ans)
Enter your name: qingtail(输入)
Name: qingtail
十一、表 Tables
1.输出
local tbl = {"This",2,9.9,true,{"ok","cool"}}
for i = 1, #tbl do
print(tbl[i])
end
This
2
9.9
true
table: 0000000000cca050
注意lua序号下标是从1开始的:
local tbl = {"This", 2, 9.9, true, {"ok","cool"}}
-- 1 2 3 4 (1) 5 (2)
print(tbl[1])
print(tbl[5][1])
print(tbl[9])
This
ok
nil
2.赋值
local a,b,c,d,e = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
local alphaNums = {1, b, 3, d, 5}
print(a)
print(alphaNums[1])
1
1
local a,b,c,d,e = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
local alphaNums = {1, b, 3, d, 5}
print(a)
print(alphaNums[2])
1
2
local alphaNums = {1, b, 3, d, 5}
print(alphaNums[2])
nil
3.插入和移除
(1)在末尾插入元素
local nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
table.insert(nums, 19)
for i = 1,#nums do
print(nums[i])
end
1
3
5
7
9
19
(2)在指定位置插入元素
local nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
table.insert(nums, 2, 19)
for i = 1,#nums do
print(nums[i])
end
1
19
3
5
7
9
(3)移除指定位置元素
local nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
table.remove(nums, 2)
for i = 1,#nums do
print(nums[i])
end
1
5
7
9
4.迭代器
local nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
for index,value in pairs(nums)do
print(index, value)
end
1 1
2 3
3 5
4 7
5 9
5.多元数组
local nums = {
{1, 8, 3}, --1
{4, 2, 6}, --2
{7, 5, 9}, --3
{7, 5, 9}, --4
{7, 5, 9}, --5
}
print(#nums) --输出nums的长度
print(#nums[1]) --输出nums[1]的长度
5
3
local nums = {
{1, 8, 3}, --1
{4, 2, 6}, --2
{7, 5, 9}, --3
}
for i = 1, #nums do
for j = 1,#nums[i] do
print(nums[i][j])
end
end
1
8
3
4
2
6
7
5
9
6.连接
local nums = {1, 2, 3}
print(table.concat(nums," "))
print(table.concat(nums,";"))
print(table.concat(nums,"-"))
1 2 3
1;2;3
1-2-3
7.字典
local tbl = {
name = "Mike",
age = 12
}
print(tbl["name"])
Mike
十二、函数 Functions
1.无参函数
local function sayHello()
print("Hello!")
end
sayHello()
Hello!
2.有参无返函数
local function sayHello(name)
local name = name or "Mike"
print("Hello "..name.."!")
end
sayHello()
sayHello("Jack")
sayHello("Sally")
Hello Mike!
Hello Jack!
Hello Sally!
3.有参有返函数
local function sum(num1, num2)
return num1 + num2
end
local x = 20
local ans = sum(10, x)
print("The answer is: ".. ans)
The answer is: 30
local function sum(num1, num2)
local val = num1 + num2
if val == 10 then
return val
end
if val < 100 then
return -val
end
return val * 2
end
local x = 20
local ans = sum(10, x)
print("The answer is: ".. ans)
The answer is: -30
十三、处理文件 Working with Files
1.创建文件
创造文件,若有同名文件则将文件内容清空。
io.output("myfile.txt")
2.读写文件
(1)简单模式
io.input("myfile.txt")
local fileData = io.read("*all")
print(fileData)
io.close()
Hello World!
mike
sally
jack
i am cool
或是另一种写法:
io.input("myfile.txt")
local fileData = io.read("*all")
io.close()
print(fileData)
Hello World!
mike
sally
jack
i am cool
(2)完全模式
file = io.open (filename [, mode])
① mode: w 打开只写文件,若文件存在则文件长度清为0,即该文件内容会消失。若文件不存在则建立该文件。
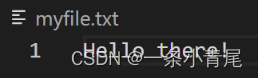
local file = io.open("myfile.txt","w")
if file ~= nil then
file:write("Hello there!")
file:close()
else
print("Could not open the file.")
end
运行:
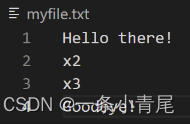
② mode: r 以只读方式打开文件,该文件必须存在。
myfile.text中内容:
local file = io.open("myfile.txt","r")
if file ~= nil then
print(file:read("*all"))
file:close()
else
print("Could not open the file.")
end
运行:
Hello there!
x2
x3
Goodbye!
local file = io.open("myfile.txt","r")
if file ~= nil then
print(file:read("*line"))
print(file:read("*line"))
file:close()
else
print("Could not open the file.")
end
Hello there!
x2
③ mode: a 以附加的方式打开只写文件。若文件不存在,则会建立该文件,如果文件存在,写入的数据会被加到文件尾,即文件原先的内容会被保留。(EOF符保留)
local file = io.open("myfile.txt","a")
if file ~= nil then
print(file:write("\nAppended text!"))
file:close()
else
print("Could not open the file.")
end
运行:

十四、自定义模块 Custom Modules
-- custom.lua
Mod = {
sum = function (x,y)
return x + y
end
}
function Mod.sayHello(name)
print("Hello, "..name)
end
return Mod
--main.lua
local mod = require("custom")
print(mod.sum(10,5))
mod.sayHello("Mike")
15
Hello, Mike
十五、面向对象的程序设计 OOP
1.面向对象
(1)创建对象
local function Pet(name)
return {
name = name or "Charlie"
}
end
local cat = Pet()
local dog = Pet("Jack")
print(cat.name)
print(dog.name)
Charlie
Jack
(2)访问属性
可以使用点.来访问类的属性:
注意局部变量无法被访问。
local function Pet(name)
local age = 10
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
daysAlive = age * 365
}
end
local cat = Pet()
local dog = Pet("Jack")
print(cat.age)
print(dog.daysAlive)
nil
3650
local function Pet(name)
local age = 10
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
speak = function ()
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating")
end
}
end
local cat = Pet()
local dog = Pet("Jack")
cat.speak()
dog.feed()
Meaw
eating
(3)访问成员函数
可以使用冒号:来访问类的成员函数:
local function Pet(name)
local age = 10
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
speak = function (self)
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating",self.name)
end
}
end
local cat = Pet()
local dog = Pet("Jack")
cat:speak()
dog:feed()
Meaw
eating Jack
local function Pet(name)
local age = 10
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
speak = function (self)
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating",self.name)
self:speak()
end
}
end
local cat = Pet()
local dog = Pet("Jack")
cat.speak()
dog:feed()
Meaw
eating Jack
Meaw
2.继承
(1)未使用继承
local function Pet(name)
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
speak = function (self)
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating",self.name)
self:speak()
end
}
end
local function Dog(name)
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
breed = "doberman",
loyalty = 0,
speak = function (self)
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating",self.name)
self:speak()
end
}
end
local doberman = Dog("Jesse")
print(doberman.name,doberman.breed)
Jesse doberman
(2)使用继承
local function Pet(name)
return {
name = name or "Charlie",
status = "hungry",
points = 10,
speak = function (self)
print("Meaw")
end,
feed = function (self)
print("eating",self.name)
self:speak()
end
}
end
local function Dog(name,breed)
local dog = Pet(name)
dog.breed = breed or "Doberman"
dog.loyalty = 0
dog.speak = function (self)
print("Woof")
end
return dog
end
local poodle = Dog("Jesse","poodle")
print(poodle.name,poodle.breed)
poodle:speak()
Jesse poodle
Woof
总结
之前看了B站有关的Lua教程:B站:Lua快速入门教程、B站:Lua进阶教程,讲的不错,中文+无废话。
Youtube这套教程比较好的是有项目实践,但是英文差有些词听不懂hhh。
本节学习了Lua的一些基础知识,在处理文件、自定义、面向对象这几方面有些模糊,不过之后在项目实践中会得到具体练习。
之后也会对此文进行补充、完善。
加油(っ*´Д`)っ笨蛋(自勉!

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








