目录
前言
说起来条件编译,可能这个词有一点点陌生,但是如果之前接触过vue写法的话,那就很明白了;
就是v-if ,当满足对应的条件,展示对应的内容!
那么在React中的条件渲染当然采用的不是v-if,需要用自己React的条件渲染方式!
基础配置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<style>
.other {
color: #ff0000;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/react/16.4.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/react-dom/16.4.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/babel-standalone/6.26.0/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
const app = document.getElementById('app')
class Demo extends React.Component {
state = {
type: 1
}
render() {
const {type} = this.state
return (
<div>
{type}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, app)
</script>
</body>
</html>页面展示

1. 声明一个函数,返回对应的内容
//1. 第一种方法,声明函数返回dom
showMsg = () => {
let type = this.state.type
if (type === 1) {
return (<h2>第一种写法:type值等于1</h2>)
} else {
return (<h2 className="other">第一种写法:type值不等于1</h2>)
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.showMsg()}
</div>
);
}页面展示:

2. 使用元素变量
render() {
const {type} = this.state
//2. 第二种方法 声明变量 给变量赋值
let test = null
if (type === 1) {
test = <h2>第二种写法:type值等于1</h2>
} else {
test = <h2 className="other">第二种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
}
return (
<div>
{test}
</div>
);
}页面展示:

3. 使用三目运算符
render() {
const {type} = this.state
return (
<div>
{
//3. 第三种方法,利用三元运算符渲染需要渲染的变量
type === 1 ? <h2>第三种写法:type值等于1</h2> :
<h2 className="other">第三种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
}
</div>
);
}页面展示:

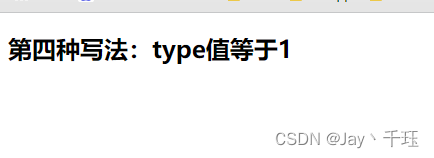
4. 使用与运算符&&
render() {
const {type} = this.state
return (
<div>
{type === 1 && <h2>第四种写法:type值等于1</h2>}
{type !== 1 && <h2 className="other">第四种写法:type值不等于1</h2>}
</div>
);
}页面展示:
总结
我这边开发中使用频率比较高的,应该是第三种和第四种: 三目运算符,用于一个值为真或者为假;与运算符用于写,多个类型值展示不同的内容
完整示例
<script type="text/babel">
const app = document.getElementById('app')
class Demo extends React.Component {
state = {
type: 1
}
//1. 第一种方法,声明函数返回dom
showMsg = () => {
let type = this.state.type
if (type === 1) {
return (<h2>第一种写法:type值等于1</h2>)
} else {
return (<h2 className="other">第一种写法:type值不等于1</h2>)
}
}
render() {
const {showMsg} = this
const {type} = this.state
//2. 第二种方法 声明变量 给变量赋值
let test = null
if (type === 1) {
test = <h2>第二种写法:type值等于1</h2>
} else {
test = <h2 className="other">第二种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
}
return (
<div>
{
//1. 第一种写法
showMsg()
}
{
// 2. 第二种写法
test
}
{
//3. 第三种方法,利用三元运算符渲染需要渲染的变量
type === 1 ? <h2>第三种写法:type值等于1</h2> : <h2 className="other">第三种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
}
{
// 4. 第四种方法,使用逻辑运算符
type === 1 && <h2>第四种写法:type值等于1</h2>
}
{type !== 1 && <h2 className="other">第四种写法:type值不等于1</h2>}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, app)
</script>页面展示:

当我们随意改变state中的type值,只要不让 type ===1 就好,

判断生效,问题不大























 1431
1431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










