bigcache 源码解析
1、使用样例
func main() {
f, _ := os.Open("D:\\测试.csv")
r := csv.NewReader(f)
res, _ := r.ReadAll()
b, _ := json.Marshal(res)
cache, _ := bigcache.New(context.Background(), bigcache.DefaultConfig(10*time.Minute))
err := cache.Set("my-unique-key", b)
if err != nil {
return
}
entry, _ := cache.Get("my-unique-key")
fmt.Println(len(string(entry)))
}
以上就是我们从git 上拷贝的样例,其中我们可以看到,第一步先new出一个cache 出来,这里主要包含两个参数,一个上下文,一个是Config对象。
为什么要传递上线文呢,上下文可以作为协程之间的通信,通过我们对于每个请求都会创建一个上下文,用于在函数之间的传递,其中包括WithCancle,WithDateLine,WithTimeOut,WithValue。其中当ctx.Down时,会向chan 中写数据,其他协程可以在select 中监听到该信号,具体查看context包详解。
Config 对象就是我们的cache的一个核心配置对象了,我们来看一看config 对象都有些什么。
2、config 配置
//英文注释都是源代码的,我这里加上我的中文注释
// Config for BigCache
type Config struct {
// Number of cache shards, value must be a power of two
// 缓存的分片数,这个数必须是2的幂 也就是2 4 8 16 32 64 ..
Shards int
// Time after which entry can be evicted
// 多长时间之后entry 也就是我们存储的实体能被驱逐
LifeWindow time.Duration
// Interval between removing expired entries (clean up).
// If set to <= 0 then no action is performed. Setting to < 1 second is counterproductive — bigcache has a one second resolution.
// 删除过期条目之间的时间间隔
// 如果你设置了它<=0,那么久没有操作被执行,也就是不会被删除,如果你设置了它<1s,那么会适得其反,因为bigcache 有一个1s的什么操作
CleanWindow time.Duration
// Max number of entries in life window. Used only to calculate initial size for cache shards.
// When proper value is set then additional memory allocation does not occur.
// MaxEntriesInWindow 表示活着的窗口的最大的条目数量,仅仅用来计算cache的分片初始化的大小的
// 如果我们设置了正确的值,那么将不会发生额外的内存分配
MaxEntriesInWindow int
// Max size of entry in bytes. Used only to calculate initial size for cache shards.
// MaxEntrySize 表示entry的最大字节数,他仅仅是用来计算cache的shards 的初始化大小。
MaxEntrySize int
// StatsEnabled if true calculate the number of times a cached resource was requested.
// StatsEnabled这个属性,如果为true,则计算这个cache资源被请求的次数
StatsEnabled bool
// Verbose mode prints information about new memory allocation
// Verbose模式打印关于新内存的分配
Verbose bool
// Hasher used to map between string keys and unsigned 64bit integers, by default fnv64 hashing is used.
// hasher使用一种映射,用于string 的key 和无符号的整数,默认使用的hash是fnv64这个方法。
Hasher Hasher
// HardMaxCacheSize is a limit for BytesQueue size in MB.
// It can protect application from consuming all available memory on machine, therefore from running OOM Killer.
// Default value is 0 which means unlimited size. When the limit is higher than 0 and reached then
// the oldest entries are overridden for the new ones. The max memory consumption will be bigger than
// HardMaxCacheSize due to Shards' s additional memory. Every Shard consumes additional memory for map of keys
// and statistics (map[uint64]uint32) the size of this map is equal to number of entries in
// cache ~ 2×(64+32)×n bits + overhead or map itself.
// HardMaxCacheSize 这个属性,是一个ByteQueue的字节大小的限制
// 它能保护应用程序,避免消耗机器上的所有可用的内存,从而避免运行oom killer
// 默认这个值是0,意思是不限制大小,
HardMaxCacheSize int
// OnRemove is a callback fired when the oldest entry is removed because of its expiration time or no space left
// for the new entry, or because delete was called.
// Default value is nil which means no callback and it prevents from unwrapping the oldest entry.
// ignored if OnRemoveWithMetadata is specified.
OnRemove func(key string, entry []byte)
// OnRemoveWithMetadata is a callback fired when the oldest entry is removed because of its expiration time or no space left
// for the new entry, or because delete was called. A structure representing details about that specific entry.
// Default value is nil which means no callback and it prevents from unwrapping the oldest entry.
// OnRemoveWithMetadata是一个回调,当最旧的条目由于其过期时间或没有剩余空间而被删除时触发
//
// 默认值为nil,这意味着没有回调,并且可以防止打开最旧的条目。
OnRemoveWithMetadata func(key string, entry []byte, keyMetadata Metadata)
// OnRemoveWithReason is a callback fired when the oldest entry is removed because of its expiration time or no space left
// for the new entry, or because delete was called. A constant representing the reason will be passed through.
// Default value is nil which means no callback and it prevents from unwrapping the oldest entry.
// Ignored if OnRemove is specified.
// 这段注释,我用自己的话表述一下,OnRemoveWithReason 意思是出现一下三种情况会触发回调,哪三种情况呢,
// 1、当我们的key过期了
// 2、当我们的调用set的时候,这个时候的cache 大小处于最大值,或者他的条目(entry)超过了最大碎片(shard)大小。
// 3、当我们主动调用delete的时候
// 回调有三个参数,key entry,reason
// reason值表示的含义 1 : expired 2:nospace 3:delete was called
// 当我们知道了OnRemoveWithReason 回调含义之后,我们可以做一下操作,用来监控我们程序,例如可以观察,nospace的情况
// delete的情况
OnRemoveWithReason func(key string, entry []byte, reason RemoveReason)
onRemoveFilter int
// Logger is a logging interface and used in combination with `Verbose`
// Defaults to `DefaultLogger()`
Logger Logger
}
// Response will contain metadata about the entry for which GetWithInfo(key) was called
type Response struct {
EntryStatus RemoveReason
}
// RemoveReason is a value used to signal to the user why a particular key was removed in the OnRemove callback.
// RemoveReason是一个值,用于向用户发出在OnRemove回调中删除特定键的原因
type RemoveReason uint32
const (
// Expired means the key is past its LifeWindow.
// Expired 意思是这个key超过存活窗口了,也就是已经过期啦
Expired = RemoveReason(1)
// NoSpace means the key is the oldest and the cache size was at its maximum when Set was called, or the
// entry exceeded the maximum shard size.
// NoSpace 意思是这个key 是最久的并且当set被调用的时候这个cache的大小处于最大值,或者这个条目超过了最大碎片大小。
NoSpace = RemoveReason(2)
// Deleted means Delete was called and this key was removed as a result.
// Deleted 意思是调用了删除,这个key 被移除了。
Deleted = RemoveReason(3)
)
// Metadata contains information of a specific entry
// Meatedata包含的就是一个32位无符号的整型表示这个这个entry
type Metadata struct {
RequestCount uint32
}
3、回调实现部分
首先看一下newCache的实现部分,我们先从回调实现开始看
func newBigCache(ctx context.Context, config Config, clock clock) (*BigCache, error) {
if !isPowerOfTwo(config.Shards) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Shards number must be power of two")
}
if config.MaxEntrySize < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("MaxEntrySize must be >= 0")
}
if config.MaxEntriesInWindow < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("MaxEntriesInWindow must be >= 0")
}
if config.HardMaxCacheSize < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("HardMaxCacheSize must be >= 0")
}
if config.Hasher == nil {
config.Hasher = newDefaultHasher()
}
cache := &BigCache{
shards: make([]*cacheShard, config.Shards),
lifeWindow: uint64(config.LifeWindow.Seconds()),
clock: clock,
hash: config.Hasher,
config: config,
shardMask: uint64(config.Shards - 1),
close: make(chan struct{}),
}
var onRemove func(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason)
if config.OnRemoveWithMetadata != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemoveWithMetadata
} else if config.OnRemove != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemove
} else if config.OnRemoveWithReason != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemoveWithReason
} else {
onRemove = cache.notProvidedOnRemove
}
for i := 0; i < config.Shards; i++ {
cache.shards[i] = initNewShard(config, onRemove, clock)
}
if config.CleanWindow > 0 {
go func() {
ticker := time.NewTicker(config.CleanWindow)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println("ctx done, shutting down bigcache cleanup routine")
return
case t := <-ticker.C:
cache.cleanUp(uint64(t.Unix()))
case <-cache.close:
return
}
}
}()
}
return cache, nil
}
从上述的代码看,很清晰看到,回调的实现部分
var onRemove func(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason)
if config.OnRemoveWithMetadata != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemoveWithMetadata
} else if config.OnRemove != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemove
} else if config.OnRemoveWithReason != nil {
onRemove = cache.providedOnRemoveWithReason
} else {
onRemove = cache.notProvidedOnRemove
}
在bigCache 的内部自己实现了4个函数,分别为
// 对应OnRemoveWithMetadata
func (c *BigCache) providedOnRemoveWithMetadata(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason) {
hashedKey := c.hash.Sum64(readKeyFromEntry(wrappedEntry))
shard := c.getShard(hashedKey)
c.config.OnRemoveWithMetadata(readKeyFromEntry(wrappedEntry), readEntry(wrappedEntry), shard.getKeyMetadata(hashedKey))
}
// 对应OnRemove
func (c *BigCache) providedOnRemove(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason) {
c.config.OnRemove(readKeyFromEntry(wrappedEntry), readEntry(wrappedEntry))
}
// 对应OnRemoveWithReason
func (c *BigCache) providedOnRemoveWithReason(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason) {
if c.config.onRemoveFilter == 0 || (1<<uint(reason))&c.config.onRemoveFilter > 0 {
c.config.OnRemoveWithReason(readKeyFromEntry(wrappedEntry), readEntry(wrappedEntry), reason)
}
}
// 对应nil 不需要回调
func (c *BigCache) notProvidedOnRemove(wrappedEntry []byte, reason RemoveReason) {
}
func (s *cacheShard) getKeyMetadata(key uint64) Metadata {
return Metadata{
RequestCount: s.hashmapStats[key],
}
}
//从[]byte 中读取key
func readKeyFromEntry(data []byte) string {
length := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[timestampSizeInBytes+hashSizeInBytes:])
// copy on read
dst := make([]byte, length)
copy(dst, data[headersSizeInBytes:headersSizeInBytes+length])
return bytesToString(dst)
}
//从[]byte中读取entry
func readEntry(data []byte) []byte {
length := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[timestampSizeInBytes+hashSizeInBytes:])
// copy on read
dst := make([]byte, len(data)-int(headersSizeInBytes+length))
copy(dst, data[headersSizeInBytes+length:])
return dst
}
从回调的这几个函数看,bigcache 内部无非使用到了这样两个函数
一个是readKeyFromEntry、readEntry
从字面上看一个是获取key一个是获取value。简而言之就是getkey、getvalue
那么我们看一下readKeyFromEntry 和readEntry怎么实现的
首先我们看一下wrapEntry这个函数,这个函数是保证entry 的函数,也就是我们想要知道readKeyFromEntry 和readEntry怎么获取对应值
的,我们先得了解一下entry的组成部分
const (
timestampSizeInBytes = 8 // Number of bytes used for timestamp
hashSizeInBytes = 8 // Number of bytes used for hash
keySizeInBytes = 2 // Number of bytes used for size of entry key
headersSizeInBytes = timestampSizeInBytes + hashSizeInBytes + keySizeInBytes // Number of bytes used for all headers
)
// headersSizeInBytes的长度10字节
func wrapEntry(timestamp uint64, hash uint64, key string, entry []byte, buffer *[]byte) []byte {
keyLength := len(key)
blobLength := len(entry) + headersSizeInBytes + keyLength
if blobLength > len(*buffer) {
*buffer = make([]byte, blobLength)
}
blob := *buffer
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(blob, timestamp) //设置timestamp 8字节
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(blob[timestampSizeInBytes:], hash) //设置hash 8字节
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(blob[timestampSizeInBytes+hashSizeInBytes:], uint16(keyLength)) //设置key 的长度2字节
copy(blob[headersSizeInBytes:], key) //10字节之后存放的数据先放key
copy(blob[headersSizeInBytes+keyLength:], entry) //10字节加上keyLength 之后存放的就是我们的数据
return blob[:blobLength] // 返回包结构
}
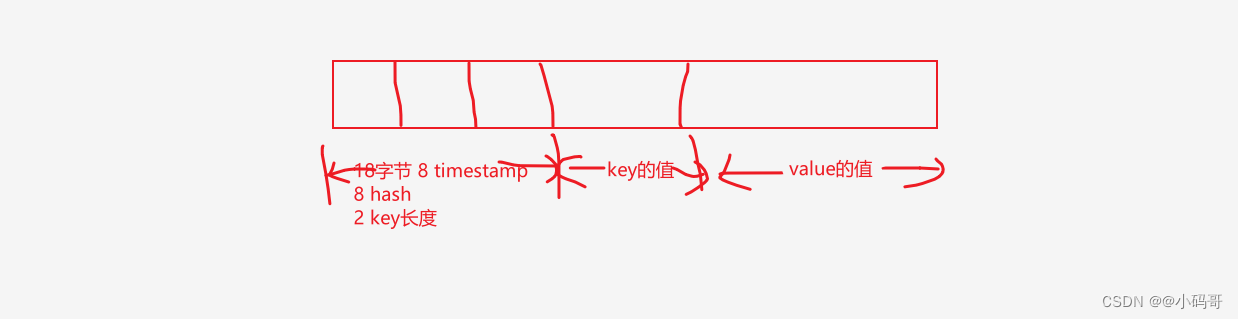
blob 的结构像什么样子,如下图
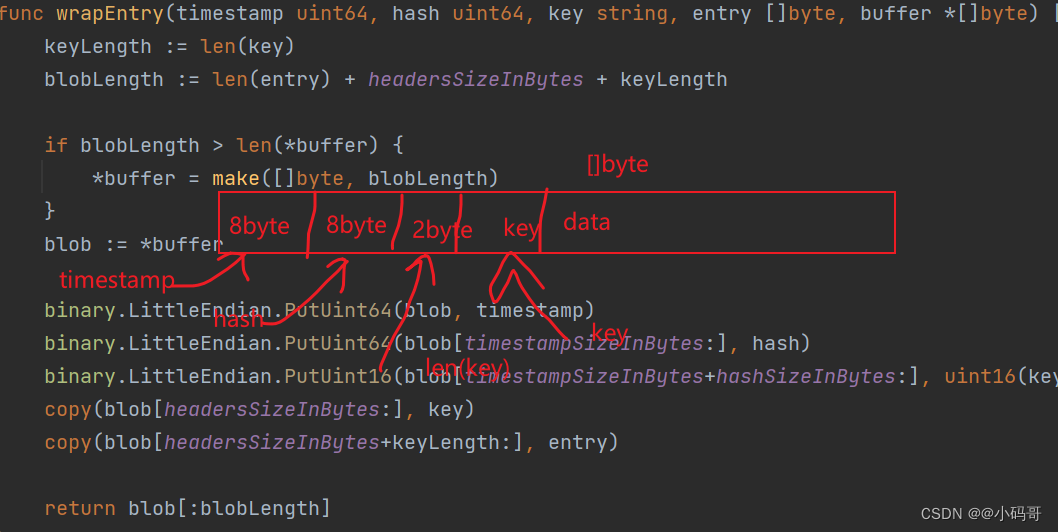
通过这个结构,我们很容易想到,我们在进行网络编程时,需要进行自定义协议,那么通常我们在自定义协议的时候需要进行包封装,通常为了处理粘连包时,我们都会定义包的大小,通常都会,告诉当前包的长度是多少,哪些个位置是放什么数据的。
画得稍微好一点就是下面这张图
shard 初始化逻辑
// 初始化shard
for i := 0; i < config.Shards; i++ {
cache.shards[i] = initNewShard(config, onRemove, clock)
}
// 初始化shard
func initNewShard(config Config, callback onRemoveCallback, clock clock) *cacheShard {
// byte队列的大小 = 初始化shard * 每个entry 的最大容量 其中MaxEntrySize 在前面的配置中我们已经提到了
bytesQueueInitialCapacity := config.initialShardSize() * config.MaxEntrySize
// maximumShardSizeInBytes 的计算是按照每个shard 我们能分到的大小
maximumShardSizeInBytes := config.maximumShardSizeInBytes()
if maximumShardSizeInBytes > 0 && bytesQueueInitialCapacity > maximumShardSizeInBytes {
bytesQueueInitialCapacity = maximumShardSizeInBytes
}
return &cacheShard{
hashmap: make(map[uint64]uint32, config.initialShardSize()),
hashmapStats: make(map[uint64]uint32, config.initialShardSize()),
entries: *queue.NewBytesQueue(bytesQueueInitialCapacity, maximumShardSizeInBytes, config.Verbose),
entryBuffer: make([]byte, config.MaxEntrySize+headersSizeInBytes),
onRemove: callback,
isVerbose: config.Verbose,
logger: newLogger(config.Logger),
clock: clock,
lifeWindow: uint64(config.LifeWindow.Seconds()),
statsEnabled: config.StatsEnabled,
cleanEnabled: config.CleanWindow > 0,
}
}
// initialShardSize computes initial shard size
// 初始化shard 的个数
func (c Config) initialShardSize() int {
// 在前面config 的配置中已经提到过MaxEntriesInWindow 这个属性了,用于计算shard 的初始化大小
// minimumEntriesInShard 10
// 最小shard 为10 否则shard 为 c.MaxEntriesInWindow/c.Shards
return max(c.MaxEntriesInWindow/c.Shards, minimumEntriesInShard)
}
// maximumShardSizeInBytes computes maximum shard size in bytes
// 按照字节来计算每个shard 的大小。
func (c Config) maximumShardSizeInBytes() int {
maxShardSize := 0
if c.HardMaxCacheSize > 0 {
// 前面我们将配置的时候也说过HardMaxCacheSize 是字节队列的大小。
// convertMBToBytes 函数作用将 c.HardMaxCacheSize * 1024 * 1024 也就是我们配置的HardMaxCacheSize 的单位是MB,每个分片分得的最大的数据量是 总的byte/分片数量 这也就是为什么shards 必须是2的幂的原因了。
maxShardSize = convertMBToBytes(c.HardMaxCacheSize) / c.Shards
}
return maxShardSize
}
//cacheShard 的数据结构
type cacheShard struct {
hashmap map[uint64]uint32
entries queue.BytesQueue
lock sync.RWMutex
entryBuffer []byte
onRemove onRemoveCallback
isVerbose bool
statsEnabled bool
logger Logger
clock clock
lifeWindow uint64
hashmapStats map[uint64]uint32
stats Stats
cleanEnabled bool
}
type BytesQueue struct {
full bool //字节数组是否满了
array []byte //字节数组
capacity int
maxCapacity int
head int //头指针
tail int //尾指针
count int //entry 的数量
rightMargin int
headerBuffer []byte
verbose bool
}
// NewBytesQueue initialize new bytes queue.
// capacity is used in bytes array allocation
// When verbose flag is set then information about memory allocation are printed
func NewBytesQueue(capacity int, maxCapacity int, verbose bool) *BytesQueue {
return &BytesQueue{
array: make([]byte, capacity),
capacity: capacity,
maxCapacity: maxCapacity,
headerBuffer: make([]byte, binary.MaxVarintLen32),
tail: leftMarginIndex,
head: leftMarginIndex,
rightMargin: leftMarginIndex,
verbose: verbose,
}
}
// 每一个shard 都会有一个ByteQueue
// arrray 的大小是capacity 的大小
// maxCapacity 的大小,取决于我们的config 配置 HardMaxCacheSize 如果为0 则表示不限制大小
// headerBuffer是一个5 字节的byte bufer 用于编码entry的数据包长度
// tail 尾指针,其中tail 从下标1开始,
// head 头指针,用于表示当前shard 最旧的entry,也就是第一加入bytequeue的entry
set 设置值的过程
// Set saves entry under the key
func (c *BigCache) Set(key string, entry []byte) error {
// key转为uint64
hashedKey := c.hash.Sum64(key)
// 将当前key 映射到其中一个shard中
shard := c.getShard(hashedKey)
//调用set 方法
return shard.set(key, hashedKey, entry)
}
func (c *BigCache) getShard(hashedKey uint64) (shard *cacheShard) {
return c.shards[hashedKey&c.shardMask]
}
func (s *cacheShard) set(key string, hashedKey uint64, entry []byte) error {
//获取当前时间戳转成uint64
currentTimestamp := uint64(s.clock.Epoch())
//加锁
s.lock.Lock()
// 通过hashmap 判断当前hashKey是否存在,previousIndex 就是[]byte中改key的下标
// 通过previousIndex 可以得到一个经过编码的uint64
// 这个uint64 就是warpEntry的len 我们看一下Get 方法是怎么实现的
if previousIndex := s.hashmap[hashedKey]; previousIndex != 0 {
if previousEntry, err := s.entries.Get(int(previousIndex)); err == nil {
// 如果获取到了之后,我们调用 resetKeyFromEntry 将这个key 从我们的entry中重置
resetKeyFromEntry(previousEntry)
//remove hashkey
delete(s.hashmap, hashedKey)
}
}
if !s.cleanEnabled {
if oldestEntry, err := s.entries.Peek(); err == nil {
s.onEvict(oldestEntry, currentTimestamp, s.removeOldestEntry)
}
}
// 封装一个warpEntry 也就是一个[]byte 其中包含18字节的头部,其他的就是value数据啦
w := wrapEntry(currentTimestamp, hashedKey, key, entry, &s.entryBuffer)
for {
// 调用Push 方法
if index, err := s.entries.Push(w); err == nil {
s.hashmap[hashedKey] = uint32(index)
s.lock.Unlock()
return nil
}
if s.removeOldestEntry(NoSpace) != nil {
s.lock.Unlock()
return fmt.Errorf("entry is bigger than max shard size")
}
}
}
func resetKeyFromEntry(data []byte) {
//我们看一下是怎么重置的,将timestatmSizeInBytes之后的空间置为0
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(data[timestampSizeInBytes:], 0)
}
// Get reads entry from index
// Get 主要调用了一下peek方法
func (q *BytesQueue) Get(index int) ([]byte, error) {
data, _, err := q.peek(index)
return data, err
}
// peek returns the data from index and the number of bytes to encode the length of the data in uvarint format
func (q *BytesQueue) peek(index int) ([]byte, int, error) {
//校验index 是否合法
err := q.peekCheckErr(index)
if err != nil {
return nil, 0, err
}
// 从index 之后中读取一个 uint64,其中blockSize就是这个值,n表示这个值在byte占的大小
// 注意这个blockSize 这个值不仅包含了warpEntry的长度,还加了了n的长度
blockSize, n := binary.Uvarint(q.array[index:])
// blockSize是什么东西,这个值的大小是warpEntry的长度加上n
// 所以warpEntry应该从哪个地方取,应该从index+n 然后到index+blockSize的位置
// 所以这个q.array[index+n : index+int(blockSize)]我们就理解是什么意思了,index+n 已经去掉了解码部分了,blockSize是整个部分的
return q.array[index+n : index+int(blockSize)], int(blockSize), nil
}
// Peek reads the oldest entry from list without moving head pointer
func (q *BytesQueue) Peek() ([]byte, error) {
data, _, err := q.peek(q.head)
return data, err
}
// peekCheckErr is identical to peek, but does not actually return any data
func (q *BytesQueue) peekCheckErr(index int) error {
// bytequeue 为空
if q.count == 0 {
return errEmptyQueue
}
// 无效的index
if index <= 0 {
return errInvalidIndex
}
// 超长的index
if index >= len(q.array) {
return errIndexOutOfBounds
}
return nil
}
// Push copies entry at the end of queue and moves tail pointer. Allocates more space if needed.
// Returns index for pushed data or error if maximum size queue limit is reached.
func (q *BytesQueue) Push(data []byte) (int, error) {
// 调用getNeededSize函数,
// needSize 大小 data的长度加上 编解码data 数字所需要的长度
// 也就是什么呢?假设data的长度是100 编码100这个数字 需要1个byte
// neededSize 的大小就是101
neededSize := getNeededSize(len(data))
if !q.canInsertAfterTail(neededSize) {
if q.canInsertBeforeHead(neededSize) {
q.tail = leftMarginIndex
} else if q.capacity+neededSize >= q.maxCapacity && q.maxCapacity > 0 {
return -1, &queueError{"Full queue. Maximum size limit reached."}
} else {
// 分配额外的内存空间
q.allocateAdditionalMemory(neededSize)
}
}
// index 就是当前的尾指针,可以看到最开始尾是1
index := q.tail
// 调用push 方法
q.push(data, neededSize)
return index, nil
}
// canInsertBeforeHead returns true if it's possible to insert an entry of size of need before the head of the queue
func (q *BytesQueue) canInsertBeforeHead(need int) bool {
//能否插入在头部
// 如果队列已满 返回false
if q.full {
return false
}
// 当尾指针大于等于头
// 此时byte queue 已经存在数据
if q.tail >= q.head {
return q.head-leftMarginIndex == need || q.head-leftMarginIndex >= need+minimumHeaderSize
}
return q.head-q.tail == need || q.head-q.tail >= need+minimumHeaderSize
}
// canInsertAfterTail returns true if it's possible to insert an entry of size of need after the tail of the queue
func (q *BytesQueue) canInsertAfterTail(need int) bool {
//是否能插入尾部
// 判断队列是否已满
//如果已经满了,表示不能插入尾部了
if q.full {
return false
}
// 如果q.tail >= q.head
//这个时候表示queue没数据或者已经有数据但还没有满
if q.tail >= q.head {
// 判断容量是否能够放得下 need
// 将capacity-q.tail,也就是容量减去尾指针
return q.capacity-q.tail >= need
}
// 1. there is exactly need bytes between head and tail, so we do not need
// to reserve extra space for a potential empty entry when realloc this queue
// 2. still have unused space between tail and head, then we must reserve
// at least headerEntrySize bytes so we can put an empty entry
return q.head-q.tail == need || q.head-q.tail >= need+minimumHeaderSize
}
// minimun 的大小就是neededSize
func (q *BytesQueue) allocateAdditionalMemory(minimum int) {
//记录开始时间
start := time.Now()
//当容量小于capacity 时,进行扩容
if q.capacity < minimum {
q.capacity += minimum
}
//当前容量加上needSize * 2
q.capacity = q.capacity * 2
if q.capacity > q.maxCapacity && q.maxCapacity > 0 {
q.capacity = q.maxCapacity
}
oldArray := q.array
q.array = make([]byte, q.capacity)
if leftMarginIndex != q.rightMargin {
copy(q.array, oldArray[:q.rightMargin])
if q.tail <= q.head {
if q.tail != q.head {
// created slice is slightly larger then need but this is fine after only the needed bytes are copied
q.push(make([]byte, q.head-q.tail), q.head-q.tail)
}
q.head = leftMarginIndex
q.tail = q.rightMargin
}
}
q.full = false
// 打印分配内存的日志
if q.verbose {
log.Printf("Allocated new queue in %s; Capacity: %d \n", time.Since(start), q.capacity)
}
}
// 入参data 就是warpEntry
// len 的值是len(data) + header
// 其中header的大小从getNeedSize 中获取
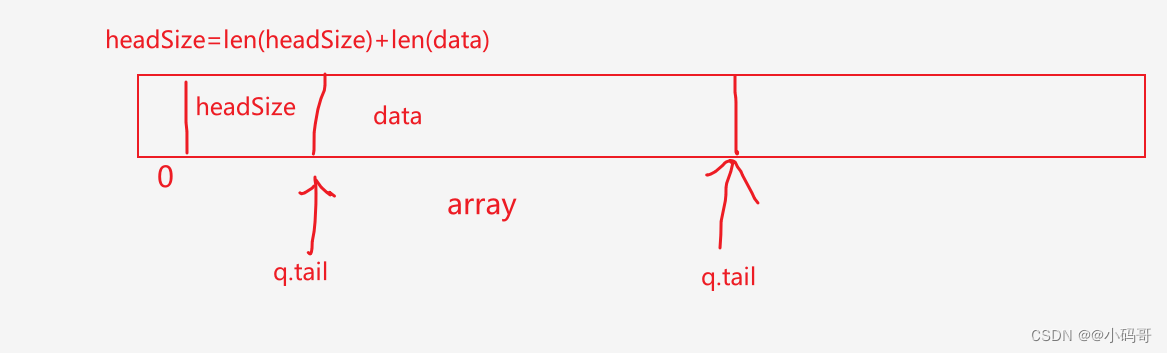
func (q *BytesQueue) push(data []byte, len int) {
// headerEntrySize 是将这101这个数字进行编码
headerEntrySize := binary.PutUvarint(q.headerBuffer, uint64(len))
//
q.copy(q.headerBuffer, headerEntrySize)
// 拷贝len-headerEntrySize 是什么意思呢?
// 刚开始的时候我们已经算过len 是多少了,len是101,那么我们编解码这个len 之后 headerEntrySize 的大小其实是1
// 所以我们用len - headerEntrySize 之后,实际上又是100了
// 所以我们再次理解一下headerBuffer 的作用,实际上headerBufer 这个字节序列的长度就是什么东西,就是告诉我们,这个编码数的长度,同时
// 我们如果解码会解出什么东西,会解出,len(data) + n 这么个东西
q.copy(data, len-headerEntrySize)
if q.tail > q.head {
q.rightMargin = q.tail
// q.rightMargin 和尾指针保持一致
}
if q.tail == q.head {
//当头和尾一致时,表示byteQueue已满
q.full = true
}
//设置一个entry 之后,计数器加加
q.count++
}
func (q *BytesQueue) copy(data []byte, len int) {
//这个copy 函数干了什么事呢?
// q.tail 最开始是1 也就是从1开始 将编码的这个放在了array 的后面,具体看图解
q.tail += copy(q.array[q.tail:], data[:len])
}
// getNeededSize returns the number of bytes an entry of length need in the queue
func getNeededSize(length int) int {
var header int
switch {
case length < 127: // 1<<7-1
header = 1
case length < 16382: // 1<<14-2
header = 2
case length < 2097149: // 1<<21 -3
header = 3
case length < 268435452: // 1<<28 -4
header = 4
default:
header = 5
}
return length + header
}
工具类
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
func convertMBToBytes(value int) int {
return value * 1024 * 1024
}
func isPowerOfTwo(number int) bool {
return (number != 0) && (number&(number-1)) == 0
}





















 4359
4359











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








