一遍文章了解Java集合框架TreeMap实现原理
本文大纲:
1.分析Java TreeMap源码了解其实现原理
2.根据Java TreeMap实现原理自定义实现MyTreeMap
基本概念:
TreeMap基于红黑树数据结构实现
Entry就是树的节点node
红黑树数据结构特点:
1.从根节点开始,左边小,右边大
2.从整个树来看,最左边的子节点最小,最右边的子节点最大
数据结构示意图:
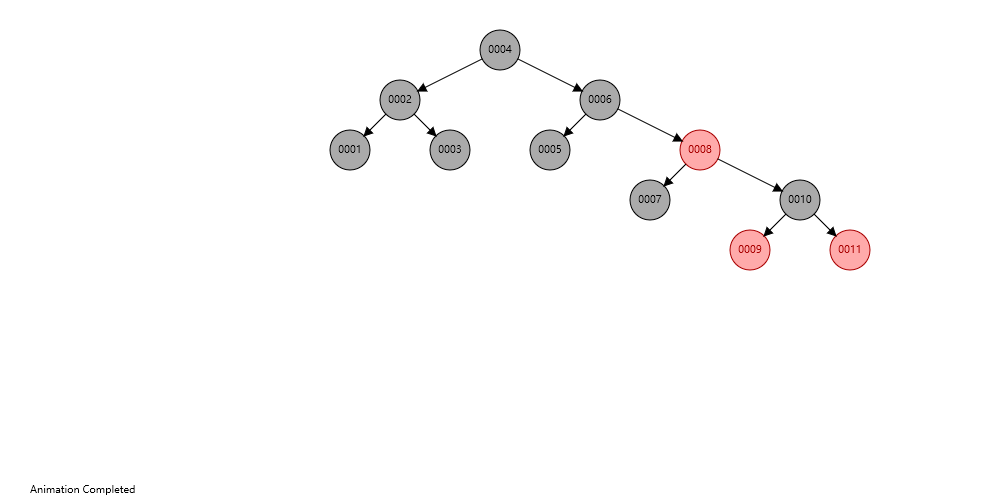
Entry 实体属性:
K key; //键
V value;//值
Entry<K,V> left;//左边节点引用
Entry<K,V> right;//右边节点引用
Entry<K,V> parent;//父节点引用
boolean color = BLACK;//节点类型 红色/黑色
put 元素流程:
- 判断有没有根节点,如果没有就先创建根节点
- 获取比较器 有比较器则使用比较器判断大小,没有则使用 key的比较规则
- 根据比较结果 从根节点,根据 key 与 每个节点的key 进行比较,小于从左边搜索 ,大于从右边搜索 直到没有子节点
- 创建Entry对象 初始化key value 以找到的节点为parent 并且根据最后的比较结果判断放left 还是 right
- 对树进行平衡优化
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//1.判断有没有根节点,如果没有就先创建跟节点
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
//2.获取排序器,有比较规则使用排序器判断大小,没有则使用 key的比较规则
//直接使用new TreeMap 创建对象排序器为空
//会取key作为比较,而相对于String类型 默认是ASCII进行比较
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
//3.根据排序器 查找放到哪个树节点下面,
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//4.从根节点,根据key 与 节点key进行比较,小的从左边搜索 ,大的从右边搜索 直到没有子节点
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//如果两个key相等 则覆盖原来key的值
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//获取key的比较规则 key必须继承Comparable 并且实现compareTo方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//找到当前key合适的父节点
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
//从根节点,根据key 与 节点key进行比较,小的从左边搜索 ,大的从右边搜索 直到没有子节点
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//相同则覆盖当前值 并且返回
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//创建Entry
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//根据最后的比较结果得出放节点左边还是右边
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//对树结构进行平衡优化
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
get元素流程:
-
判断是否使用了比较器
-
使用了比较器规则根据比较器判断搜索方向
-
如果 key 与节点 key 相等则返回结果
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
//判断是否存在比较器
if (comparator != null)
//根据比较器找到Entry
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
//key==null 抛异常
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//获取比较器
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//获取根节点
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//遍历树 直到没有子节点或者两个key相同就返回entry实体
while (p != null) {
//拿key 和 节点key 进行比较 得出从哪边进行查找
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
//从左边寻找
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
//从右边寻找
p = p.right;
else
//相同直接返回
return p;
}
return null;
}
//根据比较器获取
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
//获取比较器
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//判断表器不为空
if (cpr != null) {
//从root节点开始
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
//比较大小 判断从那边进行搜索
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
//搜到到直接返回
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
迭代算法:
next获取流程:
1.找到数的最左边,就是最小值
2.判断是否有右边节点,有则切换到最左边,否则判断是否有父节点
3.有父节点,并且当前节点是父节点的右边(在当前父子节点下一已经是最大的了),则切到父节点的父节点
4.返回当前节点(不是next值 是当前值)
以entrySet方法为例:
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
//迭代器实现方法 实例化迭代器
//getFirstEntry() 获取数最左边的元素
return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
}
//获取最左边的元素 也就是最左边的元素
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
//调用父类nextEntry
return nextEntry();
}
}
//PrivateEntryIterator父类nextEntry实现
PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
//设置初始第一节点
next = first;
}
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//判断修改次数是否一致
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
//选择元素
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
//返回当前节点
return e;
}
//从最左边搜索元素 从大到小一次排列
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
//判断节点右边是否有值
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
//循环切换到最左边的值
p = p.left;
//返回从右边找到的下一个值
return p;
} else {
//右边节点没有从父节点找
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
//如果是当前节点在父节点的右边,则获取到父节点的父节点
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
//根据上述结构原理,自己实现TreeMap
为了简洁易懂 主要实现如下三个方法:
put
get
entrySet
自定义具体实现如下:
package com.kexun;
import java.util.*;
public class MyTreeMap<K, V> {
private MyEntry<K, V> root;
private int size = 0;
private int modCount = 0;
private MyEntrySet entrySet;
public V put(K key, V value) {
MyEntry<K, V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
//初始化跟节点
root = new MyEntry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
//key不能为空
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//这里只使用key的比较器
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//存放找到的放元素的节点
MyEntry<K, V> parent;
//比较结果
int cmp;
//寻找子节点存放元素
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
//相同接替换掉
return t.setValue(value);
}
} while (t != null);
MyEntry<K, V> e = new MyEntry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//优化平衡树结构
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
public V get(Object key) {
MyEntry<K, V> entry = getEntry(key);
if (entry != null) {
return entry.value;
}
return null;
}
private MyEntry<K, V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//从跟节点开始寻找
MyEntry<K, V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
//根据红黑树特性 选择是从左边还是右边寻找
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
p = p.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
p = p.right;
} else {
//如果相等返回
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
public MyEntrySet entrySet() {
//缓存 避免多次初始化
MyEntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new MyEntrySet());
}
//自定义entry
class MyEntrySet {
public MyEntryIterator<MyEntry<K, V>> iterator() {
return new MyEntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
public int size() {
return MyTreeMap.this.size;
}
}
//获取红黑数最左边 也就是最小的元素
private MyEntry<K, V> getFirstEntry() {
MyEntry<K, V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
//自定义迭代器
class MyEntryIterator<T> {
MyEntry<K, V> next;
MyEntry<K, V> lastReturned;
int expectedModCount;
MyEntryIterator(MyEntry<K, V> first) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
}
//获取下一个元素
public MyEntry<K, V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
//是否存在下一个
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
//获取下一个元素
public MyEntry<K, V> nextEntry() {
MyEntry<K, V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
//具体获取方法
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
//找出下一个元素
private <K, V> MyEntry<K, V> successor(MyEntry<K, V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
MyEntry<K, V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
MyEntry<K, V> p = t.parent;
MyEntry<K, V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
}
//自定义Entry数节点对象
static final class MyEntry<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
MyEntry<K, V> left;
MyEntry<K, V> right;
MyEntry<K, V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
MyEntry(K key, V value, MyEntry<K, V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public String toString() {
return "key:" + key + " value:" + value;
}
}
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
/*下面是红黑树实现算法 可忽略 我也是从Jdk源码复制的*/
private static <K, V> boolean colorOf(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color);
}
private static <K, V> MyEntry<K, V> parentOf(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
return (p == null ? null : p.parent);
}
private static <K, V> void setColor(MyEntry<K, V> p, boolean c) {
if (p != null)
p.color = c;
}
private static <K, V> MyEntry<K, V> leftOf(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null : p.left;
}
private static <K, V> MyEntry<K, V> rightOf(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null : p.right;
}
/**
* From CLR
*/
private void rotateLeft(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
if (p != null) {
MyEntry<K, V> r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
r.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
p.parent.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
/**
* From CLR
*/
private void rotateRight(MyEntry<K, V> p) {
if (p != null) {
MyEntry<K, V> l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
/**
* From CLR
*/
private void fixAfterInsertion(MyEntry<K, V> x) {
x.color = RED;
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
MyEntry<K, V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
MyEntry<K, V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
}
使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTreeMap<Integer, Object> myTreeMap = new MyTreeMap<>();
myTreeMap.put(1, "111");
myTreeMap.put(2, "222");
myTreeMap.put(3, "333");
Object put = myTreeMap.put(3, "33333");
System.out.println("相同值替换" + put);
MyTreeMap<Integer, Object>.MyEntrySet myEntrySet = myTreeMap.entrySet();
MyTreeMap<Integer, Object>.MyEntryIterator<MyTreeMap.MyEntry<Integer, Object>> iterator = myEntrySet.iterator();
System.out.println("迭代器输出:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MyTreeMap.MyEntry<Integer, Object> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getKey() + "---" + next.getValue());
}
}
以上就是本期内容,感谢大家的阅读

程序员MuziDong





















 1274
1274











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








