文章目录
1.什么是时间复杂度?
时间复杂度是计算机科学中用来描述算法执行时间效率的一个概念。它表示了算法执行时间与输入数据量之间的关系,通常用大O符号(Big O notation)来表示。
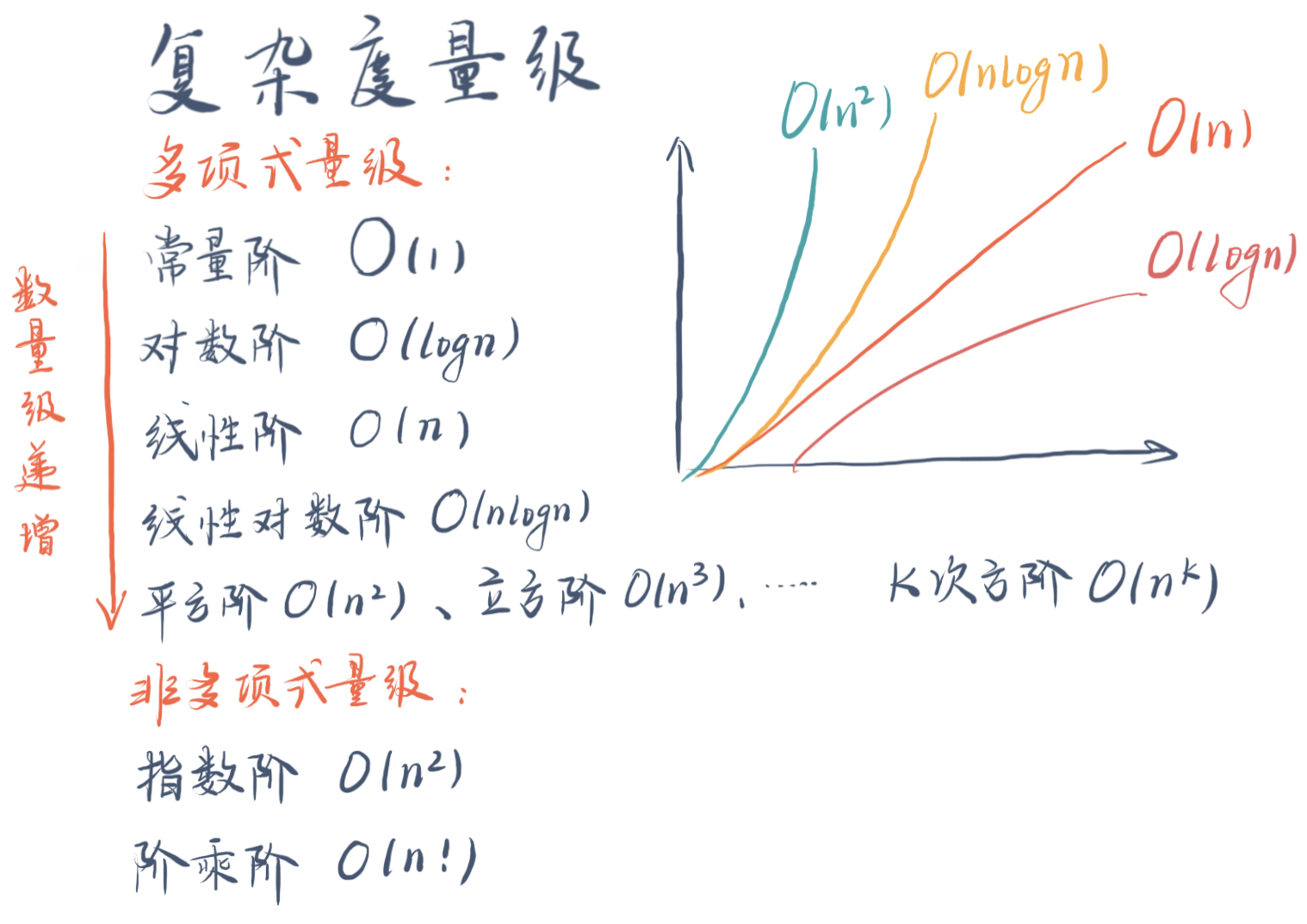
2.时间复杂度类别
复杂度排序:
O(1) < O(log n) < O(n) < O(n log n) < O(n2) < O(2n) < O(n!)
2.1 常量阶 O(1)
public class ArrayAccessExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 访问数组的第一个元素,时间复杂度为 O(1)
System.out.println(array[0]);
}
}
代码不会因为n输入的多少时间发生改变,只执行一次。故为O(1)。
2.2 对数阶 O(log n)
public class SimpleBinarySearchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一个已排序的数组
int[] sortedArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int target = 5;
boolean found = binarySearch(sortedArray, target);
if (found) {
System.out.println("Element found in the array.");
} else {
System.out.println("Element not found in the array.");
}
}
public static boolean binarySearch(int[] array, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
// 找到中间索引
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 检查中间元素
if (array[mid] == target) {
return true; // 找到目标值,返回true
} else if (array[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1; // 调整左边界
} else {
right = mid - 1; // 调整右边界
}
}
// 如果循环结束时没有找到目标值,则返回false
return false;
}
}
时间复杂度按照 对数级 递减。
2.3 线性阶 O(n)
public class LinearComplexityExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// 计算数组元素的总和
int sum = calculateSum(array);
System.out.println("The sum of the array elements is: " + sum);
}
public static int calculateSum(int[] array) {
int sum = 0;
// 遍历数组,累加每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
sum += array[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
因为数组中的每个元素都被访问了一次,所以这个函数的时间复杂度是O(n),其中n是数组的长度。
2.4 线性对数阶 O(n log n)
public class QuickSort {
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// 找到基准值的位置
int pivotIndex = partition(arr, low, high);
// 递归排序左半部分
quickSort(arr, low, pivotIndex - 1);
// 递归排序右半部分
quickSort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, high);
}
}
private static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
// 选择最后一个元素作为基准
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low; // 比基准小的元素的索引
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// 如果当前元素小于或等于基准
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
// 交换 arr[i] 和 arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
}
}
// 交换 arr[i+1] 和 arr[high] (或基准)
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i ;
}
// 测试快速排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = arr.length;
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
快速排序法的平均时间复杂度为O(n log n)
如果基准值每次都能将数组分成大致相等的两部分,那么递归树的深度将是log n,每次分区操作的时间复杂度是O(n),因此总体的时间复杂度是O(n log n)。
但在最坏的情况下(比如数组已经是正序或逆序时),时间复杂度会退化为O(n2)。
2.5 平方阶 O(n2)
public class PairProductExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 计算并打印所有可能的数对乘积
printPairProducts(array);
}
public static void printPairProducts(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 打印当前数对的乘积
System.out.println("Product of pair (" + array[i] + ", " + array[j] + ") = " + (array[i] * array[j]));
}
}
}
}
外循环遍历数组的每个元素,而内循环则遍历数组中的每个元素,与外循环的当前元素形成一对,并计算它们的乘积。因为这两个循环都是线性的,所以总体的时间复杂度是O(n^2)。























 1536
1536

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










