IO流(下)
传送门:IO流(上)
10. BufferedReader
带有缓冲区的字符输入流,使用这个流的时候不需要自定义char数组,或者说不需要自定义byte数组,自带缓冲
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileReader reader = new FileReader("test.txt");
//当一个流的构造方法需要一个流的时候,这个被传进去的流叫做:节点流
//外部负责包装的这个流叫做:包装流/处理流
//当前这个程序:FileReader就是节点流,BufferedReader就是包装流/处理流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
//当readLine读到文件最后时,会返回null,且readLine方法读取不带换行符
String s = null;
while((s =br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(s);
}
//对于包装类来说,只需要关闭最外层流就行,里面的节点流会自动关闭(在调用外层流close()方法时,会在方法内调用节点流的close()方法)
br.close();
}
}
BufferedReader构造方法只能传入字符流,如果想要传进去字节流怎么办?
采用转换流InputStreamReader/OutputStreamReader进行转换
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//字节流
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
//通过转换流转换
//in是节点流,reader是包装流
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in);
//只能传入字符流,不能传入字节流
//reader是节点流,br是包装流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
//合并 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt")));
//关闭最外层即可
br.close();
}
}
11. BufferedWriter
带有缓冲的字符输出流
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("copy"));
//BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("copy")));
//开始写
out.write("hello world\n");
out.write("hello zhangsan");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
12. DataOutputStream
数据专属的流,这个流可以将数据连通数据的类型一并写入文件。
注:这个文件不是普通文本文档(记事本打不开)
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data"));
byte b =100;
short s = 200;
float f =3.0F;
boolean sex = false;
char c ='a';
//写数据
dos.writeByte(b);
dos.writeShort(s);
dos.writeFloat(f);
dos.writeBoolean(sex);
dos.writeChar(c);
dos.flush();
dos.close();
}
}
13. DataInputStream
数据字节输入流,DataOutputStream写的文件,只能使用DataInputStream去读,并且读的时候需要提前知道写入的顺序。读的顺序需要和写的顺序一致,才可以正常取出数据。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data"));
//读数据
byte b =dis.readByte();
short s =dis.readShort();
float f = dis.readFloat();
boolean sex = dis.readBoolean();
char c = dis.readChar();
dis.close();
}
}
14. PrintStream
标准的字节输出流,默认输出到控制台,标准输出流不需要手动close()关闭
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//联合写
System.out.println("hello world");
//分开写
//System类中out属性返回值为PrintSteam类型
PrintStream ps = System.out;
//PrintStream类中的静态方法println()
ps.println("hello world");
}
}
-
System类常用的方法和属性
System.gc(); System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out; System.exit(0); System.arraycopy(...); -
修改输入流的方向
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //标准输出流不再指向控制台,指向log文件 PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log")); //修改输出方向,将输出方向修改为log文件 System.setOut(printStream); //再输出 直接输出在文件里了 System.out.println("hello world"); } } -
实际应用(记录日志文件)
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //测试 log("调用了....方法"); log("账号被登录"); } public static void log(String msg){ //标准输出流不再指向控制台,指向log文件 PrintStream printStream = null; try { printStream = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log.txt",true)); //修改输出方向,将输出方向修改为log文件 System.setOut(printStream); Date date = new Date(); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS"); String strTime = sdf.format(date); System.out.println(strTime +": "+msg); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }结果图:

15. File类
- File类和四大家族没有关系,所以File类不能完成文件的读和写
- File对象是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式,一个File对象有可能对应的是目录,也可能是文件
(1)File类中常用的方法
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个File对象
File f1 = new File("E:\\test");
//1.如果E:\test不存在,则以文件的形式创建
if(!f1.exists()){
f1.createNewFile();
}
//2.如果E:\test不存在,则以目录的形式创建
if(!f1.exists()){
f1.mkdir();
}
File f2 = new File("E:/a/b/c/d/e");
if(!f2.exists()){
//3.多重目录的形式创建
f2.mkdirs();
}
File f3 = new File("E:\\Java-Project\\test.txt");
//4.获取文件的父路径,返回的是String类型
String parentPath = f3.getParent();
System.out.println(parentPath); //E:\Java-Project
//5.获取文件父路径,返回的File类型
File parentFile = f3.getParentFile();
System.out.println("获取绝对路径:"+parentFile.getAbsolutePath());//6.获取绝对路径:E:\Java-Project
File f4 = new File("E:\\Java-Project\\test.txt");
//7.获取文件名
System.out.println(f4.getName()); //test.txt
//8.判断是否是一个目录
System.out.println(f4.isDirectory()); //false
//9.判断是否是一个文件
System.out.println(f4.isFile()); //true
//10.获取文件最后一次修改时间
long updateTime = f4.lastModified(); //返回的是从1970年到现在的毫秒数
//将毫秒转换为日期
Date time = new Date(updateTime);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
String strTime = sdf.format(updateTime);
System.out.println(strTime); //2021-12-09 21:08:08 835
//11.获取文件大小
System.out.println(f4.length()); //3字节
//12.获取当前目录下所有的子文件
File f5 = new File("E:\\Java-Project\\Java-Code");
File[] files = f5.listFiles(); //返回的是一个File数组
for(File file : files){
System.out.print(file.getName()+" ");//.idea Java-Code.iml out src
}
}
}
(2)目录复制
public class Copy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//源目录
File sourceDir = new File("E:\\test");
//目标目录
File desDir = new File("C:\\copy");
copy(sourceDir,desDir);
}
public static void copy(File sourceDir, File desDir) throws Exception{
//如果源是一个文件,结束递归
if(sourceDir.isFile()){
String sourcePath = sourceDir.getAbsolutePath();
String desPath = desDir.getAbsolutePath();
//新的目的路径
String desNew = (desPath.endsWith("\\") ? desPath : desPath + "\\") + sourcePath.substring(3);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sourceDir);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(desNew);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int readCount = 0;
while((readCount = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,readCount);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close();
fis.close();
return;
}
//否则就是目录 获取子目录
File[] files= sourceDir.listFiles();
for(File file : files){
String sourcePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
String desPath = desDir.getAbsolutePath();
//新的目的路径
String desNew = (desPath.endsWith("\\") ? desPath : desPath + "\\") + sourcePath.substring(3);
if(file.isDirectory()){
File newDir= new File(desNew);
if(!newDir.exists()) {
newDir.mkdirs();
}
}
copy(file,desDir);
}
}
}
16. 序列化与反序列化
- 参与序列化和反序列化的对象,必须要实现Serializable接口,否则会出现java.io.NotSerializableException
- Serializable接口是一个标志接口,在接口当中什么代码都没有,它只是起到标识作用,java虚拟机看到这个类实现了这个接口,会进行特殊待遇,自动生成一个序列化版本号,没有手动写出,java虚拟机会自动默认提供这个序列化版本号
(1)图解

对于下面的操作,全部基于该Student类
public class Student implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(2)序列化
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建java对象
Student s = new Student(123,"zhangsan");
//序列化
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("students")); //存入students文件
//序列化对象
oos.writeObject(s);
//刷新
oos.flush();
//关闭
oos.close();
}
}
执行结果:
生成一个文件存储的Student对象,该文件无法正常打开,需进行反序列化操作
(3)反序列化
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("students"));//反序列化的文件
//读出来的是Object类型,底层是Student
Object obj = ois.readObject();
//自动调用Student类的toString()方法
System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
}
}
执行结果:
(4)一次多个对象序列化和反序列化
将对象放到集合当中,再序列化集合
-
序列化
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>(); studentList.add(new Student(123,"lisi")); studentList.add(new Student(124,"zhangsan")); studentList.add(new Student(125,"wangwu")); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("studentlist")); oos.writeObject(studentList); oos.flush(); oos.close(); } } -
反序列化
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("studentlist")); List<Student> studentList = (List<Student>) ois.readObject(); for(Student student : studentList){ System.out.println(student); } ois.close(); } }执行结果:
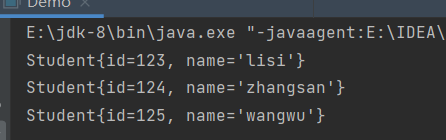
注:参与序列化的ArrayList集合以及集合中的元素Student都需要实现java.io.Serializable接口
(5)transient
transient关键字表示游离,不参与序列化
//将上面Student类的属性改为
public class Student implements Serializable {
private int id;
private transient String name; //name不参与序列化操作
}
再进行同样的序列化和反序列化操作,得到的结果:
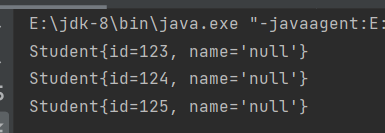
(6)序列化版本号
-
Java虚拟机看到Serializable接口之后,会自动生成一个序列化版本号
-
当一个类修改了源代码后,需要重新编译,编译之后生成全新的字节码文件,并且java虚拟机生成的序列化版本号也发生改变
比如:修改源代码后,直接进行反序列化,则会出现:
Exception in thread "main" java.io.InvalidClassException: com.study.www.Student; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 8628483378815559334,(修改代码之前的序列号) local class serialVersionUID = -1019878040008205449(修改代码之后的序列号)这代表着java虚拟机认为这是不同的两个类
不同的人编写了同一个类,但这两个类确实不是同一个类,这时候序列化版本号就起作用了。对于java虚拟机来说,是可以区分这两个类的,因为这两个类都实现了Serializable接口,都有默认的序列化版本号。
-
java语言采用什么机制来区分类呢?
- 首先通过类名进行对比,如果类名不一样,肯定不是一个类
- 如果类名一样,则靠序列化版本号进行区分
-
自动生成序列化版本号有什么缺陷?
一旦代码确定之后,不能进行后续的修改,因为只要修改,必须会重新编译,此时会生成全新的序列化版本号,这时候java虚拟机就会认为这是一个全新的类
结论:凡是一个类实现了Serializable接口,建议给该类提供一个固定不变的序列化版本号。这样,以后这个类即使修改了代码,但是版本号不变,java虚拟机会认为是同一个类
public class Student implements Serializble{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//...
}
17. IO和Properties联合使用
Properties是一个Map集合,key和value都是String类型
此处用IO流和Properties联合使用将工程下的userinfo属性文件中的数据加载到Properties对象当中

public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//新建一个输入流
FileReader reader = new FileReader("userinfo");
//新建一个Map集合
Properties pro = new Properties();
//调用Properties对象的load方法将文件中的数据加载到Map集合中
pro.load(reader);//文件中的数据顺着管道加载到Map集合中,其中等号=左边做key,右边做value
//通过key来获取value
String username = pro.getProperty("username");
System.out.println(username); //root
}
}
以后经常改变的数据,可以单独写到一个文件中,使用程序动态获取。将来只要修改这个文件的内容,java代码不需要改动,不需要重新编译,服务器也不需要重启,就可以动态拿到信息
- 类似于userinfor的内容格式key1=value的时候,我峨嵋你把这种配置文件叫做属性配置文件。
- Java规范中要求:属性配置文件建议以**.properties**结尾,但不是必须的
- 在属性配置文件中井号(#)是注释,属性配置文件的key重复的话,value会自动覆盖





















 1319
1319











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








