文章目录
第1章 Flume概述
1.1 Flume概念
1.2 Flume组成架构
1.2.1 Agent
1.2.2 Source
1.2.3 Channel
1.2.4 Sink
1.2.5 Event
1.3 Flume拓扑结构
1.4 Flume Agent内部原理
第2章 快速入门
2.1 Flume安装地址
2.2 安装部署
第3章 案例实操
3.1 监控端口数据官方案例
3.2 实时读取本地文件到HDFS案例
3.3 实时读取目录文件到HDFS案例
3.4 单数据源多出口案例(一)
3.5 单数据源多出口案例(二)
3.6 多数据源汇总案例
第4章 Flume监控之Ganglia
4.1 Ganglia的安装与部署
4.2 操作Flume测试监控
第5章 自定义MySQLSource
5.1 自定义Source说明
5.3 自定义MySQLSource组成
5.2 自定义MySQLSource步骤
5.4 代码实现
5.4.1 导入pom依赖
5.4.2 添加配置信息
5.4.3 SQLSourceHelper
5.4.4 MySQLSource
5.5 测试
5.5.1 jar包准备
5.5.2 配置文件准备
5.5.3 mysql表准备
5.5.4 测试并查看结果
第6章 常见正则表达式语法
第1章 Flume概述
1.1 Flume概念
Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统。Flume基于流式架构,灵活简单。

1.2 Flume组成架构
Flume组成架构如图1-1,图1-2所示:

图1-1 Flume组成架构

图1-2 Flume组成架构详解
下面我们来详细介绍一下Flume架构中的组件。
1.2.1 Agent
Agent是一个JVM进程,它以事件的形式将数据从源头送至目的,是Flume数据传输的基本单元。
Agent主要有3个部分组成,Source、Channel、Sink。
1.2.2 Source
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
1.2.3 Channel
Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel允许Source和Sink运作在不同的速率上。Channel是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个Source的写入操作和几个Sink的读取操作。
Flume自带两种Channel:Memory Channel和File Channel。
Memory Channel是内存中的队列。Memory Channel在不需要关心数据丢失的情景下适用。如果需要关心数据丢失,那么Memory Channel就不应该使用,因为程序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都会导致数据丢失。
File Channel将所有事件写到磁盘。因此在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不会丢失数据。
1.2.4 Sink
Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent,Sink就利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
Sink组件目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、HBase、solr、自定义。
1.2.5 Event
传输单元,Flume数据传输的基本单元,以事件的形式将数据从源头送至目的地。
1.3 Flume拓扑结构
Flume的拓扑结构如图1-3、1-4、1-5和1-6所示:
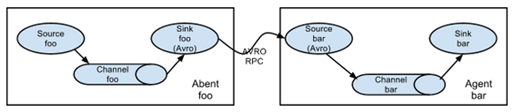
图1-3 Flume Agent连接

图1-4 单source,多channel、sink

图1-5 Flume负载均衡

图1-6 Flume Agent聚合
1.4 Flume Agent内部原理

第2章 快速入门
2.1 Flume安装地址
1) Flume官网地址
http://flume.apache.org/
2)文档查看地址
http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html
3)下载地址
http://archive.apache.org/dist/flume/
2.2 安装部署
1)将apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz上传到linux的/opt/software目录下
2)解压apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz到/opt/module/目录下
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ tar -zxf apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
3)修改apache-flume-1.7.0-bin的名称为flume
[atguigu@hadoop102 module]$ mv apache-flume-1.7.0-bin flume
4) 将flume/conf下的flume-env.sh.template文件修改为flume-env.sh,并配置flume-env.sh文件
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ mv flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ vi flume-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_144
第3章 案例实操
3.1 监控端口数据官方案例
1)案例需求:首先,Flume监控本机44444端口,然后通过telnet工具向本机44444端口发送消息,最后Flume将监听的数据实时显示在控制台。
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
1.安装telnet工具
在/opt/software目录下创建flume-telnet文件夹。
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ mkdir flume-telnet
再将rpm软件包(xinetd-2.3.14-40.el6.x86_64.rpm、telnet-0.17-48.el6.x86_64.rpm和telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64.rpm)拷入/opt/software/flume-telnet文件夹下面。执行RPM软件包安装命令:
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ sudo rpm -ivh xinetd-2.3.14-40.el6.x86_64.rpm
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ sudo rpm -ivh telnet-0.17-48.el6.x86_64.rpm
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ sudo rpm -ivh telnet-server-0.17-48.el6.x86_64.rpm
2.判断44444端口是否被占用
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume-telnet]$
功能描述:netstat命令是一个监控TCP/IP网络的非常有用的工具,它可以显示路由表、实际的网络连接以及每一个网络接口设备的状态信息。
基本语法:netstat [选项]
选项参数:
-t或–tcp:显示TCP传输协议的连线状况;
-u或–udp:显示UDP传输协议的连线状况;
-n或–numeric:直接使用ip地址,而不通过域名服务器;
-l或–listening:显示监控中的服务器的Socket;
-p或–programs:显示正在使用Socket的程序识别码和程序名称;
3.创建Flume Agent配置文件flume-telnet-logger.conf
在flume目录下创建job文件夹并进入job文件夹。
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ mkdir job
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ cd job/
在job文件夹下创建Flume Agent配置文件flume-telnet-logger.conf。
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ touch flume-telnet-logger.conf
在flume-telnet-logger.conf文件中添加如下内容。
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ vim flume-telnet-logger.conf
添加内容如下:
#Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
#Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
#Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
注:配置文件来源于官方手册http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html

4. 先开启flume监听端口
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/flume-telnet-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
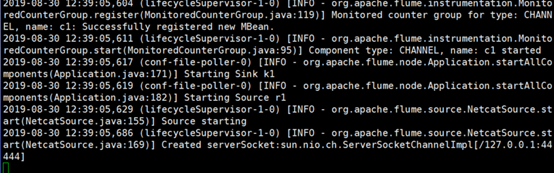
参数说明:
–conf conf/ :表示配置文件存储在conf/目录
–name a1 :表示给agent起名为a1
–conf-file job/flume-telnet.conf :flume本次启动读取的配置文件是在job文件夹下的flume-telnet.conf文件。
-Dflume.root.logger==INFO,console :-D表示flume运行时动态修改flume.root.logger参数属性值,并将控制台日志打印级别设置为INFO
级别。日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error。
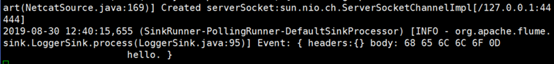
5.使用telnet工具向本机的44444端口发送内容
$ telnet localhost 44444

发送hello后查看flume监控情况
3.2 实时读取本地文件到HDFS案例
1)案例需求:实时监控Hive日志,并上传到HDFS中
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
1.Flume要想将数据输出到HDFS,必须持有Hadoop相关jar包
将commons-configuration-1.6.jar、
hadoop-auth-2.7.2.jar、
hadoop-common-2.7.2.jar、
hadoop-hdfs-2.7.2.jar、
commons-io-2.4.jar、
htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar拷贝到/opt/module/flume/lib文件夹下。
提示:标红的jar为1.99版本flume必须引用的jar。其他版本可以不引用。
2.创建flume-file-hdfs.conf文件
创建文件
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ touch flume-file-hdfs.conf
注:要想读取Linux系统中的文件,就得按照Linux命令的规则执行命令。由于hive日志在Linux系统中所以读取文件的类型选择:exec即execute执行的意思。表示执行Linux命令来读取文件。
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ vim flume-file-hdfs.conf
添加如下内容
#Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2
#Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r2.type = exec
a2.sources.r2.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log
a2.sources.r2.shell = /bin/bash -c
#Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1
#Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r2.channels = c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2
3.执行监控配置
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/flume-file-hdfs.conf
4.开启hadoop和hive并操作hive产生日志
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
[atguigu@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive
hive (default)>
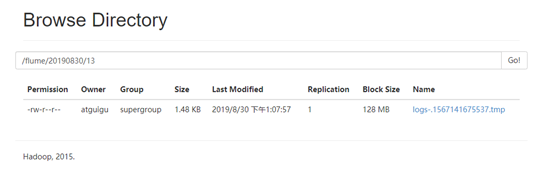
5.在HDFS上查看文件。
3.3 实时读取目录文件到HDFS案例
1)案例需求:使用flume监听整个目录的文件
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
1.创建配置文件flume-dir-hdfs.conf
创建一个文件
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ touch flume-dir-hdfs.conf
打开文件
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ vim flume-dir-hdfs.conf
添加如下内容
a3.sources = r3
a3.sinks = k3
a3.channels = c3
#Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r3.type = spooldir
a3.sources.r3.spoolDir = /opt/module/flume/upload
a3.sources.r3.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED
a3.sources.r3.fileHeader = true
#忽略所有以.tmp结尾的文件,不上传
a3.sources.r3.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*\.tmp)
#Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k3.type = hdfs
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/flume/upload/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.filePrefix = upload-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是128M
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1
#Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a3.channels.c3.type = memory
a3.channels.c3.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r3.channels = c3
a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3
2.启动监控文件夹命令
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/flume-dir-hdfs.conf
说明:在使用Spooling Directory Source时
1)不要在监控目录中创建并持续修改文件
2)上传完成的文件会以.COMPLETED结尾
3) 被监控文件夹每600毫秒扫描一次文件变动
3.向upload文件夹中添加文件
在/opt/module/flume目录下创建upload文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ mkdir upload
向upload文件夹中添加文件
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ cp NOTICE upload/
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ cp README.md upload/README.tmp
4.查看HDFS上的数据
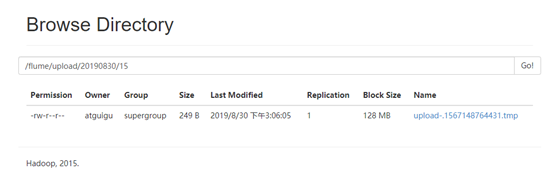
5.等待1s,再次查询upload文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ ll upload/
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 249 8月 30 15:06 NOTICE.COMPLETED
-rw-r--r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 2520 8月 30 15:12 README.tmp
后缀名为tmp的文件未变,其他文件后缀名已被改为completed
[atguigu@hadoop102 upload]$ ll
总用量 0
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 0 5月 20 22:31 atguigu.log.COMPLETED
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 0 5月 20 22:31 atguigu.tmp
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 0 5月 20 22:31 atguigu.txt.COMPLETED
3.4 单数据源多出口案例(一)
单Source多Channel、Sink如图7-2所示

图7-2 单Source多Channel、Sink
1)案例需求:使用flume-1监控文件变动,flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-2,flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-3,flume-3负责输出到local filesystem。
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
0.准备工作
在/opt/module/flume/job目录下创建group1文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ cd group1/
在/opt/module/datas/目录下创建flume3文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 datas]$ mkdir flume3
1.创建flume-file-flume.conf
配置1个接收日志文件的source和两个channel、两个sink,分别输送给flume-flume-hdfs和flume-flume-dir。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-file-flume.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-file-flume.conf
添加如下内容
#Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
#将数据流复制给多个channel
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c
#Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142
#Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
注:Avro是由Hadoop创始人Doug Cutting创建的一种语言无关的数据序列化和RPC框架。
注:RPC(Remote Procedure Call)—远程过程调用,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络技术的协议。
2.创建flume-flume-hdfs.conf
配置上级flume输出的source,输出是到hdfs的sink。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-flume-hdfs.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-flume-hdfs.conf
添加如下内容
#Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
#Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141
#Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9000/flume2/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = flume2-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是128M
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1
#Describe the channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
3.创建flume-flume-dir.conf
配置上级flume输出的source,输出是到本地目录的sink。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-flume-dir.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-flume-dir.conf
添加如下内容
#Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c2
#Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 4142
#Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/module/datas/flume3
#Describe the channel
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c2
提示:输出的本地目录必须是已经存在的目录,如果该目录不存在,并不会创建新的目录。
4.执行配置文件
分别开启对应配置文件:flume-flume-dir,flume-flume-hdfs,flume-file-flume。
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume-dir.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume-hdfs.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group1/flume-file-flume.conf
5.启动hadoop和hive
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
[atguigu@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive
hive (default)>
6.检查HDFS上数据
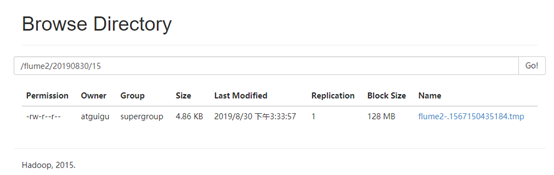
7检查/opt/module/datas/flume3目录中数据
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume3]$ ll
总用量 8
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 4977 8月 30 15:35 1567150371752-1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 0 8月 30 15:35 1567150371752-2
-rw-rw-r--. 1 atguigu atguigu 0 8月 30 15:35 1567150371752-3
3.5 单数据源多出口案例(二)
单Source、Channel多Sink(负载均衡)如图7-3所示

图7-3 单Source、Channel多Sink
1)案例需求:使用flume-1监控文件变动,flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-2,flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-3,flume-3也负责存储到HDFS
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
0.准备工作
在/opt/module/flume/job目录下创建group2文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ cd group1/
1.创建flume-netcat-flume.conf
配置1个接收日志文件的source和1个channel、两个sink,分别输送给flume-flume1和flume-flume2。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-netcat-flume.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-netcat-flume.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector.maxTimeOut=10000
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
注:Avro是由Hadoop创始人Doug Cutting创建的一种语言无关的数据序列化和RPC框架。
注:RPC(Remote Procedure Call)—远程过程调用,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络技术的协议。
2.创建flume-flume1.conf
配置上级flume输出的source,输出是到本地控制台。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-flume1.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-flume1.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Describe the channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
3.创建flume-flume2.conf
配置上级flume输出的source,输出是到本地控制台。
创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ touch flume-flume2.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-flume2.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c2
# Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 4142
# Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Describe the channel
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c2
4.执行配置文件
分别开启对应配置文件:flume-flume2,flume-flume1,flume-netcat-flume。
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group1/flume-netcat-flume.conf
5.使用telnet工具向本机的44444端口发送内容
$ telnet localhost 44444
6.查看flume2及flume3的控制台打印日志
3.6 多数据源汇总案例
多Source汇总数据到单Flume如图7-4所示

图7-4多Flume汇总数据到单Flume
1) 案例需求:
hadoop103上的flume-1监控文件hive.log,
hadoop104上的flume-2监控某一个端口的数据流,
flume-1与flume-2将数据发送给hadoop102上的flume-3,flume-3将最终数据打印到控制台
2)需求分析:

3)实现步骤:
0.准备工作
分发flume
[atguigu@hadoop102 module]$ xsync flume
在hadoop102、hadoop103以及hadoop104的/opt/module/flume/job目录下创建一个group2文件夹
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ mkdir group2
[atguigu@hadoop103 job]$ mkdir group2
[atguigu@hadoop104 job]$ mkdir group2
1.创建flume1.conf
配置source用于监控hive.log文件,配置sink输出数据到下一级flume。
在hadoop103上创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop103 group2]$ touch flume1.conf
[atguigu@hadoop103 group2]$ vim flume1.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/group.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
2.创建flume2.conf
配置source监控端口44444数据流,配置sink数据到下一级flume:
在hadoop104上创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop104 group2]$ touch flume2.conf
[atguigu@hadoop104 group2]$ vim flume2.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = netcat
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop104
a2.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = avro
a2.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a2.sinks.k1.port = 4141
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
3.创建flume3.conf
配置source用于接收flume1与flume2发送过来的数据流,最终合并后sink到控制台。
在hadoop102上创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 group2]$ touch flume3.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 group2]$ vim flume3.conf
添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
# Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Describe the channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
4.执行配置文件
分别开启对应配置文件:flume3.conf,flume2.conf,flume1.conf。
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group2/flume3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[atguigu@hadoop104 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group2/flume2.conf
[atguigu@hadoop103 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group2/flume1.conf
5.在hadoop103上向/opt/module目录下的group.log追加内容
[atguigu@hadoop103 module]$ echo 'hello' > group.log
6.在hadoop104上向44444端口发送数据
可以使用hadoop102发送
[atguigu@hadoop102 module]$ telnet hadoop104 44444
Trying 192.168.1.104...
Connected to hadoop104.
Escape character is '^]'.
Hello
OK
[atguigu@hadoop104 flume]$ telnet hadoop104 44444
7.检查hadoop102上数据

第4章 Flume监控之Ganglia
4.1 Ganglia的安装与部署
1)安装httpd服务与php
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum -y install httpd php
2)安装其他依赖
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum -y install rrdtool perl-rrdtool rrdtool-devel
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum -y install apr-devel
3)安装ganglia
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-web
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo yum install -y ganglia-gmond
4)修改配置文件ganglia.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
修改为的配置:
# Ganglia monitoring system php web frontend
Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
<Location /ganglia>
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from all
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
# Allow from .example.com
</Location>
5)修改配置文件gmetad.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
修改为:
data_source "hadoop102" 192.168.1.102
6)修改配置文件gmond.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
修改为:
cluster {
name = "hadoop102"
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine's hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
host = 192.168.1.102
port = 8649
ttl = 1
}
udp_recv_channel {
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
bind = 192.168.1.102
retry_bind = true
# Size of the UDP buffer. If you are handling lots of metrics you really
# should bump it up to e.g. 10MB or even higher.
# buffer = 10485760
}
7)修改配置文件config
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/selinux/config
修改为:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
尖叫提示:selinux本次生效关闭必须重启,如果此时不想重启,可以临时生效之:
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo setenforce 0
5)启动ganglia
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo service httpd start
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo service gmetad start
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo service gmond start
6)打开网页浏览ganglia页面
http://192.168.1.102/ganglia

尖叫提示:如果完成以上操作依然出现权限不足错误,请修改/var/lib/ganglia目录的权限:
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia
4.2 操作Flume测试监控
1)修改/opt/module/flume/conf目录下的flume-env.sh配置:
JAVA_OPTS="-Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia
-Dflume.monitoring.hosts=192.168.9.102:8649
-Xms100m
-Xmx200m"
2)启动flume任务
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent \
--conf conf/ \
--name a1 \
--conf-file job/flume-telnet-logger.conf \
-Dflume.root.logger==INFO,console \
-Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia \
-Dflume.monitoring.hosts=192.168.1.102:8649
3)发送数据观察ganglia监测图
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ telnet localhost 44444
样式如图:

图例说明:

第5章 自定义MySQLSource
5.1 自定义Source说明
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。官方提供的source类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些source。
如:实时监控MySQL,从MySQL中获取数据传输到HDFS或者其他存储框架,所以此时需要我们自己实现MySQLSource。
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:
官网说明:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source
5.2 自定义MySQLSource组成

图6-1 自定义MySQLSource组成
5.3 自定义MySQLSource步骤
根据官方说明自定义mysqlsource需要继承AbstractSource类并实现Configurable和PollableSource接口。
实现相应方法:
getBackOffSleepIncrement()//暂不用
getMaxBackOffSleepInterval()//暂不用
configure(Context context)//初始化context
process()//获取数据(从mysql获取数据,业务处理比较复杂,所以我们定义一个专门的类——SQLSourceHelper来处理跟mysql的交互),封装成event并写入channel,这个方法被循环调用
stop()//关闭相关的资源
5.4 代码实现
5.4.1 导入pom依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.27</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
5.4.2 添加配置信息
在classpath下添加jdbc.properties和log4j. properties
jdbc.properties:
dbDriver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
dbUrl=jdbc:mysql://hadoop102:3306/mysqlsource?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
dbUser=root
dbPassword=000000
log4j. properties:
#--------console-----------
log4j.rootLogger=info,myconsole,myfile
log4j.appender.myconsole=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.myconsole.layout=org.apache.log4j.SimpleLayout
#log4j.appender.myconsole.layout.ConversionPattern =%d [%t] %-5p [%c] - %m%n
#log4j.rootLogger=error,myfile
log4j.appender.myfile=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.myfile.File=/tmp/flume.log
log4j.appender.myfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.myfile.layout.ConversionPattern =%d [%t] %-5p [%c] - %m%n
5.4.3 SQLSourceHelper
1)属性说明:

2)方法说明:

3)代码实现:
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.conf.ConfigurationException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
public class SQLSourceHelper {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SQLSourceHelper.class);
private int runQueryDelay, //两次查询的时间间隔
startFrom, //开始id
currentIndex, //当前id
recordSixe = 0, //每次查询返回结果的条数
maxRow; //每次查询的最大条数
private String table, //要操作的表
columnsToSelect, //用户传入的查询的列
customQuery, //用户传入的查询语句
query, //构建的查询语句
defaultCharsetResultSet;//编码集
//上下文,用来获取配置文件
private Context context;
//为定义的变量赋值(默认值),可在flume任务的配置文件中修改
private static final int DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY = 10000;
private static final int DEFAULT_START_VALUE = 0;
private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_ROWS = 2000;
private static final String DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT = "*";
private static final String DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET = "UTF-8";
private static Connection conn = null;
private static PreparedStatement ps = null;
private static String connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword;
//加载静态资源
static {
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(SQLSourceHelper.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
connectionURL = p.getProperty("dbUrl");
connectionUserName = p.getProperty("dbUser");
connectionPassword = p.getProperty("dbPassword");
Class.forName(p.getProperty("dbDriver"));
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
LOG.error(e.toString());
}
}
//获取JDBC连接
private static Connection InitConnection(String url, String user, String pw) {
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw);
if (conn == null)
throw new SQLException();
return conn;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//构造方法
SQLSourceHelper(Context context) throws ParseException {
//初始化上下文
this.context = context;
//有默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数,读不到的采用默认值
this.columnsToSelect = context.getString("columns.to.select", DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT);
this.runQueryDelay = context.getInteger("run.query.delay", DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY);
this.startFrom = context.getInteger("start.from", DEFAULT_START_VALUE);
this.defaultCharsetResultSet = context.getString("default.charset.resultset", DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET);
//无默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数
this.table = context.getString("table");
this.customQuery = context.getString("custom.query");
connectionURL = context.getString("connection.url");
connectionUserName = context.getString("connection.user");
connectionPassword = context.getString("connection.password");
conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword);
//校验相应的配置信息,如果没有默认值的参数也没赋值,抛出异常
checkMandatoryProperties();
//获取当前的id
currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom);
//构建查询语句
query = buildQuery();
}
//校验相应的配置信息(表,查询语句以及数据库连接的参数)
private void checkMandatoryProperties() {
if (table == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("property table not set");
}
if (connectionURL == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.url property not set");
}
if (connectionUserName == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.user property not set");
}
if (connectionPassword == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.password property not set");
}
}
//构建sql语句
private String buildQuery() {
String sql = "";
//获取当前id
currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom);
LOG.info(currentIndex + "");
if (customQuery == null) {
sql = "SELECT " + columnsToSelect + " FROM " + table;
} else {
sql = customQuery;
}
StringBuilder execSql = new StringBuilder(sql);
//以id作为offset
if (!sql.contains("where")) {
execSql.append(" where ");
execSql.append("id").append(">").append(currentIndex);
return execSql.toString();
} else {
int length = execSql.toString().length();
return execSql.toString().substring(0, length - String.valueOf(currentIndex).length()) + currentIndex;
}
}
//执行查询
List<List<Object>> executeQuery() {
try {
//每次执行查询时都要重新生成sql,因为id不同
customQuery = buildQuery();
//存放结果的集合
List<List<Object>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (ps == null) {
//
ps = conn.prepareStatement(customQuery);
}
ResultSet result = ps.executeQuery(customQuery);
while (result.next()) {
//存放一条数据的集合(多个列)
List<Object> row = new ArrayList<>();
//将返回结果放入集合
for (int i = 1; i <= result.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) {
row.add(result.getObject(i));
}
results.add(row);
}
LOG.info("execSql:" + customQuery + "\nresultSize:" + results.size());
return results;
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOG.error(e.toString());
// 重新连接
conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword);
}
return null;
}
//将结果集转化为字符串,每一条数据是一个list集合,将每一个小的list集合转化为字符串
List<String> getAllRows(List<List<Object>> queryResult) {
List<String> allRows = new ArrayList<>();
if (queryResult == null || queryResult.isEmpty())
return allRows;
StringBuilder row = new StringBuilder();
for (List<Object> rawRow : queryResult) {
Object value = null;
for (Object aRawRow : rawRow) {
value = aRawRow;
if (value == null) {
row.append(",");
} else {
row.append(aRawRow.toString()).append(",");
}
}
allRows.add(row.toString());
row = new StringBuilder();
}
return allRows;
}
//更新offset元数据状态,每次返回结果集后调用。必须记录每次查询的offset值,为程序中断续跑数据时使用,以id为offset
void updateOffset2DB(int size) {
//以source_tab做为KEY,如果不存在则插入,存在则更新(每个源表对应一条记录)
String sql = "insert into flume_meta(source_tab,currentIndex) VALUES('"
+ this.table
+ "','" + (recordSixe += size)
+ "') on DUPLICATE key update source_tab=values(source_tab),currentIndex=values(currentIndex)";
LOG.info("updateStatus Sql:" + sql);
execSql(sql);
}
//执行sql语句
private void execSql(String sql) {
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
LOG.info("exec::" + sql);
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取当前id的offset
private Integer getStatusDBIndex(int startFrom) {
//从flume_meta表中查询出当前的id是多少
String dbIndex = queryOne("select currentIndex from flume_meta where source_tab='" + table + "'");
if (dbIndex != null) {
return Integer.parseInt(dbIndex);
}
//如果没有数据,则说明是第一次查询或者数据表中还没有存入数据,返回最初传入的值
return startFrom;
}
//查询一条数据的执行语句(当前id)
private String queryOne(String sql) {
ResultSet result = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
result = ps.executeQuery();
while (result.next()) {
return result.getString(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//关闭相关资源
void close() {
try {
ps.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int getCurrentIndex() {
return currentIndex;
}
void setCurrentIndex(int newValue) {
currentIndex = newValue;
}
int getRunQueryDelay() {
return runQueryDelay;
}
String getQuery() {
return query;
}
String getConnectionURL() {
return connectionURL;
}
private boolean isCustomQuerySet() {
return (customQuery != null);
}
Context getContext() {
return context;
}
public String getConnectionUserName() {
return connectionUserName;
}
public String getConnectionPassword() {
return connectionPassword;
}
String getDefaultCharsetResultSet() {
return defaultCharsetResultSet;
}
}
5.4.4 MySQLSource
代码实现:
package com.atguigu.source;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class SQLSource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
//打印日志
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SQLSource.class);
//定义sqlHelper
private SQLSourceHelper sqlSourceHelper;
@Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
try {
//初始化
sqlSourceHelper = new SQLSourceHelper(context);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
try {
//查询数据表
List<List<Object>> result = sqlSourceHelper.executeQuery();
//存放event的集合
List<Event> events = new ArrayList<>();
//存放event头集合
HashMap<String, String> header = new HashMap<>();
//如果有返回数据,则将数据封装为event
if (!result.isEmpty()) {
List<String> allRows = sqlSourceHelper.getAllRows(result);
Event event = null;
for (String row : allRows) {
event = new SimpleEvent();
event.setBody(row.getBytes());
event.setHeaders(header);
events.add(event);
}
//将event写入channel
this.getChannelProcessor().processEventBatch(events);
//更新数据表中的offset信息
sqlSourceHelper.updateOffset2DB(result.size());
}
//等待时长
Thread.sleep(sqlSourceHelper.getRunQueryDelay());
return Status.READY;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.error("Error procesing row", e);
return Status.BACKOFF;
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void stop() {
LOG.info("Stopping sql source {} ...", getName());
try {
//关闭资源
sqlSourceHelper.close();
} finally {
super.stop();
}
}
}
5.5 测试
5.5.1 jar包准备
1)将mysql驱动包也放入flume的lib目录下
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ cp \
/opt/sorfware/mysql-libs/mysql-connector-java-5.1.27/mysql-connector-java-5.1.27-bin.jar \
/opt/module/flume/lib/
2)打包项目并将jar包放入flume的lib目录下
5.5.2 配置文件准备
1)创建配置文件并打开
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ touch mysql.conf
[atguigu@hadoop102 job]$ vim mysql.conf
2)添加如下内容
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = mysqlsour.SQLSource
a1.sources.r1.connection.url = jdbc:mysql://192.168.9.102:3306/mysqlsource
a1.sources.r1.connection.user = root
a1.sources.r1.connection.password = 000000
a1.sources.r1.table = wlslog
a1.sources.r1.columns.to.select = *
a1.sources.r1.incremental.column.name = id
a1.sources.r1.incremental.value = 0
a1.sources.r1.run.query.delay=5000
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
5.5.3 mysql表准备
1)创建mysqlsource数据库
CREATE DATABASE mysqlsource;
2)在mysqlsource数据库下创建数据表student和元数据表flume_meta
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `flume_meta` (
`source_tab` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`currentIndex` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`source_tab`)
);
3)向数据表中添加数据
1 zhangsan
2 lisi
3 wangwu
4 zhaoliu
5.5.4 测试并查看结果
1)任务执行
[atguigu@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 \
--conf-file job/mysql.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
2)结果展示,如图6-2所示:

图6-2 结果展示
第6章 常见正则表达式语法






















 2416
2416











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








