例子源于OpenCV官网–基于梯度结构张量的各向异性图像分割
(https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d4/d70/tutorial_anisotropic_image_segmentation_by_a_gst.html)
什么是结构张量

如何用梯度结构张量估计各向异性图像的方向和相干性
如何用梯度结构张量分割具有单一局部方向的各向异性图像
代码:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import argparse
W = 52 # window size is WxW
C_Thr = 0.43 # threshold for coherency
LowThr = 35 # threshold1 for orientation, it ranges from 0 to 180
HighThr = 57 # threshold2 for orientation, it ranges from 0 to 180
#函数calcGST()使用梯度结构张量计算方向和相干性。输入参数w定义了窗口大小:
def calcGST(inputIMG, w):
img = inputIMG.astype(np.float32)
# GST components calculation (start)
# J = (J11 J12; J12 J22) - GST
imgDiffX = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_32F, 1, 0, 3)
imgDiffY = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_32F, 0, 1, 3)
imgDiffXY = cv.multiply(imgDiffX, imgDiffY)
imgDiffXX = cv.multiply(imgDiffX, imgDiffX)
imgDiffYY = cv.multiply(imgDiffY, imgDiffY)
J11 = cv.boxFilter(imgDiffXX, cv.CV_32F, (w,w))
J22 = cv.boxFilter(imgDiffYY, cv.CV_32F, (w,w))
J12 = cv.boxFilter(imgDiffXY, cv.CV_32F, (w,w))
# GST components calculations (stop)
# eigenvalue calculation (start)
# lambda1 = 0.5*(J11 + J22 + sqrt((J11-J22)^2 + 4*J12^2))
# lambda2 = 0.5*(J11 + J22 - sqrt((J11-J22)^2 + 4*J12^2))
tmp1 = J11 + J22
tmp2 = J11 - J22
tmp2 = cv.multiply(tmp2, tmp2)
tmp3 = cv.multiply(J12, J12)
tmp4 = np.sqrt(tmp2 + 4.0 * tmp3)
lambda1 = 0.5*(tmp1 + tmp4) # biggest eigenvalue
lambda2 = 0.5*(tmp1 - tmp4) # smallest eigenvalue
# eigenvalue calculation (stop)
# Coherency calculation (start)
# Coherency = (lambda1 - lambda2)/(lambda1 + lambda2)) - measure of anisotropism
# Coherency is anisotropy degree (consistency of local orientation)
imgCoherencyOut = cv.divide(lambda1 - lambda2, lambda1 + lambda2)
# Coherency calculation (stop)
# orientation angle calculation (start)
# tan(2*Alpha) = 2*J12/(J22 - J11)
# Alpha = 0.5 atan2(2*J12/(J22 - J11))
imgOrientationOut = cv.phase(J22 - J11, 2.0 * J12, angleInDegrees = True)
imgOrientationOut = 0.5 * imgOrientationOut
# orientation angle calculation (stop)
return imgCoherencyOut, imgOrientationOut
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Code for Anisotropic image segmentation tutorial.')
#parser.add_argument('-i', '--input', help='Path to input image.', default='cards.png'required=True)
parser.add_argument('-i', '--input', help='Path to input image.', default='stone.png')
args = parser.parse_args()
imgIn = cv.imread(args.input, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
if imgIn is None:
print('Could not open or find the image: {}'.format(args.input))
exit(0)
#各向异性图像分割算法包括梯度结构张量计算、方向计算、相干计算以及方向和相干阈值:
imgCoherency, imgOrientation = calcGST(imgIn, W)
"""
下面的代码将阈值LowThr和HighThr应用于图像方向,
并将阈值C_Thr应用于前面函数计算的图像一致性。
LowThr和HighThr定义方向范围:
"""
_, imgCoherencyBin = cv.threshold(imgCoherency, C_Thr, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
_, imgOrientationBin = cv.threshold(imgOrientation, LowThr, HighThr, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
#最后我们结合阈值结果:
imgBin = cv.bitwise_and(imgCoherencyBin, imgOrientationBin)
imgCoherency = cv.normalize(imgCoherency, None, alpha=0, beta=1, norm_type=cv.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv.CV_32F)
imgOrientation = cv.normalize(imgOrientation, None, alpha=0, beta=1, norm_type=cv.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv.CV_32F)
cv.imshow('result.jpg', np.uint8(0.5*(imgIn + imgBin)))
cv.imshow('Coherency.jpg', imgCoherency)
cv.imshow('Orientation.jpg', imgOrientation)
cv.waitKey(0)
运行结果:
下图是真实的单方向各向异性图像:
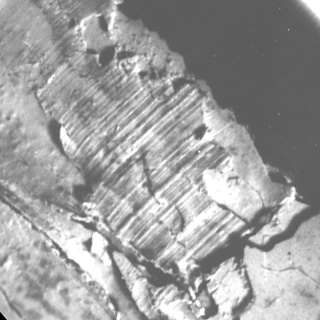
分割图像:
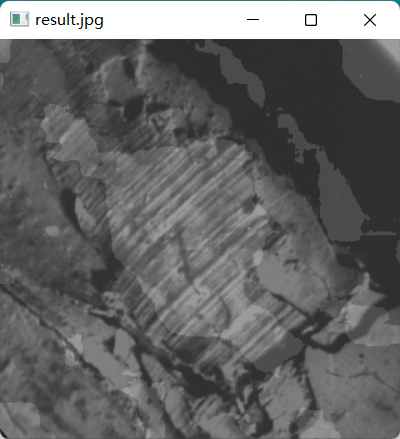
下图是各向异性图像的方向和相干性:
方向:

相干性:























 436
436











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








