上一篇文章监控pod资源,但是pod的删除与创建使用的是直接操作API Server,现在我们使用编程方式创建删除管理pod
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
//"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
//"strings"
)
func main() {
// uses the current context in kubeconfig
// path-to-kubeconfig -- for example, /root/.kube/config
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", "C:\\Users\\HJW\\.kube\\config")
if err!= nil{
panic(err)
}
// creates the clientset
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err!= nil{
panic(err)
}
//pod模版
newPod := &corev1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod1",
},
Spec: corev1.PodSpec{
Containers: []corev1.Container{
{Name: "busybox", Image: "busybox:latest", Command: []string{"sleep", "1000"}},
},
},
}
//创建pod
pod, err := clientset.CoreV1().Pods("kube-system").Create(context.Background(), newPod, metav1.CreateOptions{})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Created pod %q.\n", pod.GetObjectMeta().GetName())
}
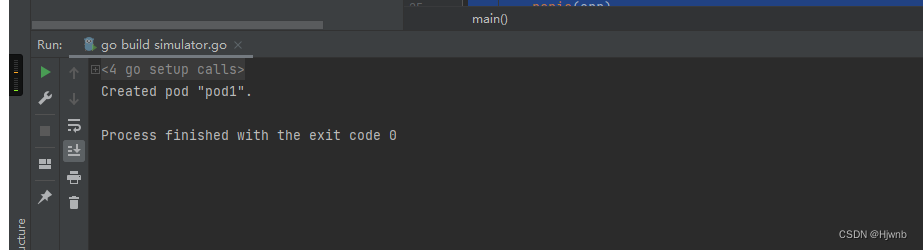
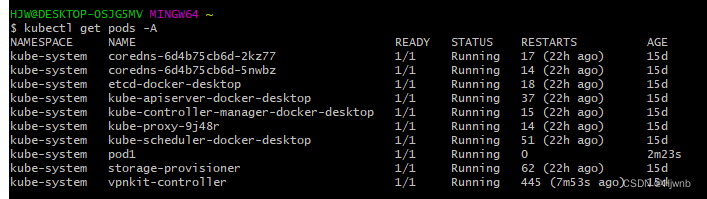
可以看到pod1已经被创建,查看具体描述如下
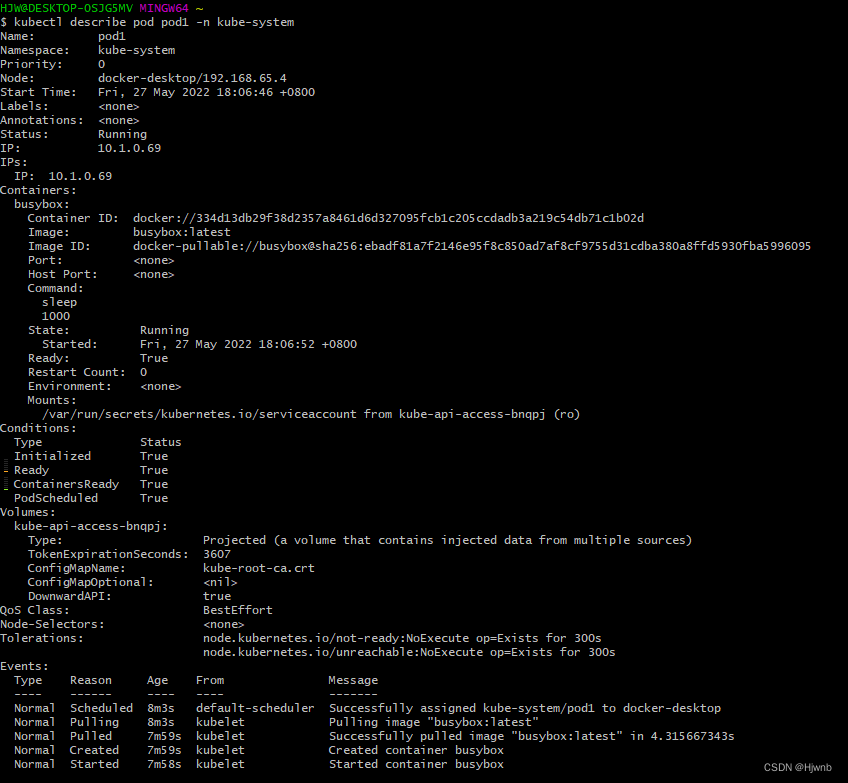
那我们想要丰富pod信息,例如提出cpu和内存的需求与限制,怎么做呢
package main
import (
//"context"
//"fmt"
//corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
//"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/api/resource"
//metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
//v1 "k8s.io/client-go/applyconfigurations/core/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
//"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
//"strings"
"context"
"fmt"
"k8s.io/api/core/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/api/resource"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
)
func getResourceList(cpu, memory string) v1.ResourceList {
res := v1.ResourceList{}
if cpu != "" {
res[v1.ResourceCPU] = resource.MustParse(cpu)
}
if memory != "" {
res[v1.ResourceMemory] = resource.MustParse(memory)
}
return res
}
func getResourceRequirements(requests, limits v1.ResourceList) v1.ResourceRequirements {
res := v1.ResourceRequirements{}
res.Requests = requests
res.Limits = limits
return res
}
func main() {
// uses the current context in kubeconfig
// path-to-kubeconfig -- for example, /root/.kube/config
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", "C:\\Users\\HJW\\.kube\\config")
if err!= nil{
panic(err)
}
// creates the clientset
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err!= nil{
panic(err)
}
//pod模版
newPod := &v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod2",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
Containers: []v1.Container{
{Name: "pod2", Image: "busybox:latest", Command: []string{"sleep", "1000"},
Resources: getResourceRequirements(getResourceList("10m", "1Gi"), getResourceList("50m", "1Gi"))},
},
},
}
//创建pod
pod, err := clientset.CoreV1().Pods("kube-system").Create(context.Background(), newPod, metav1.CreateOptions{})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Created pod %q.\n", pod.GetObjectMeta().GetName())
}
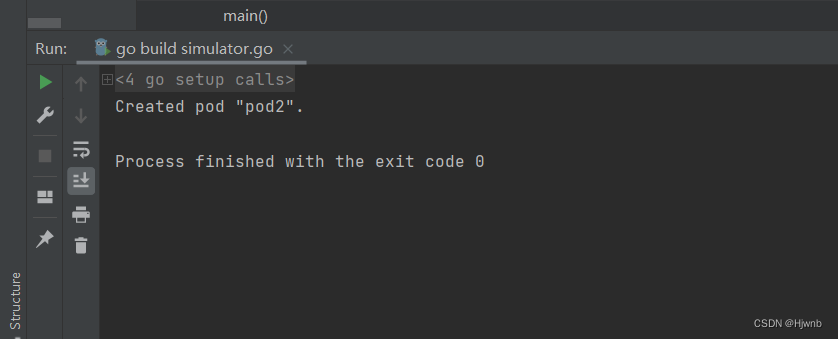
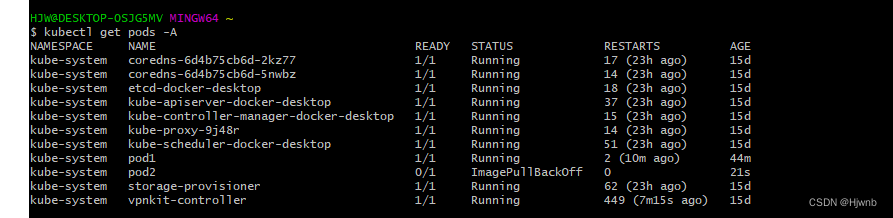
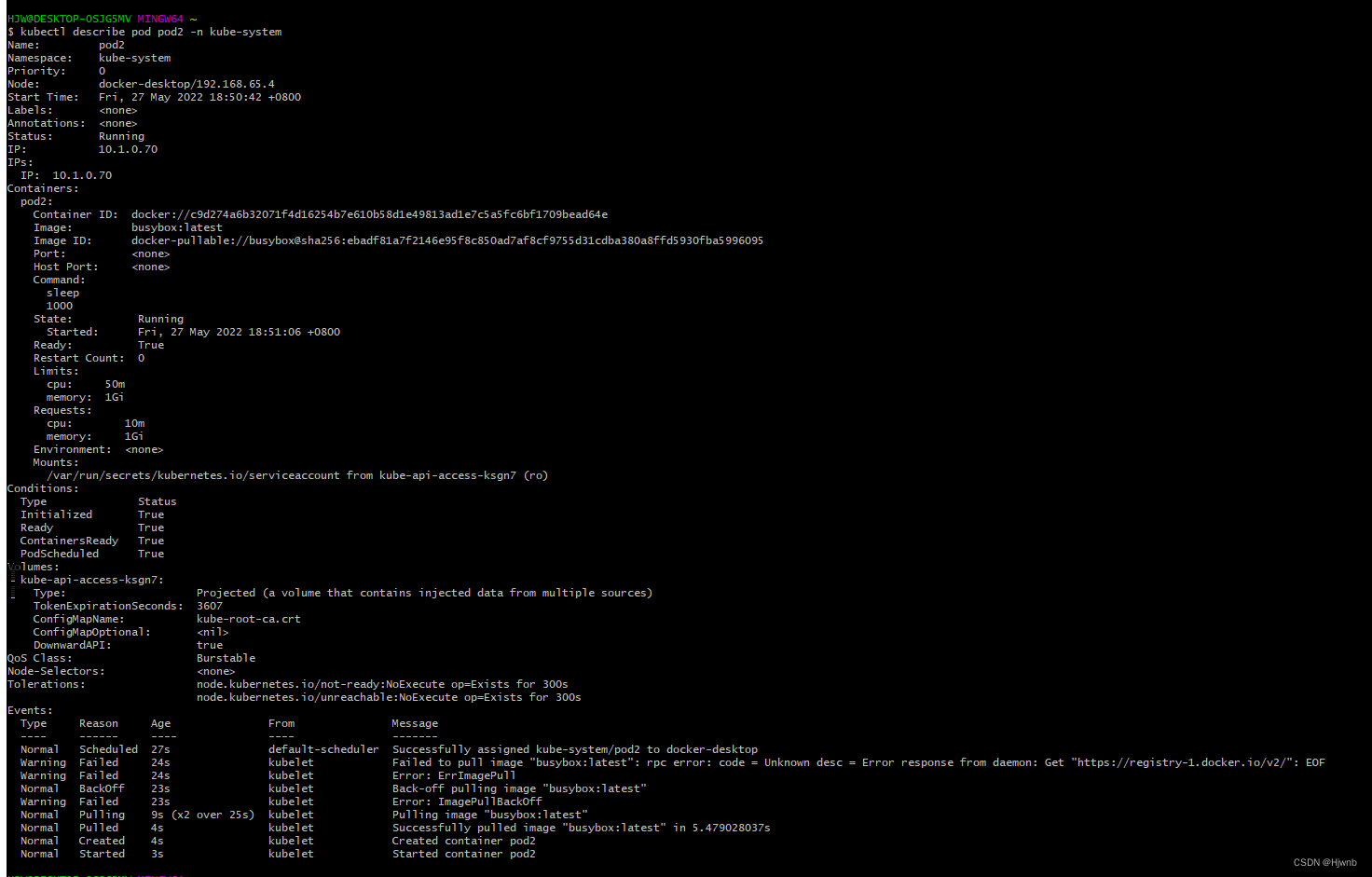
pod2已经被成功创建,从描述信息可以知道,cpu与内存的限制与申请已经生效了。
那这一部分的工作先做到这儿,有几个问题还有待解决。
这个是types.go里面对Container的描述,编程的时候要对应

type Container struct {
// Name of the container specified as a DNS_LABEL.
// Each container in a pod must have a unique name (DNS_LABEL).
// Cannot be updated.
Name string `json:"name" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
// Docker image name.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images
// This field is optional to allow higher level config management to default or override
// container images in workload controllers like Deployments and StatefulSets.
// +optional
Image string `json:"image,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=image"`
// Entrypoint array. Not executed within a shell.
// The docker image's ENTRYPOINT is used if this is not provided.
// Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the container's environment. If a variable
// cannot be resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. Double $$ are reduced
// to a single $, which allows for escaping the $(VAR_NAME) syntax: i.e. "$$(VAR_NAME)" will
// produce the string literal "$(VAR_NAME)". Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless
// of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell
// +optional
Command []string `json:"command,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=command"`
// Arguments to the entrypoint.
// The docker image's CMD is used if this is not provided.
// Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the container's environment. If a variable
// cannot be resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. Double $$ are reduced
// to a single $, which allows for escaping the $(VAR_NAME) syntax: i.e. "$$(VAR_NAME)" will
// produce the string literal "$(VAR_NAME)". Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless
// of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell
// +optional
Args []string `json:"args,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,rep,name=args"`
// Container's working directory.
// If not specified, the container runtime's default will be used, which
// might be configured in the container image.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
WorkingDir string `json:"workingDir,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=workingDir"`
// List of ports to expose from the container. Exposing a port here gives
// the system additional information about the network connections a
// container uses, but is primarily informational. Not specifying a port here
// DOES NOT prevent that port from being exposed. Any port which is
// listening on the default "0.0.0.0" address inside a container will be
// accessible from the network.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
// +patchMergeKey=containerPort
// +patchStrategy=merge
// +listType=map
// +listMapKey=containerPort
// +listMapKey=protocol
Ports []ContainerPort `json:"ports,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"containerPort" protobuf:"bytes,6,rep,name=ports"`
// List of sources to populate environment variables in the container.
// The keys defined within a source must be a C_IDENTIFIER. All invalid keys
// will be reported as an event when the container is starting. When a key exists in multiple
// sources, the value associated with the last source will take precedence.
// Values defined by an Env with a duplicate key will take precedence.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
EnvFrom []EnvFromSource `json:"envFrom,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,19,rep,name=envFrom"`
// List of environment variables to set in the container.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
// +patchMergeKey=name
// +patchStrategy=merge
Env []EnvVar `json:"env,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"name" protobuf:"bytes,7,rep,name=env"`
// Compute Resources required by this container.
// Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
// +optional
Resources ResourceRequirements `json:"resources,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,8,opt,name=resources"`
// Pod volumes to mount into the container's filesystem.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
// +patchMergeKey=mountPath
// +patchStrategy=merge
VolumeMounts []VolumeMount `json:"volumeMounts,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"mountPath" protobuf:"bytes,9,rep,name=volumeMounts"`
// volumeDevices is the list of block devices to be used by the container.
// +patchMergeKey=devicePath
// +patchStrategy=merge
// +optional
VolumeDevices []VolumeDevice `json:"volumeDevices,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"devicePath" protobuf:"bytes,21,rep,name=volumeDevices"`
// Periodic probe of container liveness.
// Container will be restarted if the probe fails.
// Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
// +optional
LivenessProbe *Probe `json:"livenessProbe,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,10,opt,name=livenessProbe"`
// Periodic probe of container service readiness.
// Container will be removed from service endpoints if the probe fails.
// Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
// +optional
ReadinessProbe *Probe `json:"readinessProbe,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,11,opt,name=readinessProbe"`
// StartupProbe indicates that the Pod has successfully initialized.
// If specified, no other probes are executed until this completes successfully.
// If this probe fails, the Pod will be restarted, just as if the livenessProbe failed.
// This can be used to provide different probe parameters at the beginning of a Pod's lifecycle,
// when it might take a long time to load data or warm a cache, than during steady-state operation.
// This cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
// +optional
StartupProbe *Probe `json:"startupProbe,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,22,opt,name=startupProbe"`
// Actions that the management system should take in response to container lifecycle events.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
Lifecycle *Lifecycle `json:"lifecycle,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,12,opt,name=lifecycle"`
// Optional: Path at which the file to which the container's termination message
// will be written is mounted into the container's filesystem.
// Message written is intended to be brief final status, such as an assertion failure message.
// Will be truncated by the node if greater than 4096 bytes. The total message length across
// all containers will be limited to 12kb.
// Defaults to /dev/termination-log.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
TerminationMessagePath string `json:"terminationMessagePath,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,13,opt,name=terminationMessagePath"`
// Indicate how the termination message should be populated. File will use the contents of
// terminationMessagePath to populate the container status message on both success and failure.
// FallbackToLogsOnError will use the last chunk of container log output if the termination
// message file is empty and the container exited with an error.
// The log output is limited to 2048 bytes or 80 lines, whichever is smaller.
// Defaults to File.
// Cannot be updated.
// +optional
TerminationMessagePolicy TerminationMessagePolicy `json:"terminationMessagePolicy,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,20,opt,name=terminationMessagePolicy,casttype=TerminationMessagePolicy"`
// Image pull policy.
// One of Always, Never, IfNotPresent.
// Defaults to Always if :latest tag is specified, or IfNotPresent otherwise.
// Cannot be updated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#updating-images
// +optional
ImagePullPolicy PullPolicy `json:"imagePullPolicy,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,14,opt,name=imagePullPolicy,casttype=PullPolicy"`
// SecurityContext defines the security options the container should be run with.
// If set, the fields of SecurityContext override the equivalent fields of PodSecurityContext.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/
// +optional
SecurityContext *SecurityContext `json:"securityContext,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,15,opt,name=securityContext"`
// Variables for interactive containers, these have very specialized use-cases (e.g. debugging)
// and shouldn't be used for general purpose containers.
// Whether this container should allocate a buffer for stdin in the container runtime. If this
// is not set, reads from stdin in the container will always result in EOF.
// Default is false.
// +optional
Stdin bool `json:"stdin,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,16,opt,name=stdin"`
// Whether the container runtime should close the stdin channel after it has been opened by
// a single attach. When stdin is true the stdin stream will remain open across multiple attach
// sessions. If stdinOnce is set to true, stdin is opened on container start, is empty until the
// first client attaches to stdin, and then remains open and accepts data until the client disconnects,
// at which time stdin is closed and remains closed until the container is restarted. If this
// flag is false, a container processes that reads from stdin will never receive an EOF.
// Default is false
// +optional
StdinOnce bool `json:"stdinOnce,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,17,opt,name=stdinOnce"`
// Whether this container should allocate a TTY for itself, also requires 'stdin' to be true.
// Default is false.
// +optional
TTY bool `json:"tty,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,18,opt,name=tty"`
}
我的go语言编程能力还有待增强,这个代码我也是参考了官方源码来写的github地址






















 6646
6646











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








