文本文件编辑命令
一、概述
这里就是记录一些查看文件内容的命令,主要是查看和查询文件中文本相关内容。并不涉及到文件的编辑功能。
二、查看文件
1. cat : 用于查看纯文本文件(内容较少的)
最常用的命令就是 cat -n 文件
带n 参数就能显示行号,方便查看
zhy@zhy-Uos:~$ cat -n .python_history
1 exit()
2 quit
3 quit()
zhy@zhy-Uos:~$ cat --help
用法:cat [选项]... [文件]...
连接所有指定文件并将结果写到标准输出。
如果没有指定文件,或者文件为"-",则从标准输入读取。
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t 与-vT 等价
-T, --show-tabs 将跳格字符显示为^I
-u (被忽略)
-v, --show-nonprinting 使用^ 和M- 引用,除了LFD和 TAB 之外
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
--version 显示版本信息并退出
示例:
cat f - g 先输出f 的内容,然后输出标准输入的内容,最后输出g 的内容。
cat 将标准输入的内容复制到标准输出。
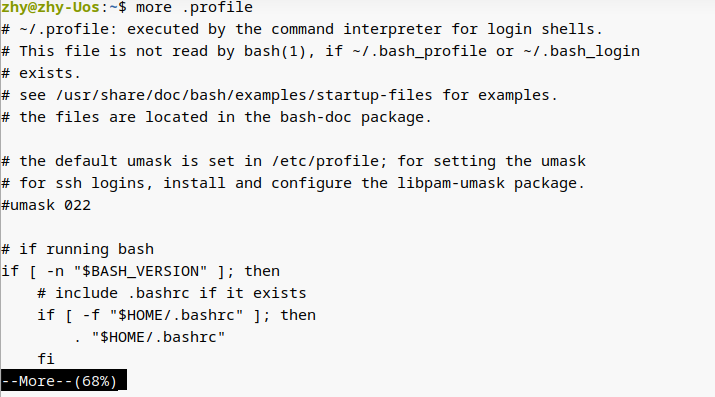
2. more : 用于查看纯文本文件(内容较多的)
因为使用 cat 命令阅读长篇的文本内容,信息就会在屏幕上快速翻滚,导致自己还没有来得及看到,内容就已经翻篇了。因此对于长篇的文本内容,推荐使用 more 命令来查看。more命令会在最下面使用百分比的形式来提示您已经阅读了多少内容。您还可以使用空格键或回车键向下翻页:
3. head : 用于查看纯文本文档的前 N 行
如果只想看文本的前10行,就可以用 head 命令,带参数-n。
zhy@zhy-Uos:~$ head -n 10 .profile
# ~/.profile: executed by the command interpreter for login shells.
# This file is not read by bash(1), if ~/.bash_profile or ~/.bash_login
# exists.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files for examples.
# the files are located in the bash-doc package.
# the default umask is set in /etc/profile; for setting the umask
# for ssh logins, install and configure the libpam-umask package.
#umask 022
4. tail : 用于查看纯文本文档的后 N 行或持续刷新内容
这个和tail类似,如需要查看文本内容的最后 10 行,这时就需要用到tail 命令了。tail 命令的操作方法与 head 命令非常相似,只需要执行“tail -n 20 文件名”命令就可以达到这样的效果。tail 命令最强悍的功能是可以持续刷新一个文件的内容,当想要实时查看最新日志文件时,这特别有用,此时的命令格式为“tail -f 文件名”:
zhy@zhy-Uos:~$ tail -n 10 .profile
# set PATH so it includes user's private bin if it exists
if [ -d "$HOME/bin" ] ; then
PATH="<







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










