关注 M r . m a t e r i a l , \color{Violet} \rm Mr.material\ , Mr.material , 更 \color{red}{更} 更 多 \color{blue}{多} 多 精 \color{orange}{精} 精 彩 \color{green}{彩} 彩!
主要专栏内容包括:
†《LAMMPS小技巧》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag《LAMMPS小技巧》:}}
†《LAMMPS小技巧》: 主要介绍采用分子动力学(
L
a
m
m
p
s
Lammps
Lammps)模拟相关安装教程、原理以及模拟小技巧(难度:
★
\bigstar
★)
††《LAMMPS实例教程—In文件详解》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag\dag《LAMMPS实例教程—In文件详解》:}}
††《LAMMPS实例教程—In文件详解》: 主要介绍采用分子动力学(
L
a
m
m
p
s
Lammps
Lammps)模拟相关物理过程模拟。(包含:热导率计算、定压比热容计算,难度:
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★)
†††《Lammps编程技巧及后处理程序技巧》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag\dag\dag《Lammps编程技巧及后处理程序技巧》:}}
†††《Lammps编程技巧及后处理程序技巧》: 主要介绍针对分子模拟的动力学过程(轨迹文件)进行后相关的处理分析(需要一定编程能力。难度:
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★)。
††††《分子动力学后处理集成函数—Matlab》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag\dag\dag\dag《分子动力学后处理集成函数—Matlab》:}}
††††《分子动力学后处理集成函数—Matlab》: 主要介绍针对后处理过程中指定函数,进行包装,方便使用者直接调用(需要一定编程能力,难度:
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★)。
†††††《SCI论文绘图—Python绘图常用模板及技巧》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag\dag\dag\dag\dag《SCI论文绘图—Python绘图常用模板及技巧》:}}
†††††《SCI论文绘图—Python绘图常用模板及技巧》: 主要介绍针对处理后的数据可视化,并提供对应的绘图模板(需要一定编程能力,难度:
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★)。
††††††《分子模拟—Ovito渲染案例教程》:
‾
\textbf{ \underline{\dag\dag\dag\dag\dag\dag《分子模拟—Ovito渲染案例教程》:}}
††††††《分子模拟—Ovito渲染案例教程》: 主要采用
O
v
i
t
o
\rm Ovito
Ovito软件,对
L
a
m
m
p
s
\rm Lammps
Lammps 生成的轨迹文件进行渲染(难度:
★
\bigstar
★
★
\bigstar
★)。
专栏说明(订阅后可浏览对应专栏全部博文):
‾
\color{red}{\textbf{ \underline{专栏说明(订阅后可浏览对应专栏全部博文):}}}
专栏说明(订阅后可浏览对应专栏全部博文):
注意:
\color{red} 注意:
注意:如需只订阅某个单独博文,请联系博主邮箱咨询。
l
a
m
m
p
s
_
m
a
t
e
r
i
a
l
s
@
163.
c
o
m
\rm lammps\_materials@163.com
lammps_materials@163.com
♠
\spadesuit
♠
†
\dag
† 开源后处理集成程序:请关注专栏《LAMMPS后处理——MATLAB子函数合集整理》
♠
\spadesuit
♠
†
\dag
†
†
\dag
† 需要付费定制后处理程序请邮件联系:
l
a
m
m
p
s
_
m
a
t
e
r
i
a
l
s
@
163.
c
o
m
\rm lammps\_materials@163.com
lammps_materials@163.com
热导率计算—分子动力学
L
a
m
m
p
s
\rm Lammps
Lammps 官方案例中,提供了计算热导率的五种方法。但是按计算方法来说其实知识分为两种:平衡态分子动力学(
E
M
D
\rm EMD
EMD)、非平衡态分子动力学(
N
E
M
D
\rm NEMD
NEMD 或
R
N
E
M
D
\rm RNEMD
RNEMD)。


文章目录
- 热导率计算—分子动力学
- 注意
- 一、热传导的基本概念
- 二、大规模循环不同工况的脚本
- 三、Lammps的输出文件读取脚本—Matlab
- 四、详解五种热导率计算方法—In文件脚本
- 一、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—速度重标法 f i x e h e x \rm fix\ ehex fix ehex
- 二、非平衡态分子动力学 ( N E M D ) \rm (NEMD) (NEMD)—局部热浴法 f i x L a n g v e i n \rm fix \ Langvein fix Langvein
- 三、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—动量交换法 ( f i x t h e r m a l / c o n d u c t i v i t y ) \rm (fix\ thermal/conductivity) (fix thermal/conductivity)
- 四、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—速度重标法 ( f i x h e a t ) \rm (fix\ heat) (fix heat)
- 五、平衡态分子动力学 ( E M D ) \rm (EMD) (EMD)— G K 法 \rm GK法 GK法
- 六、五种方法结果对比
注意
1. 动态 g r o u p \rm group group 设置
针对于流体体系, 热源和热汇需要设置为动态 g r o u p \rm group group。
region left_heat_flux block ${1_lattice_unit} ${10_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
region right_heat_flux block ${11_lattice_unit} ${all_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
group left_heat_flux dynamic all region left_heat_flux every 1
group right_heat_flux dynamic all region right_heat_flux every 1
2. 代码说明
以固态
60
K
\rm 60\ K
60 K 下的
A
r
g
o
n
\rm Argon
Argon 为例进行测试,脚本分为两个:
R
u
n
.
i
n
\rm Run.in
Run.in,以及几种不同方法。
运行
r
u
n
.
i
n
\rm run.in
run.in 在循环脚本中打开对应的方法即可。

3. 代码获取
(1) 全部
i
n
in
in 文件已经开源在博客,可以直接复制;
(2)
P
y
t
h
o
n
Python
Python 绘图脚本以及
I
n
In
In 文件需要打包文件请下载:
链接:请点击
6xvm
一、热传导的基本概念
1、平衡态和非平衡定态
非平衡定态
\color{red}非平衡定态
非平衡定态
体系初一环境不变的情况下,经过一定时间后,体系必将达到一个宏观上不随时间变化的状态,尽管还不一定是平衡态,但是体系将长久地保持这一状态,这样的状态称为非平衡定态,简称定态或者稳态(
s
t
a
t
i
o
n
a
r
y
s
t
a
t
e
\rm stationary\ state
stationary state).
这里环境不变的状态指的恒定外场,不变的体系体积等。当处于稳定热传导过程中,体系在宏观上属于定态,不属于平衡态,因为有热流的存在。
平衡态 \color{red}平衡态 平衡态
若处于定态的体系,同时它的环境的宏观状态也不变,则这个体系成为平衡态。
当体系从非平衡态到平衡态时,描述体系宏观状态所需的宏观参量个数达到最小。
2、热传导
首先,我们先看看传热学是如何定义热传导的。
物体各部分之间不发生相对位移时,依靠分子、原子及自由电子等微观粒子的热运动而产生的热能传递,成为热传导。(
h
e
a
t
c
o
n
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
heat\ conduction
heat conduction)下文中简称:热导。
热导现象,例如,温度较高的物体,把热量传递给与直接触的温度较低的另一固体。
热导现象的规律被总结傅里叶定律(
F
o
u
r
i
e
r
\rm Fourier
Fourier)
简单地说,对于一个一维导热问题,任意一个厚度为 d x dx dx 的单元来说。单位时间内通过该层的导热热量,与温度变化率以及平板面积 ( A A A) 成正比,即:单位时间穿过单位面积的热量,在数量上正比于温度梯度。
ϕ = − λ \phi =-\color{red}{\lambda} ϕ=−λ A d T d x A\frac{dT}{dx} AdxdT
这里的比例系数 λ \color{red}{\lambda} λ 即为导热系数。 T h e r m a l c o n d u c t i v i t y \rm Thermal\ conductivity Thermal conductivity.
显然,从上面的公式可以看出, λ \color{red}{\lambda} λ 越大代表热量越容易被输运。相同的,由于温度的不均匀性引起的能量运输称为热导现象,其运输系数称为 热导率 \rm \color{red}热导率 热导率。由于速度的不均匀性引起的动量运输,称之为黏性现象;由于体系粒子数密度的不均匀性引起的质量运输,称为扩散现象。
那么如何去计算这个热量的“运输系数”呢?这里就涉及到了,平衡态方法和非平衡态的方法。
关于这里“平衡态方法和非平衡态”的定义请参考博文《LAMMPS非平衡分子动力学 (NEMD) 纳米线热导率教程—一个代码循环计算不同温度和尺寸》
其他相关参考:
1. 《Lammps之MP方法粘度计算(包含in文件)》
2. 《轨迹分析—Matlab计算均方位移》
二、大规模循环不同工况的脚本
这里只展示代码,相关博文请参考《Lammps如何大规模循环计算?一个脚本循环不同工况》
#------------------------------------------------#
# Author_Email: lammps_materials@163.com #
#------------------------------------------------#
###################
# initial setting #
###################
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# loop make all_file
echo screen
print " ------------------------------------------------"
print " -----------------NOW making files---------------"
print " ------------------------------------------------"
label out_makefile
variable number_out loop 1
variable file_name_out index 60
shell mkdir ${file_name_out}
shell cp Ar_ehex.in ${file_name_out}
shell cd ${file_name_out}
# loop make in_file
label in_makefile
variable number_in loop 1
variable file_name_in index 10
shell mkdir ${file_name_in}
shell cp Ar_ehex.in ${file_name_in}
next number_in
next file_name_in
jump Ar_ehex.in in_makefile
clear
# loop make in_file
shell cd ..
next number_out
next file_name_out
jump Ar_ehex.in out_makefile
clear
print " ------------------------------------------"
print " ------------------Finish!-----------------"
print " ------------------------------------------"
# loop make all_file
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
label calculation_in_outfile
variable loop_number_out loop 1
# water fraction
variable loop_file_out_name index 60
shell cd ${loop_file_out_name}
log ${loop_file_out_name}.log
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
label calculation_in_infile
variable loop_number_in loop 1
variable loop_file_in_name index 10
shell cd ${loop_file_in_name}
log ${loop_file_in_name}.log
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
print " --------------------------------------------------------------------"
print " ----------Now the temperature is ${loop_file_out_name}-----------"
print " ------Now lattice replicate number is ${loop_file_in_name}------"
print " --------------------------------------------------------------------"
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
include Ar_ehex.in
#--------------------------------------------------------------#
shell cd ..
clear
next loop_file_in_name
jump Ar_ehex.in calculation_in_infile
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
shell cd ..
clear
next loop_file_out_name
jump Ar_ehex.in calculation_in_outfile
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------#
三、Lammps的输出文件读取脚本—Matlab
clc;clear;
file = "all.temp";
%--------------------------------------------------%
num_blocks = 20; % 体系分为20个块,这里是bin数量
num_outputs = 100;% 采样100,也就是100个温度曲线
%--------------------------------------------------%
[Chunk Coord1 Ncount v_all_temp] ...
= textread(file, '%n%n%n%n', 'headerlines', 3, 'emptyvalue', 0);
temp = [Chunk Coord1 Ncount v_all_temp]; nall = length(temp) / (num_blocks+1);
clear Chunk Coord1 Ncount v_all_temp;
%--------------------------------------------------%
for i =1:nall
temp((i-1)*num_blocks+1,:)=[];
end
temp = reshape(temp(:, end), num_blocks, num_outputs);
%这里需要对温度曲线进行平均
new_temp = ave_variable(1,20,temp(:,:));
temp_all = sum(temp,2)./num_outputs;
四、详解五种热导率计算方法—In文件脚本
这里以
60
K
60K
60K
A
r
Ar
Ar的热导率为例进行对比。
非平衡分子动力学
(
N
E
M
D
)
\rm (NEMD)
(NEMD) 这里指的是通过控制温度,即施加已知温度大小的温差,计算热流。相同的
R
N
E
M
D
\rm RNEMD
RNEMD 指的是通过指定热流,计算温度梯度。
因此,采用
F
i
x
e
h
e
x
\rm Fix\ ehex
Fix ehex、
m
p
\rm mp
mp 方法的为
R
N
E
M
D
RNEMD
RNEMD;采用
F
i
x
L
a
n
g
v
e
i
n
Fix\ Langvein
Fix Langvein施加温度梯度,计算热流的为
N
E
M
D
\rm NEMD
NEMD。
一、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—速度重标法 f i x e h e x \rm fix\ ehex fix ehex
关于这个fix ehex,这个命令针对fix heat 命令的能量漂移问题,进行了修正。一些比较老的教程中可能还采用的fix heat。
核心命令 \color{red}核心命令 核心命令
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all ehex 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all ehex 1 -${POWER} region cold

clear
echo screen
units metal
dimension 3
boundary p p p
atom_style full
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable TS equal 0.01 ### ${TS} timestep
variable Tdamp equal 100*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable Pdamp equal 1000*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable T equal ${loop_file_out_name} ### ${T} initial temperature
variable POWER equal 0.08
timestep ${TS}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# unit cell
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable x_length equal ${loop_file_in_name}
variable half_x equal ${x_length}*0.5
variable lattice_unit equal 5.4*2
variable x_length equal ${lattice_unit}*${x_length}
variable y_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
variable z_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
region box block 0 ${x_length} &
0 ${y_length} &
0 ${z_length} units box
create_box 1 box
lattice fcc 5.4
create_atoms 1 box
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable materials_length equal (${half_x}-1)*${lattice_unit}
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
print "The material length is ${materials_length}"
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# group setting #
###################
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# setting mass
mass 1 40 # mass for Ar
group Ar type 1
velocity all create ${T} 12345 loop local #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
write_data system.data
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# pair interaction #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pair_style lj/cut 10
pair_coeff * * 1.032e-2 3.405
neighbor 0.5 bin
neigh_modify every 5 delay 0 check no
#----------------------------------------------------------#
thermo 1000
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 1 #
###################
# loop relax system 500 ps
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 50_ps equal 50/${TS}
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
variable loop_all_num equal 10
variable relax_system loop ${loop_all_num}
label loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${50_ps}
unfix NVT
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
next relax_system
jump SELF loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${500_ps}
unfix NVT
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# heat region define
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ^ <------------------------> ^ <------------------------>
# | 9 units | 9 units
# hot cold
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Real length = 9*units
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 1_lattice_unit equal 1*${lattice_unit}
variable 10_lattice_unit equal ${half_x}*${lattice_unit}
variable 11_lattice_unit equal (${half_x}+1)*${lattice_unit}
# heat region
region heat block 0 ${1_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
# cold region
region cold block ${10_lattice_unit} ${11_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
variable all_lattice_unit equal ${x_length}*${lattice_unit}
group heat dynamic all region heat every 1
group cold dynamic all region cold every 1
variable heat_flux_length equal ${10_lattice_unit}-${1_lattice_unit}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
region left_heat_flux block ${1_lattice_unit} ${10_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
region right_heat_flux block ${11_lattice_unit} ${all_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
group left_heat_flux dynamic all region left_heat_flux every 1
group right_heat_flux dynamic all region right_heat_flux every 1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable HOT_temp equal ${T}+20
variable COLD_temp equal ${T}-20
compute heat heat temp/region heat
compute cold cold temp/region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all ehex 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all ehex 1 -${POWER} region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 2 #
###################
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
run ${500_ps}
#run 10
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_2
#----------------------------------------------------------#
reset_timestep 0
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# all temp
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable KB equal 8.625e-5
compute KE all ke/atom
variable all_temp atom c_KE/${KB}/1.5
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all ehex 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all ehex 1 -${POWER} region cold
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press c_heat c_cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute PE all pe/atom
compute V all stress/atom NULL virial
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute J1 left_heat_flux heat/flux KE PE V
compute J2 right_heat_flux heat/flux KE PE V
variable JJ_1 equal c_J1[1]/${heat_flux_length}
variable JJ_2 equal c_J2[1]/${heat_flux_length}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable block_num equal 20
variable reduced equal 1/${block_num}
compute layers all chunk/atom bin/1d x lower ${reduced} units reduced
# output_1 heat flux
fix heat_flux_layer all ave/time 1 1 1 &
v_JJ_1 v_JJ_2 file heat_flux.txt
# output_2 temperature
fix temp1 all ave/chunk 10 10 1000 layers &
v_all_temp file all.temp
# output_3 temperature for hot/cold
fix ave all ave/time 1000 1 1000 c_heat c_cold file temp.txt
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 3 #
###################
thermo 1000
variable 1ns equal 1000/${TS}
run ${1ns}
#run 10
相关文献:P. Jund and R. Jullien, Molecular-dynamics calculation of the thermal conductivity of vitreous silica, Physical Review B 59, 13707 (1999).
1. 后处理分析以及计算结果

1
、这里的交换的能量为
0.08
e
v
/
p
s
1、这里的交换的能量为 0.08 ev/ps
1、这里的交换的能量为0.08ev/ps
EV = 0.08
2
、将单位转换为
W
2、将单位转换为 W
2、将单位转换为W
power = EV*1.6e-7
3
、计算传热截面
3、计算传热截面
3、计算传热截面
A = 54*54*1e-20
4
、计算传热截面
4、计算传热截面
4、计算传热截面
注意,热流需要除以
2
!
\color{red}注意,热流需要除以2!
注意,热流需要除以2!
Q = power/A/2
2. Python绘图
import os
def make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename):
# filepath 存储路径; filename:创建文件夹的名字 savename:存储图片的名字
save_path = filepath+os.sep+filename+os.sep+savename
all_path = filepath+os.sep+filename
if not os.path.exists(all_path):
os.mkdir(all_path)
plt.savefig(save_path,dpi=300)
filepath = r"Ar热导率"
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
# Global setting
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# coding:utf-8
import pylab
import matplotlib.ticker as plticker
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
import xlrd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import math
from scipy import optimize
def f_1(x, A, B):
return A * x + B
from scipy import optimize
plt.style.use('science')
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
def setup(ax,x_label,y_label):
# 边框线的线宽设置
width = 1.5
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(width)
# 边框上的ticks的出现
ax.tick_params(top='on', bottom='on', left='on', right='on', direction='in')
# 边框上的ticks对应的lable,即数字的尺寸
ax.tick_params(labelsize=20,pad=6)
#ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.50, length=6)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=0)
# 边框上的ticks的出现的间隔
locx = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=108/2) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(locx)
locy = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=1) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(locy)
# 边框上的注释labels
labels = ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels()
[label.set_fontname('Times New Roman') for label in labels]
# 边框上的注释labels距离坐标轴的距离
xAxisLable = x_label
yAxisLable = y_label
ax.set_xlabel(xAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
ax.set_ylabel(yAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 读取excel
excel_path = r"Ar_108.xlsx"
work_sheet = xlrd.open_workbook(excel_path);
# sheet的数量
sheet_num = work_sheet.nsheets;
# 获取sheet name
sheet_name = []
for sheet in work_sheet.sheets():
sheet_name.append(sheet.name)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
for sheet_num in range(1):
# 选取sheet
now_sheet = work_sheet.sheets()[0]
# sheet的行
row = now_sheet.nrows
# sheet的列
ncol = now_sheet.ncols
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# temp
y10 = now_sheet.col_values(0)
y10_matrix = list(filter(None, y10[0:]))
markersize = 10
linewidth = 1
markevery =1
alpha =1
p_1 = dict(marker='o',color = 'r',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',
markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axe = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5,5))
xxx = np.arange(20)
length_10 =108
# 108 162 216 270
axe.plot(np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20), y10_matrix,**p_1,label='10.8 nm')
scale1_left = 2
scale1_right = 10
scale2_left = 12
scale2_right = 20
EV = 0.08
power = EV*1.6e-7
A = 54*54*1e-20
Q = power/A/2
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 10
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
x_10_1 = np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20)
A10_1, B10_1 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x_10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right], y10_matrix[scale1_left:scale1_right])[0]
y10_1 = A10_1 * x_10_1 + B10_1
axe.plot(x_10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right], y10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right] , "r",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 10.8 nm')
x_10_2 = np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20)
A10_2, B10_2 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x_10_1[scale2_left:scale2_right], y10_matrix[scale2_left:scale2_right])[0]
y10_2 = A10_2 * x_10_1 + B10_2
axe.plot(x_10_2[scale2_left:scale2_right], y10_2[scale2_left:scale2_right] , "r",ls='--',lw=2)
print('A10')
print('the mean is:',np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]),'the std is:',np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))
temp_10_1 = (np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)])+np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))*1e10
temp_10_2 = (np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)])-np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))*1e10
kappa10_1 = Q/temp_10_1;
kappa10_2 = Q/temp_10_2;
print('the kappa is:',np.mean([kappa10_1,kappa10_2]),'the std is:',np.std([kappa10_1,kappa10_2]))
print('---------------------------------------------')
axe.set_ylim(57, 63)
axe.set_xlim(0, 108)
setup(axe,r'Thickness\ /$\rm \AA$',r'$\rm Temperature\ /K$')
axe.legend(loc='best', frameon=False, \
labelspacing=0.3)
axe.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), \
loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='xx-large')
#axe[1].legend(loc='best', frameon=False, labelspacing=0.3)
#axe[1].legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='x-large')
# ============================================================#
filename = "Aroutput"
savename = "60.jpg"
make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename)
#figureFileName = "Amorphous_overlop.pdf"
figureFileName = "Jump_temp.pdf"
#plt.savefig(figureFileName, dpi=300)
#plt.xscale("log")
#plt.yscale("log")
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
plt.show()

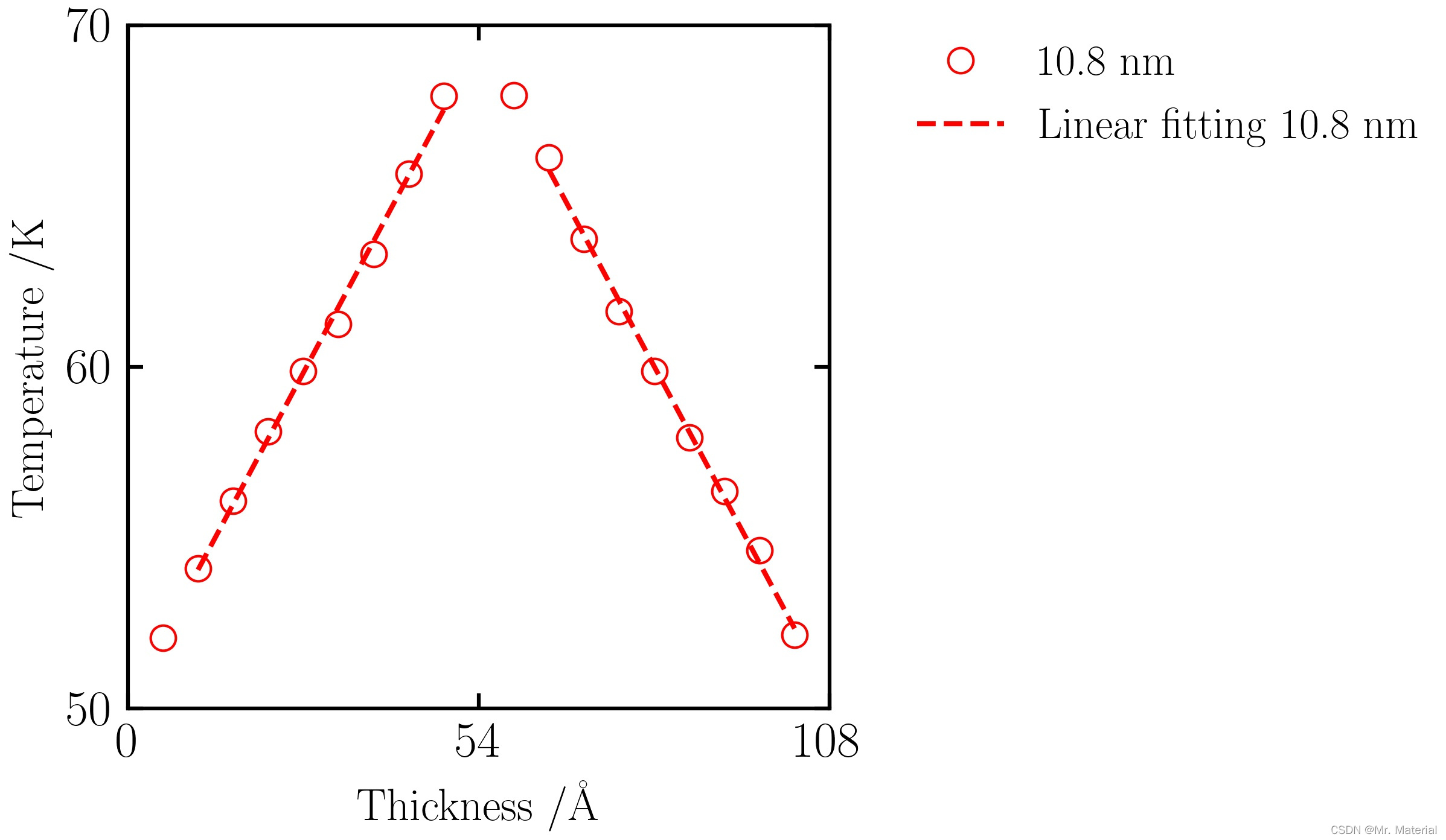
3. 报道结果
注意:这是10.8 nm,60 K下的计算结果
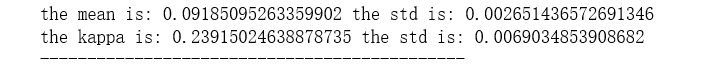
二、非平衡态分子动力学 ( N E M D ) \rm (NEMD) (NEMD)—局部热浴法 f i x L a n g v e i n \rm fix \ Langvein fix Langvein
核心命令 \color{red}核心命令 核心命令
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT heat langevin 70 70 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
fix COLD cold langevin 50 50 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
这里我们对热源和热汇采用 L a n g v e i n Langvein Langvein 热浴进行控温,计算热流大小。
clear
echo screen
units metal
dimension 3
boundary p p p
atom_style full
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable TS equal 0.01 ### ${TS} timestep
variable Tdamp equal 100*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable Pdamp equal 1000*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable T equal ${loop_file_out_name} ### ${T} initial temperature
variable POWER equal 0.08
timestep ${TS}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# unit cell
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable x_length equal ${loop_file_in_name}
variable half_x equal ${x_length}*0.5
variable lattice_unit equal 5.4*2
variable x_length equal ${lattice_unit}*${x_length}
variable y_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
variable z_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
region box block 0 ${x_length} &
0 ${y_length} &
0 ${z_length} units box
create_box 1 box
lattice fcc 5.4
create_atoms 1 box
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable materials_length equal (${half_x}-1)*${lattice_unit}
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
print "The material length is ${materials_length}"
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# group setting #
###################
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# setting mass
mass 1 40 # mass for Ar
group Ar type 1
velocity all create ${T} 12345 loop local #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
write_data system.data
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# pair interaction #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pair_style lj/cut 10
pair_coeff * * 1.032e-2 3.405
neighbor 0.5 bin
neigh_modify every 5 delay 0 check no
#----------------------------------------------------------#
thermo 1000
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 1 #
###################
# loop relax system 500 ps
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 50_ps equal 50/${TS}
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
#variable loop_all_num equal 1
#variable relax_system loop ${loop_all_num}
#label loop
#fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
#run ${50_ps}
#run 10
#unfix NVT
#minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
#minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
#next relax_system
#jump SELF loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${500_ps}
#run 10
unfix NVT
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# heat region define
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ^ <------------------------> ^ <------------------------>
# | 9 units | 9 units
# hot cold
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Real length = 9*units
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 1_lattice_unit equal 1*${lattice_unit}
variable 10_lattice_unit equal ${half_x}*${lattice_unit}
variable 11_lattice_unit equal (${half_x}+1)*${lattice_unit}
# heat region
region heat block 0 ${1_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
# cold region
region cold block ${10_lattice_unit} ${11_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
variable all_lattice_unit equal ${x_length}*${lattice_unit}
group heat dynamic all region heat every 1
group cold dynamic all region cold every 1
variable heat_flux_length equal ${10_lattice_unit}-${1_lattice_unit}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
region left_heat_flux block ${1_lattice_unit} ${10_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
region right_heat_flux block ${11_lattice_unit} ${all_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
group left_heat_flux dynamic all region left_heat_flux every 1
group right_heat_flux dynamic all region right_heat_flux every 1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable HOT_temp equal ${T}+20
variable COLD_temp equal ${T}-20
compute heat heat temp/region heat
compute cold cold temp/region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT heat langevin 70 70 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
fix COLD cold langevin 50 50 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 2 #
###################
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
run ${500_ps}
#run 10
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_2
#----------------------------------------------------------#
reset_timestep 0
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# all temp
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable KB equal 8.625e-5
compute KE all ke/atom
variable all_temp atom c_KE/${KB}/1.5
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT heat langevin 70 70 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
fix COLD cold langevin 50 50 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press c_heat c_cold f_HEAT f_COLD
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute PE all pe/atom
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable block_num equal 20
variable reduced equal 1/${block_num}
compute layers all chunk/atom bin/1d x lower ${reduced} units reduced
# output_1 temperature
fix temp1 all ave/chunk 10 10 1000 layers &
v_all_temp file all.temp
# output_2 exchange energy
fix heat_flux_layer all ave/time 10 10 100 &
f_HEAT f_COLD file heat_flux_exchange.txt
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 3 #
###################
thermo 1000
variable 1ns equal 1000/${TS}
run ${1ns}
#run 10
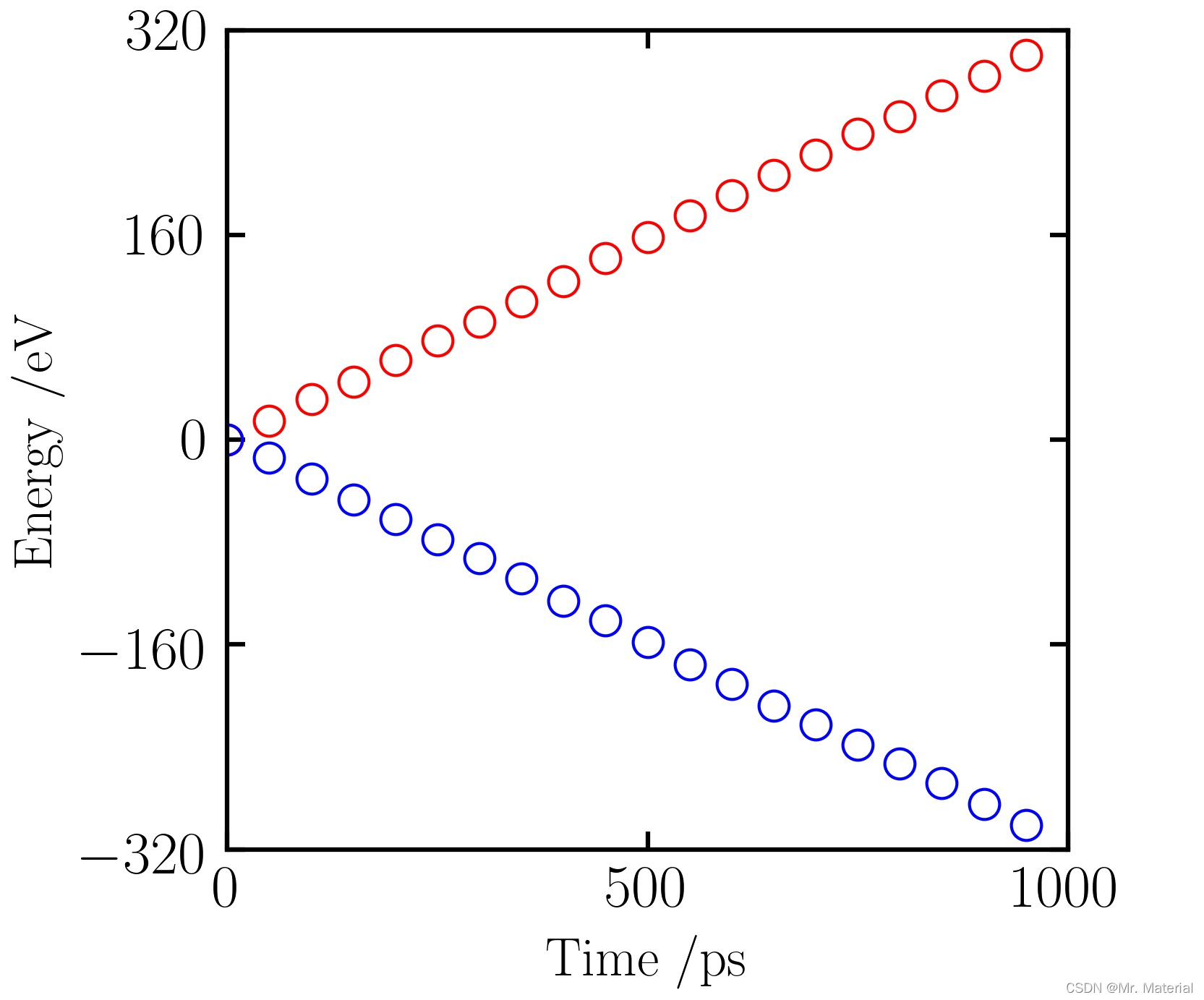
1. 后处理分析以及计算结果
热功率计算
这里我们根据在统计热源、热汇和热浴交换的能量,计算热功率。这里我们统计了1 n s \rm ns ns,总能量为316 e V \rm eV eV,那么交换的热功率为0.3 e V / p s \rm eV/ps eV/ps.
核心命令 \color{red} 核心命令 核心命令
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT heat langevin 70 70 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
fix COLD cold langevin 50 50 ${Tdamp} 699483 tally yes
...
# output_2 exchange energy
fix heat_flux_layer all ave/time 10 10 100 &
f_HEAT f_COLD file heat_flux_exchange.txt
import os
def make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename):
# filepath 存储路径; filename:创建文件夹的名字 savename:存储图片的名字
save_path = filepath+os.sep+filename+os.sep+savename
all_path = filepath+os.sep+filename
if not os.path.exists(all_path):
os.mkdir(all_path)
plt.savefig(save_path,dpi=300)
filepath = r"Ar热导率"
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
# Global setting
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# coding:utf-8
import pylab
import matplotlib.ticker as plticker
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
import xlrd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import math
from scipy import optimize
def f_1(x, A, B):
return A * x + B
from scipy import optimize
plt.style.use('science')
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
def setup(ax,x_label,y_label):
# 边框线的线宽设置
width = 1.5
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(width)
# 边框上的ticks的出现
ax.tick_params(top='on', bottom='on', left='on', right='on', direction='in')
# 边框上的ticks对应的lable,即数字的尺寸
ax.tick_params(labelsize=20,pad=6)
#ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.50, length=6)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=0)
# 边框上的ticks的出现的间隔
locx = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=500) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(locx)
locy = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=320/2) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(locy)
# 边框上的注释labels
labels = ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels()
[label.set_fontname('Times New Roman') for label in labels]
# 边框上的注释labels距离坐标轴的距离
xAxisLable = x_label
yAxisLable = y_label
ax.set_xlabel(xAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
ax.set_ylabel(yAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 读取excel
excel_path = r"Ar_108.xlsx"
work_sheet = xlrd.open_workbook(excel_path);
# sheet的数量
sheet_num = work_sheet.nsheets;
# 获取sheet name
sheet_name = []
for sheet in work_sheet.sheets():
sheet_name.append(sheet.name)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
for sheet_num in range(1):
# 选取sheet
now_sheet = work_sheet.sheets()[0]
# sheet的行
row = now_sheet.nrows
# sheet的列
ncol = now_sheet.ncols
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# temp
hot = now_sheet.col_values(2)
hot_matrix = list(filter(None, hot[1:]))
cold = now_sheet.col_values(3)
cold_matrix = list(filter(None, cold[1:]))
markersize = 10
linewidth = 1
markevery =50
alpha =1
p_1 = dict(marker='o',color = 'r',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',
markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_2 = dict(marker='o',color = 'b',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',
markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axe = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5,5))
xxx = np.arange(20)
length_10 =108
# 108 162 216 270
axe.plot(np.arange(len(hot_matrix)), hot_matrix,**p_1)
axe.plot(np.arange(len(hot_matrix)), cold_matrix,**p_2)
axe.set_ylim(-320, 320)
axe.set_xlim(0, 1000)
setup(axe,r'Time\ /$\rm ps$',r'$\rm Energy\ /eV$')
axe.legend(loc='best', frameon=False, \
labelspacing=0.3)
axe.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), \
loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='xx-large')
#axe[1].legend(loc='best', frameon=False, labelspacing=0.3)
#axe[1].legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='x-large')
# ============================================================#
filename = "Aroutput"
savename = "eV.jpg"
make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename)
#figureFileName = "Amorphous_overlop.pdf"
figureFileName = "Jump_temp.pdf"
#plt.savefig(figureFileName, dpi=300)
#plt.xscale("log")
#plt.yscale("log")
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
plt.show()
2. 温度梯度拟合
import os
def make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename):
# filepath 存储路径; filename:创建文件夹的名字 savename:存储图片的名字
save_path = filepath+os.sep+filename+os.sep+savename
all_path = filepath+os.sep+filename
if not os.path.exists(all_path):
os.mkdir(all_path)
plt.savefig(save_path,dpi=300)
filepath = r"Ar热导率"
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
# Global setting
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# coding:utf-8
import pylab
import matplotlib.ticker as plticker
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
import xlrd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import math
from scipy import optimize
def f_1(x, A, B):
return A * x + B
from scipy import optimize
plt.style.use('science')
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
def setup(ax,x_label,y_label):
# 边框线的线宽设置
width = 1.5
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(width)
# 边框上的ticks的出现
ax.tick_params(top='on', bottom='on', left='on', right='on', direction='in')
# 边框上的ticks对应的lable,即数字的尺寸
ax.tick_params(labelsize=20,pad=6)
#ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.50, length=6)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=0)
# 边框上的ticks的出现的间隔
locx = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=108/2) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(locx)
locy = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=10) # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(locy)
# 边框上的注释labels
labels = ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels()
[label.set_fontname('Times New Roman') for label in labels]
# 边框上的注释labels距离坐标轴的距离
xAxisLable = x_label
yAxisLable = y_label
ax.set_xlabel(xAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
ax.set_ylabel(yAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 读取excel
excel_path = r"Ar_108.xlsx"
work_sheet = xlrd.open_workbook(excel_path);
# sheet的数量
sheet_num = work_sheet.nsheets;
# 获取sheet name
sheet_name = []
for sheet in work_sheet.sheets():
sheet_name.append(sheet.name)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
for sheet_num in range(1):
# 选取sheet
now_sheet = work_sheet.sheets()[0]
# sheet的行
row = now_sheet.nrows
# sheet的列
ncol = now_sheet.ncols
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# temp
y10 = now_sheet.col_values(1)
y10_matrix = list(filter(None, y10[1:]))
markersize = 10
linewidth = 1
markevery =1
alpha =1
p_1 = dict(marker='o',color = 'r',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',
markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axe = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5,5))
xxx = np.arange(20)
length_10 =108
# 108 162 216 270
axe.plot(np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20), y10_matrix,**p_1,label='10.8 nm')
scale1_left = 2
scale1_right = 10
scale2_left = 12
scale2_right = 20
EV = 0.3
power = EV*1.6e-7
A = 54*54*1e-20
Q = power/A/2
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 10
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
x_10_1 = np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20)
A10_1, B10_1 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x_10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right], y10_matrix[scale1_left:scale1_right])[0]
y10_1 = A10_1 * x_10_1 + B10_1
axe.plot(x_10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right], y10_1[scale1_left:scale1_right] , "r",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 10.8 nm')
x_10_2 = np.arange(len(y10_matrix))*np.array(length_10)/np.array(20)
A10_2, B10_2 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x_10_1[scale2_left:scale2_right], y10_matrix[scale2_left:scale2_right])[0]
y10_2 = A10_2 * x_10_1 + B10_2
axe.plot(x_10_2[scale2_left:scale2_right], y10_2[scale2_left:scale2_right] , "r",ls='--',lw=2)
print('A10')
print('the mean is:',np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]),'the std is:',np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))
temp_10_1 = (np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)])+np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))*1e10
temp_10_2 = (np.mean([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)])-np.std([abs(A10_2),abs(A10_1)]))*1e10
kappa10_1 = Q/temp_10_1;
kappa10_2 = Q/temp_10_2;
print('the kappa is:',np.mean([kappa10_1,kappa10_2]),'the std is:',np.std([kappa10_1,kappa10_2]))
print('---------------------------------------------')
axe.set_ylim(50, 70)
axe.set_xlim(0, 108)
setup(axe,r'Thickness\ /$\rm \AA$',r'$\rm Temperature\ /K$')
axe.legend(loc='best', frameon=False, \
labelspacing=0.3)
axe.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), \
loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='xx-large')
#axe[1].legend(loc='best', frameon=False, labelspacing=0.3)
#axe[1].legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.,fontsize='x-large')
# ============================================================#
filename = "Aroutput"
savename = "langvein.jpg"
make_save_file(filepath,filename,savename)
#figureFileName = "Amorphous_overlop.pdf"
figureFileName = "Jump_temp.pdf"
#plt.savefig(figureFileName, dpi=300)
#plt.xscale("log")
#plt.yscale("log")
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
plt.show()
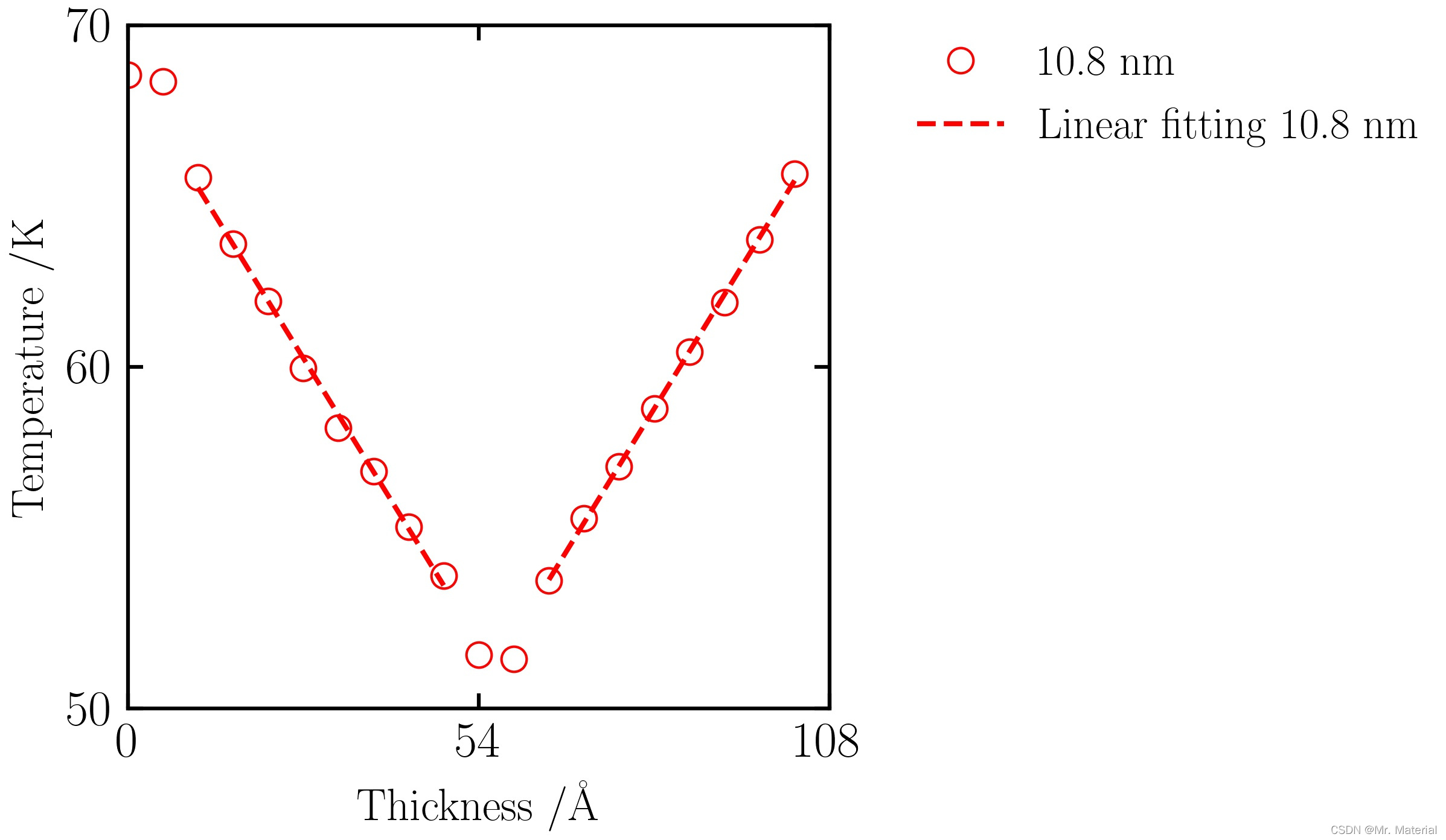
3. 报道结果

三、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—动量交换法 ( f i x t h e r m a l / c o n d u c t i v i t y ) \rm (fix\ thermal/conductivity) (fix thermal/conductivity)
核心命令:
\color{red}核心命令:
核心命令:
这里注意分块一定要是整数。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ^ <------------------------> ^ <------------------------>
# | 9 units | 9 units
# hot cold
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix mp all thermal/conductivity 10 x 20
clear
echo screen
units metal
dimension 3
boundary p p p
atom_style full
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable TS equal 0.01 ### ${TS} timestep
variable Tdamp equal 100*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable Pdamp equal 1000*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable T equal ${loop_file_out_name} ### ${T} initial temperature
variable POWER equal 0.08
timestep ${TS}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# unit cell
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable x_length equal ${loop_file_in_name}
variable half_x equal ${x_length}*0.5
variable lattice_unit equal 5.4*2
variable x_length equal ${lattice_unit}*${x_length}
variable y_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
variable z_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
region box block 0 ${x_length} &
0 ${y_length} &
0 ${z_length} units box
create_box 1 box
lattice fcc 5.4
create_atoms 1 box
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable materials_length equal (${half_x}-1)*${lattice_unit}
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
print "The material length is ${materials_length}"
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# group setting #
###################
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# setting mass
mass 1 40 # mass for Ar
group Ar type 1
velocity all create ${T} 12345 loop local #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
write_data system.data
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# pair interaction #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pair_style lj/cut 10
pair_coeff * * 1.032e-2 3.405
neighbor 0.5 bin
neigh_modify every 5 delay 0 check no
#----------------------------------------------------------#
thermo 1000
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 1 #
###################
# loop relax system 500 ps
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 50_ps equal 50/${TS}
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
variable loop_all_num equal 10
variable relax_system loop ${loop_all_num}
label loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${50_ps}
unfix NVT
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
next relax_system
jump SELF loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${500_ps}
unfix NVT
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# heat region define
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ^ <------------------------> ^ <------------------------>
# | 9 units | 9 units
# hot cold
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Real length = 9*units
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 1_lattice_unit equal 1*${lattice_unit}
variable 10_lattice_unit equal ${half_x}*${lattice_unit}
variable 11_lattice_unit equal (${half_x}+1)*${lattice_unit}
# heat region
region heat block 0 ${1_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
# cold region
region cold block ${10_lattice_unit} ${11_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
variable all_lattice_unit equal ${x_length}*${lattice_unit}
group heat dynamic all region heat every 1
group cold dynamic all region cold every 1
variable heat_flux_length equal ${10_lattice_unit}-${1_lattice_unit}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
region left_heat_flux block ${1_lattice_unit} ${10_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
region right_heat_flux block ${11_lattice_unit} ${all_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
group left_heat_flux dynamic all region left_heat_flux every 1
group right_heat_flux dynamic all region right_heat_flux every 1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable HOT_temp equal ${T}+20
variable COLD_temp equal ${T}-20
compute heat heat temp/region heat
compute cold cold temp/region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix mp all thermal/conductivity 10 x 20
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 2 #
###################
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
run ${500_ps}
#run 10
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_2
#----------------------------------------------------------#
reset_timestep 0
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# all temp
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable KB equal 8.625e-5
compute KE all ke/atom
variable all_temp atom c_KE/${KB}/1.5
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix mp all thermal/conductivity 10 x 20
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press c_heat c_cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute PE all pe/atom
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable block_num equal 20
variable reduced equal 1/${block_num}
compute layers all chunk/atom bin/1d x lower ${reduced} units reduced
# output_1 temperature
fix temp1 all ave/chunk 10 10 1000 layers &
v_all_temp file all.temp
# output_2 temperature for hot/cold
fix ave all ave/time 10 10 1000 c_heat c_cold file temp.txt
# output_3 energy
fix ave all ave/time 10 10 1000 f_mp file ev.txt
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 3 #
###################
thermo 1000
variable 1ns equal 1000/${TS}
run ${1ns}
#run 10
1. 能量输出
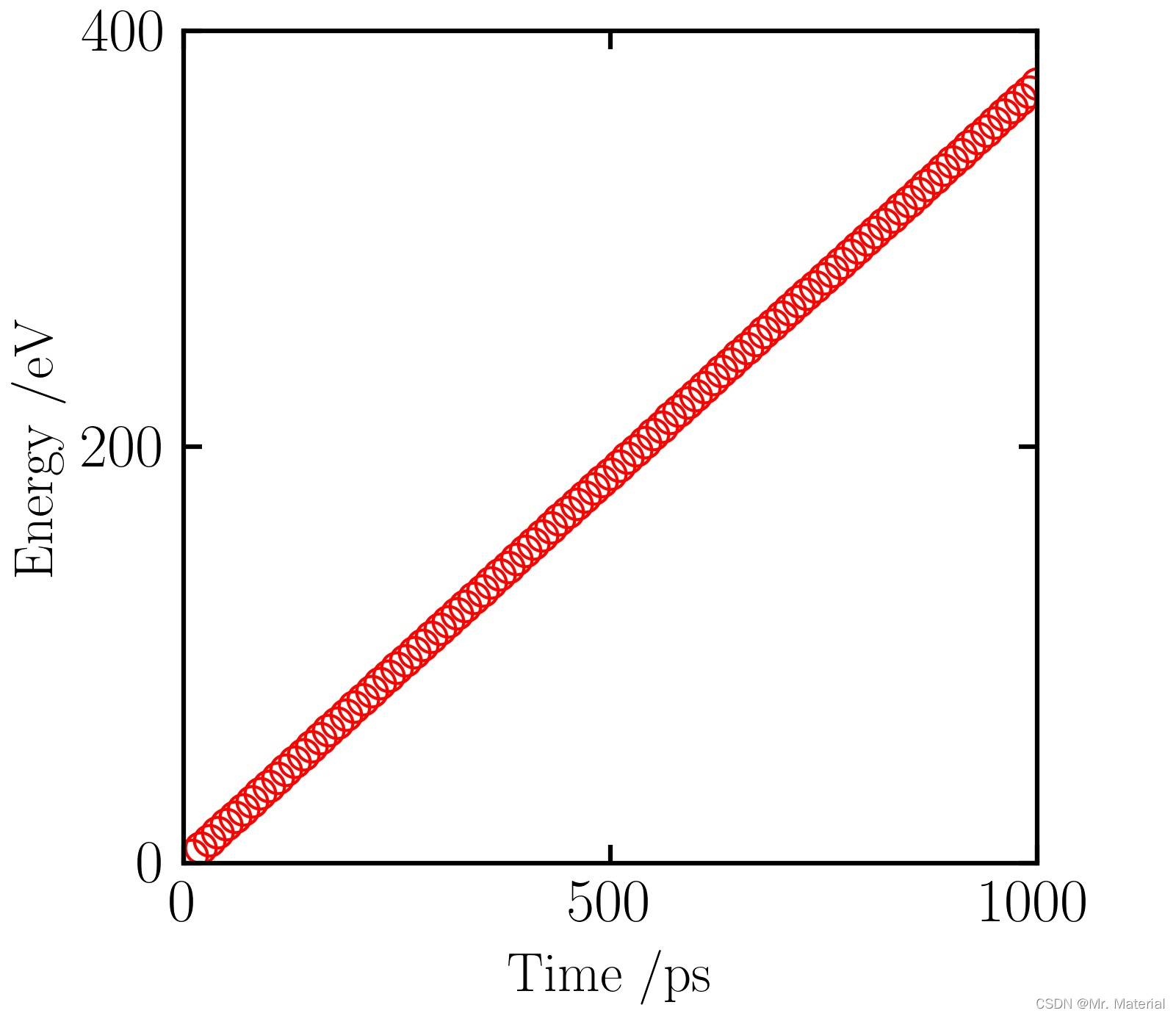
2. 温度拟合
3. 报道结果

四、非平衡态分子动力学 ( R N E M D ) \rm (RNEMD) (RNEMD)—速度重标法 ( f i x h e a t ) \rm (fix\ heat) (fix heat)
核心命令: \color{red}核心命令: 核心命令:
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all heat 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all heat 1 -${POWER} region cold
这里的后处理的方法, f i x h e a t fix\ heat fix heat 和 f i x e h x fix\ ehx fix ehx 方法完全类似,这里不再赘述。
clear
echo screen
units metal
dimension 3
boundary p p p
atom_style full
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable TS equal 0.01 ### ${TS} timestep
variable Tdamp equal 100*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable Pdamp equal 1000*${TS} ### ${Tdamp} Tdamp
variable T equal ${loop_file_out_name} ### ${T} initial temperature
variable POWER equal 0.08
timestep ${TS}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# unit cell
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable x_length equal ${loop_file_in_name}
variable half_x equal ${x_length}*0.5
variable lattice_unit equal 5.4*2
variable x_length equal ${lattice_unit}*${x_length}
variable y_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
variable z_length equal ${lattice_unit}*5
region box block 0 ${x_length} &
0 ${y_length} &
0 ${z_length} units box
create_box 1 box
lattice fcc 5.4
create_atoms 1 box
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable materials_length equal (${half_x}-1)*${lattice_unit}
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
print "The material length is ${materials_length}"
print "=========================================="
print "=========================================="
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# group setting #
###################
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# setting mass
mass 1 40 # mass for Ar
group Ar type 1
velocity all create ${T} 12345 loop local #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
write_data system.data
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# pair interaction #
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pair_style lj/cut 10
pair_coeff * * 1.032e-2 3.405
neighbor 0.5 bin
neigh_modify every 5 delay 0 check no
#----------------------------------------------------------#
thermo 1000
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 1 #
###################
# loop relax system 500 ps
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 50_ps equal 50/${TS}
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
variable loop_all_num equal 10
variable relax_system loop ${loop_all_num}
label loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${50_ps}
unfix NVT
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
next relax_system
jump SELF loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${500_ps}
unfix NVT
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# heat region define
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ##
# ^ <------------------------> ^ <------------------------>
# | 9 units | 9 units
# hot cold
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Real length = 9*units
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
variable 1_lattice_unit equal 1*${lattice_unit}
variable 10_lattice_unit equal ${half_x}*${lattice_unit}
variable 11_lattice_unit equal (${half_x}+1)*${lattice_unit}
# heat region
region heat block 0 ${1_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
# cold region
region cold block ${10_lattice_unit} ${11_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
variable all_lattice_unit equal ${x_length}*${lattice_unit}
group heat dynamic all region heat every 1
group cold dynamic all region cold every 1
variable heat_flux_length equal ${10_lattice_unit}-${1_lattice_unit}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
region left_heat_flux block ${1_lattice_unit} ${10_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
region right_heat_flux block ${11_lattice_unit} ${all_lattice_unit} INF INF INF INF units box
group left_heat_flux dynamic all region left_heat_flux every 1
group right_heat_flux dynamic all region right_heat_flux every 1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable HOT_temp equal ${T}+20
variable COLD_temp equal ${T}-20
compute heat heat temp/region heat
compute cold cold temp/region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_1
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all heat 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all heat 1 -${POWER} region cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 2 #
###################
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
run ${500_ps}
#run 10
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# heat process_2
#----------------------------------------------------------#
reset_timestep 0
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# all temp
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable KB equal 8.625e-5
compute KE all ke/atom
variable all_temp atom c_KE/${KB}/1.5
#----------------------------------------------------------#
fix NVE all nve
fix HEAT all heat 1 ${POWER} region heat
fix COLD all heat 1 -${POWER} region cold
thermo_style custom step temp pe etotal press c_heat c_cold
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute PE all pe/atom
compute V all stress/atom NULL virial
#----------------------------------------------------------#
compute J1 left_heat_flux heat/flux KE PE V
compute J2 right_heat_flux heat/flux KE PE V
variable JJ_1 equal c_J1[1]/${heat_flux_length}
variable JJ_2 equal c_J2[1]/${heat_flux_length}
#----------------------------------------------------------#
variable block_num equal 20
variable reduced equal 1/${block_num}
compute layers all chunk/atom bin/1d x lower ${reduced} units reduced
# output_1 heat flux
fix heat_flux_layer all ave/time 1 1 1 &
v_JJ_1 v_JJ_2 file heat_flux.txt
# output_2 temperature
fix temp1 all ave/chunk 10 10 1000 layers &
v_all_temp file all.temp
# output_3 temperature for hot/cold
fix ave all ave/time 1000 1 1000 c_heat c_cold file temp.txt
#----------------------------------------------------------#
###################
# run 3 #
###################
thermo 1000
variable 1ns equal 1000/${TS}
run ${1ns}
#run 10
1. 后处理分析以及计算结果
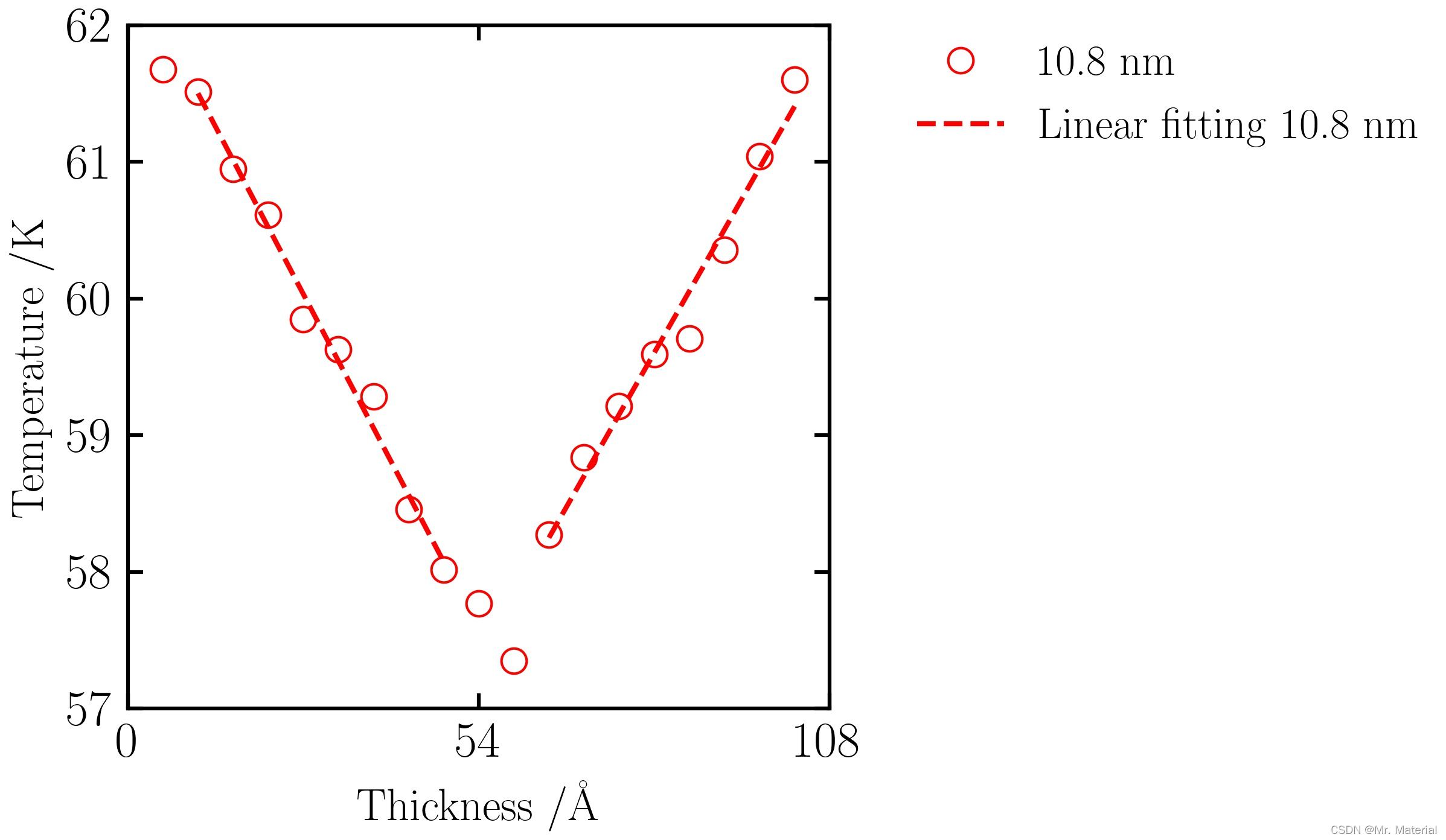
2. 报道结果

五、平衡态分子动力学 ( E M D ) \rm (EMD) (EMD)— G K 法 \rm GK法 GK法
1. 方法说明
通过平衡态方法计算热导率,这里采用格林-久保公式,即非平衡过程的输运系数与平衡态中相 应物理量的涨落相关联。根据热流自关联函数计算出的热导率。这里没有太多技术上的问题,整体的代码也很类似,手册也给出了案例。
具体请参考:https://docs.lammps.org/compute_heat_flux.html
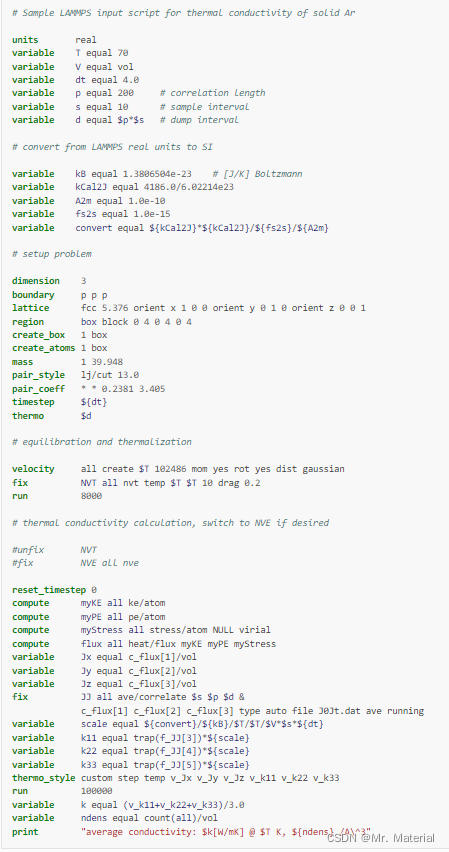
核心命令
:
\color{red}核心命令:
核心命令:
compute myKE all ke/atom
compute myPE all pe/atom
compute myStress all stress/atom NULL virial
compute flux all heat/flux myKE myPE myStress
variable Jx equal c_flux[1]/vol
variable Jy equal c_flux[2]/vol
variable Jz equal c_flux[3]/vol
fix JJ all ave/correlate $s $p $d &
c_flux[1] c_flux[2] c_flux[3] type auto file J0Jt.dat ave running
注意:
\color{red}注意:
注意:
平衡态的方法主要适用于各相同性体系,计算出来的热导率是针对于无限大的体系。但是在计算位力中,
L
a
m
m
p
s
\rm Lammps
Lammps 中的命令只适用于两体势。

2. 报道结果
这里我们只采用结果(
60
K
A
r
的热导率
60K\ Ar的热导率
60K Ar的热导率)进行对比。
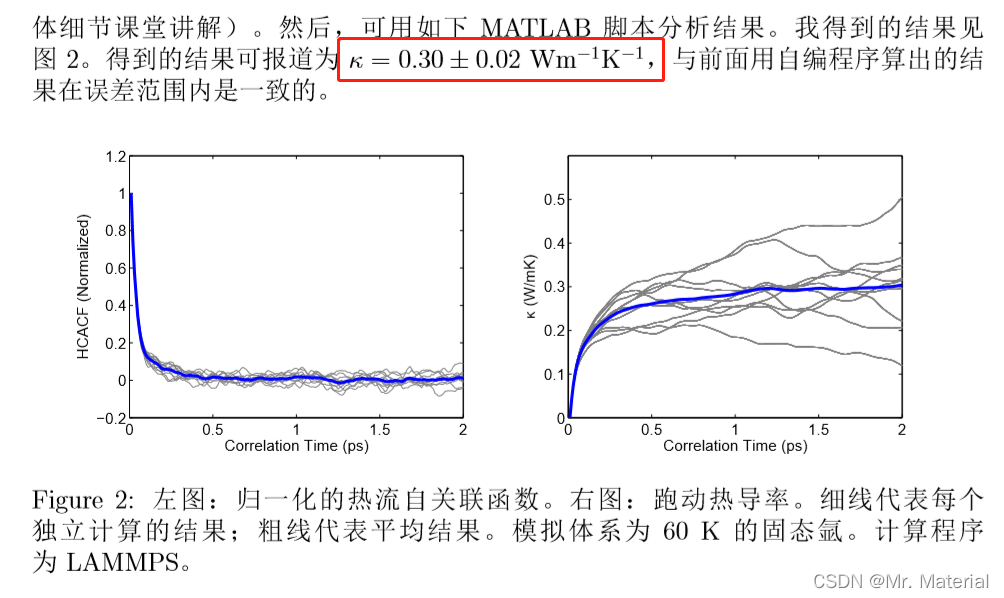
六、五种方法结果对比
感谢阅读,注意:具体问题具体分析,以下结果只提供参考!
\rm \color{red} 感谢阅读,注意:具体问题具体分析,以下结果只提供参考!
感谢阅读,注意:具体问题具体分析,以下结果只提供参考!
E
M
D
\rm EMD
EMD 计算的为
60
K
\rm 60\ K
60 K 下无限大体系的热导率;
N
E
M
D
\rm NEMD
NEMD 以及
R
N
E
M
D
\rm RNEMD
RNEMD 计算的为
10.8
n
m
\rm 10.8\ nm
10.8 nm 的热导率;









 本文详述使用LAMMPS进行热导率计算的五种方法,包括平衡态的GK法和非平衡态的NEMD/RNEMD(速度重标法、局部热浴法、动量交换法)。文章提供动态group设置、脚本获取、后处理分析和结果对比,适用于不同工况的热导率研究。
本文详述使用LAMMPS进行热导率计算的五种方法,包括平衡态的GK法和非平衡态的NEMD/RNEMD(速度重标法、局部热浴法、动量交换法)。文章提供动态group设置、脚本获取、后处理分析和结果对比,适用于不同工况的热导率研究。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










