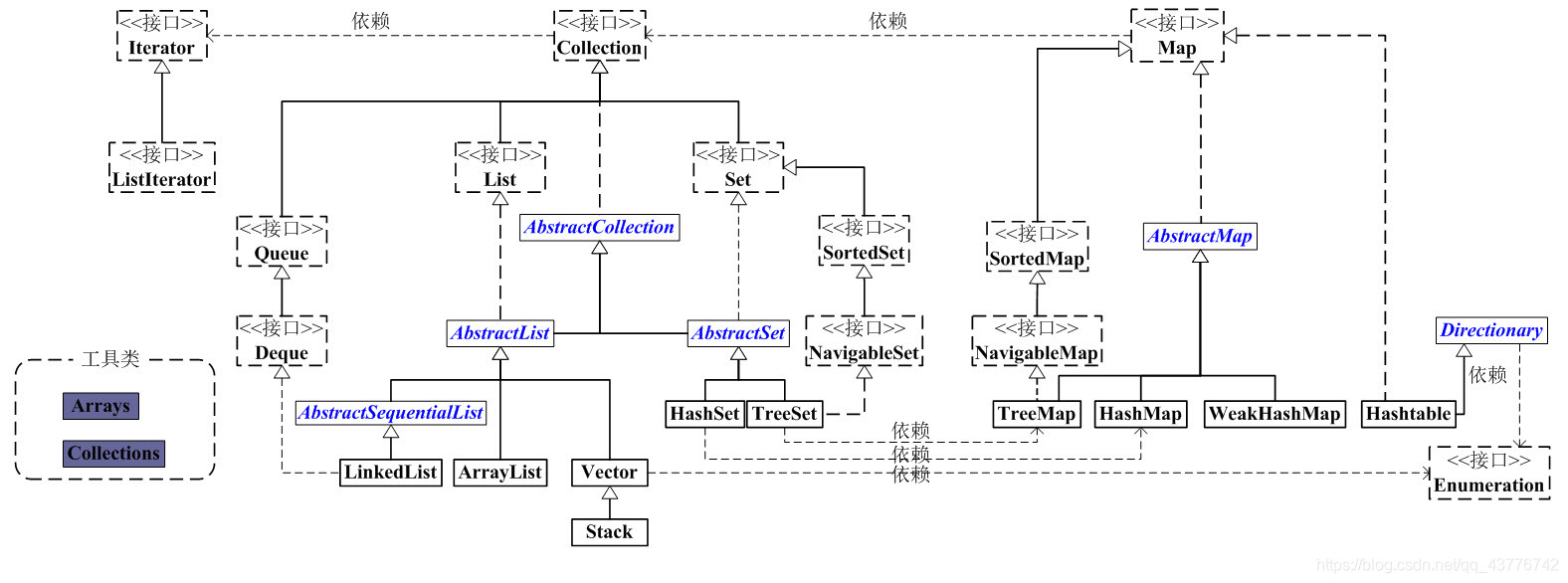
集合框架结构图:

ArrayList:
ArrayList 是一个数组队列,相当于 动态数组。与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长。它继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
ArrayList详细介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308556.html
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
向集合中添加元素:
arrayList.add(); --加入一个元素(Object)
arrayList.add(index, element); --在指定位置添加元素
arrayLIst.addAll(); --加入集合元素(Collection)
删除集合中的元素:
arrayList.remove();
替换集合中的元素:
arrayList.set(index, element);
输出ArrayList集合的长度:
arrayList.size();
查看某元素在集合中的下标:
arrayLIst.indexOf(); ----从前往后查找
arrayList.lastIndexOf(); ----从后向前查找
判断ArrayList集合中是否包含某个元素:
arrayList.contains();
截取下标1-3(不包括3)的子集合:
arrayList.subList(1, 3);
遍历集合:
//通过for循环来遍历
for(int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));
}
//通过foreach循环来遍历
for(Object o:arrayList) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//通过迭代器来遍历 Iterator
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Vector:
Vector 是矢量队列。Vector 继承了AbstractList,实现了List;所以,它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。Vector 实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。
详细介绍 https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308833.html
Vector vector = new Vector();
添加元素:
vector.add();
vector.addElement();
删除元素:
vector.remove();
判断集合是否为空:
vector.isEmpty();
Stack(后进先出):
详细介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308852.html
Stack stack = new Stack();
添加元素:
stack.push();
访问栈顶元素
stack.peek();
取出栈顶元素:
stack.pop();
LinkedList(先进先出):
详细介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308807.html
1. LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
2. LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
3. LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
4. LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
5. LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
6. LinkedList 是非同步的。
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
添加元素:
linkedList.add();
linkedList.offer(); ---向集合的尾部添加元素
linkedList.offerLast(); ---向集合的尾部添加元素
linkedList.addLast(); ---向集合的尾部添加元素
linkedList.offerFirst(); ---向集合的头部添加元素
linkedList.push(); ---向集合的头部添加元素
linkedList.addFirst(); ---向集合的头部添加元素
访问元素:
linkedList.peek(); ---访问队列的第一个元素
linkedList.peekFirst(); ---访问队列的第一个元素
linkedList.peekLast(); ---访问队列的最后一个元素
取出元素:
linkedList.pop(); ---取出队列的第一个元素
linkedList.poll(); ---取出队列的第一个元素
linkedList.pollFirst(); ---取出队列的第一个元素
linkedList.getFirst(); ---取出队列的第一个元素
linkedList.pollLast(); ---取出队列的最后一个元素
linkedList.getLast(); ---取出队列的最后一个元素
linkedList.get(index); ---取出指定位置的元素
List总结(LinkedList, ArrayList等使用场景和性能分析)
转载处:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308900.html
PriorityQueue:
在实际开发中,不能直接实例化Queue的对象来完成操作,需要实例化其实现类,Queue的实现类是AbstractQueue,AbstractQueue是一个抽象类,开发时需要对其子类进行实例化PriorityQueue进行实例化。
PriorityQueue使用时需要注意,添加到该队列的数据必须是有序,即对象具备排序的功能,自定义的类需要实现Comparable。
public class StackTraceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.add("Hello");
stack.add("World");
stack.add("Java");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack);
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
list.add("Java");
System.out.println(list.pop());
System.out.println(list);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue();
//创建User对象
User user1 = new User(1,"张三");
User user2 = new User(2,"李四");
queue.add(user1);
queue.add(user2);
//queue.add(null);
// queue.add(1);
// queue.add(2);
// queue.add(4);
// queue.add(3);
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
*****************************************************************
public class User implements Comparable{
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 对象的排序方法
* A与B比较
* A.compareTo(B)
* 1:A>B
* 0:A=B
* -1:A<B
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
User user = (User) o;
if(this.id > user.getId()) {
return 1;
}else if(this.id == user.getId()) {
return 0;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 1;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return true;
}
}
Set:

Set接口是Collection的子接口,Set接口采用的是散列的存储方式,所以集合中的元素没有顺序,Set可以存储一组无序,唯一(不可重复)的对象。
实际开发中不能直接实例化Set对象,需要对其实现类进行实例化操作完成业务代码,Set的常用的实现类有HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet。
HashSet:
HashSet是开发中经常使用到的Set的实现类,存储一组无序,唯一(不可重复)的对象,这里的无序是指元素的存储顺序和遍历顺序是不一致的。
参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3311252.html
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add("Hello");
hashSet.add("World");
hashSet.add("Java");
hashSet.add("JavaSE");
hashSet.add("JavaME");
hashSet.add("JavaEE");
hashSet.add("Hello");
System.out.println(hashSet);
//使用增强型for循环遍历集合
for(Object obj:hashSet) {
String str = (String) obj;
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("**************************");
//使用迭代器遍历集合
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String str = (String) iterator.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
//获取hashset的长度
System.out.println(hashSet.size());
//删除元素
hashSet.remove("JavaSE");
System.out.println(hashSet.size());
//思考下面的两个User为什么会都打印出来:
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new User(1,"张三"));
hashSet.add(new User(1,"张三"));
for(Object obj:hashSet) {
User user = (User) obj;
System.out.println(user);
}
TreeSet
TreeSet 是一个有序的集合,它的作用是提供有序的Set集合。它继承于AbstractSet抽象类,实现了NavigableSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable接口。
参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3311268.html
TreeSet的构造函数:
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeSet中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。
TreeSet()
// 创建的TreeSet包含collection
TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> collection)
// 指定TreeSet的比较器
TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator)
// 创建的TreeSet包含set
TreeSet(SortedSet<E> set)
Map

-
E:Element元素,是指代保存到集合中的数据对象,Element/E本身不是一个Java类,只是具有指代意义的一个单词
-
K:Key键值对的键,指代保存到集合中的键元素
-
V:Value键值对的值,指代保存到集合中的值元素
-
T:Type类型,指代某个数据类型
Map中保存的数据是成对出现的,元素以对(两个)为单位保存在Map集合中,一对元素对应的关系是key-value,在Map集合中,这对元素首先封装成Map.Entry对象,再将Map.Entry对象保存到Map集合中。
Map的常用子类:
(01) Map 是映射接口,Map中存储的内容是键值对(key-value)。
(02) AbstractMap 是继承于Map的抽象类,它实现了Map中的大部分API。其它Map的实现类可以通过继承AbstractMap来减少重复编码。
(03) SortedMap 是继承于Map的接口。SortedMap中的内容是排序的键值对,排序的方法是通过比较器(Comparator)。
(04) NavigableMap 是继承于SortedMap的接口。相比于SortedMap,NavigableMap有一系列的导航方法;如"获取大于/等于某对象的键值对"、“获取小于/等于某对象的键值对”等等。
(05) TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,且实现了NavigableMap接口;因此,TreeMap中的内容是“有序的键值对”!
(06) HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,但没实现NavigableMap接口;因此,HashMap的内容是**“键值对,但不保证次序”!
(07) Hashtable 虽然不是继承于AbstractMap,但它继承于Dictionary(Dictionary也是键值对的接口),而且也实现Map接口;因此,Hashtable的内容也是“键值对,也不保证次序”**。但和HashMap相比,Hashtable是线程安全的,而且它支持通过Enumeration去遍历。
(08) WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap。它和HashMap的键类型不同,WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。
转载处:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308931.html
常用方法:
- public void clear() 清空Map集合
- public boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合中是否存在key值
- public boolean conatinsValue(Object value) 判断集合中是否存在value值
- public Set<Map.Entry> entrySet() 取出Map集合中的Entry,转换成Set集合
- public boolean equals(Object o) 判断两个集合是否相等
- public V get(Object key) 根据key值获取对应的value
- public int hashCode() 返回哈希值
- public boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空
- public Set keySet() 返回集合中的所有key值,封装到一个Set集合中
- public Collection values() 返回集合中的所有value值,封装到一个Collection集合中
- public void putAll(Map m) 想集合中添加另外一个集合的所有元素
- public V put(K key, V value) 向集合中添加元素(成对 key-value)
- public V remove(Object key) 删除集合中的key,以及对应的value
- public int size() 返回集合的长度
hashMap
参考介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310835.html
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
添加元素:
hashMap.put(key, value);
取出元素
hashMap.get(key);
判断指定的key或者value是否存在
hashMap.containsKey(key);
hashMap.containsValue(value);
输出全部values值
Collection collection = hashMap.values();
Iterator iter2 = collection.iterator();
while(iter2.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter2.next());
}
hashTable
参考介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310887.html
Hashtable:线程安全,性能较差
HashMap:线程不安全,性能较高
Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<String,String>();
treeMap
参考介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310928.html
TreeMap可以按照 key进行排序,根据 key值对应的数值进行升序排序,
如果是一个自定义数据类型,则该类必须实现Comparable,并且实现
compareTo方法,在该方法中自定义当前类对象的排序规则。
1. 遍历:
public static void getAll() {
TreeMap<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
map.put(3, "Java");
map.put(1, "Hello");
map.put(4, "JavaSE");
map.put(6, "JavaEE");
map.put(2, "World");
map.put(5, "JavaME");
//通过Map.Entry遍历
Set<Entry<Integer,String>> entry = map.entrySet();
Iterator entryIterator = entry.iterator();
while(entryIterator.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer,String> item = (Entry<Integer, String>) entryIterator.next();
Integer key = item.getKey();
String value = item.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"---"+value);
}
System.out.println("************************************");
for(Entry<Integer,String> item:entry) {
Integer key = item.getKey();
String value = item.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"---"+value);
}
System.out.println("************************************");
//通过key遍历
Set<Integer> keys = map.keySet();
Iterator keysIterator = keys.iterator();
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = (Integer) keysIterator.next();
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"---"+value);
}
System.out.println("************************************");
for(Integer key:keys) {
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"---"+value);
}
System.out.println("************************************");
//遍历values
Collection<String> values = map.values();
Iterator valuesIterator = values.iterator();
while(valuesIterator.hasNext()) {
String value = (String) valuesIterator.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("************************************");
for(String value:values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2. 其他操作
public static void others() {
TreeMap<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
map.put(3, "Java");
map.put(1, "Hello");
map.put(4, "JavaSE");
map.put(6, "JavaEE");
map.put(2, "World");
map.put(5, "JavaME");
//获取集合的第一个key值
Integer firstKey = map.firstKey();
System.out.println("集合的第一个key:"+firstKey);
//获取集合的第一个entry
Entry<Integer,String> firstEntry = map.firstEntry();
System.out.println("集合的第一个entry:"+firstEntry+":"+firstEntry.getKey()+"---"+firstEntry.getValue());
//获取集合的最后一个key值
Integer lastKey = map.lastKey();
System.out.println("集合的最后一个key:"+lastKey);
//获取集合的最后一个entry
Entry<Integer,String> lastEntry = map.lastEntry();
System.out.println("集合的最后一个entry:"+lastEntry+":"+lastEntry.getKey()+"---"+lastEntry.getValue());
//获取集合中key值大于3的最小key
Integer higherKey = map.higherKey(3);
System.out.println("集合中key值大于3的最小key:"+higherKey);
//获取集合中key值小于3的最大key
Integer lowerKey = map.lowerKey(3);
System.out.println("集合中key值小于3的最大key:"+lowerKey);
//获取集合中key值大于3的最小entry
Entry<Integer,String> higherEntry = map.higherEntry(3);
System.out.println("集合中key值大于3的最小entry:"+higherEntry);
//获取集合中key值小于3的最大entry
Entry<Integer,String> lowerEntry = map.lowerEntry(3);
System.out.println("集合中key值小于3的最大entry:"+lowerEntry);
//截取集合
SortedMap<Integer,String> map2 = map.subMap(3, 5);
System.out.println(map2);
}
WeakHashMap
参考说明:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3311092.html
Map总结(HashMap, Hashtable, TreeMap, WeakHashMap等使用场景)
第1部分 Map概括
第2部分 HashMap和Hashtable异同
第3部分 HashMap和WeakHashMap异同
参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3311126.html
Collections:
Collections VS Collection
- Collection是一个集合接口,用来存储数据的
- Collections是一个集合的工具类,用来操作集合中的数据的
Collections常用方法:
1.public static boolean addAll(Collection c,Collection c) //将一个集合添加到另外一个集合中
2.public static T max(Collection c) //返回集合中的最大值
3.public static T min(Collection c) //返回集合中的最小值
4.public static boolean replaceAll(List list, T oldValue,T newVlaue) //将list集合中的oldValue全部替换为newValue
5.public static void reverse(List list) //将集合中的元素反转
6.public static int binarySearch(List list,T key) //查找集合中指定的元素
7.public static final List emptyList() //清空List集合
8.public static final Map<K,V> emptyMap() //清空Map集合
9.public static final Set emptySet() //清空Set集合
10.public static void sort(List list) //对集合进行排序操作,规则根据T实现的ComparTo来决定
11.public static void swap(List list,int i,int j) //交换指定位置的元素
/**
* emptyList
* emptySet
* emptyMap
* 获取不可变的集合
*
*/
List list = Collections.emptyList();
Set set = Collections.emptySet();
Map map = Collections.emptyMap();
/**
* addAll
* 向集合添加元素,元素个数没有要求
*
*/
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
System.out.println("添加之前:"+list);
Collections.addAll(list, "Java","JavaSE","JavaME");
System.out.println("添加之后:"+list);
/**
* replaceAll
* 替换集合中的内容
*/
Collections.replaceAll(list, oldVal, newVal);
System.out.println(list);
/**
* swap
* 交换指定位置的元素
*
*/
System.out.println("交换之前:"+list);
Collections.swap(list, 1, 3);
System.out.println("交换之后:"+list);
/**
* reverse
* 将集合中的元素进行反转
*/
System.out.println("反转之前:"+list);
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("反转之后:"+list);
/**
* sort
* 对集合进行排序,必须是相同类型才能进行排序。
* 默认是进行的升序排列, 降序排列只需调用reverse对升序排列进行反转。
*/
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Collections.addAll(list,3,5,1,4,6,2);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
/**
* binarySearch:集合中元素的数据类型要一致,集合中的元素按照升序进行排列
* 检索元素在集合中的位置,若结果大于等于0则表示集合中存在该元素
* 若结果小于0则表示集合中不存在该元素
*/
int index = Collections.binarySearch(list, "Hello");
System.out.println(index);
知识点补充:
public static int add(int... nums) { //设置可变参数
int result = 0;
for(int num :nums) {
result += num;
}
return result;
}
实际开发中,用集合来描述对象和对象之间的关系。
- 一对一:两个对象之间的关系是一对一,A中只能有一个B,B中只能有一个A。
人和身份证:一个人只能有一个身份证,一个身份证只能对应一个人。
/**
* 一对一
*/
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("张三");
person.setAge(22);
Card card = new Card();
card.setId("12345678909876");
card.setProvince("河北省");
//建立person和card的关系
person.setCard(card);
card.setPerson(person);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(card);
________________________________________________________________
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Card card;
...
}
________________________________________________________________
public class Card {
private String id;
private String province;
private Person person;
...
}
- 一对多:两个对象之间的关系是一对多,A中只能有一个B,B中可以有多个A。
客户和订单:一个订单只能对应一个客户,一个客户可以对应多个订单。
/**
* 一对多
*/
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(1);
customer.setName("张三");
Order order1 = new Order();
order1.setId(1);
order1.setName("订单1");
order1.setCustomer(customer);
Order order2 = new Order();
order2.setId(2);
order2.setName("订单2");
order2.setCustomer(customer);
List orders = new ArrayList();
orders.add(order1);
orders.add(order2);
customer.setOrders(orders);
System.out.println("order1的信息:");
System.out.println(order1.getId());
System.out.println(order1.getName());
System.out.println(order1.getCustomer());
System.out.println("order2的信息:");
System.out.println(order2.getId());
System.out.println(order2.getName());
System.out.println(order2.getCustomer());
System.out.println("customer的信息:");
System.out.println(customer.getId());
System.out.println(customer.getName());
List list = customer.getOrders();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Order order = (Order) list.get(i);
System.out.println(order);
}
_______________________________________________________________
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private List orders;
...
}
_______________________________________________________________
public class Order {
private int id;
private String name;
private Customer customer;
...
}
- 多对多:两个对象之间的关系是多对多,A中可以有多个B,B中也可也有多个A。
学生和选课:一个学生可以选择多门课,一门课可以被多个学生选择。
/**
* 多对多
*/
//创建两个学生
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setNum(1);
student1.setName("张三");
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setNum(2);
student2.setName("李四");
//创建三门课程
Course course1 = new Course();
course1.setId(1);
course1.setName("数据结构与算法");
Course course2 = new Course();
course2.setId(2);
course2.setName("Java高级编程");
Course course3 = new Course();
course3.setId(3);
course3.setName("MySQL数据库");
//学生选课,张三选了Java和MySQL
//让学生来维护关系
List courses = new ArrayList();
courses.add(course2);
courses.add(course3);
student1.setCourses(courses);
System.out.println("学生的选课信息");
System.out.println("学生学号:"+student1.getNum());
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+student1.getName());
System.out.println("选课记录:");
List list = student1.getCourses();
for(Object obj:list) {
Course course = (Course) obj;
System.out.println("课程编号:"+course.getId());
System.out.println("课程名称:"+course.getName());
}
System.out.println("************************************");
//李四选择数据结构,Java,MySQL
//让课程来维护关系
List students = new ArrayList();
students.add(student2);
course1.setStudents(students);
System.out.println("课程被选记录");
System.out.println("课程信息");
System.out.println("课程编号:"+course1.getId());
System.out.println("课程名称:"+course1.getName());
System.out.println("选择该课程的学生记录");
List list2 = course1.getStudents();
for(Object obj:list2) {
Student student = (Student) obj;
System.out.println("学生学号:"+student.getNum());
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+student.getName());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
List list3 = new ArrayList();
list3.add(student1);
list3.add(student2);
course2.setStudents(list3);
System.out.println("课程信息");
System.out.println("课程编号:"+course2.getId());
System.out.println("课程名称:"+course2.getName());
System.out.println("选择该课程的学生记录");
List list4 = course2.getStudents();
for(Object obj:list4) {
Student student = (Student) obj;
System.out.println("学生学号:"+student.getNum());
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+student.getName());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
List list5 = new ArrayList();
list5.add(student1);
list5.add(student2);
course3.setStudents(list5);
System.out.println("课程信息");
System.out.println("课程编号:"+course3.getId());
System.out.println("课程名称:"+course3.getName());
System.out.println("选择该课程的学生记录");
List list6 = course3.getStudents();
for(Object obj:list6) {
Student student = (Student) obj;
System.out.println("学生学号:"+student.getNum());
System.out.println("学生姓名:"+student.getName());
}
_______________________________________________________________
public class Student {
private int num;
private String name;
private List courses;
...
}
________________________________________________________________
public class Course {
private int id;
private String name;
private List students;
...
}
Iterator和Enumeration比较
一:比较
1. 函数接口不同
Enumeration只有2个函数接口。通过Enumeration,我们只能读取集合的数据,而不能对数据进行修改。
Iterator只有3个函数接口。Iterator除了能读取集合的数据之外,也能数据进行删除操作。
2. Iterator支持fail-fast机制,而Enumeration不支持。
二:接口实现代码
Enumeration是一个接口,它的源码如下:
package java.util;
public interface Enumeration<E> {
boolean hasMoreElements();
E nextElement();
}
Iterator也是一个接口,它的源码如下:
package java.util;
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
void remove();
}
三:Iterator和Enumeration实例
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Random;
/*
* 测试分别通过 Iterator 和 Enumeration 去遍历Hashtable
* @author Chenny
*/
public class IteratorEnumeration {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int val;
Random r = new Random();
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++) {
// 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
val = r.nextInt(100);
table.put(String.valueOf(i), val);
}
// 通过Iterator遍历Hashtable
iterateHashtable(table) ;
// 通过Enumeration遍历Hashtable
enumHashtable(table);
}
/*
* 通过Iterator遍历Hashtable
*/
private static void iterateHashtable(Hashtable table) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator iter = table.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
//System.out.println("iter:"+iter.next());
iter.next();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
countTime(startTime, endTime);
}
/*
* 通过Enumeration遍历Hashtable
*/
private static void enumHashtable(Hashtable table) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Enumeration enu = table.elements();
while(enu.hasMoreElements()) {
//System.out.println("enu:"+enu.nextElement());
enu.nextElement();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
countTime(startTime, endTime);
}
private static void countTime(long start, long end) {
System.out.println("time: "+(end-start)+"ms");
}
}
运行结果如下:
time: 9ms
time: 5ms
从中,我们可以看出。Enumeration 比 Iterator 的遍历速度更快。为什么呢?
这是因为,Hashtable中Iterator是通过Enumeration去实现的,而且Iterator添加了对fail-fast机制的支持;所以,执行的操作自然要多一些。
fail-fast总结(通过ArrayList来说明fail-fast的原理、解决办法)
fail-fast 机制是java集合(Collection)中的一种错误机制。当多个线程对同一个集合的内容进行操作时,就可能会产生fail-fast事件。
参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308762.html





















 448
448











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








