一、多线程简介
1、什么是多线程:
如果在一个进程中同时运行了多个线程,用来完成不同的工作,则称之为“多线程”。
多个线程交替占用CPU资源,而非真正的并行执行。
2、多线程的好处:
(1)充分利用CPU的资源。
(2)简化编程模型。
(3)带来良好的用户体验。
3、代码介绍:
public class MyThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获得主线程对象
System.out.println("当前线程是:"+t.getName());
//主线程
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("线程的初始名字是:"+name);
//将主线程的名字改为“hello”(也就是设置线程名)
Thread.currentThread().setName("hello");
name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("重命名成功,线程现在的名字是:"+name);
}
}
4、运行结果图:

二、多线程的Thread类
1、Java提供了java.lang.Thread类支持多线程编程。
2、主线程:
2.1、main()方法即为主程序入口。
2.2、产生其他子线程的线程。
2.3、必须最后完成执行,因为它执行各种关闭动作。
3、创建线程的两种方式:
1、创建方式和使用线程的步骤:

2、举例说明:
2.1、例子1:定义MyThread类继承Thread类。


2.1.1、代码展示:
/**
* 继承Thread 类,重写run方法,在方法中编写相关代码
* 启动线程用:start
*/
public class MyThread1 extends Thread{
//打印10个当前运行的线程的名字
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 myThread1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread1 myThread2 = new MyThread1();
myThread1.run();
System.out.println("======================");
myThread2.run(); //启动主线程:Thread.currentThread().getName()=main
myThread2.start(); //启动子线程:Thread.currentThread().getName()=Thread-1
}
}
2.1.2、运行截图:


2.2、例子2:定义MyRunnable类实现Runnable接口。


2.2.1、代码展示:
/**
* 继承Runnable 接口
* 启动线程用:start
*/
public class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread2 myThread2 = new MyThread2();
Thread thread = new Thread(myThread2);
thread.start();
}
}
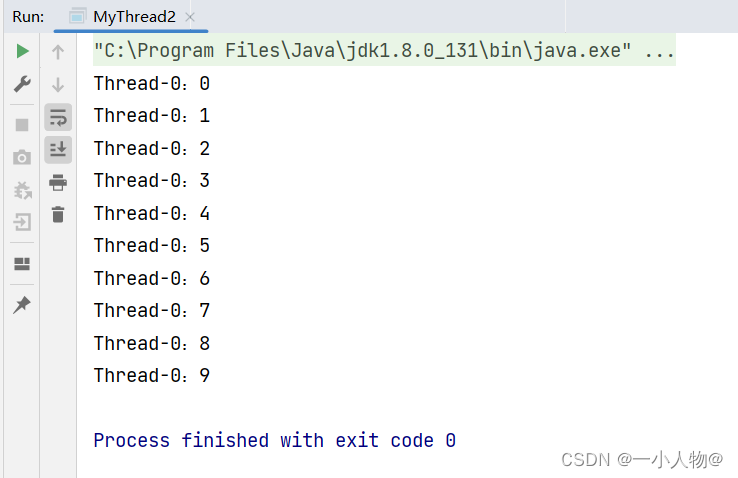
2.2.2、运行截图:
三、线程的状态与调度:
1、线程状态:
1.1、创建状态——>就绪状态<——阻塞状态<——运行状态——>死亡状态。

1.2、代码展示:
public class MyThread3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("线程运行......");
Thread.sleep(500);
int a = 10/0;
System.out.println("运行继续......");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("线程执行中断......");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new MyThread3());
System.out.println("创建状态......");
thread.start();
System.out.println("就绪状态......");
}
}
1.3、运行截图:

2、线程调度:
2.1、指的是按照特定机制为多个线程分配CPU的使用权。【优先级:thread1.getPriority()】


2.2、代码展示:
/**
* 优先级的设置
*/
public class MyThread4 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new MyThread4(),"AAA");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new MyThread4(),"bbbb");
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
System.out.println(thread1.getPriority());
System.out.println(thread2.getPriority());
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
2.3、运行截图:

四、休眠+强制执行:
1、休眠:
1.1、休眠的代码写法:Thread.sleep(500); //1000毫秒=1秒

2、强制执行:
2.1、线程的强制执行:执行的线程.join();

3、代码展示:
/**
* 休眠+强制执行
*/
public class MyThread5 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread5 myThread5 = new MyThread5();
Thread thread = new Thread(myThread5);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i==5){
//强制执行
try {
thread.join();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行:"+i);
}
}
}
4、运行截图:


五、线程的礼让:
1、线程礼让的调用写法:Thread.yield();

2、代码展示:
/**
* 线程的礼让,两种结果:让还是不让
*/
public class MyThread6 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
if(i==3){
System.out.println("礼让......");
//线程礼让
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new MyThread6(),"AAA");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new MyThread6(),"BBB");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
3、运行截图:

六、给代码块加锁(在接口中实现):
1、synchronized(类名.class){}或synchronized(this){}

2、加锁的作用:括号里面的内容其实就是一个监听,监听在它的大括号里面的代码变化情况。






















 3815
3815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










