文件描述符和打开模式
文件描述符
一种特殊的索引,实际上就是进程中file_struct结构体成员fd_array的数组下标
文件打开模式
主模式:
- O_RDONLY:只读模式
- O_WRONLY:只写模式
- O_RDWR:读写,模式
副模式:
- O_CREAT:当文件不存在,需要去创建文件
- O_APPEND:追加模式
- O_DIRECT:直接IO模式
- O_SYNC:同步模式
- O_NOBLOCK:非阻塞模式
open_close函数
OPEN函数
头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
函数原型:
-
当文件存在时
int open(const char* pathname,int flags) -
当文件不存在时
int open (const char* pathname,int flags,int perms)
参数说明:
-
pathname
要打开或创建的目标文件 -
flags
打开文件时,可以传入多个参数选项,用下面的一个或者多个常量进行“或”运算,构成falgs参数:
O_RDONLY: 只读打开;
O_WRONLY: 只写打开;
O_RDWR: 读写打开;
以上这三个常量,必须制定一个且只能指定一个O_CREAT: 若文件不存在,则创建它,需要使用mode选项。来指明新文件的访问权限。
O_APPEND: 追加写,如果文件已经有内容,这次打开文件所写的数据附加到文件的末尾而不覆盖原来的内容。
返回值:
成功:文件描述符
失败:-1
CLOSE函数
头文件:
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:
int close(int fd)
功能:
关闭一个已经打开的文件
参数说明:
fd:是需要关闭的文件描述符
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
示例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
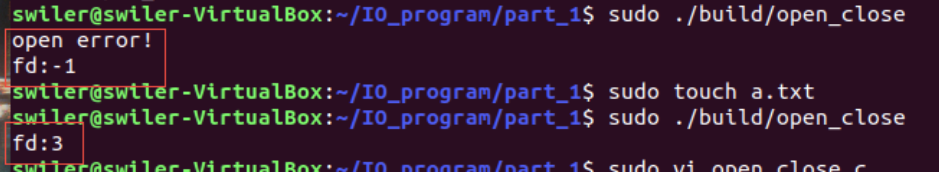
fd = open("./a.txt",O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open error!\r\n");
}
printf("fd:%d\r\n",fd);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
结果:-1表示没有该文件,3表示成功
示例:带权限配置和自动创建文件的open_close()
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
fd = open("./b.txt",O_CREAT, 0666);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open error!\r\n");
}
printf("fd:%d\r\n",fd);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//0代表8进制,打开b.txt文件,如果没有则创建一个b.txt
read_write函数
read函数
头文件
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型
ssize_t read(int fd,void *buff,size_t count)
返回值
成功:
- count:成功读取全部字节
- 0~count:
- 剩余文件长度小于count
- 读取期间被异步信号打断
失败:
- -1,读取错误
write函数
头文件
同read函数
函数原型
ssize_t write(int fd,void *buff,size_t count)
返回值
成功:
- count:成功写入全部字节
- 0~count:
- 写入期间被异步信号打断
失败:
- -1,读取错误
示例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
int fd1,fd2;
char buf[512];
int read_size;
if(argc != 3)
{
printf("error !!\r\n");
return -1;
}
fd1 = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
fd2 = open(argv[2],O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0666);
if(fd1 < 0 || fd2 < 0)
{
printf("open error !!\r\n");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
read_size = read(fd1,buf,512);
if(read_size == 0)
break;
write(fd2,buf,read_size);
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
return 0;
}
lseek和sync函数
lseek函数
功能
设置文件读写位置
头文件
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型
off_t lseek(int fd,off_t offset,int whence)
- 若whence为SEEK_SET,基准点为文件开头
- 若whence为SEEK_CUR,基准点为当前位置
- 若whence为SEEK_END,基准点为文件末尾
返回值
成功:文件偏移位置值
失败:-1
sync函数
页缓存和回写
功能
强制把修改过的页缓存区数据写入磁盘
头文件
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型
void sync(void);
返回值
无
示例
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("file",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0666);
write(fd,"123",3);
lseek(fd,100,SEEK_CUR);
write(fd,"ABC",3);
sync();
close(fd);
return 0;
}
结果:创建了一个file文件

file文件内部:123,然后空100个字符,ABC























 1390
1390











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








