IO代表了input output,即输入输出,而输入输出流是以内存为参考的。
IO流的分类:
1、根据处理的数据类型不同可以分为:字符流(以字符为单位读写)和字节流(以字节为单位读写)。
2、根据数据的流向不同可以分为:输入流和输出流。

一般情况下,如果要读写的数据是字符数据,我们使用字符流,如:文本文件。如果要读写其他类型的数据,如:图片数据、视频数据,我们使用字节流。字节流可以读取任何类型的文件,即使用字节流也可以读写字符数据,而字符流只能读取文本文件。
fileReader.read() 以两种方式读取
一次读取一个字符(返回值就是该字符的ASCII码值,当没有读取到字符时,返回-1):
public void testFileReader() {
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("io.txt");
int ch1 = fileReader.read();
System.out.println(ch1);
System.out.println((char)ch1);
int ch2 = fileReader.read();
System.out.println(ch2);
System.out.println((char)ch2);
int ch3 = fileReader.read();
System.out.println(ch3);
System.out.println((char)ch3);
int ch4 = fileReader.read();
System.out.println(ch4);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileReader != null) {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
也可以通过while语句来实现循环读取(注意:赋值语句是有结果的,结果就是赋给该变量的值):
int ch = -1;
while ((ch = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(ch);
System.out.println((char)ch);
}
一次读取多个字符(返回值是读取到的字符数,当没有读取到字符时,返回-1):
io.txt:
1234567890ab
public void testFileReader1() {
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("io.txt");
int length = -1;
char[] buffer = new char[5];
// 假设有12个字符
// 第一次 length: 5
// 第二次 length: 5
// 第三次 length: 2
// 第四次 length: -1
while ((length = fileReader.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileReader != null) {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
输出结果:
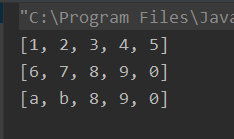
从结果可以看出:如果读取不出字符数组大小的字符数,那么字符数组中没有读取到新的字符的位置仍然是上一次读取的字符
字符流操作实现复制文本文件:
public void testFileWriter() {
FileReader fileReader = null;
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("io.txt");
fileWriter = new FileWriter("io_back.txt");
char[] buffer = new char[5];
int length = -1;
while ((length = fileReader.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
// fileWriter.write(buffer);
// 写入的时候提供偏移量和写入的长度,能够准确的写入
// 因为最后一次写入可能不需要把整个字符数组里面的数据写入
fileWriter.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 先打开的后关闭
if (fileWriter != null) {
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileReader != null) {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
字节流操作实现复制图片:
public void testInputOutputStream() {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("zcd.png");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("zcd_back.png");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length = -1;
while ((length = fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
注意:一般来说复制文件都用字节流,如果要获取某个文本文件中的字符,可以用字符流
流关闭时的原则
1、先打开的后关闭,后打开的先关闭
2、流A依赖于流B,先关闭流A,再关闭流B
序列化和反序列化
实现把对象保存到文件(注意:对应的类要实现Serializable可序列化接口):
public void testObjectOutputStream() {
Student student = new Student(1, "zhangsan");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("student");
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(student);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (objectOutputStream != null) {
try {
objectOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
实现从文件中读取对象(反序列化):
public void testObjectInputStream() {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
try {
// 反序列化
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("student");
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
Student student = (Student) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(student);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (objectInputStream != null) {
try {
objectInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}






















 4952
4952











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








