Webpack 简介
什么是 Webpack?
Webpack 是一个现代 JavaScript 应用程序的静态模块打包器(static module bundler)。它将项目中的各种资源(JavaScript、CSS、图片、字体等)视为模块,通过分析模块间的依赖关系,将它们打包成一个或多个 bundle 文件。
配置详情
1. 基础配置
entry(入口)
module.exports = {
// 单入口
entry: './src/index.js',
// 多入口
entry: {
app: './src/app.js',
admin: './src/admin.js'
},
// 动态入口
entry: () => './src/index.js'
}
output(输出)
module.exports = {
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'), // 输出目录
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js', // 输出文件名
publicPath: '/', // 公共路径
clean: true, // 清理输出目录
chunkFilename: '[name].[contenthash].chunk.js', // 非入口chunk文件名
assetModuleFilename: 'assets/[hash][ext][query]', // 资源模块文件名
library: 'MyLibrary', // 库名称
libraryTarget: 'umd', // 库目标
globalObject: 'this' // 全局对象
}
}
mode(模式)
module.exports = {
mode: 'development', // 'development' | 'production' | 'none'
}
2. 模块处理
module.rules(模块规则)
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/, // 匹配文件
exclude: /node_modules/, // 排除文件
include: path.resolve('src'), // 包含文件
use: [ // 使用的loader
{
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env']
}
}
]
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)$/,
type: 'asset/resource' // 资源模块类型
}
]
}
}
resolve(解析)
module.exports = {
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.jsx', '.ts', '.tsx'], // 自动解析扩展名
alias: { // 别名
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
'components': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/components')
},
modules: ['node_modules', 'src'], // 模块搜索目录
mainFields: ['browser', 'module', 'main'], // package.json字段优先级
mainFiles: ['index'], // 默认文件名
symlinks: false, // 是否解析符号链接
fallback: { // polyfill
"crypto": require.resolve("crypto-browserify")
}
}
}
3. 插件配置
plugins(插件)
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
filename: 'index.html',
chunks: ['app']
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: '[name].[contenthash].css'
})
]
}
4. 开发配置
devtool(源码映射)
module.exports = {
devtool: 'source-map', // 'eval' | 'cheap-source-map' | 'inline-source-map' 等
}
devServer(开发服务器)
module.exports = {
devServer: {
port: 3000, // 端口
host: 'localhost', // 主机
hot: true, // 热更新
open: true, // 自动打开浏览器
compress: true, // gzip压缩
historyApiFallback: true, // HTML5 History API
static: { // 静态文件
directory: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
},
proxy: { // 代理
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:8080',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': ''
}
}
},
headers: { // 响应头
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
},
https: false, // HTTPS
client: { // 客户端配置
overlay: true, // 错误覆盖层
progress: true // 进度条
}
}
}
5. 优化配置
optimization(优化)
module.exports = {
optimization: {
minimize: true, // 是否压缩
minimizer: [ // 压缩器
new TerserPlugin(),
new CssMinimizerPlugin()
],
splitChunks: { // 代码分割
chunks: 'all',
cacheGroups: {
vendor: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
name: 'vendors',
chunks: 'all'
}
}
},
runtimeChunk: 'single', // 运行时chunk
moduleIds: 'deterministic', // 模块ID生成方式
chunkIds: 'deterministic', // chunk ID生成方式
usedExports: true, // 标记未使用导出
sideEffects: false, // 副作用
concatenateModules: true, // 模块连接
mangleExports: true // 导出名称混淆
}
}
6. 性能配置
performance(性能)
module.exports = {
performance: {
hints: 'warning', // 'error' | 'warning' | false
maxEntrypointSize: 250000, // 入口点最大大小
maxAssetSize: 250000, // 资源最大大小
assetFilter: function(assetFilename) {
return assetFilename.endsWith('.js');
}
}
}
7. 外部依赖
externals(外部扩展)
module.exports = {
externals: {
jquery: 'jQuery', // 排除jQuery
lodash: '_'
},
// 或者使用函数
externals: [
function(context, request, callback) {
if (/^yourregex$/.test(request)){
return callback(null, 'commonjs ' + request);
}
callback();
}
]
}
8. 监听配置
watch 和 watchOptions
module.exports = {
watch: true, // 启用监听
watchOptions: {
aggregateTimeout: 300, // 延迟时间
poll: 1000, // 轮询间隔
ignored: /node_modules/ // 忽略文件
}
}
9. 统计信息
stats(统计)
module.exports = {
stats: {
colors: true, // 彩色输出
modules: false, // 显示模块信息
children: false, // 显示子编译信息
chunks: false, // 显示chunk信息
chunkModules: false // 显示chunk模块信息
}
}
10. 其他配置
target(目标环境)
module.exports = {
target: 'web', // 'node' | 'webworker' | 'electron-main' 等
}
context(上下文)
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'), // 基础目录
}
cache(缓存)
module.exports = {
cache: {
type: 'filesystem', // 'memory' | 'filesystem'
buildDependencies: {
config: [__filename] // 构建依赖
}
}
}
experiments(实验性功能)
module.exports = {
experiments: {
topLevelAwait: true, // 顶层await
outputModule: true // 输出ES模块
}
}
完整示例
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
entry: {
app: './src/index.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
clean: true
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: 'babel-loader'
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, 'css-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html'
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin()
],
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all'
}
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.jsx'],
alias: {
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
}
}
};
工作原理
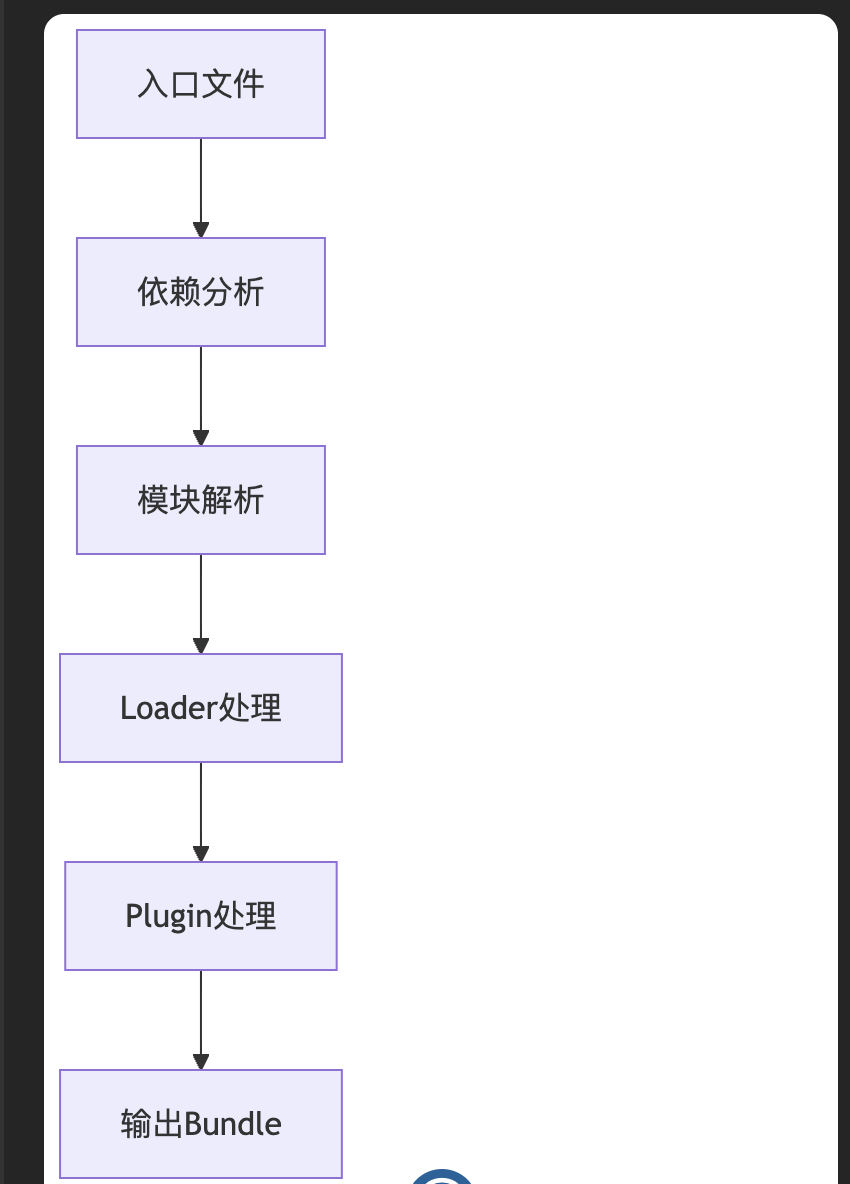
- 依赖分析:从入口文件开始,递归分析所有依赖
- 模块解析:解析模块路径,确定模块位置
- Loader 处理:使用相应 Loader 处理不同类型文件
- Plugin 处理:执行插件逻辑,优化和转换代码
- 输出 Bundle:生成最终的打包文件
发展历程
| 版本 | 发布时间 | 主要特性 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.x | 2014 | 基础打包功能 |
| 2.x | 2017 | 代码分割、Tree Shaking |
| 3.x | 2017 | Scope Hoisting |
| 4.x | 2018 | 零配置、性能优化 |
| 5.x | 2020 | 模块联邦、持久化缓存 |
使用场景
🌐 单页应用(SPA)
// React 应用
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
📚 多页应用(MPA)
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
entry: {
home: './src/home.js',
about: './src/about.js',
contact: './src/contact.js'
}
};
📦 库开发
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
library: 'MyLibrary',
libraryTarget: 'umd'
}
};
🔧 Node.js 应用
module.exports = {
target: 'node',
entry: './src/server.js'
};
生态系统
常用 Loader
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, use: 'babel-loader' },
{ test: /\.css$/, use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'] },
{ test: /\.scss$/, use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'sass-loader'] },
{ test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)$/, use: 'file-loader' },
{ test: /\.ts$/, use: 'ts-loader' }
]
}
};
常用 Plugin
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html'
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: '[name].[contenthash].css'
})
]
};
优势与挑战
✅ 优势
- 模块化支持:支持多种模块规范
- 丰富生态:大量 Loader 和 Plugin
- 性能优化:代码分割、Tree Shaking 等
- 开发体验:热更新、源码映射
- 灵活配置:高度可定制
⚠️ 挑战
- 学习曲线:配置复杂,概念较多
- 构建速度:大型项目构建可能较慢
- 配置维护:需要持续维护配置文件
- 版本兼容:不同版本间可能存在兼容性问题
替代方案对比
| 工具 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| Webpack | 功能全面,生态丰富 | 复杂应用,需要精细控制 |
| Vite | 开发快速,基于 ESM | 现代浏览器,Vue/React 项目 |
| Rollup | 输出简洁,适合库 | 库开发,简单应用 |
| Parcel | 零配置,开箱即用 | 快速原型,小型项目 |
| esbuild | 构建极快 | 需要极致性能的场景 |
JavaScript 模块规范详解
什么是模块?
模块是一种将代码分割成独立、可重用单元的方式。每个模块都有自己的作用域,可以导出功能供其他模块使用,也可以导入其他模块的功能。
主要模块规范
1. CommonJS(Node.js 标准)
特点:
- 同步加载
- 主要用于服务端(Node.js)
- 运行时加载
- 值的拷贝
语法:
// 导出 - module.exports
// math.js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function subtract(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
// 方式1:直接赋值
module.exports = {
add,
subtract
};
// 方式2:逐个导出
exports.add = add;
exports.subtract = subtract;
// 方式3:导出单个函数
module.exports = add;
// 导入 - require()
// app.js
const math = require('./math');
const { add, subtract } = require('./math');
const add = require('./math'); // 如果导出的是单个函数
console.log(math.add(2, 3)); // 5
特点示例:
// counter.js
let count = 0;
function increment() {
count++;
}
function getCount() {
return count;
}
module.exports = { increment, getCount, count };
// main.js
const counter1 = require('./counter');
const counter2 = require('./counter');
console.log(counter1 === counter2); // true,模块会被缓存
counter1.increment();
console.log(counter1.getCount()); // 1
console.log(counter2.getCount()); // 1,同一个实例
2. AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition)
特点:
- 异步加载
- 主要用于浏览器端
- 依赖前置
- RequireJS 是其主要实现
语法:
// 定义模块 - define()
// math.js
define(function() {
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function subtract(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
return {
add: add,
subtract: subtract
};
});
// 带依赖的模块
// calculator.js
define(['./math'], function(math) {
function calculate(operation, a, b) {
if (operation === 'add') {
return math.add(a, b);
} else if (operation === 'subtract') {
return math.subtract(a, b);
}
}
return {
calculate: calculate
};
});
// 使用模块 - require()
// main.js
require(['./calculator'], function(calculator) {
console.log(calculator.calculate('add', 2, 3)); // 5
});
// 配置
require.config({
paths: {
'jquery': 'https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min'
}
});
3. CMD (Common Module Definition)
特点:
- 异步加载
- 依赖就近
- SeaJS 是其主要实现
- 现在较少使用
语法:
// 定义模块
// math.js
define(function(require, exports, module) {
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
exports.add = add;
});
// 使用模块
// main.js
define(function(require) {
var math = require('./math');
console.log(math.add(2, 3));
});
4. UMD (Universal Module Definition)
特点:
- 通用模块定义
- 兼容 AMD、CommonJS 和全局变量
- 主要用于库的发布
语法:
// umd-module.js
(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dependency'], factory);
} else if (typeof module === 'object' && module.exports) {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dependency'));
} else {
// 全局变量
root.MyModule = factory(root.Dependency);
}
}(typeof self !== 'undefined' ? self : this, function (dependency) {
// 模块代码
function myFunction() {
return 'Hello from UMD module';
}
return {
myFunction: myFunction
};
}));
5. ES6 Modules (ESM)
特点:
- 官方标准
- 静态分析
- 编译时确定依赖
- 引用的拷贝(live binding)
语法:
// 导出 - export
// math.js
// 命名导出
export function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
export function subtract(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
export const PI = 3.14159;
// 批量导出
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
function divide(a, b) {
return a / b;
}
export { multiply, divide };
// 重命名导出
export { multiply as mul, divide as div };
// 默认导出
export default function(a, b) {
return a ** b;
}
// 导入 - import
// main.js
// 命名导入
import { add, subtract } from './math.js';
// 重命名导入
import { add as plus, subtract as minus } from './math.js';
// 导入所有
import * as math from './math.js';
// 默认导入
import power from './math.js';
// 混合导入
import power, { add, subtract } from './math.js';
// 动态导入
import('./math.js').then(math => {
console.log(math.add(2, 3));
});
// 仅执行模块
import './init.js';
Live Binding 示例:
// counter.js
export let count = 0;
export function increment() {
count++;
}
// main.js
import { count, increment } from './counter.js';
console.log(count); // 0
increment();
console.log(count); // 1,实时更新
| 特性 | CommonJS | AMD | CMD | ES6 Modules | UMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 加载方式 | 同步 | 异步 | 异步 | 静态/动态 | 通用 |
| 运行环境 | Node.js | 浏览器 | 浏览器 | 现代环境 | 通用 |
| 依赖处理 | 运行时 | 依赖前置 | 就近依赖 | 编译时 | 兼容多种 |
| 语法复杂度 | 简单 | 中等 | 中等 | 简洁 | 复杂 |
| Tree Shaking | 不支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 循环依赖 | 支持 | 复杂 | 支持 | 支持 | 取决于环境 |
现代开发中的选择
推荐使用 ES6 Modules
// 现代项目结构
// utils/index.js
export { default as debounce } from './debounce.js';
export { default as throttle } from './throttle.js';
export * from './validators.js';
// components/Button.js
import React from 'react';
import { debounce } from '../utils/index.js';
export default function Button({ onClick, children }) {
const debouncedClick = debounce(onClick, 300);
return <button onClick={debouncedClick}>{children}</button>;
}
// main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import Button from './components/Button.js';
const app = createApp({
components: { Button }
});
兼容性处理
// package.json
{
"type": "module", // 使用 ES modules
"main": "dist/index.cjs", // CommonJS 入口
"module": "dist/index.mjs", // ES module 入口
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.mjs",
"require": "./dist/index.cjs"
}
}
}
总结
- ES6 Modules 是现代标准,推荐在新项目中使用
- CommonJS 仍然是 Node.js 的主要模块系统
- AMD/CMD 主要用于老旧浏览器环境
- UMD 适合发布通用库
- 现代构建工具(如 Webpack、Vite)可以处理多种模块格式的转换和兼容























 687
687

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








