面试经典算法27 - 二叉搜索树中的众数
LeetCode.501
公众号:阿Q技术站
问题描述
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
- 结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
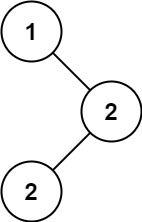
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0]
输出:[0]
思路
递归
- 对 BST 进行中序遍历,在遍历的过程中记录当前节点值以及出现的次数。
- 使用一个变量
maxCount来记录出现次数最多的节点值的次数。 - 在中序遍历的过程中,如果当前节点值等于上一个节点值,则增加该节点值的出现次数;否则,更新上一个节点值的出现次数,并检查是否需要更新
maxCount。 - 最后,再次遍历 BST,将出现次数等于
maxCount的节点值加入结果集中。
非递归
-
初始化一个栈
stack和一个哈希表count,用于存储节点值的出现次数。 -
初始化一个变量
maxCount,用于记录最大出现次数。 -
从根节点开始,进行循环遍历直到栈为空:
对于当前节点,如果其存在左子节点,则将其左子节点入栈,并将当前节点指向左子节点;否则,弹出栈顶节点,并进行如下处理:
- 统计该节点值的出现次数,更新
count和maxCount。 - 如果该节点存在右子节点,则将右子节点入栈,并将当前节点指向右子节点。
- 统计该节点值的出现次数,更新
-
遍历完成后,遍历
count,将出现次数等于maxCount的节点值加入结果集。
图解
今天就不给大家画图了,把这个非常详细的流程分享给大家,如果自己有不懂的地方,可以根据这个流程画一个很直观的流程图。
1. 初始化空向量 modes 和辅助栈 s
2. 如果根节点为空,返回空向量 modes
3. 初始化哈希表 count,用于存储节点值的出现次数,和最大出现次数 maxCount 为 0
4. 初始化当前节点指针 curr 为根节点
5. 循环直到当前节点为空且栈为空
5.1. 循环直到当前节点为空
5.1.1. 将当前节点入栈
5.1.2. 更新当前节点为当前节点的左子节点
5.2. 弹出栈顶节点作为当前节点
5.3. 更新节点值的出现次数
5.4. 更新最大出现次数
5.5. 更新当前节点为当前节点的右子节点
6. 遍历哈希表 count
6.1. 如果节点值的出现次数等于最大出现次数,将节点值加入向量 modes
7. 返回向量 modes
参考代码
C++
递归
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树节点的定义
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// 中序遍历二叉树,同时统计每个节点值出现的次数,并找出最大出现次数
void inorder(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<int, int>& count, int& maxCount) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
inorder(root->left, count, maxCount);
// 统计当前节点值的出现次数
count[root->val]++;
maxCount = max(maxCount, count[root->val]);
inorder(root->right, count, maxCount);
}
// 查找二叉搜索树中的众数
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> modes;
if (!root) {
return modes;
}
unordered_map<int, int> count; // 用于统计每个节点值出现的次数
int maxCount = 0; // 最大出现次数
// 中序遍历统计每个节点值的出现次数,并找出最大出现次数
inorder(root, count, maxCount);
// 再次中序遍历,将出现次数等于最大出现次数的节点值加入结果集中
for (auto& entry : count) {
if (entry.second == maxCount) {
modes.push_back(entry.first);
}
}
return modes;
}
};
// 创建二叉树
TreeNode* createTree(vector<int>& nodes, int index) {
if (index >= nodes.size() || nodes[index] == -1) {
return nullptr; // 如果节点为空,则返回nullptr
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nodes[index]); // 创建当前节点
root->left = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 1); // 创建左子树
root->right = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 2); // 创建右子树
return root; // 返回当前节点
}
int main() {
vector<int> nodes = {1, 2, 2}; // 二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列
TreeNode* root = createTree(nodes, 0); // 创建二叉树
Solution solution;
vector<int> modes = solution.findMode(root); // 查找众数
for (int mode : modes) {
cout << mode << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
非递归
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// 二叉树节点的定义
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> modes;
if (!root) {
return modes; // 如果根节点为空,直接返回空结果
}
stack<TreeNode*> s; // 辅助栈,用于模拟中序遍历过程
unordered_map<int, int> count; // 用于存储节点值的出现次数
int maxCount = 0; // 记录最大出现次数
TreeNode* curr = root; // 当前节点指针,从根节点开始
while (curr || !s.empty()) {
while (curr) {
s.push(curr); // 将当前节点入栈
curr = curr->left; // 遍历左子树
}
curr = s.top(); // 获取栈顶节点
s.pop(); // 弹出栈顶节点
count[curr->val]++; // 统计节点值的出现次数
maxCount = max(maxCount, count[curr->val]); // 更新最大出现次数
curr = curr->right; // 处理右子节点
}
// 遍历统计结果,将出现次数等于最大出现次数的节点值加入结果集
for (auto& entry : count) {
if (entry.second == maxCount) {
modes.push_back(entry.first);
}
}
return modes; // 返回结果集
}
};
// 创建二叉树
TreeNode* createTree(vector<int>& nodes, int index) {
if (index >= nodes.size() || nodes[index] == -1) {
return nullptr; // 如果节点为空,则返回nullptr
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nodes[index]); // 创建当前节点
root->left = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 1); // 创建左子树
root->right = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 2); // 创建右子树
return root; // 返回当前节点
}
int main() {
vector<int> nodes = {1, 2, 2}; // 二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列
TreeNode* root = createTree(nodes, 0); // 创建二叉树
Solution solution;
vector<int> modes = solution.findMode(root); // 查找众数
for (int mode : modes) {
cout << mode << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
// 二叉树节点的定义
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> modes = new ArrayList<>(); // 用于存储众数的列表
if (root == null) {
return new int[0]; // 如果根节点为空,直接返回空数组
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); // 辅助栈,用于模拟中序遍历
Map<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap<>(); // 用于存储节点值及其出现次数的映射
int maxCount = 0; // 最大出现次数
TreeNode curr = root; // 当前节点
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr); // 将当前节点入栈
curr = curr.left; // 遍历左子树
}
curr = stack.pop(); // 弹出栈顶节点
count.put(curr.val, count.getOrDefault(curr.val, 0) + 1); // 更新节点值出现次数
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, count.get(curr.val)); // 更新最大出现次数
curr = curr.right; // 处理右子节点
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : count.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() == maxCount) {
modes.add(entry.getKey()); // 将出现次数等于最大出现次数的节点值加入众数列表
}
}
// 将众数列表转换为数组并返回
return modes.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
// 创建二叉树
public TreeNode createTree(Integer[] nodes, int index) {
if (index >= nodes.length || nodes[index] == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nodes[index]);
root.left = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 1);
root.right = createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 2);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] nodes = {1, null, 2, 2};
Solution solution = new Solution();
TreeNode root = solution.createTree(nodes, 0);
int[] modes = solution.findMode(root);
for (int mode : modes) {
System.out.print(mode + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Python
from typing import List
from collections import Counter
from queue import LifoQueue
from typing import Optional
# 二叉树节点的定义
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
modes = [] # 存储众数的列表
if not root:
return modes # 如果根节点为空,直接返回空列表
stack = LifoQueue() # 辅助栈,用于模拟中序遍历
count = Counter() # 用于存储节点值及其出现次数的字典
max_count = 0 # 最大出现次数
curr = root # 当前节点
while curr or not stack.empty():
while curr:
stack.put(curr) # 将当前节点入栈
curr = curr.left # 遍历左子树
curr = stack.get() # 弹出栈顶节点
count[curr.val] += 1 # 更新节点值出现次数
max_count = max(max_count, count[curr.val]) # 更新最大出现次数
curr = curr.right # 处理右子节点
for key, value in count.items():
if value == max_count:
modes.append(key) # 将出现次数等于最大出现次数的节点值加入众数列表
return modes
# 创建二叉树
def createTree(self, nodes: List[Optional[int]], index: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if index >= len(nodes) or nodes[index] is None:
return None
root = TreeNode(nodes[index])
root.left = self.createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 1)
root.right = self.createTree(nodes, 2 * index + 2)
return root
# 测试代码
nodes = [1, None, 2, 2]
solution = Solution()
root = solution.createTree(nodes, 0)
modes = solution.findMode(root)
print(modes)






















 349
349

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








