Spring注解开发AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
- GenericApplicationContext
- AbstractApplicationContext
- AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
- 推荐文章
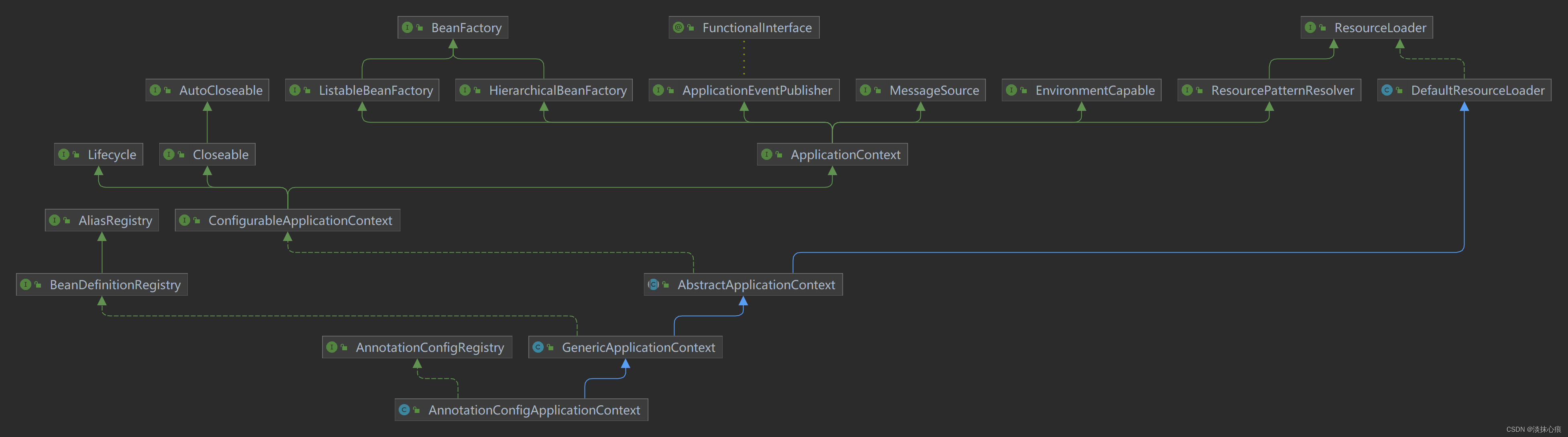
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 初始化前会先执行父类的无参构造方法
- AbstractApplicationContext 初始化了 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
- GenericApplicationContext 初始化了最为重要的 DefaultListableBeanFactory
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 开始执行自己的有参构造
-
this()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 无参构造初始化 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 和 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner -
register(componentClasses)
调用 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 注册配置类的 BeanDefinition(AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition),其中涉及到了 Bean 的 @Scope 两个属性的解析,scopeName 和 proxyMode,proxyMode 的解析主要在AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode() 和ScopedProxyUtils.createScopedProxy() -
refresh()
创建实例化对象
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
StartupStep createAnnotatedBeanDefReader = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.annotated-bean-reader.create");
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
createAnnotatedBeanDefReader.end();
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
}
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 属性初始化
有参构造
- getOrCreateEnvironment(registry) 先从 registry(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext) 查找 environment(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 找不到会的话会自己新建一个StandardEnvironment),如果找不到就 new StandardEnvironment()
- ConditionEvaluator
利用 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 注册相关注解的后置处理器
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = AnnotationBeanNameGenerator.INSTANCE;
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
private ConditionEvaluator conditionEvaluator;
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
private static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
for (Class<?> componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
public void registerBean(Class<?> beanClass) {
doRegisterBean(beanClass, null, null, null, null);
}
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
// 判断是否需要跳过注册,主要判断是否包含Conditional注解
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
// 解析 @Scope 标签,处理@Scope 标签的 scopeName 和 proxyMode 属性,封装成 ScopeMetadata
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
// 设置 BeanDefinition 的 scopeName
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
// 解析 bean 的名字,检查是否包含 @Component 注解并且 value 属性是否有值,若为blank,则生成默认名字(类名首字母小写)
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
// 处理普通注解 @Lazy,@Primary,@DependsOn,@Role,@Description
// 如果存在这些注解并且有值,则设值到 BeanDefinition 中去
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
if (customizers != null) {
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
// 执行 @Scope 的 proxyMode, 代理类创建的关键点
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
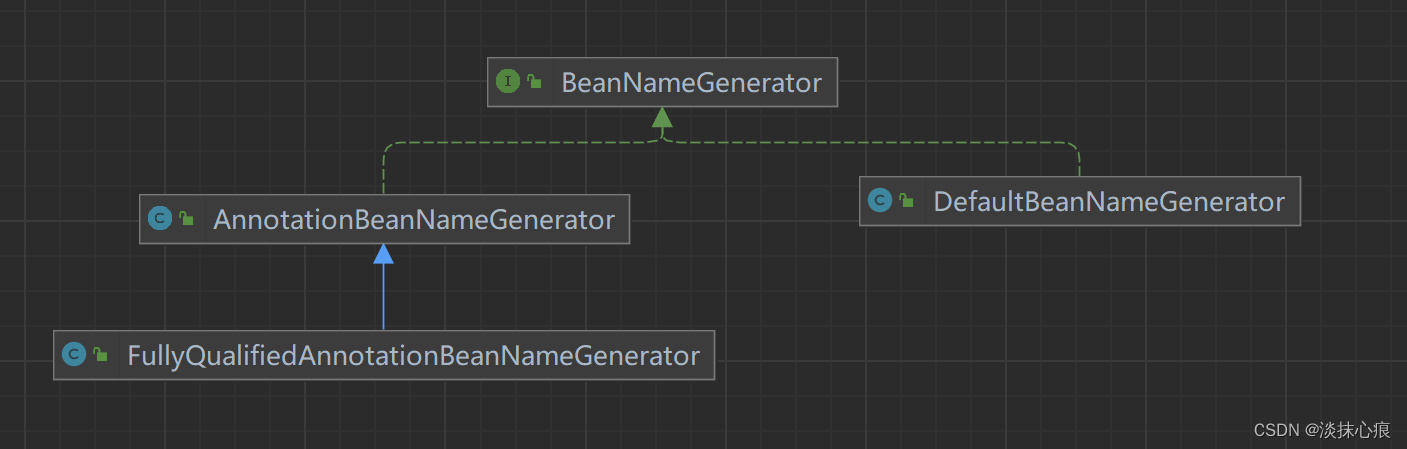
AnnotationBeanNameGenerator
/**
* {@link BeanNameGenerator} implementation for bean classes annotated with the
* {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Component @Component} annotation or
* with another annotation that is itself annotated with {@code @Component} as a
* meta-annotation. For example, Spring's stereotype annotations (such as
* {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Repository @Repository}) are
* themselves annotated with {@code @Component}.
*
* <p>Also supports Java EE 6's {@link javax.annotation.ManagedBean} and
* JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Named} annotations, if available. Note that
* Spring component annotations always override such standard annotations.
*
* <p>If the annotation's value doesn't indicate a bean name, an appropriate
* name will be built based on the short name of the class (with the first
* letter lower-cased), unless the two first letters are uppercase. For example:
*
* <pre class="code">com.xyz.FooServiceImpl -> fooServiceImpl</pre>
* <pre class="code">com.xyz.URLFooServiceImpl -> URLFooServiceImpl</pre>
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Mark Fisher
* @since 2.5
* @see org.springframework.stereotype.Component#value()
* @see org.springframework.stereotype.Repository#value()
* @see org.springframework.stereotype.Service#value()
* @see org.springframework.stereotype.Controller#value()
* @see javax.inject.Named#value()
* @see FullyQualifiedAnnotationBeanNameGenerator
*/
public class AnnotationBeanNameGenerator implements BeanNameGenerator {
/**
* A convenient constant for a default {@code AnnotationBeanNameGenerator} instance,
* as used for component scanning purposes.
* @since 5.2
*/
public static final AnnotationBeanNameGenerator INSTANCE = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator();
private static final String COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME = "org.springframework.stereotype.Component";
private final Map<String, Set<String>> metaAnnotationTypesCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public String generateBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
String beanName = determineBeanNameFromAnnotation((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) definition);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
// Explicit bean name found.
return beanName;
}
}
// Fallback: generate a unique default bean name.
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition, registry);
}
/**
* Derive a bean name from one of the annotations on the class.
* @param annotatedDef the annotation-aware bean definition
* @return the bean name, or {@code null} if none is found
*/
@Nullable
protected String determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedDef) {
AnnotationMetadata amd = annotatedDef.getMetadata();
Set<String> types = amd.getAnnotationTypes();
String beanName = null;
for (String type : types) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(amd, type);
if (attributes != null) {
Set<String> metaTypes = this.metaAnnotationTypesCache.computeIfAbsent(type, key -> {
Set<String> result = amd.getMetaAnnotationTypes(key);
return (result.isEmpty() ? Collections.emptySet() : result);
});
if (isStereotypeWithNameValue(type, metaTypes, attributes)) {
Object value = attributes.get("value");
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = (String) value;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(strVal)) {
if (beanName != null && !strVal.equals(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stereotype annotations suggest inconsistent " +
"component names: '" + beanName + "' versus '" + strVal + "'");
}
beanName = strVal;
}
}
}
}
}
return beanName;
}
/**
* Check whether the given annotation is a stereotype that is allowed
* to suggest a component name through its annotation {@code value()}.
* @param annotationType the name of the annotation class to check
* @param metaAnnotationTypes the names of meta-annotations on the given annotation
* @param attributes the map of attributes for the given annotation
* @return whether the annotation qualifies as a stereotype with component name
*/
protected boolean isStereotypeWithNameValue(String annotationType,
Set<String> metaAnnotationTypes, @Nullable Map<String, Object> attributes) {
boolean isStereotype = annotationType.equals(COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME) ||
metaAnnotationTypes.contains(COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME) ||
annotationType.equals("javax.annotation.ManagedBean") ||
annotationType.equals("javax.inject.Named");
return (isStereotype && attributes != null && attributes.containsKey("value"));
}
/**
* Derive a default bean name from the given bean definition.
* <p>The default implementation delegates to {@link #buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition)}.
* @param definition the bean definition to build a bean name for
* @param registry the registry that the given bean definition is being registered with
* @return the default bean name (never {@code null})
*/
protected String buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition);
}
/**
* Derive a default bean name from the given bean definition.
* <p>The default implementation simply builds a decapitalized version
* of the short class name: e.g. "mypackage.MyJdbcDao" → "myJdbcDao".
* <p>Note that inner classes will thus have names of the form
* "outerClassName.InnerClassName", which because of the period in the
* name may be an issue if you are autowiring by name.
* @param definition the bean definition to build a bean name for
* @return the default bean name (never {@code null})
*/
protected String buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition definition) {
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
Assert.state(beanClassName != null, "No bean class name set");
String shortClassName = ClassUtils.getShortName(beanClassName);
return Introspector.decapitalize(shortClassName);
}
}
AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver
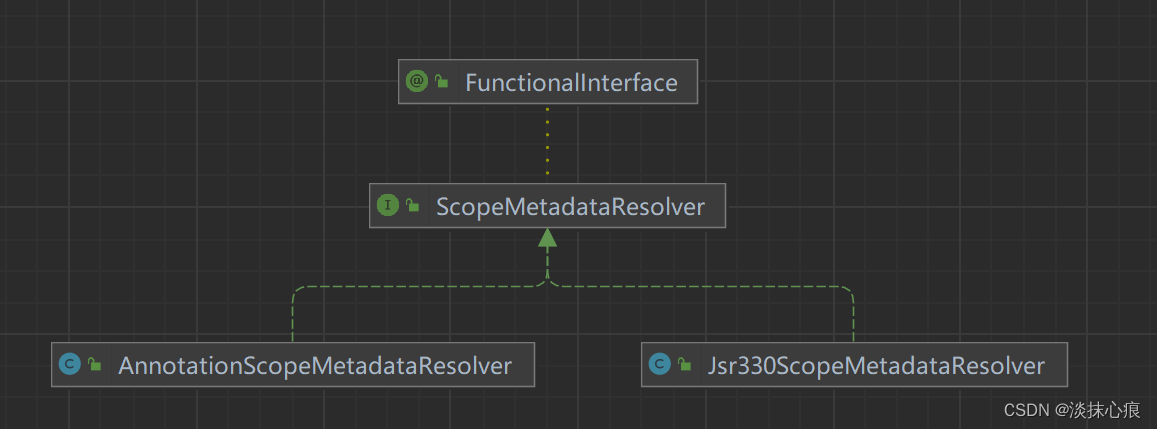
public class AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver implements ScopeMetadataResolver {
private final ScopedProxyMode defaultProxyMode;
protected Class<? extends Annotation> scopeAnnotationType = Scope.class;
/**
* Construct a new {@code AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver}.
* @see #AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver(ScopedProxyMode)
* @see ScopedProxyMode#NO
*/
public AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver() {
this.defaultProxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
}
}
/**
* Enumerates the various scoped-proxy options.
*
* <p>For a more complete discussion of exactly what a scoped proxy is, see the
* section of the Spring reference documentation entitled '<em>Scoped beans as
* dependencies</em>'.
*
* @author Mark Fisher
* @since 2.5
* @see ScopeMetadata
*/
public enum ScopedProxyMode {
/**
* Default typically equals {@link #NO}, unless a different default
* has been configured at the component-scan instruction level.
*/
DEFAULT,
/**
* Do not create a scoped proxy.
* <p>This proxy-mode is not typically useful when used with a
* non-singleton scoped instance, which should favor the use of the
* {@link #INTERFACES} or {@link #TARGET_CLASS} proxy-modes instead if it
* is to be used as a dependency.
*/
NO,
/**
* Create a JDK dynamic proxy implementing <i>all</i> interfaces exposed by
* the class of the target object.
*/
INTERFACES,
/**
* Create a class-based proxy (uses CGLIB).
*/
TARGET_CLASS
}
StandardEnvironment
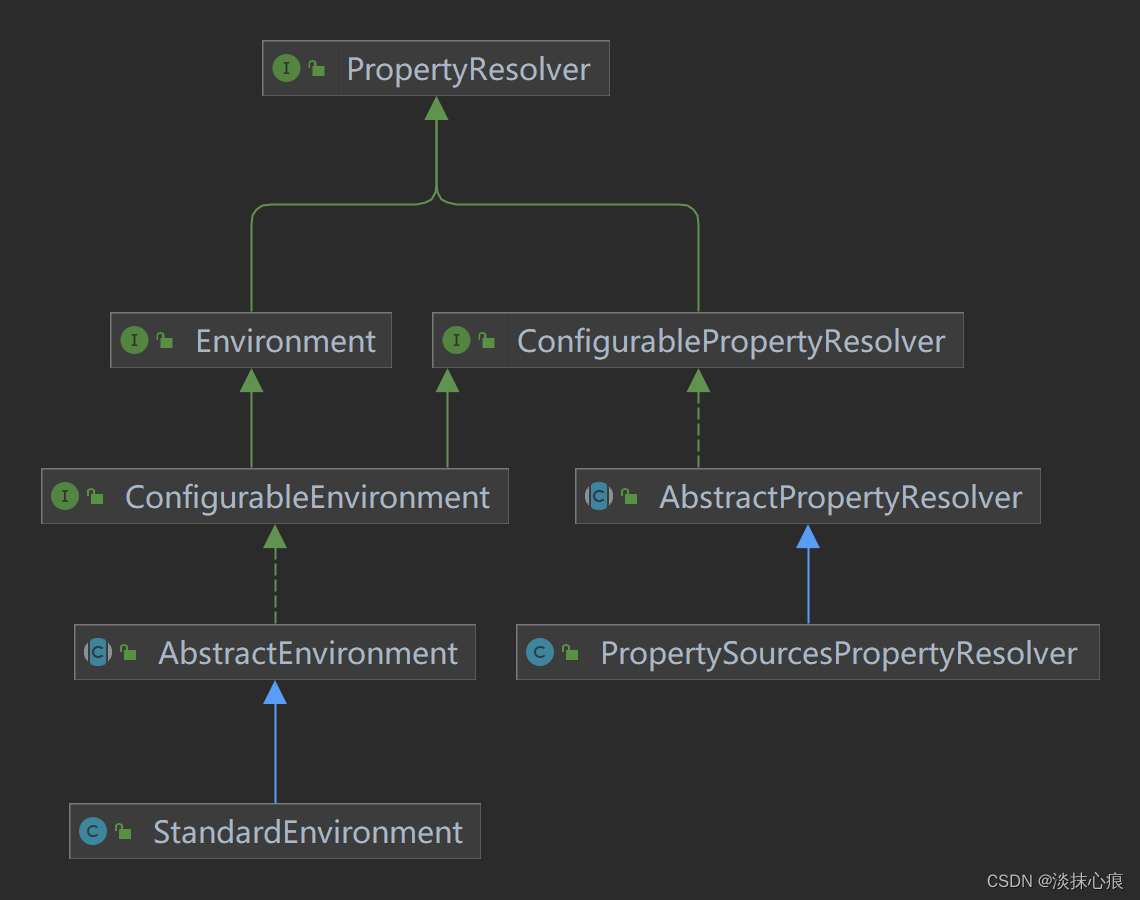
StandardEnvironment 定义了环境变量的keyname,并通过customizePropertySources() 赋值
- 系统环境变量:systemEnvironment
- JVM系统属性:systemProperties
父类 AbstractEnvironment 初始化 MutablePropertySources 和 ConfigurablePropertyResolver
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
/** System environment property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
public StandardEnvironment() {}
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources());
}
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
this.propertyResolver = createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
protected ConfigurablePropertyResolver createPropertyResolver(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
return new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(propertySources);
}
}
MutablePropertySources
PropertySources 接口的默认实现。管理多个PropertySource对象,并且有顺序相关的操作方法,与 PropertyResolver 接口搜索属性相关联
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
/**
* Create a new {@link MutablePropertySources} object.
*/
public MutablePropertySources() {
}
}
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
public class PropertySourcesPropertyResolver extends AbstractPropertyResolver {
@Nullable
private final PropertySources propertySources;
/**
* Create a new resolver against the given property sources.
* @param propertySources the set of {@link PropertySource} objects to use
*/
public PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(@Nullable PropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
}
}
AbstractPropertyResolver
默认占位符前缀为 “${”
默认占位符后缀为 “}”
默认分隔符 “;”
其实现了ConfigurablePropertyResolver的接口,重写了一个重要的方法,getConversionService(),返回类型为 ConfigurableConversionService,该接口在属性的类型转换方面起着重要作用,可以参考我的另一篇博客
public abstract class AbstractPropertyResolver implements ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Nullable
private volatile ConfigurableConversionService conversionService;
@Nullable
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper nonStrictHelper;
@Nullable
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper strictHelper;
private boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders = false;
private String placeholderPrefix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX;
private String placeholderSuffix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX;
@Nullable
private String valueSeparator = SystemPropertyUtils.VALUE_SEPARATOR;
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new LinkedHashSet<>();
@Override
public ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService() {
// Need to provide an independent DefaultConversionService, not the
// shared DefaultConversionService used by PropertySourcesPropertyResolver.
ConfigurableConversionService cs = this.conversionService;
if (cs == null) {
synchronized (this) {
cs = this.conversionService;
if (cs == null) {
cs = new DefaultConversionService();
this.conversionService = cs;
}
}
}
return cs;
}
}
ConditionEvaluator
class ConditionEvaluator {
private final ConditionContextImpl context;
/**
* Create a new {@link ConditionEvaluator} instance.
*/
public ConditionEvaluator(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.context = new ConditionContextImpl(registry, environment, resourceLoader);
}
private static class ConditionContextImpl implements ConditionContext {
@Nullable
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
@Nullable
private final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final Environment environment;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Nullable
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
public ConditionContextImpl(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
this.beanFactory = deduceBeanFactory(registry);
this.environment = (environment != null ? environment : deduceEnvironment(registry));
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null ? resourceLoader : deduceResourceLoader(registry));
this.classLoader = deduceClassLoader(resourceLoader, this.beanFactory);
}
@Nullable
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory deduceBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
return (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) source;
}
if (source instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
return (((ConfigurableApplicationContext) source).getBeanFactory());
}
return null;
}
private Environment deduceEnvironment(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) source).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
private ResourceLoader deduceResourceLoader(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ResourceLoader) {
return (ResourceLoader) source;
}
return new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
@Nullable
private ClassLoader deduceClassLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
@Nullable ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (resourceLoader != null) {
ClassLoader classLoader = resourceLoader.getClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
return classLoader;
}
}
if (beanFactory != null) {
return beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader();
}
return ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
@Override
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() {
Assert.state(this.registry != null, "No BeanDefinitionRegistry available");
return this.registry;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
@Override
public Environment getEnvironment() {
return this.environment;
}
@Override
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return this.classLoader;
}
}
}
AnnotationConfigUtils
一、查看 beanFactory.dependencyComparator 是否为 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator,不是的话则替换为 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
二、查看 beanFactory.autowireCandidateResolver是否为 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver,不是的话则替换为 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver。此前为SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver,因此需要替换 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- EventListenerMethodProcessor
- DefaultEventListenerFactory
注册流程:
- new RootBeanDefinition
- 调用 BeanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition 注册 BeanDefinition,实际上是将BeanDefinition添加到DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionMap, 并返回 BeanDefinitionHolder
- 将 BeanDefinitionHolder 添加到集合中
public abstract class AnnotationConfigUtils {
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
/**
* Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry.
* @param registry the registry to operate on
* @param source the configuration source element (already extracted)
* that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}.
* @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions
* that have actually been registered by this call
*/
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
private static BeanDefinitionHolder registerPostProcessor(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, RootBeanDefinition definition, String beanName) {
definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definition);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(definition, beanName);
}
public static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd) {
processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd, abd.getMetadata());
}
static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
AnnotationAttributes lazy = attributesFor(metadata, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
else if (abd.getMetadata() != metadata) {
lazy = attributesFor(abd.getMetadata(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
}
if (metadata.isAnnotated(Primary.class.getName())) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
AnnotationAttributes dependsOn = attributesFor(metadata, DependsOn.class);
if (dependsOn != null) {
abd.setDependsOn(dependsOn.getStringArray("value"));
}
AnnotationAttributes role = attributesFor(metadata, Role.class);
if (role != null) {
abd.setRole(role.getNumber("value").intValue());
}
AnnotationAttributes description = attributesFor(metadata, Description.class);
if (description != null) {
abd.setDescription(description.getString("value"));
}
}
static BeanDefinitionHolder applyScopedProxyMode(
ScopeMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionHolder definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = metadata.getScopedProxyMode();
if (scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.NO)) {
return definition;
}
boolean proxyTargetClass = scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
return ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(definition, registry, proxyTargetClass);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
public class AnnotationAwareOrderComparator extends OrderComparator {
/**
* Shared default instance of {@code AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}.
*/
public static final AnnotationAwareOrderComparator INSTANCE = new AnnotationAwareOrderComparator();
}
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver
public class ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver extends QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName) {
return (isLazy(descriptor) ? buildLazyResolutionProxy(descriptor, beanName) : null);
}
protected boolean isLazy(DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
for (Annotation ann : descriptor.getAnnotations()) {
Lazy lazy = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(ann, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {
return true;
}
}
MethodParameter methodParam = descriptor.getMethodParameter();
if (methodParam != null) {
Method method = methodParam.getMethod();
if (method == null || void.class == method.getReturnType()) {
Lazy lazy = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodParam.getAnnotatedElement(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
protected Object buildLazyResolutionProxy(final DependencyDescriptor descriptor, final @Nullable String beanName) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
Assert.state(beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory,
"BeanFactory needs to be a DefaultListableBeanFactory");
final DefaultListableBeanFactory dlbf = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
TargetSource ts = new TargetSource() {
@Override
public Class<?> getTargetClass() {
return descriptor.getDependencyType();
}
@Override
public boolean isStatic() {
return false;
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = (beanName != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>(1) : null);
Object target = dlbf.doResolveDependency(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);
if (target == null) {
Class<?> type = getTargetClass();
if (Map.class == type) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
else if (List.class == type) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
else if (Set.class == type || Collection.class == type) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(descriptor.getResolvableType(),
"Optional dependency not present for lazy injection point");
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (dlbf.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
dlbf.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, beanName);
}
}
}
return target;
}
@Override
public void releaseTarget(Object target) {
}
};
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.setTargetSource(ts);
Class<?> dependencyType = descriptor.getDependencyType();
if (dependencyType.isInterface()) {
pf.addInterface(dependencyType);
}
return pf.getProxy(dlbf.getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
public class QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver extends GenericTypeAwareAutowireCandidateResolver {
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> qualifierTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(2);
private Class<? extends Annotation> valueAnnotationType = Value.class;
/**
* Create a new QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver
* for Spring's standard {@link Qualifier} annotation.
* <p>Also supports JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Qualifier} annotation, if available.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver() {
this.qualifierTypes.add(Qualifier.class);
try {
this.qualifierTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Qualifier",
QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
}
ScopedProxyUtils
根据 proxyTargetClass 来判断是使用JDK动态代理还是CGLib代理
关键点在于,新建了一个BeanDefinition - proxyDefinition ,并将其 beanClass 设置为了 ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class
将原BeanDefinition注册到 registry 中,同时返回包装了 proxyDefinition 的 BeanDefinitionHolder
public abstract class ScopedProxyUtils {
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(BeanDefinitionHolder definition,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) {
String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();
BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName);
// Create a scoped proxy definition for the original bean name,
// "hiding" the target bean in an internal target definition.
RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);
proxyDefinition.setDecoratedDefinition(new BeanDefinitionHolder(targetDefinition, targetBeanName));
proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(targetDefinition);
proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource());
proxyDefinition.setRole(targetDefinition.getRole());
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName);
if (proxyTargetClass) {
targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// ScopedProxyFactoryBean's "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don't need to set it explicitly here.
}
else {
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Copy autowire settings from original bean definition.
proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate());
proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary());
if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition);
}
// The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy.
targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false);
targetDefinition.setPrimary(false);
// Register the target bean as separate bean in the factory.
registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);
// Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition
// (potentially an inner bean).
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases());
}
}
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 构造方法调用了 registerDefaultFilters,往 includeFilters 添加
- AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class)
- AnnotationTypeFilter(javax.annotation.ManagedBean)
- AnnotationTypeFilter(javax.inject.Named)
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanDefinitionDefaults beanDefinitionDefaults = new BeanDefinitionDefaults();
@Nullable
private String[] autowireCandidatePatterns;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = AnnotationBeanNameGenerator.INSTANCE;
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
private boolean includeAnnotationConfig = true;
/**
* Create a new {@code ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner} for the given bean factory.
* @param registry the {@code BeanFactory} to load bean definitions into, in the form
* of a {@code BeanDefinitionRegistry}
*/
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, true);
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters) {
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment) {
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, environment,
(registry instanceof ResourceLoader ? (ResourceLoader) registry : null));
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();
}
setEnvironment(environment);
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
}
public class ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider implements EnvironmentCapable, ResourceLoaderAware {
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
}
AnnotationTypeFilter
public class AnnotationTypeFilter extends AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter {
public AnnotationTypeFilter(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) {
this(annotationType, true, false);
}
public AnnotationTypeFilter(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType, boolean considerMetaAnnotations) {
this(annotationType, considerMetaAnnotations, false);
}
public AnnotationTypeFilter(
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType, boolean considerMetaAnnotations, boolean considerInterfaces) {
super(annotationType.isAnnotationPresent(Inherited.class), considerInterfaces);
this.annotationType = annotationType;
this.considerMetaAnnotations = considerMetaAnnotations;
}
}
public abstract class AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter implements TypeFilter {
protected AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter(boolean considerInherited, boolean considerInterfaces) {
this.considerInherited = considerInherited;
this.considerInterfaces = considerInterfaces;
}
}
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
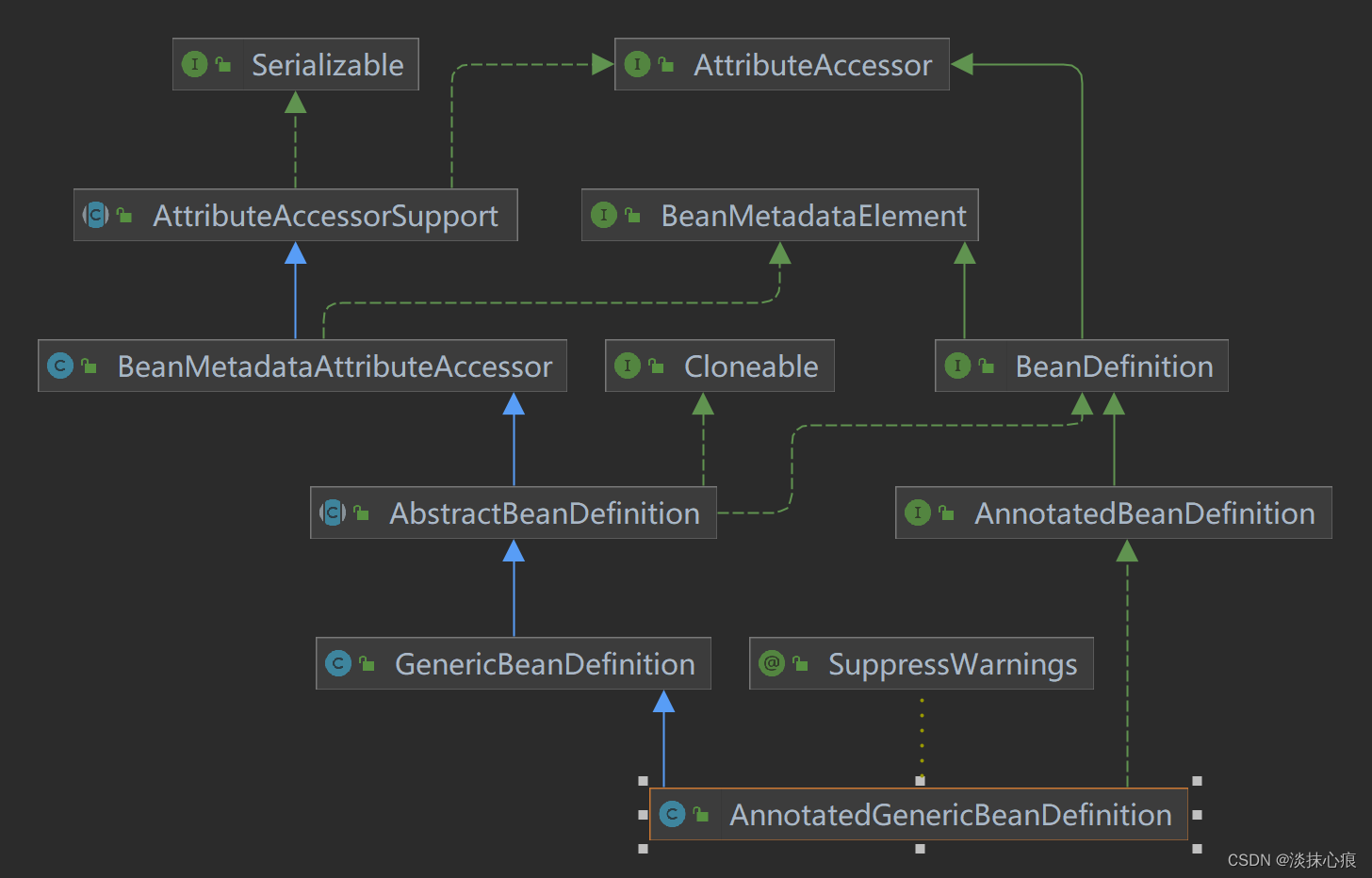
public class AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition {
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
@Nullable
private MethodMetadata factoryMethodMetadata;
/**
* Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given bean class.
* @param beanClass the loaded bean class
*/
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) {
setBeanClass(beanClass);
this.metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass);
}
}
StandardAnnotationMetadata
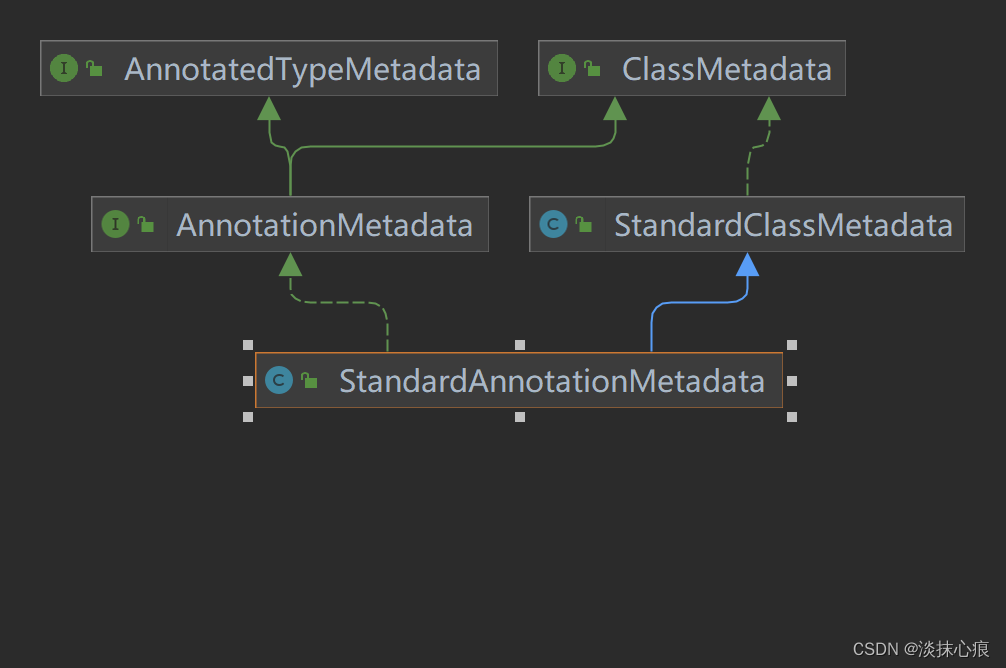
public interface AnnotationMetadata extends ClassMetadata, AnnotatedTypeMetadata {
static AnnotationMetadata introspect(Class<?> type) {
return StandardAnnotationMetadata.from(type);
}
}
public class StandardAnnotationMetadata extends StandardClassMetadata implements AnnotationMetadata {
private final MergedAnnotations mergedAnnotations;
private final boolean nestedAnnotationsAsMap;
@Nullable
private Set<String> annotationTypes;
static AnnotationMetadata from(Class<?> introspectedClass) {
return new StandardAnnotationMetadata(introspectedClass, true);
}
public StandardAnnotationMetadata(Class<?> introspectedClass, boolean nestedAnnotationsAsMap) {
super(introspectedClass);
this.mergedAnnotations = MergedAnnotations.from(introspectedClass,
SearchStrategy.INHERITED_ANNOTATIONS, RepeatableContainers.none());
this.nestedAnnotationsAsMap = nestedAnnotationsAsMap;
}
}
TypeMappedAnnotations
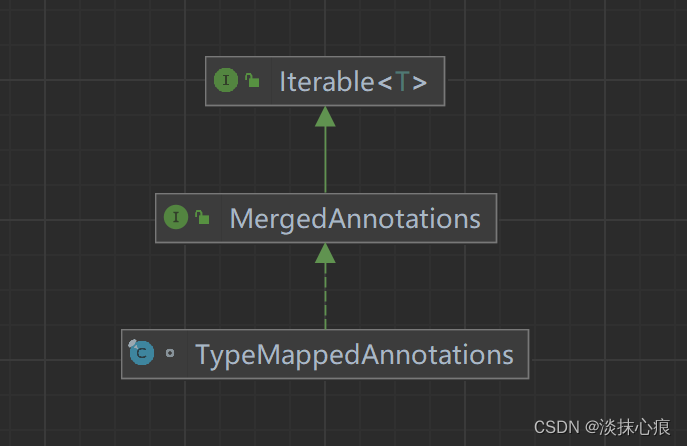
// 合并了元注解的注解
public interface MergedAnnotations extends Iterable<MergedAnnotation<Annotation>> {
static MergedAnnotations from(AnnotatedElement element, SearchStrategy searchStrategy,
RepeatableContainers repeatableContainers) {
return from(element, searchStrategy, repeatableContainers, AnnotationFilter.PLAIN);
}
static MergedAnnotations from(AnnotatedElement element, SearchStrategy searchStrategy,
RepeatableContainers repeatableContainers, AnnotationFilter annotationFilter) {
Assert.notNull(repeatableContainers, "RepeatableContainers must not be null");
Assert.notNull(annotationFilter, "AnnotationFilter must not be null");
return TypeMappedAnnotations.from(element, searchStrategy, repeatableContainers, annotationFilter);
}
}
final class TypeMappedAnnotations implements MergedAnnotations {
private TypeMappedAnnotations(AnnotatedElement element, SearchStrategy searchStrategy,
RepeatableContainers repeatableContainers, AnnotationFilter annotationFilter) {
this.source = element;
this.element = element;
this.searchStrategy = searchStrategy;
this.annotations = null;
this.repeatableContainers = repeatableContainers;
this.annotationFilter = annotationFilter;
}
static MergedAnnotations from(AnnotatedElement element, SearchStrategy searchStrategy,
RepeatableContainers repeatableContainers, AnnotationFilter annotationFilter) {
if (AnnotationsScanner.isKnownEmpty(element, searchStrategy)) {
return NONE;
}
return new TypeMappedAnnotations(element, searchStrategy, repeatableContainers, annotationFilter);
}
}
GenericApplicationContext
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory
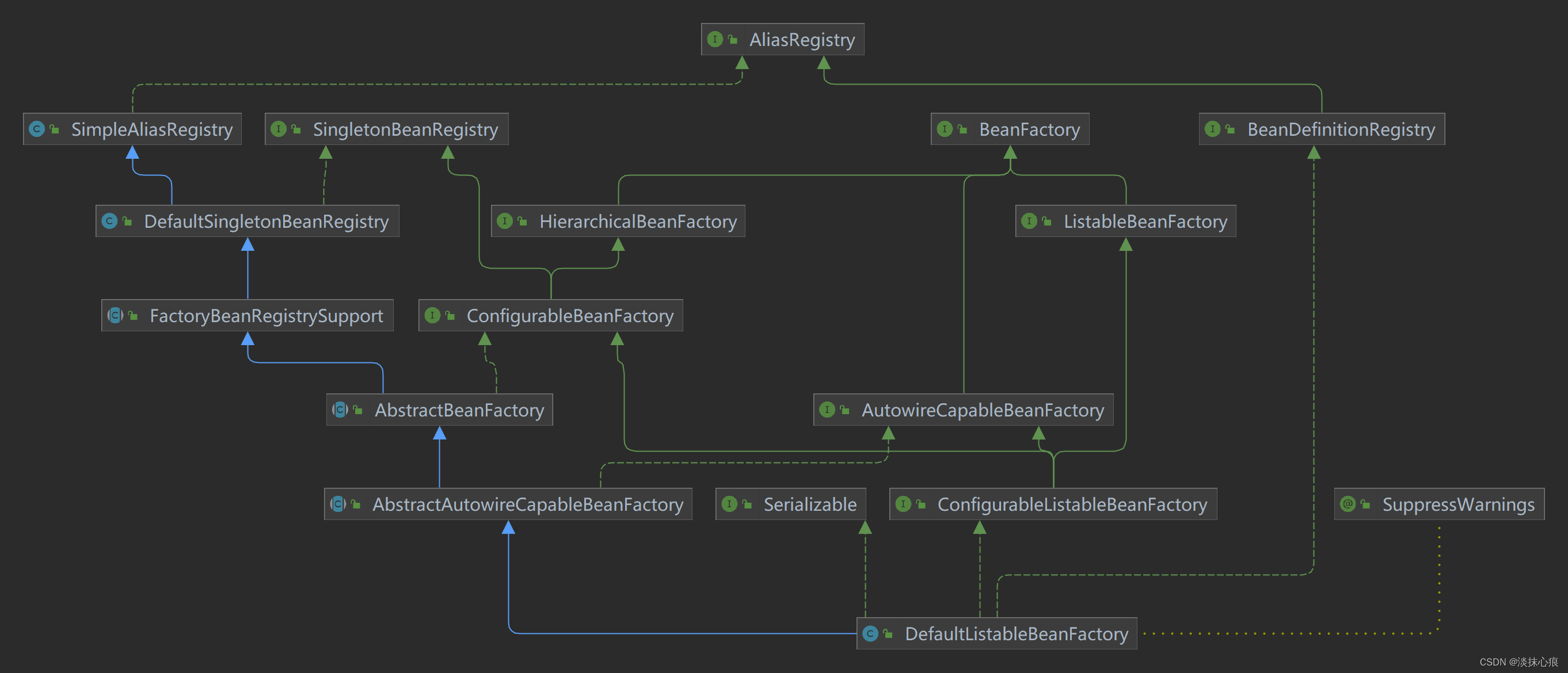
以下是 DefaultListableBeanFactory 及其父类的无参构造和属性
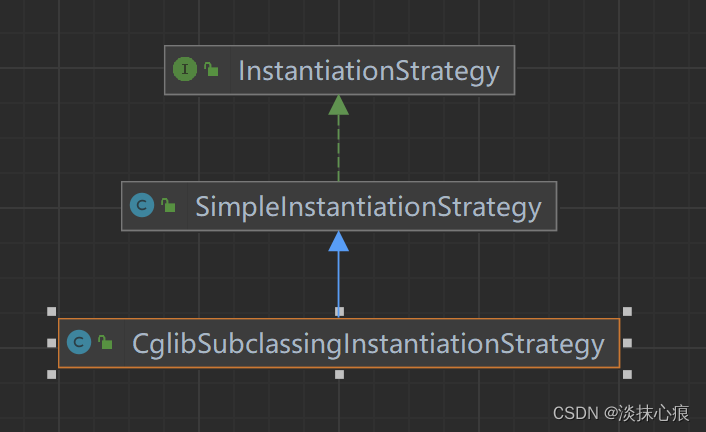
其中 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 初始化了 DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer 和 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy
DefaultListableBeanFactory 赋值 SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
/** Map from serialized id to factory instance. */
private static final Map<String, Reference<DefaultListableBeanFactory>> serializableFactories =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>(8);
/** Optional id for this factory, for serialization purposes. */
@Nullable
private String serializationId;
/** Whether to allow re-registration of a different definition with the same name. */
private boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding = true;
/** Whether to allow eager class loading even for lazy-init beans. */
private boolean allowEagerClassLoading = true;
/** Optional OrderComparator for dependency Lists and arrays. */
@Nullable
private Comparator<Object> dependencyComparator;
/** Resolver to use for checking if a bean definition is an autowire candidate. */
private AutowireCandidateResolver autowireCandidateResolver = SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver.INSTANCE;
/** Map from dependency type to corresponding autowired value. */
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> resolvableDependencies = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Map from bean name to merged BeanDefinitionHolder. */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinitionHolder> mergedBeanDefinitionHolders = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Map of singleton and non-singleton bean names, keyed by dependency type. */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> allBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/** Map of singleton-only bean names, keyed by dependency type. */
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> singletonBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order. */
private volatile List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<>(256);
/** List of names of manually registered singletons, in registration order. */
private volatile Set<String> manualSingletonNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
/** Cached array of bean definition names in case of frozen configuration. */
@Nullable
private volatile String[] frozenBeanDefinitionNames;
/** Whether bean definition metadata may be cached for all beans. */
private volatile boolean configurationFrozen;
public DefaultListableBeanFactory() {
super();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
/** Strategy for creating bean instances. */
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy;
/** Resolver strategy for method parameter names. */
@Nullable
private ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
/** Whether to automatically try to resolve circular references between beans. */
private boolean allowCircularReferences = true;
/**
* Whether to resort to injecting a raw bean instance in case of circular reference,
* even if the injected bean eventually got wrapped.
*/
private boolean allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping = false;
/**
* Dependency types to ignore on dependency check and autowire, as Set of
* Class objects: for example, String. Default is none.
*/
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyTypes = new HashSet<>();
/**
* Dependency interfaces to ignore on dependency check and autowire, as Set of
* Class objects. By default, only the BeanFactory interface is ignored.
*/
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyInterfaces = new HashSet<>();
/**
* The name of the currently created bean, for implicit dependency registration
* on getBean etc invocations triggered from a user-specified Supplier callback.
*/
private final NamedThreadLocal<String> currentlyCreatedBean = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Currently created bean");
/** Cache of unfinished FactoryBean instances: FactoryBean name to BeanWrapper. */
private final ConcurrentMap<String, BeanWrapper> factoryBeanInstanceCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/** Cache of candidate factory methods per factory class. */
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Method[]> factoryMethodCandidateCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/** Cache of filtered PropertyDescriptors: bean Class to PropertyDescriptor array. */
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, PropertyDescriptor[]> filteredPropertyDescriptorsCache =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
if (NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {
this.instantiationStrategy = new SimpleInstantiationStrategy();
}
else {
this.instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy();
}
}
public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) {
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc);
}
}
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
/** Parent bean factory, for bean inheritance support. */
@Nullable
private BeanFactory parentBeanFactory;
/** ClassLoader to resolve bean class names with, if necessary. */
@Nullable
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
/** ClassLoader to temporarily resolve bean class names with, if necessary. */
@Nullable
private ClassLoader tempClassLoader;
/** Whether to cache bean metadata or rather reobtain it for every access. */
private boolean cacheBeanMetadata = true;
/** Resolution strategy for expressions in bean definition values. */
@Nullable
private BeanExpressionResolver beanExpressionResolver;
/** Spring ConversionService to use instead of PropertyEditors. */
@Nullable
private ConversionService conversionService;
/** Custom PropertyEditorRegistrars to apply to the beans of this factory. */
private final Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> propertyEditorRegistrars = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
/** Custom PropertyEditors to apply to the beans of this factory. */
private final Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> customEditors = new HashMap<>(4);
/** A custom TypeConverter to use, overriding the default PropertyEditor mechanism. */
@Nullable
private TypeConverter typeConverter;
/** String resolvers to apply e.g. to annotation attribute values. */
private final List<StringValueResolver> embeddedValueResolvers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
/** BeanPostProcessors to apply. */
private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new BeanPostProcessorCacheAwareList();
/** Cache of pre-filtered post-processors. */
@Nullable
private volatile BeanPostProcessorCache beanPostProcessorCache;
/** Map from scope identifier String to corresponding Scope. */
private final Map<String, Scope> scopes = new LinkedHashMap<>(8);
/** Security context used when running with a SecurityManager. */
@Nullable
private SecurityContextProvider securityContextProvider;
/** Map from bean name to merged RootBeanDefinition. */
private final Map<String, RootBeanDefinition> mergedBeanDefinitions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Names of beans that have already been created at least once. */
private final Set<String> alreadyCreated = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256));
/** Names of beans that are currently in creation. */
private final ThreadLocal<Object> prototypesCurrentlyInCreation =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Prototype beans currently in creation");
/** Application startup metrics. **/
private ApplicationStartup applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT;
public AbstractBeanFactory() {}
}
public abstract class FactoryBeanRegistrySupport extends DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry {
/** Cache of singleton objects created by FactoryBeans: FactoryBean name to object. */
private final Map<String, Object> factoryBeanObjectCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
}
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
/** Maximum number of suppressed exceptions to preserve. */
private static final int SUPPRESSED_EXCEPTIONS_LIMIT = 100;
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
/** Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order. */
private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(256);
/** Names of beans that are currently in creation. */
private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
/** Names of beans currently excluded from in creation checks. */
private final Set<String> inCreationCheckExclusions =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
/** Collection of suppressed Exceptions, available for associating related causes. */
@Nullable
private Set<Exception> suppressedExceptions;
/** Flag that indicates whether we're currently within destroySingletons. */
private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
/** Disposable bean instances: bean name to disposable instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> disposableBeans = new LinkedHashMap<>();
/** Map between containing bean names: bean name to Set of bean names that the bean contains. */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
/** Map between dependent bean names: bean name to Set of dependent bean names. */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/** Map between depending bean names: bean name to Set of bean names for the bean's dependencies. */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
}
public class SimpleAliasRegistry implements AliasRegistry {
/** Map from alias to canonical name. */
private final Map<String, String> aliasMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
}
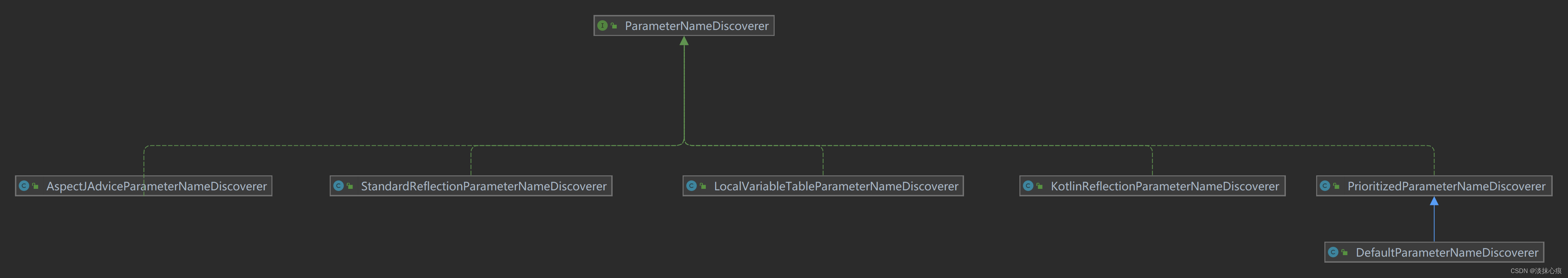
DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer
/**
* Default implementation of the {@link ParameterNameDiscoverer} strategy interface,
* using the Java 8 standard reflection mechanism (if available), and falling back
* to the ASM-based {@link LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer} for checking
* debug information in the class file.
*
* <p>If a Kotlin reflection implementation is present,
* {@link KotlinReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer} is added first in the list and
* used for Kotlin classes and interfaces. When compiling or running as a GraalVM
* native image, the {@code KotlinReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer} is not used.
*
* <p>Further discoverers may be added through {@link #addDiscoverer(ParameterNameDiscoverer)}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sebastien Deleuze
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 4.0
* @see StandardReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer
* @see LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer
* @see KotlinReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer
*/
public class DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer extends PrioritizedParameterNameDiscoverer {
public DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer() {
// TODO Remove this conditional inclusion when upgrading to Kotlin 1.5, see https://youtrack.jetbrains.com/issue/KT-44594
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && !NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {
addDiscoverer(new KotlinReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer());
}
addDiscoverer(new StandardReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer());
addDiscoverer(new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer());
}
}
/**
* {@link ParameterNameDiscoverer} implementation that tries several discoverer
* delegates in succession. Those added first in the {@code addDiscoverer} method
* have the highest priority. If one returns {@code null}, the next will be tried.
*
* <p>The default behavior is to return {@code null} if no discoverer matches.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
*/
public class PrioritizedParameterNameDiscoverer implements ParameterNameDiscoverer {
private final List<ParameterNameDiscoverer> parameterNameDiscoverers = new ArrayList<>(2);
/**
* Add a further {@link ParameterNameDiscoverer} delegate to the list of
* discoverers that this {@code PrioritizedParameterNameDiscoverer} checks.
*/
public void addDiscoverer(ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd) {
this.parameterNameDiscoverers.add(pnd);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] getParameterNames(Method method) {
for (ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd : this.parameterNameDiscoverers) {
String[] result = pnd.getParameterNames(method);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] getParameterNames(Constructor<?> ctor) {
for (ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd : this.parameterNameDiscoverers) {
String[] result = pnd.getParameterNames(ctor);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
}
CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy
/**
* Default object instantiation strategy for use in BeanFactories.
*
* <p>Uses CGLIB to generate subclasses dynamically if methods need to be
* overridden by the container to implement <em>Method Injection</em>.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 1.1
*/
public class CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy extends SimpleInstantiationStrategy {
/**
* Index in the CGLIB callback array for passthrough behavior,
* in which case the subclass won't override the original class.
*/
private static final int PASSTHROUGH = 0;
/**
* Index in the CGLIB callback array for a method that should
* be overridden to provide <em>method lookup</em>.
*/
private static final int LOOKUP_OVERRIDE = 1;
/**
* Index in the CGLIB callback array for a method that should
* be overridden using generic <em>method replacer</em> functionality.
*/
private static final int METHOD_REPLACER = 2;
}
/**
* Simple object instantiation strategy for use in a BeanFactory.
*
* <p>Does not support Method Injection, although it provides hooks for subclasses
* to override to add Method Injection support, for example by overriding methods.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.1
*/
public class SimpleInstantiationStrategy implements InstantiationStrategy {
private static final ThreadLocal<Method> currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
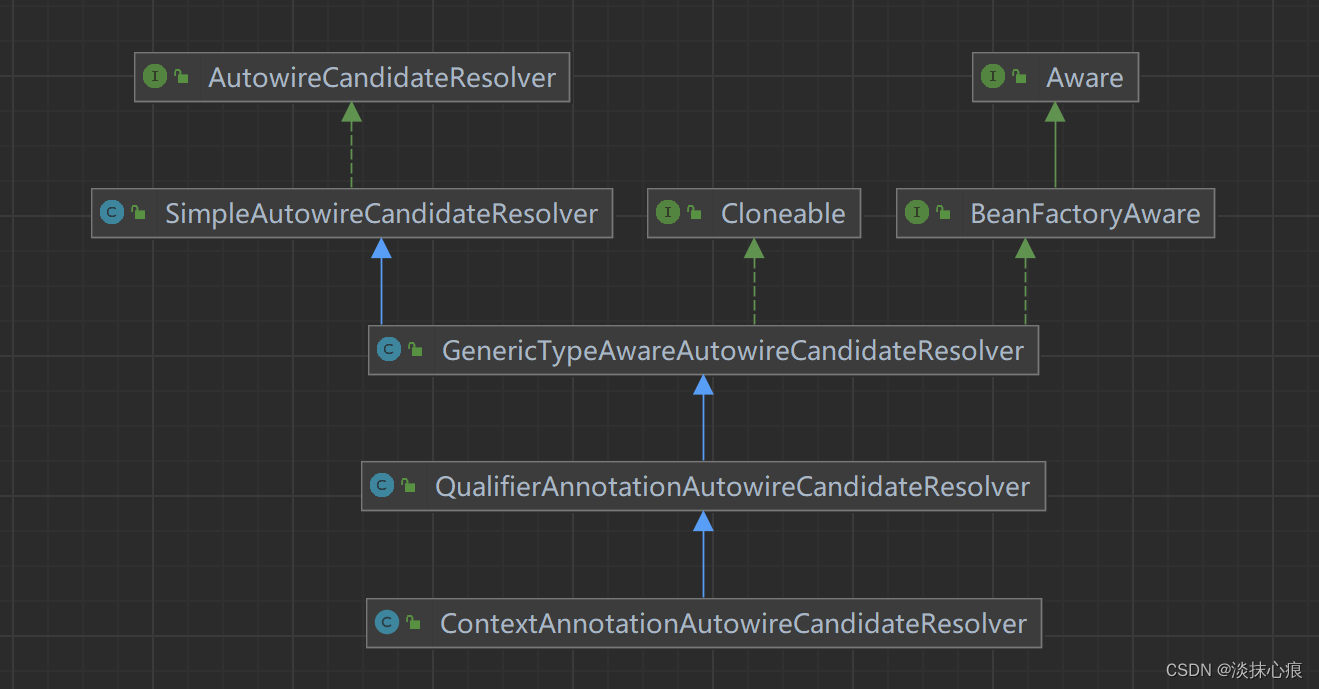
SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver
/**
* {@link AutowireCandidateResolver} implementation to use when no annotation
* support is available. This implementation checks the bean definition only.
*
* @author Mark Fisher
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.5
*/
public class SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver implements AutowireCandidateResolver {
/**
* Shared instance of {@code SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver}.
* @since 5.2.7
*/
public static final SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver INSTANCE = new SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver();
}
AbstractApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 接口的抽象实现类,使用的是模板方法设计模式,下面两个抽象方法子类必须实现
- refreshBeanFactory()
- getBeanFactory()
与 BeanFactory 不同,ApplicationContext 应该检测其内部 BeanFactory 中定义的特殊bean。这些特殊Bean包括
- BeanFactoryPostProcessors
- BeanPostProcessors
- ApplicationListeners
- MessageSource
- ApplicationEventMulticaster
同时继承了 DefaultResourceLoader,加载类路径资源
也实现了 ConfigurableEnvironment接口,createEnvironment()创建环境
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
public DefaultResourceLoader() {}
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
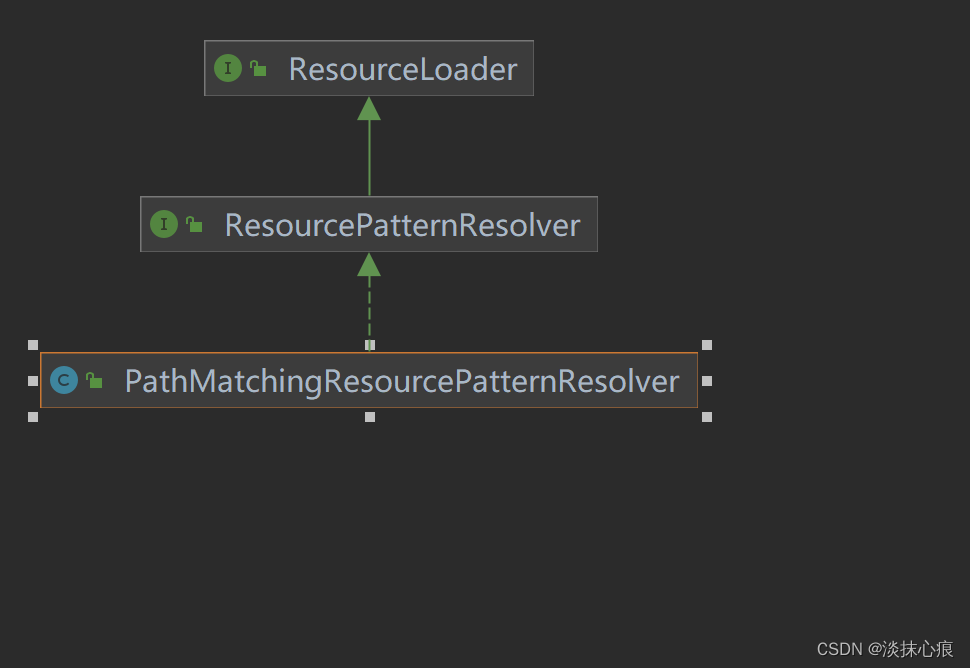
public class PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver implements ResourcePatternResolver {
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
prepareBeanFactory()
为 DefaultListableBeanFactory 设置属性
-
设置beanClassLoader
-
设置beanExpressionResolver
StandardBeanExpressionResolver,主要用于解析spel表达式(#{}),注意与环境变量占位符区分(${}) -
添加PropertyEditorRegistrar,用于注册PropertyEditor,关于PropertyEditor参照另一篇博客
Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> propertyEditorRegistrars.add(ResourceEditorRegistrar) -
注册ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,这是一个很重要的BeanPostProcessor,为实现了xxx_Aware接口的 Bean 注入各种上下文对象
-
忽略Aware接口依赖
-
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, @Nullable Object autowiredValue)
注册默认类型,当注入dependencyType类型时,默认注入autowiredValue,spring内部机制使用,向我们开发者平时注入接口需要执行实现类时,可用@Autowired + @Qualifier 或 @Resource(name)
-
注册ApplicationListenerDetector
检测spring内部实现了ApplicationListener的bean,将其加入applicationEventMulticaster,若applicationEventMulticaster为空,则加入applicationListeners中,在bean被销毁后,也将其从applicationEventMulticaster移除 -
注册环境bean
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) {
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME, getApplicationStartup());
}
}
ResourceEditorRegistrar
public class ResourceEditorRegistrar implements PropertyEditorRegistrar {
private final PropertyResolver propertyResolver;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* Create a new ResourceEditorRegistrar for the given {@link ResourceLoader}
* and {@link PropertyResolver}.
* @param resourceLoader the ResourceLoader (or ResourcePatternResolver)
* to create editors for (usually an ApplicationContext)
* @param propertyResolver the PropertyResolver (usually an Environment)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
*/
public ResourceEditorRegistrar(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, PropertyResolver propertyResolver) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
this.propertyResolver = propertyResolver;
}
/**
* Populate the given {@code registry} with the following resource editors:
* ResourceEditor, InputStreamEditor, InputSourceEditor, FileEditor, URLEditor,
* URIEditor, ClassEditor, ClassArrayEditor.
* <p>If this registrar has been configured with a {@link ResourcePatternResolver},
* a ResourceArrayPropertyEditor will be registered as well.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.InputStreamEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.InputSourceEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.FileEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.URLEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.URIEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.ClassEditor
* @see org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.ClassArrayEditor
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourceArrayPropertyEditor
*/
@Override
public void registerCustomEditors(PropertyEditorRegistry registry) {
ResourceEditor baseEditor = new ResourceEditor(this.resourceLoader, this.propertyResolver);
doRegisterEditor(registry, Resource.class, baseEditor);
doRegisterEditor(registry, ContextResource.class, baseEditor);
doRegisterEditor(registry, WritableResource.class, baseEditor);
doRegisterEditor(registry, InputStream.class, new InputStreamEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, InputSource.class, new InputSourceEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, File.class, new FileEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Path.class, new PathEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Reader.class, new ReaderEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, URL.class, new URLEditor(baseEditor));
ClassLoader classLoader = this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader();
doRegisterEditor(registry, URI.class, new URIEditor(classLoader));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Class.class, new ClassEditor(classLoader));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Class[].class, new ClassArrayEditor(classLoader));
if (this.resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
doRegisterEditor(registry, Resource[].class,
new ResourceArrayPropertyEditor((ResourcePatternResolver) this.resourceLoader, this.propertyResolver));
}
}
/**
* Override default editor, if possible (since that's what we really mean to do here);
* otherwise register as a custom editor.
*/
private void doRegisterEditor(PropertyEditorRegistry registry, Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor editor) {
if (registry instanceof PropertyEditorRegistrySupport) {
((PropertyEditorRegistrySupport) registry).overrideDefaultEditor(requiredType, editor);
}
else {
registry.registerCustomEditor(requiredType, editor);
}
}
}
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor for the given context.
*/
public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.embeddedValueResolver = new EmbeddedValueResolver(applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware ||
bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware)) {
return bean;
}
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
}
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
EmbeddedValueResolver
用于处理占位符和表达式
public class EmbeddedValueResolver implements StringValueResolver {
private final BeanExpressionContext exprContext;
@Nullable
private final BeanExpressionResolver exprResolver;
public EmbeddedValueResolver(ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.exprContext = new BeanExpressionContext(beanFactory, null);
this.exprResolver = beanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver();
}
}
ApplicationListenerDetector
class ApplicationListenerDetector implements DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor, MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ApplicationListenerDetector.class);
private final transient AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final transient Map<String, Boolean> singletonNames = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
public ApplicationListenerDetector(AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
if (ApplicationListener.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) {
this.singletonNames.put(beanName, beanDefinition.isSingleton());
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
try {
ApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster = this.applicationContext.getApplicationEventMulticaster();
multicaster.removeApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
multicaster.removeApplicationListenerBean(beanName);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ApplicationEventMulticaster not initialized yet - no need to remove a listener
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean) {
return (bean instanceof ApplicationListener);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return (this == other || (other instanceof ApplicationListenerDetector &&
this.applicationContext == ((ApplicationListenerDetector) other).applicationContext));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.applicationContext);
}
}
postProcessBeanFactory()
为空方法,留给子类实现
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
主要关注PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors())
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
按照以下优先级大小执行(序号越小优先级越高)
1. BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements PriorityOrdered
2. BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements Ordered
3. BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
4. BeanFactoryPostProcessor implements PriorityOrdered
5. BeanFactoryPostProcessor implements Ordered
6. BeanFactoryPostProcessor
执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
执行流程
先执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(),再执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()
- 查找实现 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- 实例化 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 并添加到集合
- 对 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 集合排序
- 执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()
- 查找实现 Ordered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 并重复步骤2,3,4
- 查找剩下所有的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 并重复步骤2,4
- 执行所有 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()
需要注意的是,Spring内置的 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 永远先执行。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 在前面 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 初始化的时候,通过 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 注册过BeanDefinition
即使我们自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 实现了 PriorityOrdered接口。因为第一次查找时,BeanDefinition并没有我们自己实现的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的BeanDefinition。
当然,如果我们调用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.register() 提前将自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 BeanDefinition 注册进去,应该可以使自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 先执行。
另外,在 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 执行的过程中,可能会注册其他的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 BeanDefiniton。
如 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 解析配置类,可以解析到我们自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 并注册其 BeanDefinition。
所以它并不像执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor那样,一次性获取所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor然后分类、排序、执行。
在每次执行某类 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 前,都会重新调用BeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType() 来获取最新的结果
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
详细解读请参考另一篇博客 Spring加载配置类
-
实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 用于解析主配置类的注解,注册主配置类及相关类的 BeanDefinition
-
实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory() 利用动态代理增强配置类(替换 BeanDefinition 的 beanClass 为代理类)
执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
-
查找所有 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的名字
PriorityOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 先实例化再添加到集合
Ordered/nonOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 直接将名字添加到集合 -
PriorityOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 排序并执行
-
实例化 Ordered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor ,然后再排序并执行
-
实例化 nonOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor , 然后再排序并执行
这里有一点待研究
priorityOrderedPostProcessors 集合类型为 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>
其他两种则为 List<String>
为什么不把其他两种也声明为 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>
在 registerBeanPostProcessors() 也是如此
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
这时会实例化并执行 Spring 内置的 EventListenerMethodProcessor
EventListenerMethodProcessor
Registers EventListener methods as individual ApplicationListener instances. Implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor (as of 5.1) primarily for early retrieval, avoiding AOP checks for this processor bean and its EventListenerFactory delegates.
public class EventListenerMethodProcessor
implements SmartInitializingSingleton, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false);
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories);
this.eventListenerFactories = factories;
}
}
实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()
调用 beanFactory.getBeansOfType() 获取 EventListenerFactory,此前在AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 的时候已经注册了 DefaultEventListenerFactory 的 BeanDefinition,因此此处会注册 DefaultEventListenerFactory 实例。
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate代码
final class PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate {
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors()
分了四类 BeanProcessor 进行注册
priorityOrderedPostProcessors - 直接存储 BeanPostProcessor
internalPostProcessors - priorityOrderedPostProcessors和nonOrderedPostProcessorNames 的子集
orderedPostProcessorNames - 存储 BeanPostProcessor BeanDefinition 的 key name
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames - 存储 BeanPostProcessor BeanDefinition 的 key name
注册过程
-
注册 BeanPostProcessorChecker
BeanPostProcessor that logs an info message when a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
-
调用 DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType() 查找所有 BeanPostProcessor,并分类
-
对 priorityOrderedPostProcessors 排序、注册
-
根据 orderedPostProcessorNames 实例化 BeanPostProcessor ,然后排序、注册
-
根据 orderedPostProcessorNames 实例化 BeanPostProcessor ,然后注册
-
重新注册 internalPostProcessors ,使其排到最后
-
重新注册 ApplicationListenerDetector,使其排在最后,用于检测内部 bean 是否为 ApplicationListener
需要注意的是,这里的注册不是注册 BeanPostProcessors 的 BeanDefinition,而是将 BeanPostProcessor 添加到 DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanPostProcessors 里
在执行完 registerBeanPostProcessors() 后,DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanPostProcessors 存在6个 BeanPostProcessors及其排序如下:
0 = {ApplicationContextAwareProcessor}
1 = {ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor}
2 = {PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker}
3 = {CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
4 = {AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
5 = {ApplicationListenerDetector}
其中有三个 BeanPostProcessor 在之前已经注册过了,但并未注册 BeanDefinition,也没有加到 registeredSingletons,因此第2步并不会找到这些 BeanPostProcessor
0 = {ApplicationContextAwareProcessor}
1 = {ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor}
5 = {ApplicationListenerDetector}
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 和 ApplicationListenerDetector 是在 refresh() 方法的 prepareBeanFactory() 中加进去的
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor 是在 ConfigurationClassProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 加进去的
另外有两个 BeanPostProcessor 在之前注册了 BeanDefinition,会在第2步被找到并注册
2 = {org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor - AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
3 = {org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor - CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
这两个 BeanPostProcessor 的 BeanDefinition 同 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、EventListenerMethodProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory 的 BeanDefinition,是在前面 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 初始化的时候,通过 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 注册过BeanDefinition
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理 @Autowired 注解
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理普通的注解 @PostConstruct,@PreDestroy等等
initApplicationEventMulticaster()
注册事件多播器 ApplicationEventMulticaster,主要用于管理事件监听器和发布事件(观察者模式)
Spring默认实现了一个多播器 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
registerListeners()
注册 ApplicationListener
finishBeanFactoryInitialization()
经过前面的步骤,Spring已经将其内置的组件注册进去了,剩下来的是用户自定义的bean还未注册。因此剩下的Bean都会在这里注册,详细过程请参考另一篇文章
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
}






















 6879
6879











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








