为什么要演示这个spring自定义注解呢,以前我觉得代码什么基本都看的懂,但是这天一个老师给我们讲spring基础的时候我懵逼了,他这将的不是教会你简单使用,直接进底层的。直接实现自定义注解,许多公司技术封装也就是这样,也就是spring现在这个反射读取类的过程。
大概过程就是先重写这几个注解,然后在平常业务中调用这些注解,反射读取这个包下的文件,将他们加载进去,通过map来存每一个类名和反射生成的对象,使用的时候通过map的key来找到对应的对象,再去调用。也就是spring容器的作用进行了一个自定义实现的过程。

anntation下面
package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface UdaAutowired {
boolean required() default true;
}
package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Indexed;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Indexed
public @interface UdaComponent {
String value() default "";
}
package com.example.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface UdaController {
String value() default "";
}
package com.example.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.Mapping;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface UdaRequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}
package com.example.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface UdaService {
String value() default "";
}
autoconfig
package com.example.autoconfig;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class UdaBeanFactory {
private Map<String ,Object>beanMap=new HashMap<String,Object>();
//beanMap存实列的key,value;
public Object createBean(Class<?> clz,String name) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException { //clz: com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao name:就是注解上加的东西比如@UdaComponent(“你是谁”),说就是你是谁几个字
Object instance=clz.newInstance();
//实例化一个Bean工厂类
if(name==null||name.length()==0){ //name:"u" 因为我在注解里加了个字母u
beanMap.put(lowerCase(clz.getSimpleName()),instance);
}else {
beanMap.put(name,instance);
}
beanMap.put(clz.getName(),instance); //这个beanMap里面存了两个元素,一个是key="com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao" value="UserDao@582" 一个是key="u",value="UserDao@582"
return instance;
}
private String lowerCase(String str){
return str.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + str.substring(1);
}
public void injectionFileId(Class<?>clz, Field field)throws IllegalAccessException{
Class<?> type=field.getType();
Object curObj =beanMap.get(clz.getName()); //通过类名获取到这个对象,也就是UserService@719
field.setAccessible(true);
Object injectObj =beanMap.get(type.getName()); //成员变量上的这个UserDao对象,也就是UserDao@582
field.set(curObj,injectObj);
}
public Map<String,Object> getBeans(){
return beanMap;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getBean(Class<?> clz) {
return (T) beanMap.get(clz.getName());
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) beanMap.get(name);
}
}
package com.example.autoconfig;
import com.example.annotation.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author : XuZhiYong
* @Description :
* @Date : Created in 11:20 2021/5/21
*/
//自定义Spring容器
public class UdaSpringContext {
private UdaBeanFactory beanFactory = new UdaBeanFactory();
public void initContext(String path) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
path = path.replace(".", "/"); //将com.example.ioc转变成com/example/ioc
ClassLoader classLoader = UdaSpringContext.class.getClassLoader();//类加载器这个是自定义的所以是classLoader:Launcher$AppClassLoader@497
URL url = classLoader.getResource(path);//path: "com/example/ioc" classLoader:Launcher$AppClassLoader@497 url:file:/C:/Users/study/IdeaProjects/springself/target/classes/com/example/ioc
//通过类加载器取得URL地址
File file = new File(url.getPath());
//取得根目录下所有的文件地址
List<File> clzList = new ArrayList<File>();
getFileList(file, clzList);
List<Class<?>> classList = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
for (File clz : clzList) {
//C:\Users\study\IdeaProjects\springself\target\classes\com\example\ioc\dao\UserDao.class
//C:\Users\study\IdeaProjects\springself\target\classes\com\example\ioc\service\Userservice.class 这两个
String apath = clz.getAbsolutePath();
//得到绝对地址
apath = apath.replace("\\", "/");
int pre = apath.indexOf(path); //判断这个路径出现/com/example/ioc的位置,就是第54
String clzName = apath.substring(pre); //从第54的位置截断就剩下com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao
clzName = clzName.replace(".class", "").replace("/", ".");
//得到类名
Class<?> loadClass = classLoader.loadClass(clzName); //clzName:"class com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao" 因为只是读取到了这个类名,并没有加载运行
//把类加载到运行池中
//扫描带有UdaComponent注解的
UdaComponent annotation = loadClass.getAnnotation(UdaComponent.class); //loadClass clzName:"class com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao"
//扫描带有UdaService注解的
UdaService serviceAnno=loadClass.getAnnotation(UdaService.class); //annotation:@com.example.annotation.UdaComponent(value=u)
//扫描取得项目注解,先扫描的dao里面出现的@UdaComponent注解
if (annotation != null) {
String name = annotation.value();
//注解定义的名字
beanFactory.createBean(loadClass, name);
//创建一个Bean工厂
classList.add(loadClass);
}else if (serviceAnno!=null){
String name = serviceAnno.value();
//注解定义的名字
beanFactory.createBean(loadClass, name);
//创建一个Bean工厂
classList.add(loadClass);
}
// UdaController controllerAnno=loadClass.getAnnotation(UdaController.class);
// if (controllerAnno!=null){
// beanFactory.createBean(loadClass,null);
// //类路径
// UdaRequestMapping clzMapping=loadClass.getAnnotation(UdaRequestMapping.class);
// String clzUrl=clzMapping==null?"":clzMapping.name();
// //接下来检查所有的public方法是否带有UpdRequestMapping注解修饰的
// checkMethod(loadClass,createBean,clzUrl);
// classList.add(loadClass);
// }
for(Class<?> LoadClass : classList){
injection(loadClass);
}
/* if(controllerAnno != null){
}*/
}
}
//判断哪个是文件,如果是文件就加载到clzList中
private void getFileList(File file, List<File> clzList) {
if (file.isDirectory()) { //如果该文件是个目录,就再进去一层
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
getFileList(f, clzList);
}
} else {
clzList.add(file); //C:\Users\study\IdeaProjects\springself\target\classes\com\example\ioc\dao\UserDao.class
//C:\Users\study\IdeaProjects\springself\target\classes\com\example\ioc\service\Userservice.class 这两个类就添加到列表里面了
}
}
private void injection(Class<?> loadClass) throws IllegalAccessException{ //这里开始进行反射
Field[] fields=loadClass.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:fields){
UdaAutowired fieldAnno =field.getAnnotation(UdaAutowired.class); //在service里面定义了一个成员变量,所以会执行进来
if(fieldAnno!=null){
beanFactory.injectionFileId(loadClass,field);
}
}
}
public <T> T getBean(Class<?> clz) {
return beanFactory.getBean(clz);
}
public <T> T getBean(String name){
return beanFactory.getBean(name);
}
public Map<String,Object> getBeans(){
return beanFactory.getBeans();
}
}
ioc下
package com.example.ioc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserController {
}
package com.example.ioc.dao;
import com.example.annotation.UdaComponent;
@UdaComponent("u")
public class UserDao {
public void addUser(String name){
System.out.println(String.format("用户[%s]添加成功",name));
}
}
package com.example.ioc.service;
import com.example.annotation.UdaAutowired;
import com.example.annotation.UdaService;
import com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao;
@UdaService
public class Userservice {
@UdaAutowired
UserDao userDao;
public void show(String name){
userDao.addUser(name);
}
}
package com.example;
import com.example.autoconfig.UdaSpringContext;
import com.example.ioc.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.ioc.service.Userservice;
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
UdaSpringContext context=new UdaSpringContext();
//触发自定义容器
try {
System.out.println("开始初始化容器");
long t=System.currentTimeMillis();
context.initContext("com.example.ioc"); //这是平常我们放service,dao包的地方
//扫描包下所有文件加载到容器里面
System.out.println("初始化容器成功,cost time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-t));
Userservice controller1=context.getBean(Userservice.class);
controller1.show("与子安你是个xx");
UserDao userDao=context.getBean(UserDao.class);
userDao.addUser("与子安真是个奴婢");
showBeans(context.getBeans());
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void showBeans(Map<String,Object> map){
for (String key:map.keySet()){
System.out.println("健值为"+key+",对象为"+map.get(key));
}
}
}
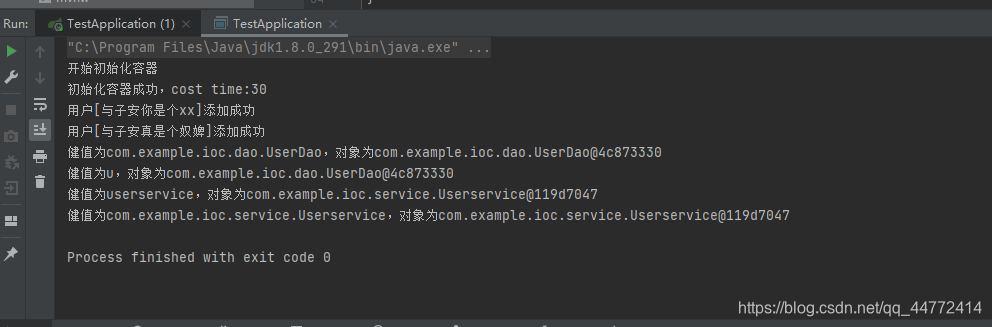
效果图如下























 7654
7654











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








