Spring框架搭建与配置文件
Spring
1. 说在前面
怎样的架构的程序,我们认为是一个优秀的架构?
我们考虑的标准:可维护性好,可扩展性好,性能。
什么叫可扩展性好?
答:就是可以做到,不断的增加代码,但是可以不修改原来的代码的程序。
如何让程序的可维护性好,可扩展性好呢?
业界有一个公认的标准,高内聚,低耦合。
高内聚:就是尽量将代码写在与之功能描述一致的模块中。如User表的操作写在UserDAO里面就不用写在非UserDAO的类里面。
低耦合:就是尽量减少类与类之间的直接关系。(重点)
直接关系: Web层依赖Service ,在Web直接new Service层的类的对象 Service层依赖Dao层,在Service层直接new Dao层的对象
Spring框架就是通过IoC/DI(控制反转/依赖注入)实现程序的解耦。从而提高程序的维护性和扩展性。
2. Spring概述
2.1.Spring是什么
Spring是一个JavaEE轻量级的一站式开发框架。
JavaEE: 就是用于开发B/S的程序。(企业级)
轻量级:使用最少代码启动框架,然后根据你的需求选择,选择你喜欢的模块使用。
重量级:早期有的EJB,开发一个HelloWorld程序都需要引入EBJ的全部模块
一站式:提供了,表示层(Struts2/SpringMVC),服务层,持久层的所有支持。
2.2.Spring框架出现的背景
在世界第一套有Java官方Sun公司推出的企业级开发框架EJB出现后,瞬间风靡全球。被各大公司所应用。
Spring之父,Rod Jonhson是一个音乐博士,在Sun公司的大力推广下,也成为EJB框架的使用者。
在深入研究完EJB框架(由Sun主导开发的一个JavaEE开发框架),无法接收这么一个框架被吹成世界第一,具体查看他吐槽EJB的书《Expert one on one J2EE design and development》
其中突出被他吐槽最厉害的一个点就EJB的重量级,就是只要使用EJB里面任何一个组件。都要将所有EJB的jar导进去。
于是他就提供了一个他的解决方案:轻量级的一站式企业开发框架。
那么什么是轻量级呢?
就是除内核模块(4个jar),其他模块由开发者自由选择使用,同时支持整合其他框架。
也可以称为就是可插拔式开发框架,像插头和插座一样,插上就用。这就是Spring框架核心理念。(Ioc)
那么什么是一站式呢?
就是Spring框架提供涵盖了JavaEE开发的表示层,服务层,持久层的所有组件功能。也就是说,原则上,学完一套Spring框架,不用其他框架就可以完成网站一条流程的开发。
如图:

2.3.Spring框架的作用
根据以上章节的描述。Spring是一个JavaEE一站式的开发框架。它提供的功能涵盖了JavaEE程序中的表示层,服务层,持久层功能组件。这意味着,使用了Spring框架,一个框架就可以满足整个JavaEE程序的开发。
但Spring框架,更加强调的是它的轻量级(模块的可插拔)!!也就是说,除了内核以外模块,如果你不想使用可以不用,它能够整合任何第三方的框架。
所以,在现实开发中,Spring主要用于整合其他框架。
2.4.总结
-
Spring是一个一站式的企业级(JavaEE)开发框架,意味着,仅仅使用一个Spring框架就可以满足JavaEE开发的表示层,服务层,持久层的开发。
-
Spring强调的理念是,轻量级。意味着Spring提供的功能模块,除了内核模块以外,开发人员可以选择性使用。
-
所以,Spring框架在现实开发中,主要的功能用于整合,各种开发来开发项目。
2.5.Spring框架包
Spring官方网站
https://spring.io/
2.5.1.框架包的下载
Spring官方提供的Maven方式的项目下载。
https://start.spring.io/
但是基于简单入门的原则,我们要通过导入包的方式来学习。需要下载框架的zip包
路径为:http://repo.springsource.org/libs-release-local/org/springframework/spring/
2.5.2.目录说明
–根目录
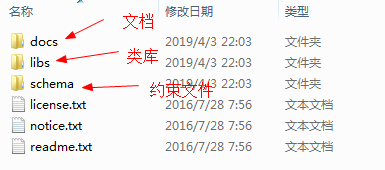
–类库规则

–包说明
包名 说明
spring-aop-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 实现了AOP的支持
spring-aspects-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar AOP框架aspects支持包
spring-beans-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 内核支撑包,实现了处理基于xml对象存取
spring-context-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 内核支撑包,实现了Spring对象容器
spring-context-support-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 容器操作扩展包,扩展了一些常用的容器对象的设置功能
spring-core-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 内核支撑包,Spring的内核
spring-expression-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 内核支撑包,实现了xml对Spring表达式的支持
spring-instrument-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 提供了一些类加载的的工具类
spring-instrument-tomcat-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 提供了一些tomcat类加载的的工具类,实现对应Tomcat服务的调用
spring-jdbc-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar SpringJDBC实现包,一个操作数据库持久层的子框架
spring-jms-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 集成jms的支持,jms:Java消息服务。
spring-messaging-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 集成messaging api和消息协议提供支持
spring-orm-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar ORM框架集成包,实现了Hibernate,IBatis,JDO的集成。
spring-oxm-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar Spring OXM对主流O/X Mapping框架做了一个统一的抽象和封装。就是对应XML读写框架的支持
spring-test-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar Spring集成JUnit测试
spring-tx-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar 事务代理的支持
spring-web-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar SpringWeb通用模块
spring-webmvc-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar SpringMVC子框架
spring-webmvc-portlet-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar Spring对门户技术(portlet)的支持
spring-websocket-4.3.2.RELEASE.jar Spring对websocket的支持
3.入门示例
Spring之所以可以实现模块的可插拔是支持依赖注入,所谓的依赖注入/控制反转就是不用new就可以创建对象。
需求:使用Spring框架不用new创建一个对象。
3.1.配置流程图

- 创建一个普通的类。
- 创建一个Spring配置文件,用于描述类与类之间的关系。
- 创建ApplicationContext容器对象根据Spring配置文件的描述,将对象创建并且放在Spring容器里面。
- 使用ApplicationContext容器对象的getBean方法,调用Spring容器里面的对象。
3.2.配置步骤说明
- 导入包
- 创建一个普通的类
- 创建一个Spring配置文件(去官方文档上拷贝约束)
- 编写一个测试类,使用ApplicationContext的子类对象根据配置文件创建容器。并且在容器里面获得创建的对象
3.3.配置步骤
3.3.1.第一步:搭建环境
1.创建一个Java项目
–选中创建

–创建目录结构
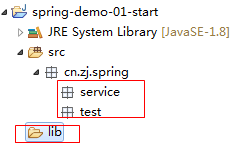
2.导入包,String的基础支撑包和依赖的日志包复制到lib文件下,并且加入项目中
—导入Spring基础支撑包
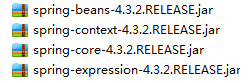
–导入Spring依赖的日志包
3.3.2.-第二步:创建配置文件
- 在项目的src下面创建配置文件applicationContext.xml中并完成配置文件的约束,约束查找位置(spring框架/docs/spring-framework-reference/html/beans.html)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
3.3.3.第三步:创建对象到容器里面
- 创建一个类
package com.zj.service;
public class HelloWorldService {
public void say(){
System.out.println("--你好世界!--");
}
}
- applicationContext.xml配置文件加入配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
<!--
<bean>标签:用于声明一个类,在启动Spring框架的时候根据该配置的类创建对象到容器里面
name
-->
<bean name="helloWorldService" class="com.zj.service.HelloWorldService"></bean>
</beans>
- 测试使用getBean获得容器中的对象。
package com.zj.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.zj.service.HelloWorldService;
public class HelloWorldServiceTest {
@Test
public void say(){
//创建一个ApplicationContext对象,根据xml配置创建一个对象
//直接读取Spring的src目录下的配置文件的子类是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorldService helloWorldService = context.getBean("helloWorldService", HelloWorldService.class);
//调用方法
helloWorldService.say();
}
}
通过代码得到,Spring框架果然不用new就可以创建对象。
3.4.Eclipse提示xml文件语法
1.联网
2.手动关联约束window->preferences

3.5.Spring容器的两个实现
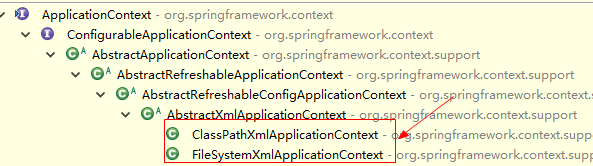
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:通过classpath路径直接获得加载的xml文件(推荐使用)
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:通过文件路径来获得加载的xml文件。

3.6.ApplicationContext类图结构图(了解)
Spring框架容器对象的继承体系

通过结构图可以看到,Spring容器顶级接口是BeanFactory,ApplicationContext是它的子接口。
4.Spring的IOC控制反转和依赖注入-重点-spring核心之一
IoC:Inverse of Control(控制反转):
读作“反转控制”,更好理解,不是什么技术,而是一种设计思想,好比于MVC。就是将原本在程序中手动创建对象的控制权,交由Spring框架来管理。
正控:若调用者需要使用某个对象,其自身就得负责该对象的创建。
反控:调用者只管负责从Spring容器中获取需要使用的对象,不关心对象的创建过程,也就是把创建对象的控制权反转给了Spring框架。
(Don’t call me ,I’ll call you)
DI:Dependency Injection(依赖注入)
从字面上分析:
IoC:指将对象的创建权,反转给了Spring容器;
DI :指Spring创建对象的过程中,将对象依赖属性(简单值,集合,对象)通过配置设值给该对象。
IoC和DI其实是同一个概念的不同角度描述,DI相对IoC而言,明确描述了“被注入对象依赖IoC容器配置依赖对象”。
Container:容器,在生活中容器就是一种盛放东西的器皿,从程序设计角度看作是装对象的对象,因为存在对对象的存入、取出等操作,所以容器还要管理对象的生命周期。

4.1.IoC(控制反转)的概述
Spring号称是一个可以实现模块可插拔的JavaEE开发框架。那么它是如何实现程序的可插拔的呢?
实现程序可以插拔的核心理念就是,控制反转(Inversion of Control,英文缩写为IoC)
所谓的控制反转,就是将代码的调用权从调用方转移给被调用方(服务提供方)。
如图所示:
-
强耦合调用方式
将A调用B的对象修改为C类的对象,修改的是调用方的代码,所以我们认为代码的调用权在调用方。

-
基于IoC(控制反转)的调用方式
将上图的需求,修改为使用Ioc的调用代码方式。就是将代码的控制权从调用方修改为被调用方,意味着,代码的调用权转移给被调用方(我们也称为服务方),不用修改调用方的的代码
只要修改配置文件就实现对象的切换。
如下图:将A类调用B类的对象修改为C类的对象,修改的是被调用方的配置文件的代码,所以代码的调用权转移到了被调用方。通过控制反转,我们可以实现增加模块或者移除模块统一由配置文件关联,增加或者移除模块,配置XML配置文件即可。
我们将代码的调用权(控制权)从调用方转移给被调用方(服务提供方)的设计模式称为控制反转(IoC)

根据上图可以的得出,实现一个IoC的框架,必须要解决两个问题:
- 被调用方(服务方),在程序启动时就要创建好对象,放在一个容器里面。
- 调用方使用一个接口或类的引用(不用使用new),就可以创建获得对象。
我们将这种不用new,而是根据接口或者类的引用就可以从被调用的容器里获得创建的对象的方式称为依赖注入。
所以,控制反转(Ioc),就是依赖注入加上面向接口的编程思想的实现。
在这里,我们首先抓住一个重点:Spring之所以可以实现可插拔程序,是实现了不用new,使用类或接口就可以获得获得对象!
4.2.项目目录结构

4.3.示例代码
4.3.1.CustomerService接口代码
package cn.zj.spring.service;
public interface CustomerService {
/**
* 保存方法
*/
public void save();
}
4.3.2.CustomerServiceImpl子类
package cn.zj.spring.service.impl;
import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService;
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("-保存客户-CustomerServiceImpl");
}
}
4.3.3.CustomerServiceImpl2子类
package cn.zj.spring.service.impl;
import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService;
public class CustomerServiceImpl2 implements CustomerService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("-保存客户-CustomerServiceImpl2");
}
}
4.3.4.CustomerClient类(调用方)
package cn.zj.spring.client;
import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService;
public class CustomerClient {
//1.声明一个父接口的引用
private CustomerService customerService;
//2.使用set方法注入对象,我们将通过方法注入的对象的方式称为依赖注入
public void setCustomerService(CustomerService customerService) {
this.customerService = customerService;
}
public void save(){
//调用服务端的方法
customerService.save();;
}
}
4.3.5.配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- <bean>标签:用于声明一个类,在启动Spring框架的时候根据该配置的类创建对象到容器里面 name -->
<!-- <bean name="customerServiceImpl" class="cn.zj.spring.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl"></bean> -->
<!--
CustomerServiceImpl修改为CustomerServiceImpl2的配置
-->
<bean name="customerServiceImpl" class="cn.zj.spring.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl2"></bean>
<bean name="customerClient" class="cn.zj.spring.client.CustomerClient">
<!-- 对应set方法关联的对象 customerService
name:关联对应的set方法,关联规则:xxx对应setXxx();如:customerService() 对应setCustomerService()
ref:指向容器中的对象
-->
<property name="customerService" ref="customerServiceImpl"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
4.3.6.测试代码
package cn.zj.spring.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.zj.spring.client.CustomerClient;
public class ClientTest {
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerClient customerClient = context.getBean("customerClient", CustomerClient.class);
// 调用方法
customerClient.save();
}
}
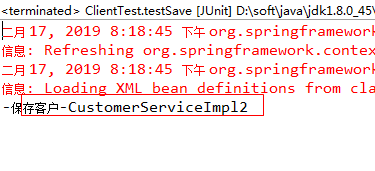
4.3.7. 测试结果
5.标签说明
5.1.alias标签
作用:为已配置的bean设置别名
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" name="test" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.User"/>
<!--
标签alias: 为已配置的bean设置别名
属性name: 必要属性, 代表为哪一个bean配置别名,
此属性的值为其他bean标签的id或name属性值
属性alias: 必要属性, 代表新命名的别名是什么
-->
<alias name="user" alias="user1"/>
</beans>
–测试代码
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.zj.entity.User;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 读取Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml");
// 通过id获取User对象
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
// 测试对象
System.out.println(user);
System.out.prntln("=====================================");
// 通过alias获取User对象
user = (User) context.getBean("user1");
// 测试对象
System.out.println(user);
}
}
5.2.bean标签的配置
5.2.1. bean标签作用
用于声明一个类,在启动Spring框架的时候根据该配置的类创建对象到容器里面
5.2.2.属性说明
<!-- <bean>标签:用于声明一个类,在启动Spring框架的时候根据该配置的类创建对象到容器里面
name:设置对象名(唯一标识符),可以有多个名称,每个名称用逗号隔开 : name1,name2
id:设置对象名(唯一标识符,功能和name一样)
class:用于指定对象对应的类名
scope:用于设置的对象的作用范围,可选参数如下:
*singleton:单例(默认)
对象出生:当程序加载配置文件创建容器时,创建
对象活着:只要容器还在,一直活着
对象死亡:应用停止,容器销毁,对象死亡
*prototype:多例(原型对象)
对象出生:当程序加载配置文件创建容器时,创建
对象活着:只要对象被使用,一直活着
对象死亡:对象长时间不用,会被Java垃圾回收机制回收
*reqeust:web项目中,Spring将创建的对象放在request作用域中
*session:web项目中,Spring将创建的对象放在session作用域中
*globalSession:web项目中,应用域portlet环境,如果没有protlet环境相当于session
init-method:设置创建对象的时候,调用初始化方法
destroy-method:设置对象被回收时,调用注销的方法
-->
<bean name="customerServiceImpl" class="com.zj.spring.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl"></bean>
5.2.3.Bean作用范围
作用范围也可以说生命周期(bean能存活多久)
<bean id="" class="" scope="作用域"/>
singleton
单例 ,在Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例 (默认的scope)
prototype 多例 ,每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时 ,相当于执行new XxxBean():
request 用于web开发,将Bean放入request范围 ,request.setAttribute(“xxx”) , 在同一个request 获得同一个Bean
==session 用于web开发,将Bean 放入Session范围,在同一个Session 获得同一个Bean ==
在开发中主要使用 scope=“singleton”、scope=“prototype”
对于MVC中的Action/Controller使用prototype类型,其他使用singleton
在Web开发的三层架构中
Web:一般都是多例
Service :单例
DAO :单例
5.3.实例化Bean的四种方式
Spring创建Java的四种方式
5.3.1.构造器实例化(无参数构造器),最标准,使用最多。
public class SomeBean1 {
public SomeBean1() {
System.out.println(“SomeBean.SomeBean1()”);
}
}
配置文件
<bean id="someBean1" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.SomeBean1"></bean>
5.3.2.通过静态方法工厂创建(了解)
–静态工厂类
SomeBean2/SomeBean2Facotry
public class SomeBean2 {
public SomeBean2() {
System.out.println(“SomeBean.SomeBean2()”);
}
}
public class SomeBean2Facotry {
//静态工厂方法
public static SomeBean2 getSomeBean2() {
System.out.println(“执行静态工厂方法”);
return new SomeBean2();
}
}
–静态工厂配置
<bean id="someBean2" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.SomeBean2Facotry"
factory-method="getSomeBean2"></bean>
5.3.3.通过实体工厂创建(了解)
–实体工厂
public class SomeBean3 {
public SomeBean3() {
System.out.println(“SomeBean.SomeBean3()”);
}
}
public class SomeBean3Facotry {
//实例工厂方法
public SomeBean3 getSomeBean3() {
System.out.println(“执行实例工厂方法”);
return new SomeBean3();
}
}
–配置方式
<!-- 1.配置工厂bean -->
<bean id="someBean3Factory" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.SomeBean3Facotry"></bean>
<!-- 2.配置bena
factory-bean : 创建bean的工厂对象对应的 id
factory-method : 工厂bean中返回 bean对象的方法
-->
<bean id="someBean3" factory-bean="someBean3Factory" factory-method="getSomeBean3"/>
5.3.4.实现FactoryBean接口实例化:实例工厂变种(了解)
实现FactoryBean接口,MyBatis和Spring集成就是使用的这种方式
此种方式,如果没有使用Bean对应的对象,Spring就不会自动创建,只有在使用的时候Spring才会创建对应的对象
public class SomeBean4 {
public SomeBean4() {
System.out.println(“SomeBean4.SomeBean4()”);
}
}
public class SomeBean4ObjectFactory implements FactoryBean{
//返回的泛型类型对应的对象
@Override
public SomeBean4 getObject() throws Exception {
SomeBean4 bean4 = new SomeBean4();
return bean4;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}
–配置方式
5.4.初始化和销毁方法
比如DataSource,SessionFactory最终都需要关闭资源:在Bean销毁之前,都要调用close方法.
init-method:bean生命周期初始化方法,对象创建后就进行调用
destroy-method:容器被销毁的时候,如果bean被容器管理,会调用该方法。
default-init-method
分析原理:
如果bean的scope=“prototype”,那么容器只负责创建和初始化,它并不会被spring容器管理。交给用户自己调用.
<beans xmlns=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:xsi=“http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xsi:schemaLocation=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd”
default-init-method="init">
<!-- 配置全局初始化方法,如果有100个bean中都有init方法,那么只要Spring容器一启动,bean对象一创建
默认对象中只要有 init方法,都全部会执行:一般不建议使用
-->
<!--
init-method : 配置初始化方法名
destroy-method : 配置销毁方法名
-->
<bean id="someBean" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.SomeBean"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destory"></bean>
所谓的依赖注入,就是属性不创建对象,通过配置文件的配置将Spring容器里面的对象注入给对应的属性
依赖注入有四种方式
6.1.setter注入,(属性注入)
1.setter注入,(也可以称之为属性注入)
使用setter注入:
1,使用bean元素的子元素设置;
1,简单类型值,直接使用value赋值;
2,引用类型,使用ref赋值;
3,集合类型,直接使用对应的集合类型元素即可。
2,spring通过属性的setter方法注入值;
3,在配置文件中配置的值都是string,spring可以自动的完成类型的转换
public class Employee {
private Integer age;
private String name;
private Department dept;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Department getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Department dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Employee [age=” + age + “, name=” + name + “, dept=” + dept + “]”;
}
}
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
<!-- 员工 -->
<bean id="employee" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Employee" >
<!-- setter方法注入: 属性注入
<property name="" value="">
name : 属性名称
value : 基本数据类型+String类型的值注入
ref : 引用类型(对象类型)的注入
value 和ref 只能二选一
-->
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="jinken"></property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 部门 -->
<bean id="dept" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Department" ></bean>
<!-- 员工 -->
<bean id="employee" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Employee" >
<!-- constructor注入 -->
<constructor-arg index="1" value="乔峰"/>
<constructor-arg index="0" value="19"/>
<constructor-arg ref="dept"/>
</bean>
<!-- 部门 -->
<bean id="dept" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Department" ></bean>
6.3.p命名空间注入
使用p命名空间注入先在约束上面引入 p标签(红色部分)
<!-- 配置部门 -->
<bean id="department" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Department"
p:id="123"
p:name="销售部"/>
<!-- 配置员工 -->
<bean id="emp" class="cn.zj.spring.pojo.Employee"
p:id="111"
p:name="西门吹雪"
p:dept-ref="department"/>
6.4.集合类型值注入
在处理的数据中,
有标量类型=基础数据类型以及包装类+String – value属性
也有Spring容器里面的对象 --ref属性
还要很多数据JDK内置的数据结构:
1.键值对 Map 、Properties
2.数组
3.集合Set、List
public class CollectionBean {
private Set set;
private List list;
private String[] array;
private Map<String, String> map;
private Properties prop; //读取本地 xxx.properties文件(本质就是一个Map集合)
}
set1
set2
set3
list1
list2
list3
AA
BB
CC
proVlaue1
proVlaue2
proVlaue3
7.获得properties文件的值
Spring配置文件支持通过xxx.properties文件的Key获得对应的值。实现该功能是通过
通过${Key}来获得Properties文件对应Key的值
使用Spring读取配置文件必须导入新的命名空间 context
导入命名空间方法
将命名空间和约束重新拷贝一份,将对于的全部替换成 context,然后关联context本地schema约束
7.1.使用Spring创建阿里巴巴 Druid连接池,读取配置文件
7.1.1.拷贝Mysql驱动包和druid连接池jar包到项目中
7.1.2.创建 db.properites
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcdemo
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.maxActive=10
7.1.3.applicationContext.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<context:property-placeholder location=“classpath:db.properties” />
7.1.4.测试代码
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);
DataSource dataSource = context.getBean(DataSource.class, "dataSource");
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println("数据库连接对象:"+conn);
}
7.1.5.效果
8.模拟注册功能
此功能重点在于将每一层对象的创建交给Spring管理,对象之间的依赖关系交给Spring来维护
8.1.Dao层接口以及实现代码
public interface UserDao {
void insert(User user);
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void insert(User user) {
System.out.println(“注册的Dao方法执行”);
}
}
8.2.Service层接口以及实现代码
public interface UserService {
void register(User user);
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
/*private UserDao dao = new UserDaoImpl(); 传统做法
* 现在交给Spring管理,使用Spring的setter方法注入
*因为要交给Spring的setter方法注入,所以(必须)提供set方法
*/
private UserDao dao;
@Override
public void register(User user) {
dao.insert(user);
}
//因为要用
public void setDao(UserDao dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
}
8.3.Web表现层实现代码
public class UserServlet {
/* 传统做法
* private UserService service = new UserServiceImpl();
* 现在交给Spring管理,使用Spring的setter方法注入
* 因为要交给Spring的setter方法注入,所以(必须)提供set方法
*/
private UserService service;
public void register(User user) {
service.register(user);
}
public void setService(UserService service) {
this.service = service;
}
}
8.4.applicationContext.xml文件配置代码(重点),一定要掌握每层的配置,和每层之间对象的依赖关系的维护
!-- 配置 项目的bean -->
<!-- 配置DAO层 -->
<bean id="userDao" class="cn.zj.spring.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"/>
<!-- 配置Service层 -->
<bean id="userService" class="cn.zj.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- DI: 依赖注入,使用 setter注入 dao层对象-->
<property name="dao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置web层/表现层 -->
<bean id="userServlet" class="cn.zj.spring.controller.UserServlet">
<!-- DI : 依赖注入,使用setter注入 service层对象 -->
<property name="service" ref="userService"/>
</bean>
8.5.测试代码
@Test
public void testRegister() throws Exception {
//创建用户对象:模拟接受用户参数,封装对象的过程
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(“张三”);
user.setPassword(“admin”);
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);
//获取表现层的Servlet即可
UserServlet userServlet = context .getBean(“userServlet”, UserServlet.class);
//执行注册操作
userServlet.register(user);
}
9.小结
1.优秀的项目架构的特点
(1)高内聚
①项目分层开发(每次处理各自的任务,职责分明)
(2)低耦合
①对象与对象之间有不直接产生依赖(不直接new对象)
2.低耦合的解决方案
(1)开发者自己底层使用反射进行封装相关代码
(2)使用优秀的框架 Spring
3.什么是Spring?
(1)轻量级一站式框架
(2)轻量级
①Spring有20个模块,只需要四个模块即可启动Spring框架,其他模块按需引入即可
(3)一站式
①Web开发的三层架构 ,Web层、Service层,Dao层 全部使用Spring框架完成
4.Spring如何实现解耦
(1)IOC :控制反转
①将对象创建权交给Spring管理
②负责对象生命周期(有效期)
③初始化方法,销毁方法
④IOC创建对象实例有四种方式
1)直接使用无参数构造函数-推荐
a.
2)使用静态工厂创建bean
3)使用实例工厂创建bean
4)使用变种实例工厂,工厂类实现 FactoryBean接口
(2)DI :依赖注入
①将对象的属性通过Spring赋值
②Setter方法(属性)注入
③构造器注入
④P命名空间注入
⑤支持值类型,引用类型和支持各种集合数据类型的注入
5.Spring读取 .Properteis配置文件
6.综合案例-模拟注册功能-使用Spring管理对象






















 1136
1136











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








