手动实现 Spring 底层机制
1.Spring整体架构分析
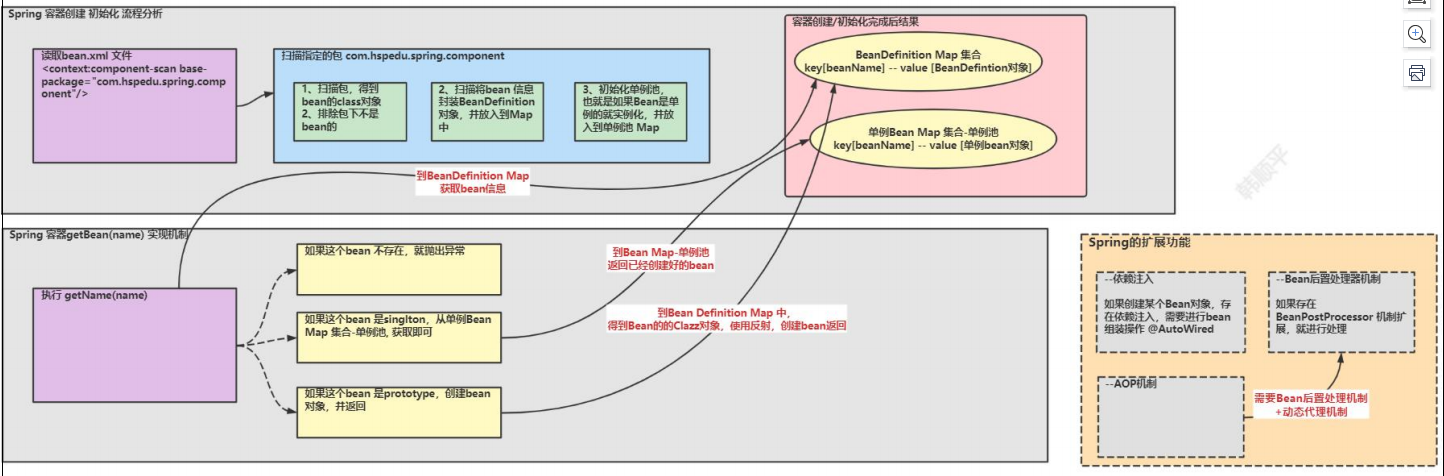
2.手动实现Spring底层机制
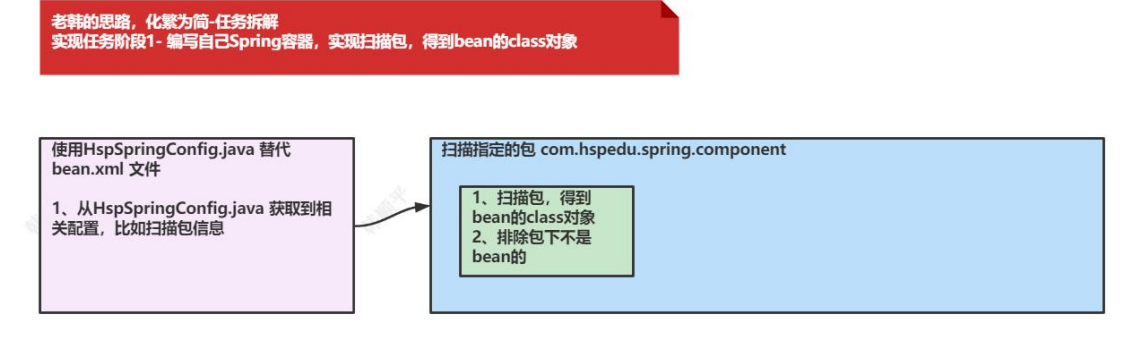
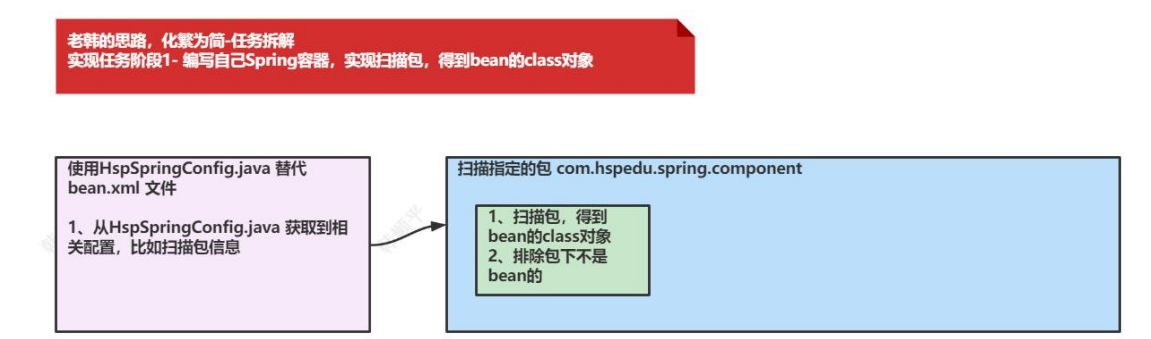
1.编写自己的Spring容器,实现扫描包,得到bean的class对象
1.补充:类加载器
● java 的类加载器 3 种
Bootstrap 类加载器--------------对应路径 jre/lib
Ext 类加载器--------------------对应路径
jre/lib/ext App 类加载器-------------------对应路径 classpath
● classpath 类路径,就是 java.exe 执行时,指定的路径,比如
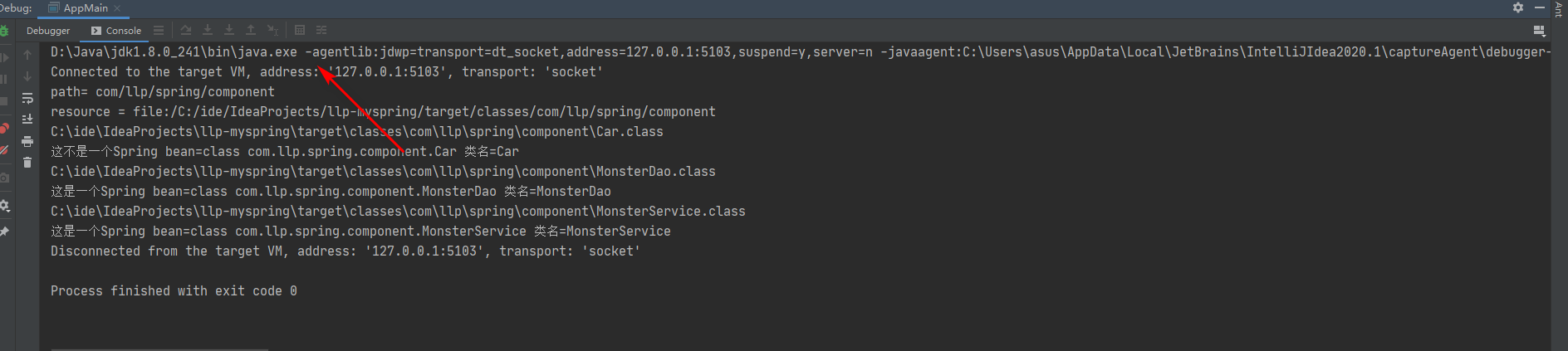
这是我们运行程序的真正位置
2.分析+代码实现+测试
● 分析示意图
● 代码实现
idea创建同级子模块工程
1.定义@ComponentScan包扫描注解
package com.llp.spring.annotaion;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
2.定义@Component注解
package com.llp.spring.annotaion;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Component {
//通过value给注入的bean指定名字,xml bean中的id
String value() default "";
}
3.定义自己的spring ioc容器
配置类
package com.llp.spring.ioc;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.ComponentScan;
/**
* 这是一个配置类, 作用类似我们原生spring的 beans.xml 容器配置文件
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.llp.spring.component")
public class LLpSpringConfig {
}
自己的spring容器
package com.llp.spring.ioc;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.Component;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.ComponentScan;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* 类的作用类似Spring原生ioc容器
*/
public class LLPSpringApplicationContext {
private Class aClass;
public LLPSpringApplicationContext(Class aClass) {
this.aClass = aClass;
//1.根据传入的LLpSpringApplicationConfig获取@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) aClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2.获取包扫描路径
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
//path= com/llp/spring/component
String path = basePackage.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("path= " + path);
//得到类型加载器 ->app类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = LLPSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据包路径获取目录的绝对路径
//file:/C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println("resource = " + resource);
///C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
String filePath = resource.getFile();
File file = new File(filePath);
//判断文件是否为目录
if (file.isDirectory()) {
//是目录,获取目录下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//获取每个文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(absolutePath);
//获取类名
String className = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//拼接得到全类名
String classFullName = basePackage + "." + className;
try {
//根据类加载器获取Class对象
Class<?> cls = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
System.out.println("这是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
} else {
System.out.println("这不是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//编写方法getBean(String name),编写方法返回对容器中对象
public Object getBean(String name) {
return null;
}
}
2.扫描将 bean 信息封装到 BeanDefinition 对象, 并放入到 Map
● 分析示意图
● 代码实现
BeanDefinition对象
package com.llp.spring.ioc;
/**
* 模拟Spring ioc容器中 BeanDefinitionMap中对应的每个value对象
*/
public class BeanDefinition {
/**
* 通过clazz拿到对应的bean信息
*/
private Class clazz;
/**
* 判断对象是单例还是多例
*/
private String scope;
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
}
自定义Spring ioc容器
package com.llp.spring.ioc;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.Component;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.ComponentScan;
import com.llp.spring.annotaion.Scope;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* 类的作用类似Spring原生ioc容器
*/
public class LLPSpringApplicationContext {
/**
* 接受配置类信息,通过配置类获取到包扫描信息
*/
private Class configClass;
/**
* 定义属性BeanDefinitionMap -> 存放BeanDefinition对象
*/
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 定义属性SingletonObjects -> 存放单例对象
*/
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public LLPSpringApplicationContext(Class aClass) {
beanDefinitionScan(aClass);
System.out.println(beanDefinitionMap);
}
/**
* 该方法完成指定包扫描,并将bean信息封装到BeanDefinition对象,在放入到map中
* @param configClass
*/
public void beanDefinitionScan(Class configClass){
this.configClass = configClass;
//1.根据传入的LLpSpringApplicationConfig获取@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2.获取包扫描路径
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
//path= com/llp/spring/component
String path = basePackage.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("path= " + path);
//得到类型加载器 ->app类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = LLPSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据包路径获取目录的绝对路径
//file:/C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println("resource = " + resource);
///C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
String filePath = resource.getFile();
File file = new File(filePath);
//判断文件是否为目录
if (file.isDirectory()) {
//是目录,获取目录下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//获取每个文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("absolutePath= " + absolutePath);
//获取类名 eg:——>MonsterDao
String className = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//拼接得到全类名
String classFullName = basePackage + "." + className;
try {
//根据类加载器获取Class对象
Class<?> cls = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component componentAnnotation = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(className);
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(cls);
//判断该类上是否有@Scope注解
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
//得到Scope注解对象
Scope scope = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
//获取scope注解配置的值,singleton-单例,prototype-原型
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
//默认为单例
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
System.out.println("这是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
} else {
System.out.println("这不是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//编写方法getBean(String name),编写方法返回对容器中对象
public Object getBean(String name) {
return null;
}
}
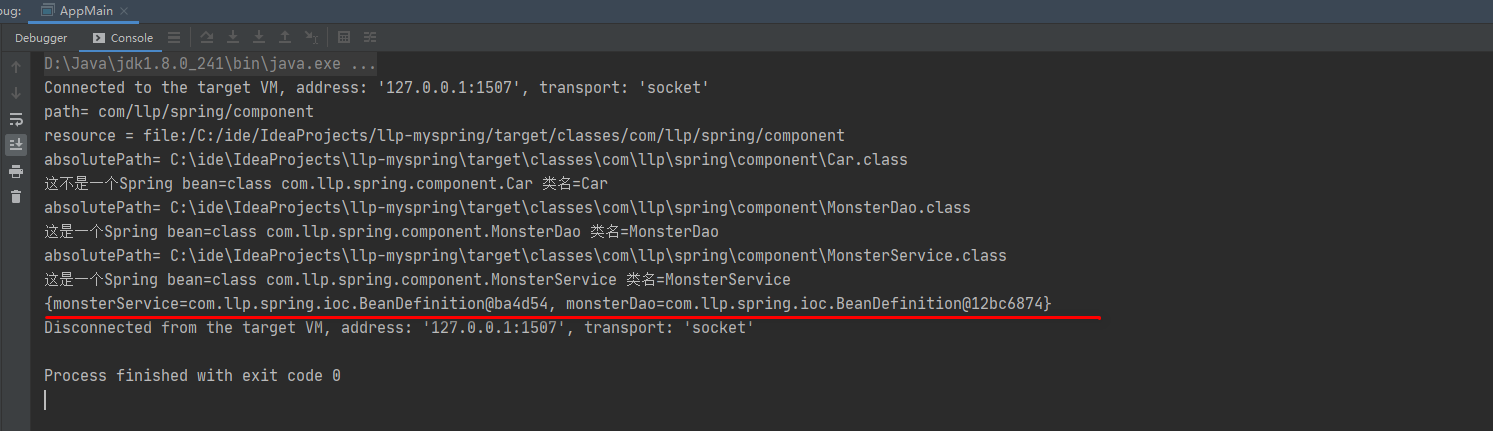
● 测试结果
3.初始化 bean 单例池,并完成 getBean 方法 , createBean 方法
● 分析示意图
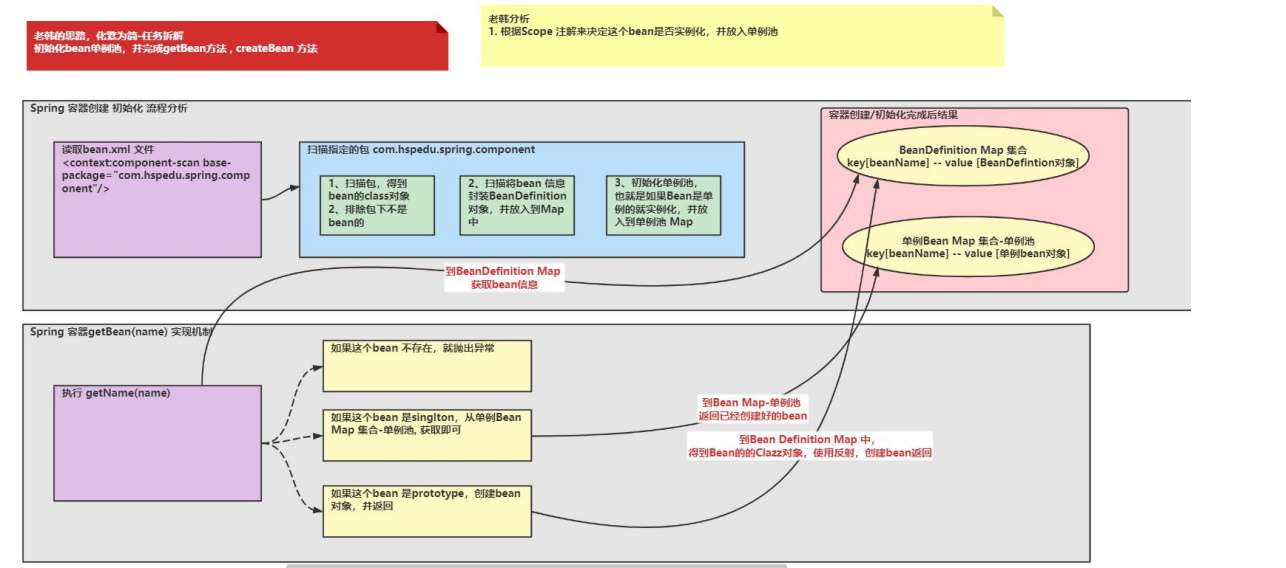
● 代码实现
/**
* 类的作用类似Spring原生ioc容器
*/
public class LLPSpringApplicationContext {
/**
* 接受配置类信息,通过配置类获取到包扫描信息
*/
private Class configClass;
/**
* 定义属性BeanDefinitionMap -> 存放BeanDefinition对象
*/
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 定义属性SingletonObjects -> 存放单例对象
*/
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public LLPSpringApplicationContext(Class aClass) {
beanDefinitionScan(aClass);
System.out.println("beanDefinitionMap= "+beanDefinitionMap);
//将单例的bean放入到singletonObjects中
setSingletonObjects();
System.out.println("singletonObjects= "+singletonObjects);
}
/**
* 将单例的bean放入到singletonObjects中
*/
public void setSingletonObjects() {
//将单例的bean放入到singletonObjects中
Enumeration<String> keys = beanDefinitionMap.keys();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String beanName = keys.nextElement();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
String scope = beanDefinition.getScope();
if ("singleton".equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
singletonObjects.put(beanName, createBean(beanDefinition));
}
}
}
/**
* 该方法完成指定包扫描,并将bean信息封装到BeanDefinition对象,在放入到map中
*
* @param configClass
*/
public void beanDefinitionScan(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
//1.根据传入的LLpSpringApplicationConfig获取@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2.获取包扫描路径
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
//path= com/llp/spring/component
String path = basePackage.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("path= " + path);
//得到类型加载器 ->app类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = LLPSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据包路径获取目录的绝对路径
//file:/C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println("resource = " + resource);
///C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
String filePath = resource.getFile();
File file = new File(filePath);
//判断文件是否为目录
if (file.isDirectory()) {
//是目录,获取目录下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//获取每个文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("absolutePath= " + absolutePath);
//获取类名 eg:——>MonsterDao
String className = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//拼接得到全类名
String classFullName = basePackage + "." + className;
try {
//根据类加载器获取Class对象
Class<?> cls = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component componentAnnotation = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(className);
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(cls);
//判断该类上是否有@Scope注解
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
//得到Scope注解对象
Scope scope = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
//获取scope注解配置的值,singleton-单例,prototype-原型
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
//默认为单例
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
System.out.println("这是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
} else {
System.out.println("这不是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 通过beanDefinition对象创建对应的实例bean
*
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object o = null;
try {
o = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
//编写方法getBean(String beanName),编写方法返回对容器中对象
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
//1.先拿到beanDefinition的scope,分别进行处理
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
String scope = beanDefinition.getScope();
//2.如果是单例的对象直接从singletonObjects(单例池)中获取对象
if ("singleton".equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
return singletonObjects.get(beanName);
} else {
//3.如果不是单例,调用createBean,反射一个对象
return createBean(beanDefinition);
}
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("没有找到该bean");
}
}
}
测试
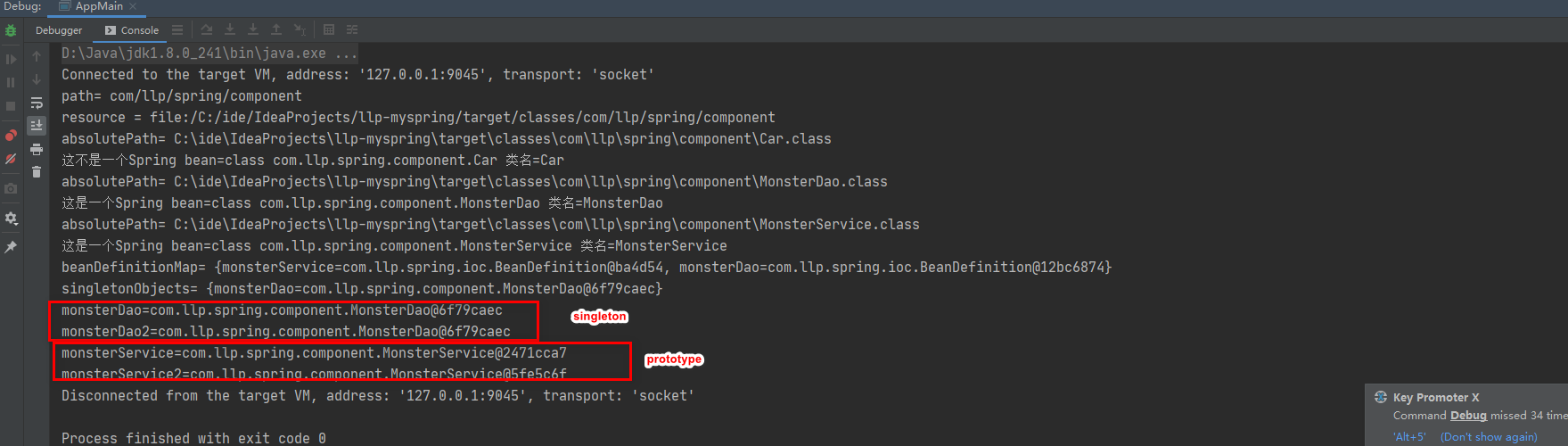
4.完成依赖注入
● 分析示意图
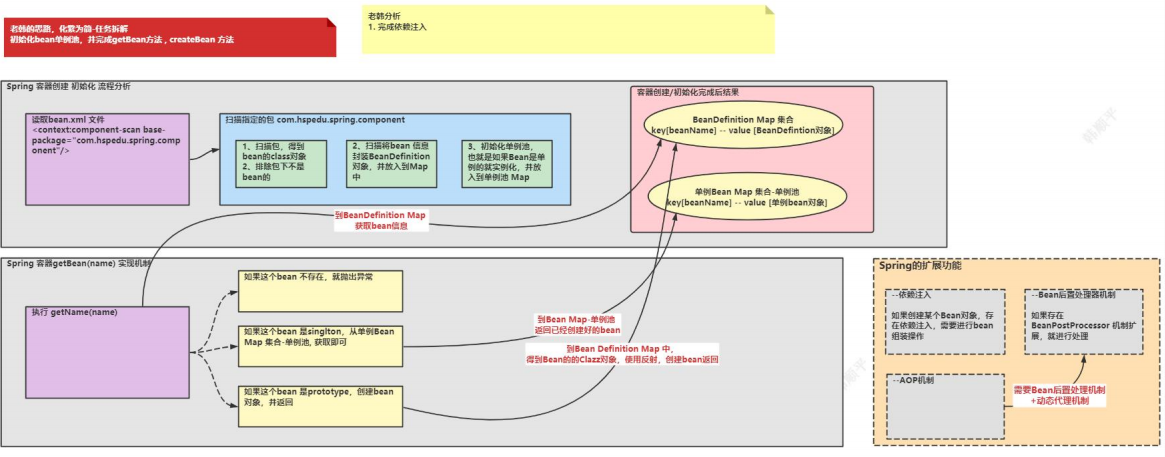
● 代码实现
自定义@Autowired注解
package com.llp.spring.annotaion;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
//required 为true是表示该bean必须存在,否则就会注入失败。
boolean required() default true;
}
@Component(value = "monsterService")
public class MonsterService {
@Autowired
private MonsterDao monsterDao;
public void hi(){
monsterDao.hi();
}
}
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class MonsterDao {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("MonsterDao-hi");
}
}
createBean方法添加依赖注入逻辑
/**
* 通过beanDefinition对象创建对应的实例bean
*
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object o = null;
try {
o = clazz.newInstance();
//依赖注入逻辑,在创建bean是给bean的字段中被@Autowired修饰的字段进行赋值
//1.获取bean中所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
//2.遍历判断字段上是否含有Autowired注解
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
//3.获取到@Autowired修饰字段的字段名称
String beanName = declaredField.getName();
//4.byName方式(根据名称匹配)获取bean对象
Object bean = getBean(beanName);
//5.拿到Autowired的required属性,如果为true则判断bean的值是否为null如果为null则表示注入失败抛出异常
Autowired declaredAnnotation = declaredField.getDeclaredAnnotation(Autowired.class);
boolean required = declaredAnnotation.required();
if(required && bean==null){
throw new RuntimeException("bean注入失败");
}
//私有属性暴破
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
//6.将字段的值赋给对象
declaredField.set(o, bean);
}
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
测试效果
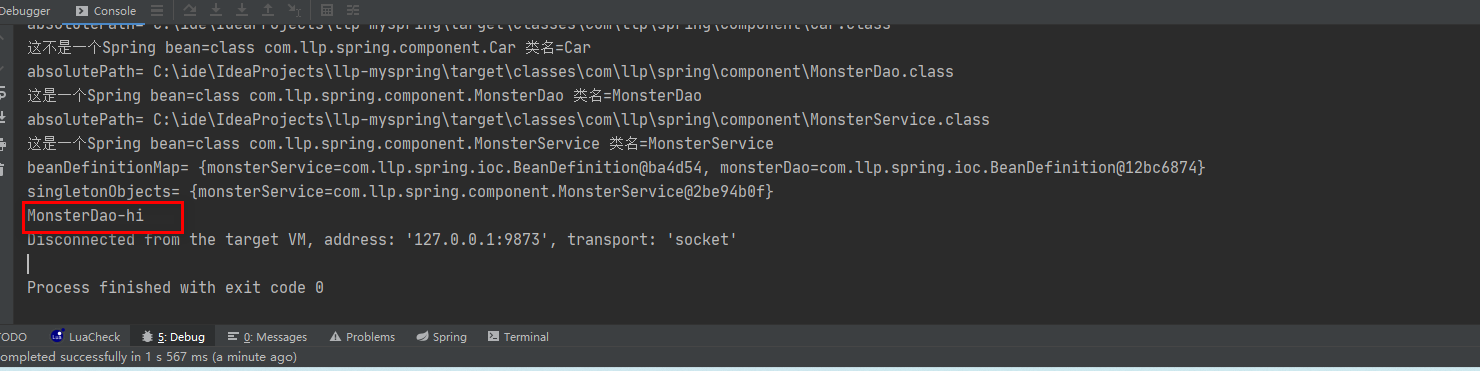
5.bean 后置处理器实现
1.后置处理回顾
/**
* 后置处理器
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 什么时候被调用:在Bean的init方法前被调用
* @param bean 传入的在ioc容器中创建/配置的bean
* @param beanName 传入的ioc容器中创建/配置bean的id
* @return Object 程序员对传入的bean 进行修改/处理【如果有需要的话】 ,返回
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization(),bean="+bean+",beanName="+beanName);
return bean;
}
/**
* 什么时候被调用:在Bean的init方法后被调用
* @param bean 传入的在ioc容器中创建/配置的bean
* @param beanName 传入的ioc容器中创建/配置bean的id
* @return 程序员对传入的bean 进行修改/处理【如果有需要的话】 ,返回
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization(),bean="+bean+",beanName="+beanName);
return bean;
}
}
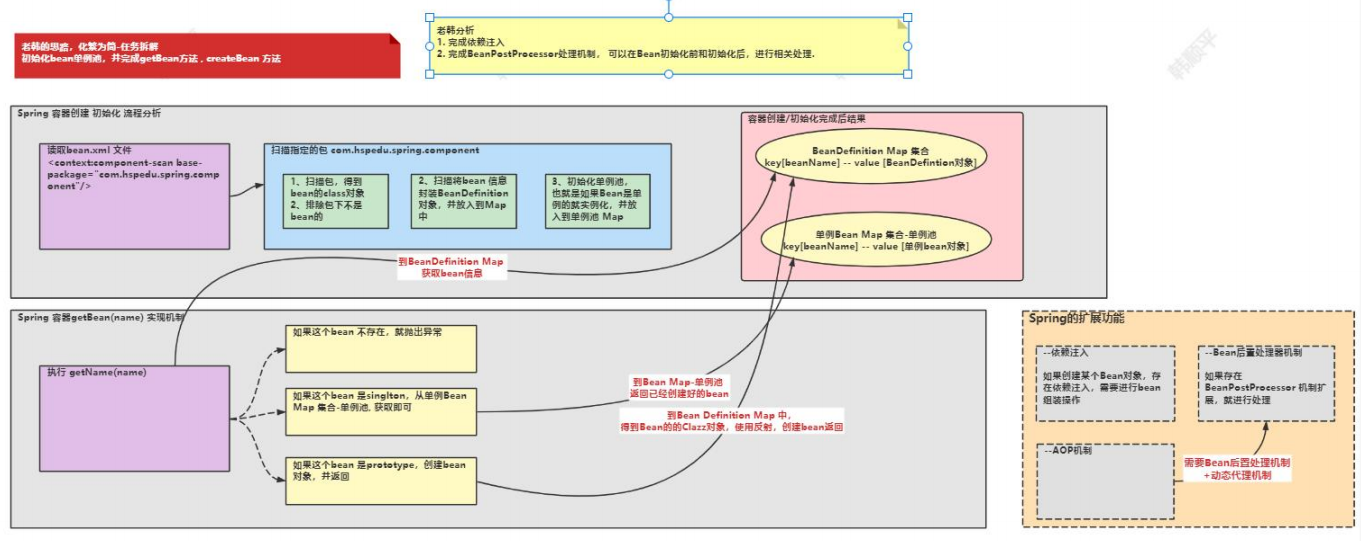
2.bean的生命周期
- 执行构造器
- 执行 set 相关方法
- 调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要配置)
- 使用 bean
- 当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁方法(需要配置)
● 分析示意图
● 代码实现
3.模拟初始化方法
/**
* 1. 我们根据原生Spring 定义了一个InitializingBean
* 2. 该InitializingBean接口有一个方法void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
* 3. afterPropertiesSet() 在Bean的 setter后执行,即就是我们原来的初始化方法
* 4. 当一个Bean实现这个接口后,就实现afterPropertiesSet() , 这个方法就是初始化方法
*/
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
4.定义自己的BeanPostProcessor接口
package com.llp.spring.processor;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 执行初始化方法之前的执行
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
/**
* 执行初始化方法之后执行
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
}
5.MonsterService实现初始化接口
@Component(value = "monsterService")
public class MonsterService implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private MonsterDao monsterDao;
public void hi(){
monsterDao.hi();
}
/**
* 执行setter方法后执行的初始化方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MonsterService 初始化方法被调用 程序员在这里加入初始化的业务..");
}
}
6.LLPSpringApplicationContext-在自定义的spring容器中添加一个用于存放自定义后置处理器的集合
//定义一个属性beanPostProcessorList, => 存放后置处理器
private List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessorList = new ArrayList<>();
7.在进行包扫描时添加BeanPostProcessor到集合中
/**
* 该方法完成指定包扫描,并将bean信息封装到BeanDefinition对象,在放入到map中
*
* @param configClass
*/
public void beanDefinitionScan(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
//1.根据传入的LLpSpringApplicationConfig获取@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2.获取包扫描路径
String basePackage = componentScan.value();
//path= com/llp/spring/component
String path = basePackage.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("path= " + path);
//得到类型加载器 ->app类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = LLPSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//根据包路径获取目录的绝对路径
//file:/C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println("resource = " + resource);
///C:/ide/IdeaProjects/llp-spring/out/production/llp-spring/com/llp/spring/component
String filePath = resource.getFile();
File file = new File(filePath);
//判断文件是否为目录
if (file.isDirectory()) {
//是目录,获取目录下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//获取每个文件的绝对路径
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("absolutePath= " + absolutePath);
//获取类名 eg:——>MonsterDao
String className = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//拼接得到全类名
String classFullName = basePackage + "." + className;
try {
//根据类加载器获取Class对象
Class<?> cls = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
//判断当前的这个clazz有没有实现BeanPostProcessor
//说明, 这里我们不能使用 instanceof 来判断clazz是否实现了BeanPostProcessor
//原因: clazz不是一个实例对象,而是一个类对象/clazz, 使用isAssignableFrom
if(BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)){
//将对象转换成BeanPostProcessor对象放入到我们定义的beanPostProcessorList集合中
//在原生的Spring容器中, 对后置处理器还是走的getBean, createBean
//但是需要我们在singletonObjects 加入相应的业务逻辑
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor)cls.newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessor);
//避免将BeanPostProcessor添加到singletonObjects中在执行时被作为bean
continue;
}
Component componentAnnotation = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(className);
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(cls);
//判断该类上是否有@Scope注解
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
//得到Scope注解对象
Scope scope = cls.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
//获取scope注解配置的值,singleton-单例,prototype-原型
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
//默认为单例
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
System.out.println("这是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
} else {
System.out.println("这不是一个Spring bean=" + cls + " 类名=" + className);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
8.在创建bean时执行初始化方法和后置处理器的before和after方法
/**
* 通过beanDefinition对象创建对应的实例bean
*
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
public Object createBean(String beanName,BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object o = null;
try {
o = clazz.newInstance();
//依赖注入逻辑,在创建bean是给bean的字段中被@Autowired修饰的字段进行赋值
//1.获取bean中所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
//2.遍历判断字段上是否含有Autowired注解
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
//3.获取到@Autowired修饰字段的字段名称
String declaredFieldName = declaredField.getName();
//4.byName方式(根据名称匹配)获取bean对象
Object bean = getBean(declaredFieldName);
//5.拿到Autowired的required属性,如果为true则判断bean的值是否为null如果为null则表示注入失败抛出异常
Autowired declaredAnnotation = declaredField.getDeclaredAnnotation(Autowired.class);
boolean required = declaredAnnotation.required();
if (required && bean == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("bean注入失败");
}
//私有属性暴破
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
//6.将字段的值赋给对象
declaredField.set(o, bean);
}
}
//执行后置处理器,初始化方法之前的before方法
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(o,beanName);
}
/**
* bean的生命周期
* 1. 执行构造器
* 2. 执行 set 相关方法
* 3. 调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要配置)
* 4. 使用 bean
* 5. 当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁方法(需要配置)
*/
//执行初始化方法
if (o instanceof InitializingBean) {
InitializingBean initializingBean = (InitializingBean) o;
try {
initializingBean.afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//执行后置处理器,初始化方法之后的after方法
//在后置处理器的after方法,可以对容器的bean实例进行处理
//然后返回处理后的bean实例, 相当于做一个后置处理
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
Object current = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(o, beanName);
if(current != null) {
o = current;
}
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
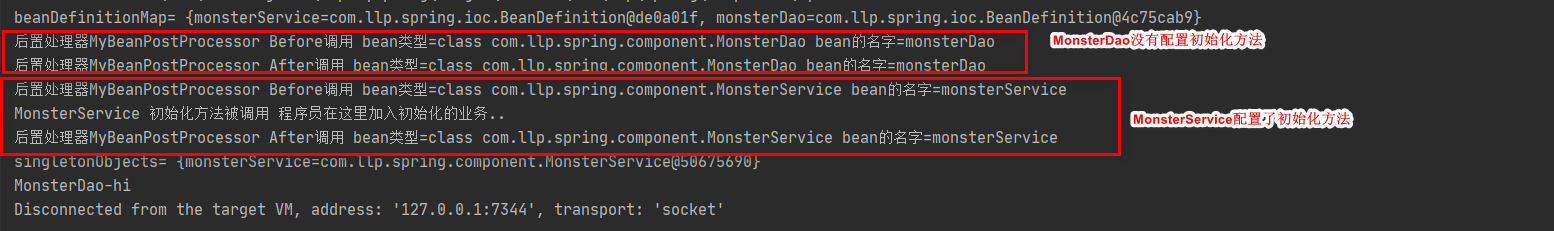
测试效果
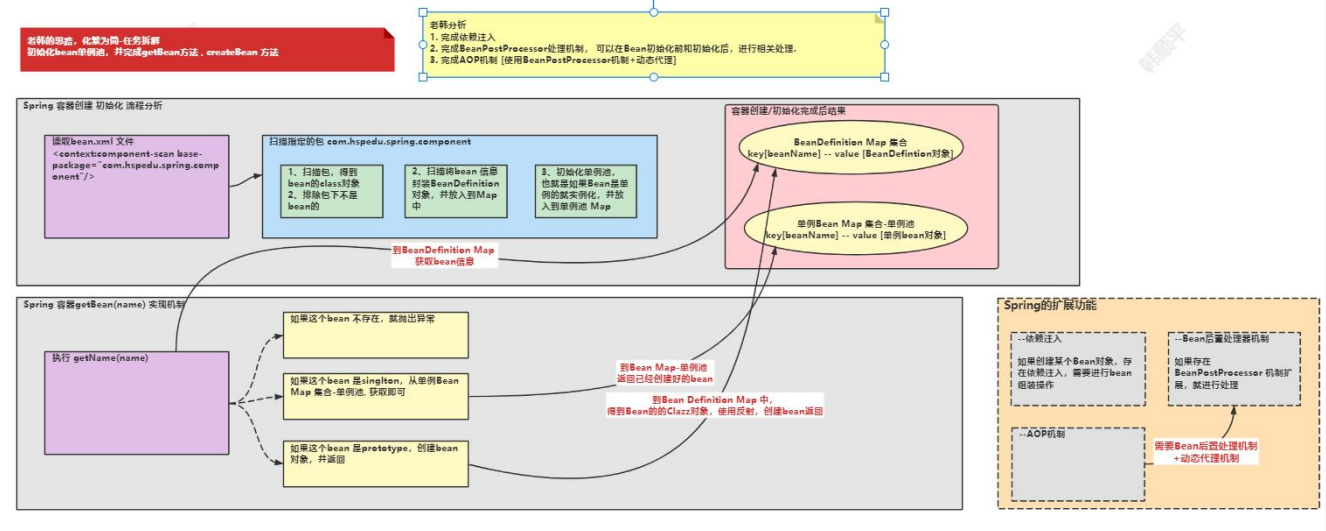
6.AOP 机制实现
● 分析示意图
1.准备工作
定义一个接口
public interface SmartAnimalable {
float getSum(float i, float j);
float getSub(float i, float j);
}
接口实现类
@Component(value = "smartDog")
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable {
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float res = i + j;
System.out.println("SmartDog-getSum-res=" + res);
return res;
}
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float res = i - j;
System.out.println("SmartDog-getSub-res=" + res);
return res;
}
}
切面类
/**
* SmartAnimalAspect当做一个切面类来使用
*/
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
public static void showBeginLog() {
System.out.println("前置通知..");
}
public static void showSuccessLog() {
System.out.println("返回通知..");
}
}
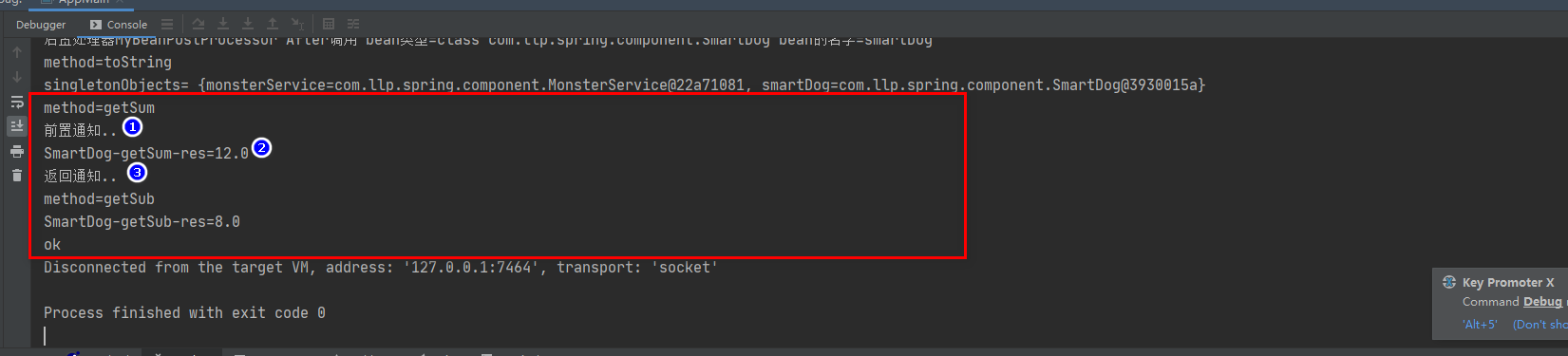
2.修改后置处理器after方法模拟AOP前置和后置通知
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("后置处理器MyBeanPostProcessor Before调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + " bean的名字=" + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("后置处理器MyBeanPostProcessor After调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + " bean的名字=" + beanName);
if ("smartDog".equals(beanName)) {
ClassLoader classLoader = MyBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = bean.getClass().getInterfaces();
Object newProxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* invoke 方法是将来执行我们的target_vehicle的方法时,会调用到
* @param proxy 表示代理对象
* @param method 就是通过代理对象调用方法时,的哪个方法 代理对象.run()
* @param args : 表示调用 代理对象.run(xx) 传入的参数
* @return 表示 代理对象.run(xx) 执行后的结果.
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("method=" + method.getName());
Object result = null;
//假如我们进行前置通知+返回通知 处理的方法是getSum
//后面可以通过注解来做的更加灵活
if ("getSum".equals(method.getName())) {
SmartAnimalAspect.showBeginLog();
result = method.invoke(bean, args);//执行目标方法
//进行返回通知的处理
SmartAnimalAspect.showSuccessLog();
} else {
result = method.invoke(bean, args);//执行目标方法
}
return result;
}
});
//如果bean是需要返回代理对象的, 这里就直接return proxyInstance
return newProxyInstance;
}
//如果不需要AOP, 返回 bean
return bean;
}
}





















 389
389











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








