算法通关村-单向链表
链表的概念
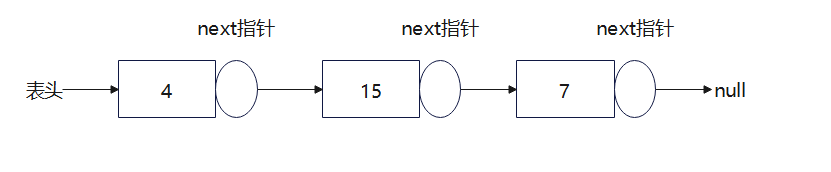
如图就是一个简单的单向单链表,元素之间互相连接,包含多个节点,每个节点有一个指向后继元素的next指针。表中最后一个元素的next指向null。
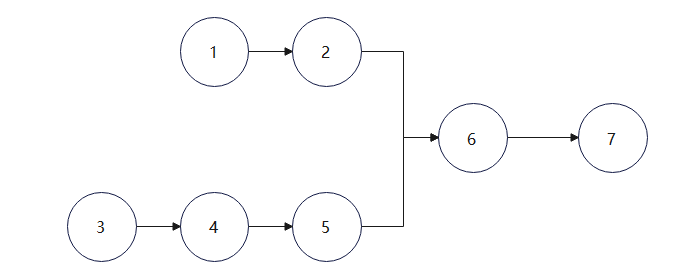
引出两个会混淆概念的图,以下哪个图符合链表的概念呢?
图一:
图二:
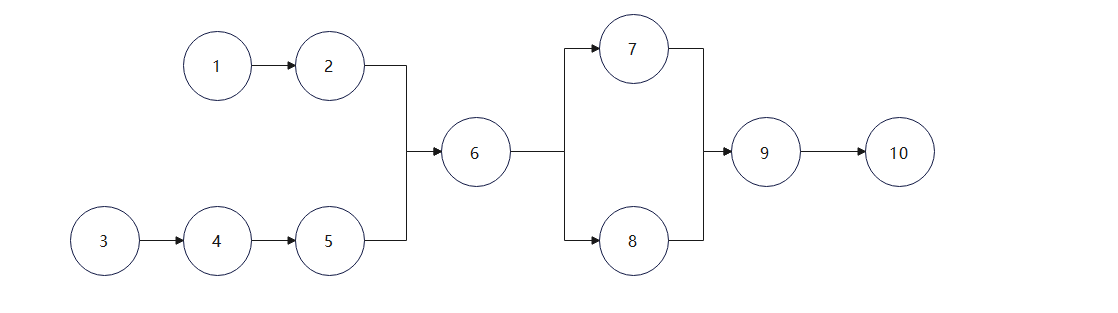
答案是第一个图符合链表的概念,核心是只能有一个后继节点,但不代表一个节点只能被一个指向,第二个图6节点有两个后继,这就不符合要求了。
节点和头节点
在链表中,每个节点都由值和指向下一个节点的地址组成,对于单链表,如果知道第一个元素,就可以通过遍历访问整个链表,第一个节点一般称为头节点
创建链表
/**
* 在算法中最常用的链表定义方式
*/
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
这里的val就是当前节点的值,next用于指向下一个节点,创建对象后可以直接使用listNode.val和listNode.next来操作。
遍历链表
表头是重中之重,千万别把指向表头的指针丢了
public class LinkList {
static class Node {
final int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// 初始化一个简单的链表
private static Node initLinkedList(int[] array) {
//cur 位置标识
Node head = null, cur = null;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node newNode = new Node(array[i]);
newNode.next = null;
if (i == 0) {
head = newNode;
cur = newNode;
} else {
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode;
}
}
return head;
}
//遍历链表长度并打印链表的data
private static int getLength(Node head){
int length = 0;
Node node = head;
while (node != null){
System.out.println(node.data);
length++;
node = node.next ;
}
System.out.println("链表的长度:"+length);
return length;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
Node head = initLinkedList(a);
getLength(head);
}
}
链表的插入
分为3个部分,表头插入,中间插入,结尾插入,各有注意点
- 表头插入要记得把新的节点作为head
- 表中插入要注意顺序,要先找到插入位置的前继节点我们称之为cur,先让新节点new的next指向cur.next既是new.next=cur.next,然后让cur.next指向new,既是cur.next=new;
- 表尾插入只需要注意将尾节点指向新节点就行了
示例代码:
public class LinkList {
static class Node {
final int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// 初始化一个简单的链表
private static Node initLinkedList(int[] array) {
//cur 位置标识
Node head = null, cur = null;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node newNode = new Node(array[i]);
newNode.next = null;
if (i == 0) {
head = newNode;
cur = newNode;
} else {
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode;
}
}
return head;
}
//遍历链表长度
private static int getLength(Node head){
int length = 0;
Node node = head;
while (node != null){
System.out.println(node.data);
length++;
node = node.next ;
}
System.out.println("链表的长度:"+length);
return length;
}
/**
* 链表插入
* 注意插入的位置 如果在表头插入 注意把新节点设成表头
* 如果在中间插入注意先后顺序 找到插入位置的上一个节点
* 让新节点的 next指向 上一个节点的next
* 上一个节点的next 指向 新节点
* @param head 链表头节点
* @param nodeInsert 待插入节点
* @param position 待插入位置,取值从1开始
* @return 插入后得到的链表头节点
*/
private static Node insertNode(Node head, Node nodeInsert, int position){
//如果头为空 直接新插入的当头返回回去
if (head == null){
return nodeInsert;
}
// 获得链表长度 防止插入位置越界
int size = getLength(head);
if (position > size + 1 || position < 1){
System.out.println("位置参数越界");
return head;
}
if (position == 1){
nodeInsert.next = head;
//注意插入的位置 如果在表头插入 注意把新节点设成表头
head = nodeInsert;
return head;
}
//把头节点保存起来做遍历
Node pNode = head;
int count = 0;
//找到了要插入新节点的位置前一个节点
while (count < position - 1 ){
pNode = pNode.next;
count++;
}
// 让新节点的 next指向 上一个节点的next
nodeInsert.next = pNode.next;
//上一个节点的next 指向 新节点
pNode.next=nodeInsert;
return head;
}
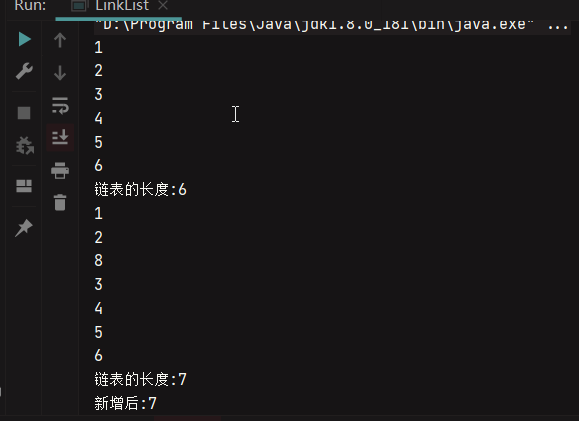
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
Node head = initLinkedList(a);
insertNode(head,new Node(8),2);
System.out.println("新增后:"+getLength(head));
}
}
链表的删除
分为3个部分,表头插入,中间插入,结尾插入,各有注意点
删除头节点:head=head.next
删除最后一个节点。找到最后一个节点的前驱节点cur,cur.next=null
删除中间节点,也是找到删除节点的前驱节点,让cur.next=cur.next.next就行了
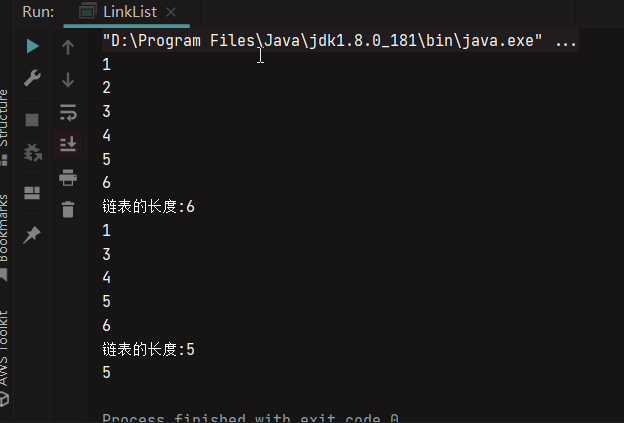
private static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position){
//如果要删除的位置是第一个节点(位置为 1),则将 head 指向下一个节点,即删除第一个节点,并返回新的头节点。
if (position == 1){
head = head.next;
return head;
}
//获取链表的长度 size,并检查要删除的位置是否是最后一个节点。如果是最后一个节点,
// 需要找到倒数第二个节点,并将其 next 指针设置为 null,即删除最后一个节点。
int size = getLength(head);
if (position == size){
Node pNode = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position -1){
pNode = pNode.next;
count++;
}
pNode.next = null;
return head;
}
//在上述两种情况之外,使用循环找到要删除节点的前一个节点,即第 position - 1 个节点。
// 将该节点的 next 指针指向要删除节点的下一个节点,从而删除指定位置的节点。
int count = 1;
Node curr = head;
while(count < position-1){
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
curr.next = curr.next.next;
return head;
}





















 166
166











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








