代码随想录刷题笔记总结:
https://www.programmercarl.com/
个人学习笔记 如有错误欢迎指正交流
1. 数组
1.1 理论基础
详细介绍:https://www.programmercarl.com/%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
- 数组下标都是从0开始的。
- 数组内存空间的地址是连续的
思维导图:

1.2 二分查找
注意: 利用二分查找的时候 如果是开闭区间 left == right
如果 最终l是第一个大于target的索引, r是第一个小于target的索引
R + 1 = L, 如果存在那么就直接返回mid
1.2.1 二分查找 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search/description/
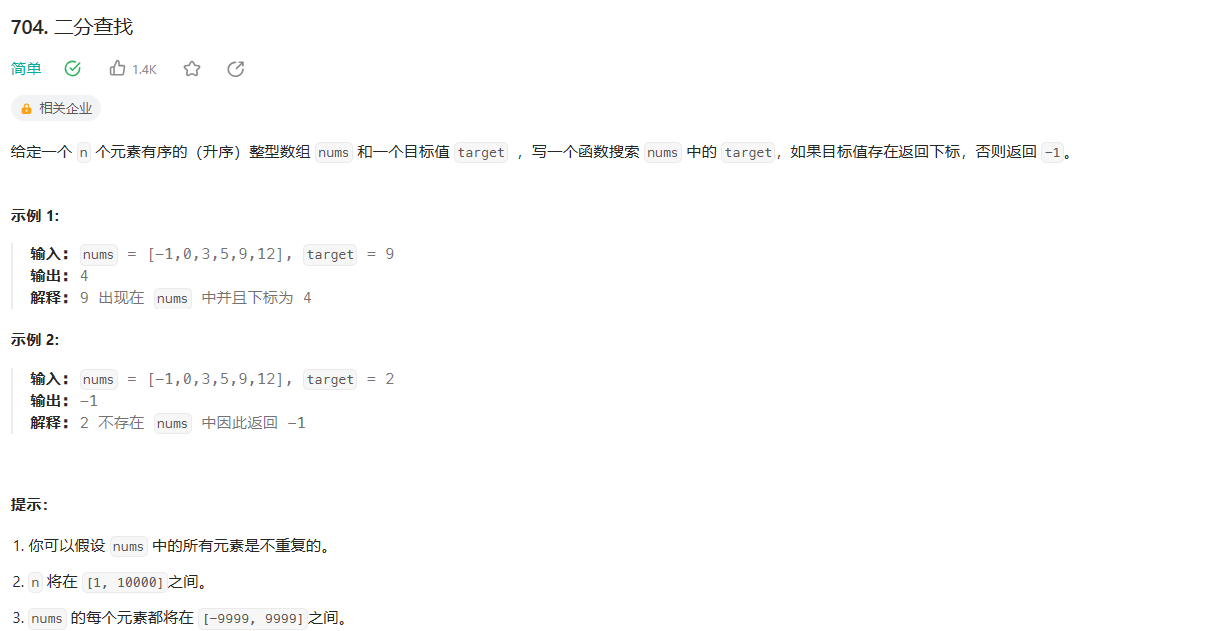
2. 思路:
-
方法1: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right] left <= right 左闭右闭
那么right = mid-1, 因为 [mid, right] 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid-1] mid -
方法2: 初始化right = len(nums), [left, right) left < right 左闭右开 那么right = mid,
因为 [mid, right) 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid) 这里就考虑mid了
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 704. 二分查找
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search/description/
思路:
mid = left + right
方法1: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right] left <= right 左闭右闭 那么right = mid-1, 因为 [mid, right] 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid-1] mid
方法2: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right) left < right 左闭右开 那么right = mid, 因为 [mid, right) 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid) 这里就考虑mid了
两个方法的剩余考虑区间保持一致
left统一写法 left = mid +1
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def search(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid -1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = left + 1
else:
return mid
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
result = solution.search(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.2 搜索插入位置
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/description/

2. 思路:
1. 利用二分查找
他的区别是 没有找到元素的情况返回的是元组插入的索引
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 35 搜索插入位置
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/description/
思路:
他的区别是 没有找到元素的情况返回的是元组插入的索引
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def searchInsert(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right: # 如果元素不存在数组种 那么跳出循环的时候left = right+1的, 最终放回left和right+1都可以
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = mid + 1
else:
return mid
return left
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 3, 5, 6]
target = 2
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.3 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
方法1: 先找到一个的位置然后向左右扩散
方法2: 分别找到左边界和右边界
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1: 先找到一个的位置然后向左右扩散
方法2: 分别找到左边界和右边界
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def searchRange(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = mid + 1
else:
temp = nums[mid]
i = mid
j = mid
while 0 <= i:
if nums[i] == target:
i -= 1
else:
break
while j <= len(nums) - 1:
if nums[j] == target:
j += 1
else:
break
return [i+1, j-1]
return [-1, -1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = []
target = 6
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchRange(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.4 x 的平方根
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sqrtx/description/

2. 思路:
这道题目和搜索插入位置题很相似 相当于从[1, 2, 3, …, x] 数组中找到根号x的插入位置
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 69 x 的平方根
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sqrtx/description/
思路:
这道题目和35题很相似 相当于从[1, 2, 3, ..., x] 数组中找到根号x的插入位置
"""
class Solution(object):
def mySqrt(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 1
right = x
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if mid * mid < x:
left = mid + 1
elif mid * mid > x:
right = mid -1
else:
return mid
return right
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = 4
solution = Solution()
result = solution.mySqrt(9)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.5 有效的完全平方数
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-perfect-square/description/

2. 思路:
相当于从[1, 2,…, x] 里面添加一个找是否存在 根号x 存在返回True 不存在则返回False
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 367. 有效的完全平方数
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-perfect-square/description/
思路:
相当于从[1, 2,..., x] 里面添加一个找是否存在 根号x 存在返回True 不存在则返回False
"""
class Solution(object):
def isPerfectSquare(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: bool
"""
left = 1
right = num
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if mid * mid < num:
left = mid + 1
elif mid * mid > num:
right = mid - 1
else:
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
num = 1
solution = Solution()
result = solution.isPerfectSquare(num)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3 移除元素
1.3.1 移除元素
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/

2. 思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管
3.1 (方法一)AC代码:
"""
题目: 27. 移除元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管
关键点:
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
val_num = 0
i = 0
while i < len(nums)-val_num:
if nums[i] == val:
val_num += 1
for j in range(i, len(nums)-val_num):
nums[j] = nums[j+1]
else:
i += 1
return len(nums)-val_num
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [3, 2, 2, 3]
val = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 27. 移除元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管(推荐使用这个方法 很优雅)
方法3: 双指针
关键点:
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
for temp in nums:
if temp != val:
nums[slow] = temp
slow += 1
return slow
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [3, 2, 2, 3]
val = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.2 删除排序数组中的重复项
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/

2. 思路:
方法1: slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow,
方法2: temp保存第一个出现的元素, 判断后续元素是否相同, 相同则直接跳过, 不同的话则重新对temp进行赋值
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 26 删除有序数组中的重复项
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/
思路:
方法1: slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow,
方法2: temp保存第一个出现的元素, 判断后续元素是否相同, 相同则直接跳过, 不同的话则重新对temp进行赋值
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
temp = nums[0]
for num in nums:
if num != temp:
slow += 1
nums[slow] = num
temp = num
print(f"slow: {slow+1}")
return slow+1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeDuplicates(nums)
print(f"result: {result}, {nums[:result]}")
3.2 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 26 删除有序数组中的重复项
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/
思路:
slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
for current in nums:
if nums[slow] != current:
slow += 1
nums[slow] = current
return slow+1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeDuplicates(nums)
print(f"result: {result}, {nums[:result]}")
1.3.3 移动零
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/description/

2. 思路:
- 用快慢指针对不是0的值依次赋值, 然后对slow之后的下标索引赋值为0
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 283. 移动零
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/description/
思路:
方法1: 用快慢指针对不是0的值依次赋值, 然后对slow之后的下标索引赋值为0
方法2:
关键词: 移除元素
"""
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
slow = 0
for num in nums:
if num != 0:
nums[slow] = num
slow += 1
for i in range(slow, len(nums)):
nums[i] = 0
# print(f"nums: {nums}")
# print(f"slow: {slow}")
return nums
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.moveZeroes(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.4 比较含退格的字符串
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/backspace-string-compare/

2. 思路:
- 利用栈去解决, 遇到字符# 进行出栈 最终比较两个栈是否相等
关键词:退格 抵消
3. AC代码:
class Solution(object):
def backspaceCompare(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
s_stack = self.backspace(s)
t_stack = self.backspace(t)
return s_stack == t_stack
def backspace(self, str):
stack = []
for word in str:
if word != '#':
stack.append(word)
else:
if stack != []:
stack.pop()
return stack
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "ab#c"
t = "ad#c"
solution = Solution()
result = solution.backspaceCompare(s, t)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.5 有序数组的平方
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
result = []
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
result.append(num * num)
return sorted(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
res = [None] * len(nums)
index = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
if nums[left] * nums[left] < nums[right] * nums[right]:
res[index] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right -= 1
else:
res[index] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left += 1
index -= 1
# print(f"res: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.4 有序数组的平方
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
result = []
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
result.append(num * num)
return sorted(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
res = [None] * len(nums)
index = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
if nums[left] * nums[left] < nums[right] * nums[right]:
res[index] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right -= 1
else:
res[index] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left += 1
index -= 1
# print(f"res: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5 长度最小的子数组
1.5.1 长度最小的子数组
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/

2. 思路:
- 滑动窗口方法,满足条件时左窗口进行滑动
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 209. 长度最小的子数组
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/
思路:
滑动窗口方法,满足条件时左窗口进行滑动
"""
class Solution(object):
def minSubArrayLen(self, target, nums):
l = 0
sum = 0
res_min = 100001
for r, num in enumerate(nums):
sum += num
while sum >= target:
res_min = min(res_min, r-l+1)
sum -= nums[l]
l += 1
# print(f"res: {res_min}")
return 0 if res_min == 100001 else res_min
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = 7
nums = [2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.minSubArrayLen(target, nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5.2 水果成篮 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/description/

2. 思路:
- 滑动窗口利用map,循环遍历fruits数组,将fruits[r]的value值加一,
- 如果map长度大于2 那么左滑动串口开始移动,直到fruit[l]的value等于0才可以删除key
- 对res_max进行赋值。返回结果
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 904. 水果成篮
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/description/
思路:
滑动窗口利用map,循环遍历fruits数组,将fruits[r]的value值加一,
如果map长度大于2 那么左滑动串口开始移动,直到fruit[l]的value等于0才可以删除key
对res_max进行赋值。返回结果
"""
class Solution:
def totalFruit(self, fruits):
l = 0
res_max = float("-inf")
fruits_map = {}
for r in range(len(fruits)):
fruits_map[fruits[r]] = fruits_map.get(fruits[r], 0) + 1
while len(fruits_map) > 2:
fruits_map[fruits[l]] -= 1
if fruits_map[fruits[l]] == 0:
del fruits_map[fruits[l]]
l += 1
res_max = max(res_max, r - l + 1)
return res_max
if __name__ == '__main__':
fruits = [0,1,2,2]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.totalFruit(fruits)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5.3 最小覆盖子串 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/

2. 思路:
- 利用map+滑动窗口
- 首先将字符串t的所有字符组成key value的形式, 以及初始化总的字符个数
- 然后遍历字符串s, 判断当前字符s[r] 是否在t_map的key中, 如果在则s[r]对应的value-1, 判断value是否为0, 如果为0, 那么require_char 可以见第减1
- 判断require_char==0, 表示当前滑动窗口包含t字符串, res_str进行赋值, 左滑动窗口向后移动进行找到最小的滑动窗口
- 返回res_str
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 76. 最小覆盖子串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/
思路:
1. 利用map+滑动窗口
2. 首先将字符串t的所有字符组成key value的形式, 以及初始化总的字符个数
3. 然后遍历字符串s, 判断当前字符s[r] 是否在t_map的key中, 如果在则s[r]对应的value-1, 判断value是否为0, 如果为0, 那么require_char 可以见第减1
4. 判断require_char==0, 表示当前滑动窗口包含t字符串, res_str进行赋值, 左滑动窗口向后移动进行找到最小的滑动窗口
5. 返回res_str
"""
class Solution(object):
def minWindow(self, s, t):
res_str = ""
t_map = {}
res_min = float("inf")
for char in t:
t_map[char] = t_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_char = len(t_map)
l = 0
r = 0
while r < len(s):
# s_map[s[r]] = s_map.get(s[r], 0) + 1
if s[r] in t_map:
t_map[s[r]] -= 1
if t_map[s[r]] == 0:
require_char -= 1
while require_char == 0: # 满足要求的时候保存字串的大小
if r - l + 1 < res_min:
res_min = min(res_min, r - l + 1)
res_str = s[l:r+1]
# print(f"res_str: {res_str}")
if s[l] in t_map:
t_map[s[l]] += 1
if t_map[s[l]] > 0:
require_char += 1
l +=1
r += 1
return res_str
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "ADOBECODEBANC"
t = "ABC"
solution = Solution()
result = solution.minWindow(s, t)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.6 螺旋矩阵
1.6.1 螺旋矩阵 II
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/

2. 思路:
- 初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
- 然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 59. 螺旋矩阵 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def generateMatrix(self, n):
num = 1
top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1
res = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
while num <= n * n:
for i in range(left, right+1):
res[top][i] = num
num += 1
top += 1
for i in range(top, down+1):
res[i][right] = num
num += 1
right -= 1
for i in range(right, left-1, -1):
res[down][i] = num
num += 1
down -= 1
for i in range(down, top-1, -1):
res[i][left] = num
num += 1
left += 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.generateMatrix(n)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.6.2 螺旋矩阵
- 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/description/

- 思路:
题目: 54. 螺旋矩阵
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/description/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
3.代码
"""
题目: 54. 螺旋矩阵
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/description/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
"""
from typing import List
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m = len(matrix)
n = len(matrix[0])
up = 0
down = m - 1
left = 0
right = n - 1
resList = []
num = 1
while num <= m * n:
for i in range(left, right + 1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(matrix[up][i])
num += 1
else:
break
up += 1
for i in range(up, down + 1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(matrix[i][right])
num += 1
else:
break
right -= 1
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(matrix[down][i])
num += 1
else:
break
down -= 1
for i in range(down, up - 1, -1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(matrix[i][left])
num += 1
else:
break
left += 1
# print(resList)
return resList
if __name__ == '__main__':
# matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
# matrix = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]]
# matrix = array = [[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]
matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[12,13,14,5],[11,16,15,6],[10,9,8,7]]
solution = Solution()
ans = solution.spiralOrder(matrix)
print(ans)
1.6.3 螺旋遍历二维数组
- 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/description/
- 思路:
题目: 146. 螺旋遍历二维数组
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/description/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
多加一个判断 判断array是不是空列表 - 代码
"""
题目: 146. 螺旋遍历二维数组
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/description/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
多加一个判断 判断array是不是空列表
"""
from typing import List
class Solution:
def spiralArray(self, array: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m = len(array)
n = len(array[0])
up = 0
down = m - 1
left = 0
right = n - 1
resList = []
num = 1
while num <= m * n:
for i in range(left, right + 1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(array[up][i])
num += 1
else:
break
up += 1
for i in range(up, down + 1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(array[i][right])
num += 1
else:
break
right -= 1
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(array[down][i])
num += 1
else:
break
down -= 1
for i in range(down, up - 1, -1):
if num <= m * n:
resList.append(array[i][left])
num += 1
else:
break
left += 1
# print(resList)
return resList
if __name__ == '__main__':
# matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
# matrix = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]]
# matrix = array = [[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]
matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[12,13,14,5],[11,16,15,6],[10,9,8,7]]
solution = Solution()
ans = solution.spiralArray(matrix)
print(ans)
1.7 数组总结
详细总结: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93%E7%AF%87.html
2. 链表
本章预览:

2.1 理论基础
什么是链表,链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向null(空指针的意思)。
详细介绍: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
2.2 移除链表元素 (**)
2. 思路
- 首先定义构造列表和遍历列表的方法(不是必要的)
- 利用pre节点
- if pre.next.val = val 删除当前节点 操作为pre.next = pre.next.next (如果当前节点的值等于val)
- 否则指针继续移动
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 203. 移除链表元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
思路:
1. 首先定义构造列表和遍历列表的方法(不是必要的)
2. 利用pre节点 删除当前节点 操作为pre.next = pre.next.next (如果当前节点的值等于val)
3. 否则指针继续移动
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
pre = ListNode(0)
pre.next = head
temp = pre
while temp.next != None:
if temp.next.val == val:
temp.next = temp.next.next
else:
temp = temp.next
return pre.next
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
# print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6]
val = 6
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
head = solution.removeElements(head, val)
get_linklist(head)
print(f"head: {head}")
2.3 设计链表
2. 思路
- 初始化pre节点和链表长度len
- 对于get, deleteatIndex, addatIndex 首先判断索引是否符合规则 不符合直接返回None或者是-1 遍历到index前一个节点即可
- 头插法和尾插入法
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 707. 设计链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/description/
思路:
1. 初始化pre节点和链表长度len
2. 对于get, deleteatIndex, addatIndex 首先判断索引是否符合规则 不符合直接返回None或者是-1 遍历到index前一个节点即可
3. 头插法和尾插入法
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class MyLinkedList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.pre = ListNode(0)
self.len = 0
# 得到链表的长度
def get_len(self, pre):
temp = self.pre.next
len = 0
while temp != None:
temp = temp.next
len += 1
return len
# 得到index索引的节点
def get(self, index):
"""
:type index: int
:rtype: int
"""
if index >= self.len:
return -1
temp = self.pre.next
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
return temp.val
# 头插法
def addAtHead(self, val):
"""
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
currentNode = ListNode(val)
head = self.pre.next
currentNode.next = head
self.pre.next = currentNode
self.len += 1
# 尾插法
def addAtTail(self, val):
"""
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
tail = self.pre
tailNode = ListNode(val)
while tail.next != None:
tail = tail.next
tail.next = tailNode
self.len += 1
# val插入到index
def addAtIndex(self, index, val):
"""
:type index: int
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
if index > self.len:
return None
temp = self.pre
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
valNode = ListNode(val)
valNode.next = temp.next
temp.next = valNode
self.len += 1
# 删除index位置的节点
def deleteAtIndex(self, index):
"""
:type index: int
:rtype: None
"""
if index >= self.len:
return None
temp = self.pre
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
self.len -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("hello solution")
2.4 反转链表 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/

2.1 (方法一) 思路
- 首先遍历一篇将所有节点存入到栈中
- 然后依次出战进行赋值构建新的链表
3. (方法一) AC代码
"""
题目: 206. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
思路:
1. 首先遍历一篇将所有节点存入到栈中
2. 然后依次出战进行赋值构建新的链表
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return None
stack = []
while head != None:
stack.append(head)
head = head.next
stack[0].next = None
res = stack.pop()
pre = res
while stack:
current = stack.pop()
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(res)
return res
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
head = ListNode(array[0])
temp = head
for value in array[1:]:
current = ListNode(value)
temp.next = current
temp = temp.next
get_linklist(head)
return head
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = []
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.reverseList(head)
2.2 (方法一) 思路
- pre 指向前一个节点 初始话一定要为null
- current 指向当前节点
- 直接改变指针的指向,
- 要注意每次改变时候pre, current指针的变化
3.2 (方法二)AC代码
"""
题目: 206. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
思路:
pre 指向前一个节点 初始话一定要为null
current 指向当前节点
直接改变指针的指向,
要注意每次改变时候pre, current指针的变化
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
if not head:
return None
pre = None
current = head
while current != None:
nextNode = current.next
current.next = pre
pre = current
current = nextNode
# print(f"nextNode: {pre.val}")
# print(f"nextNode: {nextNode.next.val}")
# get_linklist(pre)
return pre
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
head = ListNode(array[0])
temp = head
for value in array[1:]:
current = ListNode(value)
temp.next = current
temp = temp.next
get_linklist(head)
return head
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1,2,3,4,5]
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.reverseList(head)
2.5 两两交换链表中的节点 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/

2. 思路1

3. AC代码1
"""
题目: 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
思路:
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
print(f"hello world")
if not head or head.next == None:
return head
pre = ListNode()
res = pre
current = head
nextNode = head.next
while nextNode != None:
temp = nextNode.next
pre.next = nextNode
nextNode.next = current
current.next = temp
pre = current
current = temp
if temp:
nextNode = temp.next
else:
nextNode = temp
get_linklist(res.next)
return res.next
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4]
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.swapPairs(head)
2. 思路2:
递归
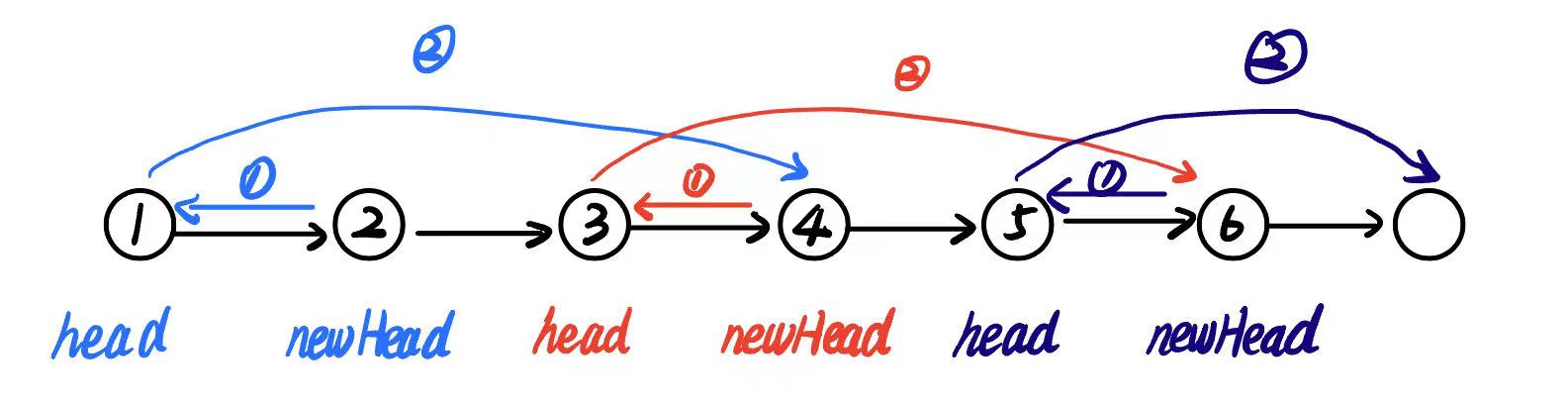
3. AC代码2:
"""
题目: 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
思路:
利用递归的方法
"""
from typing import Optional
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
newHead = head.next
head.next = self.swapPairs(newHead.next)
newHead.next = head
return newHead
if __name__ == '__main__':
2.6 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/

2. 思路
- 倒数滴n个节点相当于 index = len-n+1
- 循环遍历到索引index即可 然后执行删除操作
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
思路:
倒数滴n个节点相当于 index = len-n+1
循环遍历到索引index即可 然后执行删除操作
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return head
len = self.get_len(head)
index = len - n
# print(f"index: {index}")
pre = ListNode()
res = pre
pre.next = head
for i in range(index):
pre = pre.next
pre.next = pre.next.next
# get_linklist(res.next)
return res.next
def get_len(self, head):
temp = head
len = 0
while temp != None:
temp = temp.next
len += 1
return len
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
n = 2
solution = Solution()
head = create_linklist(head)
solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n)
2.7 链表相交 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/

2.1 (方法1)思路
- 将两个链表都存入到数组中
- 然后使得其中一个进行翻转(ListA),
- 遍历ListA, 取得ListA中在ListB中的最后一个元素
3.1 (方法1)AC代码
"""
题目: 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
思路:
将两个链表都存入到数组中
然后使得其中一个进行翻转(ListA),
遍历ListA, 取得ListA中在ListB中的最后一个元素
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
listA = self.get_NodeList(headA)
listB = self.get_NodeList(headB)
reversed(listA)
print(listA)
print(listB)
for currentNode in listA:
if currentNode in listB:
print(f"currentNode: {currentNode.val}")
return currentNode
return None
def get_NodeList(self, head):
res_list = []
temp = head
while temp != None:
res_list.append(temp)
temp = temp.next
return res_list
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
listA = [4, 1, 8, 4, 5]
print(listA.reverse())
print(listA)
listB = [5, 0, 1, 8, 4, 5]
listA = create_linklist(listA)
listB = create_linklist(listB)
solution = Solution()
solution.getIntersectionNode(listA, listB)
2.2 (方法2)思路
- 首先翻转两个链表
- 找到最后一个相似得节点保存下来进行返回
3.2 (方法2)AC代码
"""
题目: 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
思路:
首先翻转两个链表
找到最后一个相似得节点保存下来进行返回
"""
2.8 环形链表 II
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/

2.1 (方法1)思路
- 利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
3.1 (方法1)AC代码
"""
题目: 142. 环形链表 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
思路:
利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __int__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
res_list = []
current = head
while current != None:
if current not in res_list:
res_list.append(current)
else:
return current
current = current.next
return -1
2.2 (方法2)思路
- 利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
3.2 (方法2)AC代码
2.9 总结
3. 哈希表
章节预览:

3.1 理论基础
详细介绍:https://www.programmercarl.com/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
常见得三种hash数据结构。
- 数组
- set (集合)
- map(映射)
3.2 有效的字母异位词
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-anagram/description/

2. 思路:
利用map解决就行 类似76. 最小覆盖子串这道题目
利用一个requires和map就可以解决
首先将字符串s转化为一个数组, 然后依次遍历t的字符判断,
不存在直接返回False, 存在则减去1, 如果value为0并且require_chars-1
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 242. 有效的字母异位词
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-anagram/description/
思路:
利用map解决就行 类似76. 最小覆盖子串这道题目
利用一个requires和map就可以解决
首先将字符串s转化为一个数组, 然后依次遍历t的字符判断,
不存在直接返回False, 存在则减去1, 如果value为0并且require_chars-1
"""
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(s) != len(t):
return False
s_map = {}
for char in s:
s_map[char] = s_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_chars = len(s_map)
for char in t:
if char in s_map:
s_map[char] -= 1
if s_map[char] == 0: # 等于0 去除
require_chars -= 1
del s_map[char]
else:
return False
# print(require_chars)
return require_chars == 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "anagram"
t = "nagaram"
# s = "rat"
# t = "car"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isAnagram(s, t)
print(res)
3.3 两个数组的交集
1. 刷题链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/

2. 思路
- 定义res用于存放最终结果
- 遍历nums1中的每个元素 如果num在nums2列表中且不存在res 那么res列表加入当前元组
- 最终返回res列表
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 349. 两个数组的交集
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
思路:
1. 定义res用于存放最终结果
2. 遍历nums1中的每个元素 如果num在nums2列表中且不存在res 那么res列表加入当前元组
3. 最终返回res列表
"""
class Solution(object):
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
for num in nums1:
if num in nums2 and num not in res:
res.append(num)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [1, 2, 2, 1]
nums2 = [2, 2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.intersection(nums1, nums2)
print(res)
3.4 快乐数
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/

2. 思路1
- 创建一个res列表存放在sum数字,首先编写一个通过num得到sum的函数,
- 然后利用一个列表加入sum,如果当前sum在res列表中则返回False, 其他情况继续调用isHappy(sum)
- 如果1在res中返回True
sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!
3. AC代码1
"""
题目: 202. 快乐数
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/
思路:
1. 创建一个res列表存放在sum数字,首先编写一个通过num得到sum的函数,
2. 然后利用一个列表加入sum,如果当前sum在res列表中则返回False, 其他情况继续调用isHappy(sum)
3. 如果1在res中返回True
sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!
"""
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.res = []
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
self.res.append(n)
current = self.getNumSum(n)
if 1 in self.res:
return True
elif current in self.res:
return False
else:
return self.isHappy(current)
def getNumSum(self, n):
sum = 0
while n > 0:
temp = n % 10
n //= 10
sum = sum + temp * temp
return sum
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 18
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isHappy(n)
print(res)
AC 代码2
"""
题目: 202. 快乐数
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/
思路:
1. 利用for循环, 保存上次的数字
"""
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
resSum = []
current_sum = n
while current_sum != 1:
current_sum = self.sum(current_sum)
if current_sum not in resSum:
resSum.append(current_sum)
else:
return False
return True
def sum(self, number):
sum = 0
while number > 0:
sum += (number % 10) ** 2
number //= 10
return sum
3.5 两数之和
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/

2.1 (方法一)思路
- 最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
3.1 (方法一)AC代码
"""
题目: 1. 两数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/
思路:
最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
"""
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [2, 7, 11, 15]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
res = solution.twoSum(nums, target)
print(res)
2.2 (方法二)思路
- 利用map记录 key:value=元素值:索引
- 依次判断target-元素值 是否在map中 在则直接返回 不在则map[key] = value继续判断
3.2 (方法二)AC代码
"""
题目: 1. 两数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/
思路:
最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
"""
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [2, 7, 11, 15]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
res = solution.twoSum(nums, target)
print(res)
3.6 四数相加 II
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum-ii/

2. 思路
- 三/四层for循环超出时间限制, 两层for循环可以解决
- 利用两个map,用两层的for循环进行解决
- left_map存放num1, num2的和 元素和:个数
- right_map存放num3, num4的和 元素和:个数
- 最终判断key, -key是存在 存在则相加计算最终个数
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 四数相加 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum-ii/
思路:
三/四层for循环超出时间限制, 两层for循环可以解决
利用两个map,用两层的for循环进行解决
left_map存放num1, num2的和 元素和:个数
right_map存放num3, num4的和 元素和:个数
最终判断key, -key是存在 存在则相加计算最终个数
"""
class Solution(object):
def fourSumCount(self, nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:type nums3: List[int]
:type nums4: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums1)
res = 0
left_map = {}
right_map = {}
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
key = nums1[i]+nums2[j]
left_map[key] = left_map.get(key, 0) + 1
for k in range(n):
for l in range(n):
key = nums3[k] + nums4[l]
right_map[key] = right_map.get(key, 0) + 1
# print(left_map)
# print(right_map)
for key, value in left_map.items():
if -key in right_map:
res = res + (left_map[key] * right_map[-key])
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [1,2]
nums2 = [-2,-1]
nums3 = [-1,2]
nums4 = [0,2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.fourSumCount(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
print(res)
3.7 赎金信
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ransom-note/description/

2. 思路
- 将ransonNote转化为map, require_char是需要的长度
- 遍历magazine 元素, 如果在map中那么–, 最终判断require_char是否为0从而返回True or False
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 383. 赎金信
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ransom-note/description/
思路:
1. 将ransonNote转化为map, require_char是需要的长度
2. 遍历magazine 元素, 如果在map中那么--, 最终判断require_char是否为0从而返回True or False
"""
class Solution(object):
def canConstruct(self, ransomNote, magazine):
"""
:type ransomNote: str
:type magazine: str
:rtype: bool
"""
r_map = {}
for char in ransomNote:
r_map[char] = r_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_char = len(r_map)
print(require_char)
print(r_map)
for char in magazine:
if char in r_map:
r_map[char] -= 1
if r_map[char] == 0:
require_char -= 1
if require_char == 0:
return True
del r_map[char]
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
ransomNote = "aa"
magazine = "aab"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.canConstruct(ransomNote, magazine)
print(res)
3.8 三数之和 (**)
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/

2. 思路
1. 首先得对nums进行排序
2. 利用双指针 每次遍历nums,遍历i时 左指针和右指针分别为i+1 len(nums)-1
3. 然后就是去重操作 针对i得去重就是 i > 0 and nums[i] == num[i-1]
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 15. 三数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/
思路:
1. 暴力解法超出时间限制 只能过99%
2.
首先得对nums进行排序
利用双指针 每次遍历nums,遍历i时 左指针和右指针分别为i+1 len(nums)-1
然后就是去重操作 针对i得去重就是 i > 0 and nums[i] == num[i-1]
"""
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
nums.sort()
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
l = i+1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
total = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if total == 0:
res.append([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]])
# while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]: # l 去重
# l += 1
# while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]: # r 去重
# r -= 1
l += 1
r -= 1
elif total < 0:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.threeSum(nums)
print(res)
3.9 四数之和 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum/description/

2. 思路
- 和三数之和类似, 不同之处是需要去重不同
- i 去重 if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
- j 去重 j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 18. 四数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum/description/
思路:
和三数之和类似, 不同之处是需要去重不同
i 去重 if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
j 去重 j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
"""
class Solution(object):
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-3):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)-2):
if j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]: # 注意这里是i+1而不是1
continue
l = j+1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
total = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if total == target:
res.append([nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]])
while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]:
l += 1
while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]:
r -= 1
l += 1
r -= 1
elif total < target:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-2,-1,-1,1,1,2,2]
target = 0
solution = Solution()
res = solution.fourSum(nums, target)
print(res)
3.10 哈希表总结
详细总结: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93.html
4. 字符串
概览:

4.1 反转字符串
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string
2. 思路
直接进行双指针 l, r
l = 0 r = len(s)-1 交换左右指针的值 然后l++, r–
直接返回 s.reverse() 也可以
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 344. 反转字符串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string
思路:
直接进行双指针 l, r
l = 0 r = len(s)-1 交换左右指针的值 然后l++, r--
直接返回 s.reverse() 也可以
"""
class Solution(object):
def reverseString(self, s):
"""
:type s: List[str]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead.
"""
l = 0
r = len(s) - 1
while (l < r):
s[l], s[r] = s[r], s[l]
l += 1
r -= 1
return s
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = ["h", "e", "l", "l", "o"]
# s = []
solution = Solution()
res = solution.reverseString(s)
print(f"res: {res}")
4.2 反转字符串||
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string-ii
2. 思路1
首先讲字符串转成列表形式, 因为字符串本身是不可变的
然后对 [0:k], [2k, 2k+k] …[i * 2 * k:i * 2 * k+k] 部分的字符串进行反转重新赋值即可
然后利用"".join(s) 连接起来组成字符串就行了
3. AC代码1
"""
题目: 541. 反转字符串 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string-ii
思路:
首先讲字符串转成列表形式, 因为字符串本身是不可变的
然后对 [0:k], [2k, 2k+k] ...[i * 2 * k:i * 2 * k+k] 部分的字符串进行反转重新赋值即可
然后利用"".join(s) 连接起来组成字符串就行了
"""
class Solution(object):
def reverseStr(self, s, k):
"""
:type s: str
:type k: int
:rtype: str
"""
s = list(s)
if len(s) % (2 * k) == 0:
n = len(s) // (2 * k)
else:
n = len(s) // (2 * k) + 1
for i in range(n):
start = i * 2 * k
end = i * 2 * k + k
if end >= len(s):
end = len(s)
s[start:end] = self.reverseString(s[start:end])
return "".join(s)
# for i in range(0, len(s), )
def reverseString(self, s):
l = 0
r = len(s) - 1
while l < r:
s[l], s[r] = s[r], s[l]
l +=1
r -=1
return s
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "abcd"
s = "abcdefg"
k = 2
solution = Solution()
res = solution.reverseStr(s, k)
print(res)
2. 思路2
题目: 反转字符串 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string-ii/description/
思路:
定义一个新的字符串保存返回结果
反转的情况 i % 2k == 0的情况下需要反转字符串
否则不需要反转
3. AC代码2
"""
题目: 反转字符串 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string-ii/description/
思路:
定义一个新的字符串保存返回结果
反转的情况 i % 2k == 0的情况下需要反转字符串
否则不需要反转
"""
from typing import List
class Solution:
def reverseStr(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
resStr = ""
for i in range(0, len(s), k):
if i % (2 * k) == 0:
temp_str = self.reversePart(s[i:i + k])
else:
temp_str = s[i:i + k]
resStr += temp_str
return resStr
def reversePart(self, word):
new_word = ""
for char in word[::-1]:
new_word += char
return new_word
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "abcdefg"
s = "abcdefg"
k = 4
solution = Solution()
ans = solution.reverseStr(s, k)
print(ans)
4.3 路径加密
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
2. 思路
方法1. 直接利用path.replace(“.”, " “) 可以解决
方法2. 新建一个字符串res, 遍历path得到每个字符char, 然后如果是.替换为” ", 否者直接追加
3. AC代码
"""
题目: LCR 122. 路径加密
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
思路:
方法1. 直接利用path.replace(".", " ") 可以解决
方法2. 新建一个字符串res, 遍历path得到每个字符char, 然后如果是.替换为" ", 否者直接追加
"""
class Solution(object):
def pathEncryption(self, path):
"""
:type path: str
:rtype: str
"""
res = ""
for char in path:
if char == ".":
res += " "
else:
res += char
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "a.aef.qerf.bb"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.pathEncryption(path)
print(res)
4.4 反转字符串中的单词
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string
2. 思路
1. 利用s转化为一个字符串列表 s.split(" “), 如果不是”"(去除空格) 则加入一个s_list单词列表
2. 然后翻转列表即可
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 151. 反转字符串中的单词
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string
思路:
1. 利用s转化为一个字符串列表 s.split(" "), 如果不是""(去除空格) 则加入一个s_list单词列表
2. 然后翻转列表即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def reverseWords(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
s_list = []
for word in s.split(" "):
if word != "":
s_list.append(word)
l = 0
r = len(s_list) - 1
while l < r:
s_list[l], s_list[r] = s_list[r], s_list[l]
l += 1
r -= 1
# print(f"res: {s_list}")
return " ".join(s_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "the sky is blue"
# s = " hello world "
s = "a good example"
print(s.split(" "))
solution = Solution()
res = solution.reverseWords(s)
print(f"res: {res}")
4.5 动态口令
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/zuo-xuan-zhuan-zi-fu-chuan-lcof
2. 思路
方法1. 直接返回即可 password[target:] + password[:target]
方法2. 找到 [target, len(password)) 然后追加 然后在遍历 [0, target) 追加
3. AC代码
"""
题目: LCR 182. 动态口令
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/zuo-xuan-zhuan-zi-fu-chuan-lcof
思路:
方法1. 直接返回即可 password[target:] + password[:target]
方法2. 找到 [target, len(password)) 然后追加 然后在遍历 [0, target) 追加
"""
class Solution(object):
def dynamicPassword(self, password, target):
"""
:type password: str
:type target: int
:rtype: str
"""
res = ""
for i in range(target, len(password)):
res += password[i]
for i in range(target):
res += password[i]
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
password = "s3cur1tyC0d3"
target = 4
solution = Solution()
res = solution.dynamicPassword(password, target)
print(res)
4.6 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
1. 刷题链接https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string
2. 思路
1. 遍历[0, len(haystack) - len(needle) + 1)
2. 判断 haystack[i:i+len(needle)] 判断是否和 needle相等 返回i, 否则返回-1
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string
思路:
1. 遍历[0, len(haystack) - len(needle) + 1)
2. 判断 haystack[i:i+len(needle)] 判断是否和 needle相等 返回i, 否则返回-1
"""
class Solution(object):
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
:type haystack: str
:type needle: str
:rtype: int
"""
for i in range(len(haystack) - len(needle) + 1):
current_str = haystack[i:i+len(needle)]
if current_str == needle:
return i
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
haystack = "sqdbutsad"
needle = "sad"
# haystack = "leetcode"
# needle = "leeto"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.strStr(haystack, needle)
print(f"res: {res}")
4.7 重复的子字符串
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/repeated-substring-pattern
2. 思路
1. 遍历[1, len(s) // 2]
2. 判断s[0:i] 重叠 num次能不能等于s 如果等于那么直接返回true 否则返回False
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 459 重复的子字符串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/repeated-substring-pattern
思路:
1. 遍历[1, len(s) // 2]
2. 判断s[0:i] 重叠 num次能不能等于s 如果等于那么直接返回true 否则返回False
"""
class Solution(object):
def repeatedSubstringPattern(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: bool
"""
for i in range(1, len(s) // 2 + 1):
split_s = s[:i]
if len(s) % len(split_s) != 0:
continue
else:
repeat_num = len(s) // len(split_s)
if split_s * repeat_num == s:
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "abab"
# s = "aba"
s = "abcabcabcabc"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.repeatedSubstringPattern(s)
print(res)
5. 双指针法

5.1 移除元素
- 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/
- 思路
- 利用快慢指针 slow = 0, if num != val 那么慢指针赋值并移动 slow += 1
- AC代码
"""
题目: 27 移除元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/
思路:
1. 利用快慢指针 slow = 0, if num != val 那么慢指针赋值并移动 slow += 1
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
for num in nums:
if num != val:
nums[slow] = num
slow += 1
return slow
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [3, 2, 2, 3]
val = 3
solution = Solution()
res = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print(res)
5.2 反转字符串
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string
2. 思路
直接进行双指针 l, r
l = 0 r = len(s)-1 交换左右指针的值 然后l++, r–
直接返回 s.reverse() 也可以
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 344. 反转字符串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-string
思路:
直接进行双指针 l, r
l = 0 r = len(s)-1 交换左右指针的值 然后l++, r--
直接返回 s.reverse() 也可以
"""
class Solution(object):
def reverseString(self, s):
"""
:type s: List[str]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead.
"""
l = 0
r = len(s) - 1
while (l < r):
s[l], s[r] = s[r], s[l]
l += 1
r -= 1
return s
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = ["h", "e", "l", "l", "o"]
# s = []
solution = Solution()
res = solution.reverseString(s)
print(f"res: {res}")
5.3 路径加密
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
2. 思路
方法1. 直接利用path.replace(“.”, " “) 可以解决
方法2. 新建一个字符串res, 遍历path得到每个字符char, 然后如果是.替换为” ", 否者直接追加
3. AC代码
"""
题目: LCR 122. 路径加密
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
思路:
方法1. 直接利用path.replace(".", " ") 可以解决
方法2. 新建一个字符串res, 遍历path得到每个字符char, 然后如果是.替换为" ", 否者直接追加
"""
class Solution(object):
def pathEncryption(self, path):
"""
:type path: str
:rtype: str
"""
res = ""
for char in path:
if char == ".":
res += " "
else:
res += char
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "a.aef.qerf.bb"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.pathEncryption(path)
print(res)
5.4 反转字符串中的单词
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string
2. 思路
1. 利用s转化为一个字符串列表 s.split(" “), 如果不是”"(去除空格) 则加入一个s_list单词列表
2. 然后翻转列表即可
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 151. 反转字符串中的单词
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string
思路:
1. 利用s转化为一个字符串列表 s.split(" "), 如果不是""(去除空格) 则加入一个s_list单词列表
2. 然后翻转列表即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def reverseWords(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
s_list = []
for word in s.split(" "):
if word != "":
s_list.append(word)
l = 0
r = len(s_list) - 1
while l < r:
s_list[l], s_list[r] = s_list[r], s_list[l]
l += 1
r -= 1
# print(f"res: {s_list}")
return " ".join(s_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "the sky is blue"
# s = " hello world "
s = "a good example"
print(s.split(" "))
solution = Solution()
res = solution.reverseWords(s)
print(f"res: {res}")
5.5 反转链表
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list
2. 思路1
1. pre = None current = head
2. nextNode = current.next current.next = pre
3. pre = current current = nextNode 指针后移
3. AC代码1
"""
题目: 151. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list
思路:
1. pre = None current = head
2. nextNode = current.next current.next = pre
3. pre = current current = nextNode 指针后移
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val = 0, next = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
pre = None
current = head
while current != None:
nextNode = current.next
current.next = pre
pre = current
current = nextNode
return pre
def createLinked(nums):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return head
def getLinked(head):
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
new_head = createLinked(head)
print(getLinked(new_head))
# solution = Solution()
5.6 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
2. 思路
1. 首先讲A链表和B链表都转化为A节点列表和B节点列表,
2. 然后遍历A数组, 判断当前元素是否B列表中如果存在说明是第一个相交的节点则返回即可
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 151. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
思路:
1. 删除链表倒数第N个节点 相当于是删除第length - n个节点 从0开始
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
length = self.getLen(head)
pre = head
if length == n:
return head.next
for i in range(length-n-1):
pre = pre.next
if pre.next == None:
pre.next = None
else:
pre.next = pre.next.next
return head
def getLen(self, head):
current = head
count = 0
while current != None:
current = current.next
count += 1
return count
def createLinked(nums):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return head
def getLinked(head):
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
n = 2
# head = [1]
# n = 1
solution = Solution()
new_head = createLinked(head)
res = solution.removeNthFromEnd(new_head, 2)
print(getLinked(res))
5.7 链表相交
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci
2. 思路1
1. 首先讲A链表和B链表都转化为A节点列表和B节点列表,
2. 然后遍历A数组, 判断当前元素是否B列表中如果存在说明是第一个相交的节点则返回即可
3. AC代码1
"""
题目: 0207 链表相交
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci
思路:
1. 首先讲A链表和B链表都转化为A节点列表和B节点列表,
2. 然后遍历A数组, 判断当前元素是否B列表中如果存在说明是第一个相交的节点则返回即可
"""
"""
题目: 151. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list
思路:
1. pre = None current = head
2. nextNode = current.next current.next = pre
3. pre = current current = nextNode 指针后移
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val = 0, next = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
pre = None
current = head
while current != None:
nextNode = current.next
current.next = pre
pre = current
current = nextNode
return pre
def createLinked(nums):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return head
def getLinked(head):
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
new_head = createLinked(head)
print(getLinked(new_head))
# solution = Solution()
5.8 环形链表 II
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
2. 思路
思路:
1. 利用一个列表 遍历链表判断当前节点是否遍历这个列表, 不在则添加 在的话则直接返回改节点
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 142 环形链表 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
思路:
1. 利用一个列表 遍历链表判断当前节点是否遍历这个列表, 不在则添加 在的话则直接返回改节点
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val = 0, next = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
res = []
current = head
while current != None:
if current not in res:
res.append(current)
else:
return current
current = current.next
return None
def display(head):
current = head
res = []
while current != None:
res.append(current.val)
current = current.next
return res
def createLinked(nums):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return head
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [3, 2, 0, -4]
pos = 1
solution = Solution()
new_head = createLinked(head)
res = solution.detectCycle(new_head)
print(res)
2. 思路
1. 利用快慢指针slow, fast, 慢指针一次走一步, 快指针一次走两步 有环的话那么一定会相遇
2. 相遇条件 2 * (x + y) = x + y + n * (y + z) ==> x = z
3. 当fast != null fast.next != null, startA = head startB = slow 一起往后遍历第一次相遇的地方就是入环节点
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 142 环形链表 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
思路:
1. 利用快慢指针slow, fast, 慢指针一次走一步, 快指针一次走两步 有环的话那么一定会相遇
2. 相遇条件 2 * (x + y) = x + y + n * (y + z) ==> x = z
3. 当fast != null fast.next != null, startA = head startB = slow 一起往后遍历第一次相遇的地方就是入环节点
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val = 0, next = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
slow = head
fast = head
while fast != None and fast.next != None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
currentA = slow
currentB = head
while currentA != currentB:
currentA = currentA.next
currentB = currentB.next
return currentA
return None
def display(head):
current = head
res = []
while current != None:
res.append(current.val)
current = current.next
return res
def createLinked(nums):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return head
def createRingLinked(nums, pos):
head = ListNode(nums[0])
current = head
for val in nums[1:]:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
tail = current
current = head
for i in range(pos):
current = current.next
tail.next = current
return head
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [3, 2, 0, -4]
pos = 1
solution = Solution()
new_head = createRingLinked(head, 1)
# new_head = createLinked(head)
# print(display(new_head))
res = solution.detectCycle(new_head)
print(res.val)
5.9 三数之和
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum
2. 思路
1. 先对nums进行排序,然后就是去重 i 范围取值为[0:len(nums)-2)
2. 然后利用双指针 l = i + 1 r = len(nums) - 1, sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
sum < 0 l += 1 sum > 0 r += 1 如果 sum == 0 添加当前列表 (只有一个while循环, 里面是if)
去重部分: i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] continue
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 15. 三数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum
思路:
1. 先对nums进行排序,然后就是去重 i 范围取值为[0:len(nums)-2)
2. 然后利用双指针 l = i + 1 r = len(nums) - 1, sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
sum < 0 l += 1 sum > 0 r += 1 如果 sum == 0 添加当前列表 (只有一个while循环, 里面是if)
去重部分: i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] continue
"""
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
res = []
for i in range(len(nums) - 2):
if nums[i] > 0:
break
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
l = i + 1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if sum < 0:
l += 1
elif sum > 0:
r -= 1
else:
cur_list = [nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]]
if cur_list not in res:
res.append(cur_list)
l += 1
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
# nums = [-2,0,0,2,2]
# nums = [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3]
# nums = [1, 2, -2, -1]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.threeSum(nums)
print(res)
5.10 四数之和
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum
2. 思路
1. 先对nums进行排序,然后就是去重 i 范围取值为[0:len(nums)-3) j 范围取值为[i+1:len(nums)-2)
2. 然后利用双指针 l = j + 1 r = len(nums) - 1, sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]
sum < target l += 1 sum > target r += 1 如果 sum == target 添加当前列表 (只有一个while循环, 里面是if)
去重部分: i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] continue j > i + 1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1] continue
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 18. 四数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum
思路:
1. 先对nums进行排序,然后就是去重 i 范围取值为[0:len(nums)-3) j 范围取值为[i+1:len(nums)-2)
2. 然后利用双指针 l = j + 1 r = len(nums) - 1, sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]
sum < target l += 1 sum > target r += 1 如果 sum == target 添加当前列表 (只有一个while循环, 里面是if)
去重部分: i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] continue j > i + 1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1] continue
"""
class Solution(object):
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
print(nums)
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-3):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] == 0:
continue
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)-2):
if j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
continue
l = j + 1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if sum < target:
l += 1
elif sum > target:
r -= 1
else:
cur_list = [nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]]
if cur_list not in res:
res.append(cur_list)
l += 1
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
# nums = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2]
# target = 0
# nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
nums = [1, -2, -5, -4, -3, 3, 3, 5]
target = -11
solution = Solution()
res = solution.fourSum(nums, target)
print(res)
6 栈和队列
6.1 用栈实现队列
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks
2. 思路
1. 定义左右两个栈 lStack, Rstack
入队: 直接lStack入栈即可
出队: 右边的栈有元组直接出栈, 为空的话左边移到右边然后出栈
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 232.用栈实现队列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks
思路:
1. 定义左右两个栈 lStack, Rstack
入队: 直接lStack入栈即可
出队: 右边的栈有元组直接出栈, 为空的话左边移到右边然后出栈
"""
class MyQueue(object):
def __init__(self):
self.lStack = []
self.rStack = []
# 入队
def push(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.lStack.append(x)
# 出队
def pop(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
if self.rStack != []:
return self.rStack.pop()
else:
while self.lStack != []:
self.rStack.append(self.lStack.pop())
return self.rStack.pop()
# 返回队开头元素
def peek(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
if self.rStack != []:
return self.rStack[-1]
else:
while self.lStack != []:
self.rStack.append(self.lStack.pop())
return self.rStack[-1]
# 判断队列是否为空
def empty(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
if self.lStack == [] and self.rStack == []:
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
stack = []
for i in range(5):
stack.append(i)
print(stack)
stack.pop()
print(stack)
6.2 用队列实现栈
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues
2. 思路
1. 利用两个队列, 一个用于主队列, 另一个用于备份即可
2. 每次入栈直接利用主队入队即可, 出队的话就剩一个出队, 前面所有的出队依次入队到备份列表中即可
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 225. 用队列实现栈
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues
思路:
1. 利用两个队列, 一个用于主队列, 另一个用于备份即可
2. 每次入栈直接利用主队入队即可, 出队的话就剩一个出队, 前面所有的出队依次入队到备份列表中即可
"""
from collections import deque
class MyStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self.deque_main = deque()
self.deque_ci = deque()
pass
# 入栈
def push(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.deque_main.appendleft(x)
# 出栈
def pop(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
while len(self.deque_main) > 1:
print(self.deque_main)
self.deque_ci.appendleft(self.deque_main.pop())
res = self.deque_main.pop()
print(self.deque_ci)
while len(self.deque_ci) > 0:
self.deque_main.appendleft(self.deque_ci.pop())
return res
# 栈顶元素
def top(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
return self.deque_main[0]
# 栈是否为空
def empty(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
return len(self.deque_main) == 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
myStack = MyStack()
myStack.push(1)
myStack.push(2)
print(myStack.top())
print(myStack.pop())
print(myStack.empty()
6.3 有效的括号
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses
2. 思路
1. 利用栈, 如果是[“(”, “[”, “{” ]直接入栈,
否则出栈(栈非空 && 而且判断是否配对[{}, [], ()])
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 20. 有效的括号
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses
思路:
1. 利用栈, 如果是["(", "[", "{" ]直接入栈,
否则出栈(栈非空 && 而且判断是否配对[{}, [], ()])
"""
class Solution(object):
def isValid(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: bool
"""
# l =
# r = [")", "]", "}" ]
stack = []
for char in s:
if char in ["(", "[", "{" ]:
stack.append(char)
elif char == ")" and len(stack) > 0 and stack[-1] == "(":
stack.pop()
elif char == "]" and len(stack) > 0 and stack[-1] == "[":
stack.pop()
elif char == "}" and len(stack) > 0 and stack[-1] == "{":
stack.pop()
else:
return False
return len(stack) == 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "}"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isValid(s)
print(res)
6.4 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string
2. 思路
1. 入栈: 当前元素和栈顶元素不相同
2. 出栈: 栈不为空 并且 当前元素等于栈顶元素
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string
思路:
1. 入栈: 当前元素和栈顶元素不相同
2. 出栈: 栈不为空 并且 当前元素等于栈顶元素
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
stack = []
for char in s:
if len(stack) > 0 and char == stack[-1]:
stack.pop()
else:
stack.append(char)
return "".join(stack)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "abbaca"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.removeDuplicates(s)
print(res)
6.5 用队列实现栈
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/
2. 思路
1. 利用栈 如果是数字那么直接入栈,
如果是操作符入那么出栈两个元素, 第一个元素是右操作数, 第二元素是左操作数
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/
思路:
1. 利用栈 如果是数字那么直接入栈,
如果是操作符入那么出栈两个元素, 第一个元素是右操作数, 第二元素是左操作数
"""
class Solution(object):
def evalRPN(self, tokens):
"""
:type tokens: List[str]
:rtype: int
"""
stack = []
for val in tokens:
if val in ["+", "-", "*", "/"]:
rNum = int(stack.pop())
lNum = int(stack.pop())
res = 0
if val == "+":
res = lNum + rNum
elif val == "-":
res = lNum - rNum
elif val == "*":
res = lNum * rNum
elif val == "/":
res = int(lNum / rNum)
# res = lNum // rNum
stack.append(res)
else:
stack.append(val)
return int(stack.pop())
if __name__ == '__main__':
# tokens = ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
tokens = ["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"]
# tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"]
# tokens = ["-78","-33","196","+","-19","-","115","+","-","-99","/","-18","8","*","-86","-","-","16","/","26","-14","-","-","47","-","101","-","163","*","143","-","0","-","171","+","120","*","-60","+","156","/","173","/","-24","11","+","21","/","*","44","*","180","70","-40","-","*","86","132","-84","+","*","-","38","/","/","21","28","/","+","83","/","-31","156","-","+","28","/","95","-","120","+","8","*","90","-","-94","*","-73","/","-62","/","93","*","196","-","-59","+","187","-","143","/","-79","-89","+","-"]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.evalRPN(tokens)
print(res)
6.6 滑动窗口最大值
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum
2. 思路
1. 首先构造一个单调队列
push(val) 插入元素 如果val大于队尾元素那么 队尾去除, 否则插入
pop(val) 队头出队 如果val == 对头 出队, 否则不进行操作
front() 直接返回队头元素
2. 然后遍历数组[0:K], 首先将前k个元素加入队列中
然后遍历 [K:len(nums)], 先将左边的窗口出队, 然后再见右边的进行入队操作
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 239. 滑动窗口最大值
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum
思路:
1. 首先构造一个单调队列
push(val) 插入元素 如果val大于队尾元素那么 队尾去除, 否则插入
pop(val) 队头出队 如果val == 对头 出队, 否则不进行操作
front() 直接返回队头元素
2. 然后遍历数组[0:K], 首先将前k个元素加入队列中
然后遍历 [K:len(nums)], 先将左边的窗口出队, 然后再见右边的进行入队操作
"""
from collections import deque
class Solution(object):
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
singleQueue = MyQueue()
for val in nums[0:k]:
singleQueue.push(val)
res.append(singleQueue.front())
# print(res)
for i in range(k, len(nums)):
singleQueue.pop(nums[i-k])
singleQueue.push(nums[i])
res.append(singleQueue.front())
# print(res)
return res
# 单调队列
class MyQueue:
# 初始化单调队列
def __init__(self):
self.deque = deque()
# 出队头元素
def pop(self, val):
if len(self.deque) > 0 and val == self.deque[0]:
return self.deque.popleft()
# 如果队列不为空 而且当前值大于队尾, 那么直接出栈
def push(self, val):
while len(self.deque) > 0 and val > self.deque[-1]:
self.deque.pop()
self.deque.append(val)
# 返回第一个元素
def front(self):
return self.deque[0]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7]
k = 3
solution = Solution()
res = solution.maxSlidingWindow(nums, k)
print(res)
dq = deque()
for i in nums[:3]:
dq.append(i)
print(dq)
# print(dq.popleft())
print()
6.7 前 K 个高频元素
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-elements
2. 思路
1. 首先构造一个单调队列
push(val) 插入元素 如果val大于队尾元素那么 队尾去除, 否则插入
pop(val) 队头出队 如果val == 对头 出队, 否则不进行操作
front() 直接返回队头元素
2. 然后遍历数组[0:K], 首先将前k个元素加入队列中
然后遍历 [K:len(nums)], 先将左边的窗口出队, 然后再见右边的进行入队操作
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 347.前 K 个高频元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-elements
思路:
1. 利用hashmap 解决 然后利用value队value进行排序即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def topKFrequent(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res_map = {}
res = []
for num in nums:
res_map[num] = res_map.get(num, 0) + 1
res_map = dict(sorted(res_map.items(), key=lambda item:item[1], reverse=True))
count = 0
# print(res_map)
for key, value in res_map.items():
res.append(key)
count += 1
if count == k:
break
# print(res)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
solution = Solution()
# nums = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3]
nums = [4, 1, -1, 2, -1, 2, 3]
# [4, 1, -1, 2, -1, 2, 3]
k = 2
res = solution.topKFrequent(nums, k)
print(res)
8. 回溯算法
8.2 组合问题
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 n, k, startIndedx, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(lst) == k
- 搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, n] startIndex转化为 i + 1
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 77. 组合
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 n, k, startIndedx, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == k
3.搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, n] startIndex转化为 i + 1
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
"""
class Solution(object):
def combine(self, n, k):
"""
:type n: int
:type k: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(n, k, 1, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, n, k, startIndedx, lst, res):
if len(lst) == k:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndedx, n+1):
lst.append(i)
self.backtracking(n, k, i+1, lst, res)
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 4
k = 2
solution = Solution()
res = solution.combine(n, k)
print(res)
8.4 组合问题III
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 n, k, startIndedx, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(lst) == k
- 搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, 9] startIndex转化为 i + 1
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 216. 组合总和 III
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 n, k, startIndedx, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == k
3.搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, 9] startIndex转化为 i + 1
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
"""
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum3(self, k, n):
"""
:type k: int
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(k, n, 1, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, k, n, startIndex, sum, lst, res):
if sum > n:
return
if sum == n and len(lst) == k:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, 10):
sum += i
lst.append(i)
self.backtracking(k, n, i+1, sum, lst, res)
lst.pop()
sum -= i
if __name__ == '__main__':
k = 3
n = 7
solution = Solution()
res = solution.combinationSum3(k, n)
print(res)
8.5 电话号码的字母组合
-
刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number
-
思路
- 返回值和参数: 无返回值, 参数列表 s_list, startIndex, s(字符组合), res(最终结果), startIndex 其实充当这穷举for循环中的i, j , k, …角色
- 终止条件: len(s) == len(s_list) res.append(s[:]) 字符串直接相加和拷贝都行但是列表一定要拷贝
- 搜索的遍历过程: 依次遍历s_list中的元素 s_list[startIndex] startIndex 变成startIndex + 1, 之前都是变成i/i+1 因为这次是集合间的, 所以startIndex+1可以遍历下一个元素
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 17. 电话号码的字母组合
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number
思路:
1. 返回值和参数: 无返回值, 参数列表 s_list, startIndex, s(字符组合), res(最终结果), startIndex 其实充当这穷举for循环中的i, j , k, ...角色
2. 终止条件: len(s) == len(s_list) res.append(s[:]) 字符串直接相加和拷贝都行但是列表一定要拷贝
3. 搜索的遍历过程: 依次遍历s_list中的元素 s_list[startIndex] startIndex 变成startIndex + 1, 之前都是变成i/i+1 因为这次是集合间的, 所以startIndex+1可以遍历下一个元素
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
"""
class Solution(object):
def letterCombinations(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
if digits == "":
return []
number_list = ["", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"]
res = []
self.backtracking(digits, number_list, 0, "", res)
return res
def backtracking(self, digits, number_list, startIndex, lst, res):
if len(digits) == len(lst):
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in number_list[int(digits[startIndex])]:
lst += i
self.backtracking(digits, number_list, startIndex+1, lst, res)
lst = lst[:-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
digits = "23"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.letterCombinations(digits)
print(res)
8.7 组合总和
-
思路:
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 (candidates, target, sum, startIndex, lst, res)
- 函数终止条件: sum > target return sum == target res.append(lst[:])
- 搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex转化为 i
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 39. 组合总和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表 (candidates, target, sum, startIndex, lst, res)
2.函数终止条件: sum > target return sum == target res.append(lst[:])
3.搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex转化为 i
优化搜索的遍历过程: [start: n-(k-len(lst))+1 + 1)
"""
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, sum, startIndex, lst, res):
if sum > target:
return
if sum == target:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
lst.append(candidates[i])
sum += candidates[i]
self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i, lst, res)
sum -= candidates[i]
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
candidates = [2,3,6,7]
target = 7
solution = Solution()
res = solution.combinationSum(candidates, target)
print(res)
8.8 组合总和 II
-
思路
这里的关键: 先排序 然后去重- 返回值和参数: 无返回值 candidates, target(目标和), startIndex(开始), lsum(当前列表的和), lst(当前列表), res(最终结果)
- 终止条件: lsum >= target: if > 直接返回 如果 == 添加之后在返回
- 搜索的遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex变成i+1即可 因为元素不能重复使用
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 40. 组合总和 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii
思路:
这里的关键: 先排序 然后去重
1. 返回值和参数: 无返回值 candidates, target(目标和), startIndex(开始), lsum(当前列表的和), lst(当前列表), res(最终结果)
2. 终止条件: lsum >= target: if > 直接返回 如果 == 添加之后在返回
3. 搜索的遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex变成i+1即可 因为元素不能重复使用
去重: i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]:
"""
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
candidates.sort()
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, startIndex, sum, lst, res):
if sum > target:
return
if sum == target:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]:
continue
lst.append(candidates[i])
sum += candidates[i]
self.backtracking(candidates, target, i+1, sum, lst, res)
sum -= candidates[i]
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
candidates = [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5]
target = 8
solution = Solution()
res = solution.combinationSum2(candidates, target)
print(res)
- 思路2:
这里的关键: 先排序 然后去重- 返回值和参数: 无返回值 candidates, target(目标和), startIndex(开始), lsum(当前列表的和), lst(当前列表), res(最终结果)
- 终止条件: lsum >= target: if > 直接返回 如果 == 添加之后在返回
- 搜索的遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex变成i+1即可 因为元素不能重复使用
i > 0 and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1] and used[i-1] == False:
- AC代码2
"""
题目: 40. 组合总和 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii
思路:
这里的关键: 先排序 然后去重
1. 返回值和参数: 无返回值 candidates, target(目标和), startIndex(开始), lsum(当前列表的和), lst(当前列表), res(最终结果)
2. 终止条件: lsum >= target: if > 直接返回 如果 == 添加之后在返回
3. 搜索的遍历过程: [startIndex, len(candidates)) startIndex变成i+1即可 因为元素不能重复使用
"""
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
candidates.sort()
lst = []
res = []
used = [False] * len(candidates)
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, lst, res, used)
return res
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, startIndex, sum, lst, res, used):
if sum > target:
return
if sum == target:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if i > 0 and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1] and used[i-1] == False:
continue
lst.append(candidates[i])
sum += candidates[i]
used[i] = True
self.backtracking(candidates, target, i+1, sum, lst, res, used)
used[i] = False
sum -= candidates[i]
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
candidates = [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5]
target = 8
solution = Solution()
res = solution.combinationSum2(candidates, target)
print(res)
8.9 分割回文串
-
刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: s, startIndex, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(s) <= startIndex
- 搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(s)) startIndex 改变为 i+1 判断split_s 是否是回文串
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 131. 分割回文串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: s, startIndex, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(s) <= startIndex
3.搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(s)) startIndex 改变为 i+1 判断split_s 是否是回文串
"""
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(s, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, s, startIndex, lst, res):
if len(s) <= startIndex:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(s)):
split_s = s[startIndex:i+1]
if self.isPlalindrome(split_s):
lst.append(split_s)
self.backtracking(s, i+1, lst, res)
lst.pop()
def isPlalindrome(self, s):
return s == s[::-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "aab"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.partition(s)
print(res)
8.10 复原 IP 地址(**)
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: (self, s, startIndex, pointNum, ip, res)
- 函数终止条件: pointNum == 3: startIndex < len(s) and self.isValid(s[startIndex:]): 添加
- 搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(s)) startIndex 改变为 i+1 判断split_s 否是在0-255之间
验证字符串是否有效:
首先转成int类型 如果是 在[0, 256] 是符合要求的 int_s = int(s)
为了过滤 01, 012, 0123 这种数字 还要加一个判断 字符串s len(s) = len(str(int(s))) -
AC代码
"""
题目: 93. 复原 IP 地址
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/restore-ip-addresses
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: (self, s, startIndex, pointNum, ip, res)
2.函数终止条件: pointNum == 3: startIndex < len(s) and self.isValid(s[startIndex:]): 添加
3.搜索遍历过程: [startIndex, len(s)) startIndex 改变为 i+1 判断split_s 否是在0-255之间
验证字符串是否有效:
首先转成int类型 如果是 在[0, 256] 是符合要求的 int_s = int(s)
为了过滤 01, 012, 0123 这种数字 还要加一个判断 字符串s len(s) = len(str(int(s)))
"""
class Solution(object):
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
ip = []
res = []
self.backtracking(s, 0, 0, ip, res)
# print(len(res))
return res
def backtracking(self, s, startIndex, pointNum, ip, res):
if pointNum == 3:
if startIndex < len(s) and self.isValid(s[startIndex:]): # 这里数组越界得先判断 判断第四个是否合法
current_ip = ip[:] # 这里一定要拷贝, 如果使用ip会有问题
current_ip.append(s[startIndex:])
res.append(".".join(current_ip))
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(s)):
split_s = s[startIndex:i + 1]
if self.isValid(split_s):
ip.append(split_s)
self.backtracking(s, i + 1, pointNum + 1, ip, res)
ip.pop()
def isValid(self, s):
int_s = int(s)
return int_s >= 0 and int_s <= 255 and len(s) == len(str(int_s)) # 这个是为了过率 011, 022这些
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "25525511135"
# s = "0000"
s = "101023"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.restoreIpAddresses(s)
print(res)
-
思路
- 直接利用for循环暴力解的方法就能操作
- 其实回溯的本质也是for循环嵌套, 这里的for循环时是固定的(三次分割) 之前的回溯问题for嵌套个数不是固定的
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 93. 复原 IP 地址
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/restore-ip-addresses
思路:
直接利用for循环暴力解的方法就能操作
其实回溯的本质也是for循环嵌套, 这里的for循环时是固定的(三次分割) 之前的回溯问题for嵌套个数不是固定的
"""
class Solution(object):
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
res = []
for i in range(1, len(s)):
if self.isValid(s[0:i]) == False:
continue
for j in range(i + 1, len(s)):
if self.isValid(s[i:j]) == False:
continue
for k in range(j + 1, len(s)):
if self.isValid(s[j:k]) == False or self.isValid(s[k:]) == False:
continue
ip = ".".join([s[0:i], s[i:j], s[j:k], s[k:]])
# print(ip)
# one, two, three, four = s[0:i], s[i:j], s[j:k], s[k:]
res.append(ip)
return res
def isValid(self, s):
int_s = int(s)
return int_s >= 0 and int_s <= 255 and len(s) == len(str(int_s)) # 这个是为了过率 011, 022这些
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "101023"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.restoreIpAddresses(s)
print(res)
8.11 子集
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
- 搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 78. 子集
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
3.搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
"""
class Solution(object):
def subsets(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(nums, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, lst, res):
res.append(lst[:])
if startIndex >= len(nums):
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, i+1, lst, res)
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1,2,3]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.subsets(nums)
print(res)
8.13 子集 II
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
- 搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
关键点: 是如何进行去重 (其他和子集问题是一样的) - 先排序
- 然后去重:if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i-1]: continue
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 90. 子集 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets-ii
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
3.搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
关键点: 是如何进行去重 (其他和子集问题是一样的)
1.先排序
2.然后去重:if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i-1]: continue
"""
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
lst = []
res = []
self.backTracking(nums, 0, lst, res)
return res
def backTracking(self, nums, startIndex, lst, res):
res.append(lst[:])
if startIndex >= len(nums):
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backTracking(nums, i+1, lst, res)
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 2, 2, 1]
nums.sort()
solution = Solution()
res =solution.subsetsWithDup(nums)
print(res)
-
思路2
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
3.搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
关键点: 是如何进行去重 (其他和子集问题是一样的)- 先排序
- 如果nums[i] == nums[i - 1] 并且 used[i - 1] == false,
就说明:前一个树枝,使用了nums[i - 1],也就是说同一树层使用过nums[i - 1]。 如果used[i-1] == True说明同一个树枝被使用可以使用
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 90. 子集 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets-ii
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, startIndex, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(num) <= startIndex
3.搜索遍历过程:
[startIndex, len(nums))
startIndex 改变为 i+1
关键点: 是如何进行去重 (其他和子集问题是一样的)
1. 先排序
2. 如果nums[i] == nums[i - 1] 并且 used[i - 1] == false,
就说明:前一个树枝,使用了nums[i - 1],也就是说同一树层使用过nums[i - 1]。 如果used[i-1] == True说明同一个树枝被使用可以使用
"""
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
lst = []
res = []
used = [False] * len(nums)
self.backTracking(nums, 0, used, lst, res)
return res
def backTracking(self, nums, startIndex, used, lst, res):
res.append(lst[:])
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and not used[i-1]:
continue
lst.append(nums[i])
used[i] = True
self.backTracking(nums, i+1, used, lst, res )
used[i] = False
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 2, 2]
nums.sort()
solution = Solution()
res =solution.subsetsWithDup(nums)
print(res)
8.14 递增子序列
-
刷题链接
-
思路
-
AC代码
8.15 全排列
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
- 搜索遍历过程:
直接判断nums[i] 是否在lst中 在则跳过
[0, len(nums))
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 46. 全排列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
3.搜索遍历过程:
直接判断nums[i] 是否在lst中 在则跳过
[0, len(nums))
"""
class Solution(object):
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
self.backtracking(nums, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, nums, lst, res):
if len(lst) == len(nums):
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] not in lst:
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, lst, res)
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1,2,3]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.permute(nums)
print(res)
-
思路2 used
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res, used
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
3.搜索遍历过程: [0, len(nums))
used[i] == True 表示同一树枝用过 那么直接跳过
nums[i] == nums[i-1] and used[i] == False 同一层用过 有效 (本次不存在这种情况 不存在重复元素) -
AC代码
"""
题目: 46. 全排列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res, used
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
3.搜索遍历过程: [0, len(nums))
used[i] == True 表示同一树枝用过 那么直接跳过
nums[i] == nums[i-1] and used[i] == False 同一层用过 有效 (本次不存在这种情况 不存在重复元素)
"""
class Solution(object):
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
used = [False] * len(nums)
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, nums, used, lst, res):
if len(nums) == len(lst):
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if used[i]: # 判断同一树枝是否用过 如果用过则跳过
continue
used[i] = True
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
used[i] = False
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1,2,3]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.permute(nums)
print(res)
8.16 全排列 II
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
- 搜索遍历过程:
[0, len(nums))
去重过程先排序 nums.sort()
nums[i] == nums[i-1] used[i-1] == False
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 47. 全排列 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
3.搜索遍历过程:
[0, len(nums))
去重过程先排序 nums.sort()
nums[i] == nums[i-1] used[i-1] == False
"""
class Solution(object):
def permuteUnique(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
lst = []
res = []
used = [False] * len(nums)
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, nums, used, lst, res):
if len(nums) == len(lst):
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and used[i-1] == False: # 同一层使用过
continue
if used[i] == False:
used[i] = True
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
used[i] = False
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 1, 2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.permuteUnique(nums)
print(res)
-
思路2 used
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
- 函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
- 搜索遍历过程:
[0, len(nums))
去重过程 used[i] == True, lst not in res 中才添加
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 47. 全排列 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表: num, lst, res
2.函数终止条件: len(lst) == len(nums)
3.搜索遍历过程:
[0, len(nums))
去重过程 used[i] == True, lst not in res 中才添加
"""
class Solution(object):
def permuteUnique(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
lst = []
res = []
used = [False] * len(nums)
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, nums, used, lst, res):
if len(nums) == len(lst) and lst not in res:
res.append(lst[:])
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if used[i] == False:
used[i] = True
lst.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, used, lst, res)
used[i] = False
lst.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 1, 2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.permuteUnique(nums)
print(res)
8.19 重新安排行程
-
刷题链接
-
思路
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 332. 重新安排行程
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reconstruct-itinerary
思路:
// 这个方法会超时 有一个案例过不了 得用深度搜索
1.
"""
class Solution(object):
def findItinerary(self, tickets):
"""
:type tickets: List[List[str]]
:rtype: List[str]
"""
tickets.sort()
lst = ["JFK"]
res = []
used = [0] * len(tickets)
self.backtracking(tickets, used, "JFK", lst, res)
return res[0]
def backtracking(self, tickets, used, cur, lst, res):
if len(lst) == len(tickets) + 1:
res.append(lst[:])
return True
for i, ticket in enumerate(tickets):
if ticket[0] == cur and used[i] == 0:
lst.append(ticket[1])
used[i] = 1
flag = self.backtracking(tickets, used, ticket[1], lst, res)
lst.pop()
used[i] = 0
if flag:
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
tickets = [["JFK", "SFO"], ["JFK", "ATL"], ["SFO", "ATL"], ["ATL", "JFK"], ["ATL", "SFO"]]
# tickets.sort()
solution = Solution()
res = solution.findItinerary(tickets)
print(res)
8.20 N 皇后
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表(chessboard, n, 0, res)
- 函数终止条件: row = n
- 搜索遍历过程:
i [0, n)
关键点
判断是否有效 chessboard[row][i], 有效则进行递归 三个约束条件 1. 列 2. 45 3. 135
row 改变为 row+1
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 51. N 皇后
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens/
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 无返回值 参数列表(chessboard, n, 0, res)
2.函数终止条件: row = n
3.搜索遍历过程:
i [0, n)
关键点
判断是否有效 chessboard[row][i], 有效则进行递归 三个约束条件 1. 列 2. 45 3. 135
row 改变为 row+1
"""
class Solution(object):
def solveNQueens(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
chessboard = [["."] * n for _ in range(n)]
res = []
self.backtracking(chessboard, n, 0, res)
return res
def backtracking(self, chessboard, n, row, res):
if row == n:
current_chessboard = ["".join(row[:]) for row in chessboard]
res.append(current_chessboard)
return
for i in range(n): # 列索引
if self.isValid(row, i, n, chessboard):
chessboard[row][i] = "Q"
self.backtracking(chessboard, n, row+1, res)
chessboard[row][i] = "."
# 判断行列是否有效
def isValid(self, row, col, n, chessboard):
# 判断该列
for i in range(row):
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q":
return False
# 判断135
for i, j in zip(range(row-1, -1, -1), range(col-1, -1, -1)):
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q":
return False
# 判断45
for i, j in zip(range(row-1, -1, -1), range(col+1, n)):
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q":
return False
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 5
solution = Solution()
res = solution.solveNQueens(n)
print(res)
"""
[
['Q', '.', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '.', 'Q', '.', '.'],
['.', '.', '.', '.', 'Q'],
['.', 'Q', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '.', '.', 'Q', '.']]
"""
8.21 解数独
-
思路
- 返回值及参数: 返回true board即可
- 函数终止条件: 无
- 搜索遍历过程:
i [0, 9]
j [0, 9]
关键点 二维回溯
判断回溯返回值是否为True如果为True那么直接返回
否则测试所有val之后返回False
-
AC代码
"""
题目: 37. 解数独
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sudoku-solver
思路:
1.返回值及参数: 返回true board即可
2.函数终止条件: 无
3.搜索遍历过程:
i [0, 9]
j [0, 9]
关键点 二维回溯
判断回溯返回值是否为True如果为True那么直接返回
否则测试所有val之后返回False
"""
class Solution(object):
def solveSudoku(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
self.backtracking(board)
return board
def backtracking(self, board):
num_list = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9"]
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if board[i][j] == ".":
for val in num_list:
if self.isValid(i, j, board, val):
board[i][j] = val
flag = self.backtracking(board)
if flag:
return True
board[i][j] = "."
return False # 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
# print("1")
return True
def isValid(self, row, col, board, val):
# 判断行
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if board[row][j] == val:
return False
# 判断列
for i in range(len(board)):
if board[i][col] == val:
return False
# 区域
row_start = (row // 3) * 3
col_start = (col // 3) * 3
for i in range(row_start, row_start+3):
for j in range(col_start, col_start+3):
if board[i][j] == val:
return False
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
board = [
["5", "3", ".", ".", "7", ".", ".", ".", "."],
["6", ".", ".", "1", "9", "5", ".", ".", "."],
[".", "9", "8", ".", ".", ".", ".", "6", "."],
["8", ".", ".", ".", "6", ".", ".", ".", "3"],
["4", ".", ".", "8", ".", "3", ".", ".", "1"],
["7", ".", ".", ".", "2", ".", ".", ".", "6"],
[".", "6", ".", ".", ".", ".", "2", "8", "."],
[".", ".", ".", "4", "1", "9", ".", ".", "5"],
[".", ".", ".", ".", "8", ".", ".", "7", "9"]]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.solveSudoku(board)
print(res)
8.9 分割回文串
-
刷题链接
-
思路
-
AC代码
10. 动态规划
10.41 最长递增子序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/description/

2. 思路:
- dp[i]含义: dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾的最长递增子序列的长度
- 递推公式: if num[i] > num[j] j 属于[0, i) dp[i] = max(dp[j]+1, dp[i]) 如果 <= 不会影响最大递增子序列长度 可以直接不用处理
- 初始化: dp = [1] * len(nums)
- for循环遍历 i [0, len(nums) ) j 属于[0, i)
- dp数组
nums:[10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18]
dp :[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 300. 最长递增子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/description/
思路:
1. dp[i]含义: dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾的最长递增子序列的长度
2. 递推公式: if num[i] > num[j] j 属于[0, i) dp[i] = max(dp[j]+1, dp[i]) 如果 <= 不会影响最大递增子序列长度 可以直接不用处理
3. 初始化: dp = [1] * len(nums)
4. for循环遍历 i [0, len(nums) ) j 属于[0, i)
5. dp数组
nums:[10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18]
dp :[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4]
"""
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [1] * len(nums)
res = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
for j in range(i):
if nums[i] > nums[j]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1)
res = max(res, dp[i])
else: # 可省略
dp[i] = dp[i]
print(f"dp: {dp}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
# nums = [10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18]
nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 2, 3]
# nums = [7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.lengthOfLIS(nums)
print(res)
10.42 最长连续递增序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-continuous-increasing-subsequence/description/

2. 思路:
- dp[i]: dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾的最长连续递增序列的长度 由于是连续 这里只需要考虑i-1即可 这个指当前节点
- 递推公式: if num[i] > num[i-1] dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+1, dp[i]) 如果 <= 不会影响最大递增子序列长度 可以直接不用处理
- 初始化: dp = [1] * (N)
- for循环遍历i [0, len(nums) )
- 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
- dp数组中最大的返回
nums: [1, 3, 5, 4, 7]
dp: [1, 2, 3, 1, 2]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 674. 最长连续递增序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-continuous-increasing-subsequence/description/
思路:
1. dp[i]: dp[i]表示i之前包括i的以nums[i]结尾的最长连续递增序列的长度 由于是连续 这里只需要考虑i-1即可 这个指当前节点
2. 递推公式: if num[i] > num[i-1] dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+1, dp[i]) 如果 <= 不会影响最大递增子序列长度 可以直接不用处理
3. 初始化: dp = [1] * (N)
4. for循环遍历i [0, len(nums) )
5. 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
6. dp数组中最大的返回
nums: [1, 3, 5, 4, 7]
dp: [1, 2, 3, 1, 2]
"""
class Solution(object):
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [1] * len(nums)
res = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] > nums[i-1]:
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1
res = max(res, dp[i])
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1,3,5,4,7]
# nums = [2,2,2,2,2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.findLengthOfLCIS(nums)
10.43 最长重复子数组
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-length-of-repeated-subarray/description/

2. 思路:
- dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]表示i, j之前包括i的以nums1[i-1], num2[j-1]结尾最长重复子数组 最长重复子数组 返回最大值
- 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 如果不等于dp[i][j] = 0 (可以省略)
- 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(s2)+1) for _ in range(len(s1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
- 双层for循环遍历
- 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
- dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0]]
3. AC代码:
"""
"""
题目: 718. 最长重复子数组
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-length-of-repeated-subarray/description/
思路:
1. dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]表示i, j之前包括i的以nums1[i-1], num2[j-1]结尾最长重复子数组 最长重复子数组 返回最大值
2. 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 如果不等于dp[i][j] = 0 (可以省略)
3. 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums1)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
4. 双层for循环遍历
5. 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
6. dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def findLength(self, s1, s2):
"""
:type s1: List[int]
:type s2: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(s2)+1) for _ in range(len(s1) + 1)]
res = 0
# print(f"dp: {dp}")
for i in range(1, len(s1)+1):
for j in range(1, len(s2)+1):
if s1[i-1] == s2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = 0 # 可以省略
res = max(dp[i][j], res)
print(f"dp: {dp}")
# print(f"res: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
solution = Solution()
s1 = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1]
# s1 = [1, 0, 0, 0, 1]
s2 = [3, 2, 1, 4, 7]
# s2 = [1, 0, 0, 1, 1]
res = solution.findLength(s1, s2)
print(f"res: {res}")
10.44 最长公共子序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-common-subsequence/

2. 思路:
- dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
- if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 如果不等于max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
- dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
- 双层for循环遍历
- 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
- dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 3]]
3. AC代码:
"""
"""
题目: 1143. 最长公共子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-common-subsequence/
思路:
1. dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
2. 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
3. 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
4. 双层for循环遍历
5. 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
6. dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 3]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def longestCommonSubsequence(self, text1, text2):
"""
:type text1: str
:type text2: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(text2) + 1) for _ in range(len(text1) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(text1) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(text2) + 1):
if text1[i-1] == text2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else: # 这里是找除了0:i-1, 0:j-1的最大值
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j])
print(f"dp: {dp}")
return dp[i][j]
if __name__ == '__main__':
text1 = "abcde"
text2 = "ace"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2)
print(f"res: {res}")
10.45 不相交的线 (其实就是最长公共子序列)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-common-subsequence/

2. 思路:
- dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
- 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
- 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
- 双层for循环遍历
- 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
- dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 3]]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 1035. 不相交的线 其实就是最长公共子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-common-subsequence/
思路:
1. dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
2. 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
3. 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
4. 双层for循环遍历
5. 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
6. dp数组
[[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 3]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def maxUncrossedLines(self, s1, s2):
"""
:type s1: List[int]
:type s2: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(s2) + 1) for _ in range(len(s1)+1)]
for i in range(1, len(s1)+1):
for j in range(1, len(s2)+1):
if s1[i-1] == s2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
return dp[-1][-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
s1 = [1, 4, 2]
s2 = [1, 2, 4]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.maxUncrossedLines(s1, s2)
print(res)
10.46 最大子数组和
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/description/

2. 思路:
- dp[i] 表示以下标i为结尾的最大子数组和
- 递推公式: dp[i] = nums[i] + max(dp[i-1], 0)
- 初始化: nums[0]
- for循环遍历
- 返回最大的dp[i], 利用res保存进行返回
- dp数组
nums: [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]
dp : [-2, 1, -2, 4, 3, 5, 6, 1, 5]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 53. 最大子数组和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/description/
思路:
1. dp[i] 表示以下标i为结尾的最大子数组和
2. 递推公式: dp[i] = nums[i] + max(dp[i-1], 0)
3. 初始化: nums[0]
4. for循环遍历
5. 返回最大的dp[i], 利用res保存进行返回
6. dp数组
nums: [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]
dp : [-2, 1, -2, 4, 3, 5, 6, 1, 5]
"""
class Solution(object):
def maxSubArray(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
N = len(nums)
dp = [0] * N
dp[0] = nums[0]
res = nums[0]
for i in range(1, N):
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], 0) + nums[i]
res = max(res, dp[i])
print(f"nums: {nums}")
print(f"dp : {dp}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.maxSubArray(nums)
print(res)
10.47 判断子序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/is-subsequence/description/

2. 思路:
- 可以直接通过最长公共子序列判断max_len, 返回max_len==len(s)的值即可
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 392. 判断子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/is-subsequence/description/
思路:
可以直接通过最长公共子序列判断max_len, 返回max_len==len(s)的值即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def isSubsequence(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(t) + 1) for _ in range(len(s) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(s) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(t) + 1):
if s[i-1] == t[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j])
# print(f"dp: {dp}")
return dp[-1][-1] == len(s)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "abc"
t = "ahbgdc"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isSubsequence(s, t)
print(res)
2. 思路2: (递推公式简短了)
- dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
- 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 如果不等于dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1]
- 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
- 双层for循环遍历
- 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
- dp数组
s = “abc”
t = “ahbgdc”
[
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3]
]
3. AC代码2:
"""
题目: 392. 判断子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/is-subsequence/description/
思路:
思路:
1. dp[i][j]: dp[i][j]:长度为[0, i - 1]的字符串text1与长度为[0, j - 1]的字符串text2的最长公共子序列为dp[i][j] 包含i-1, j-1 这个是一片矩形区域 dp[i][j] 肯定是对角线以内最大的数字
2. 递推公式: if num1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 如果不等于dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1]
3. 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(nums2)+1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] 注意这个初始化的问题 有个细节
4. 双层for循环遍历
5. 返回最大的dp[i] [0, len(nums) ) res, res初始化为1
6. dp数组
s = "abc"
t = "ahbgdc"
[
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3]
]
"""
class Solution(object):
def isSubsequence(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(t) + 1) for _ in range(len(s) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(s)+1):
for j in range(i, len(t)+1):
if s[i-1] == t[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1]
# print(f"res: {dp[-1][-1]}")
print(f"dp: {dp}")
return dp[-1][-1] == len(s)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "abc"
t = "ahbgdc"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isSubsequence(s, t)
print(res)
10.48 不同的子序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/distinct-subsequences/description/

2. 思路:
思路:
- dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的s子序列中出现以j-1为结尾的t的个数为dp[i][j]
- 递推公式 如果s[i-1] = t[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j] 否则dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]
- 初始化dp[i][0] = 1 dp[0][j] = 0
- 双循环
s = "bagg"
t = "bag"
[
[1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 2]]
3. AC代码:
import math
import sys
"""
题目: 115. 不同的子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/distinct-subsequences/description/
思路:
1. dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的s子序列中出现以j-1为结尾的t的个数为dp[i][j]
2. 递推公式 如果s[i-1] = t[j-1] dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j] 否则dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]
3. 初始化dp[i][0] = 1 dp[0][j] = 0
4. 双循环
5.
s = "bagg"
t = "bag"
[
[1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 2]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def numDistinct(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(t) + 1) for _ in range(len(s) + 1)]
dp[0] = [0] * (len(t) + 1)
for i in range(len(s) + 1):
dp[i][0] = 1
for i in range(1, len(s) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(t) + 1):
if s[i-1] == t[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j]
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]
# print(f"dp: {dp}")
# print(f"res: {sys.maxsize}")
return dp[-1][-1] % int((math.pow(10, 9) + 7))
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "rabbbit"
t = "rabbit"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.numDistinct(s, t)
print(res)
print()
10.49 两个字符串的删除操作
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-operation-for-two-strings/

2. 思路:
可以利用最长公共子序列求
len(word1) + len(word2) - (2 * dp[-1][-1])
返回两个字符串的和然后减去公共子序列的两倍
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 583. 两个字符串的删除操作
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-operation-for-two-strings/
思路:
可以利用最长公共子序列求
len(word1) + len(word2) - (2 * dp[-1][-1])
返回两个字符串的和然后减去公共子序列的两倍
"""
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
"""
:type word1: str
:type word2: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(word2) + 1) for _ in range(len(word1) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(word1) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(word2) + 1):
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else: # 这里是找除了0:i-1, 0:j-1的最大值
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j])
# print(f"dp: {dp}")
return len(word1) + len(word2) - (2 * dp[-1][-1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
word1 = "sea"
word2 = "eat"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.minDistance(word1, word2)
print(res)
10.50 编辑距离
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/edit-distance/

2. 思路:
- dp[i][j] 表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][j]。
- 递推公式 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] else min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + 1
- 初始化 dp[i][0] = i dp[0][j] = j
- 双层for循环
- dp数组如下
word1 = “horse”
word2 = “ros”
[
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[1, 1, 2, 3],
[2, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 2, 2, 2],
[4, 3, 3, 2],
[5, 4, 4, 3]
]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 72. 编辑距离
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/edit-distance/
思路:
1. dp[i][j] 表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串word2,最近编辑距离为dp[i][j]。
2. 递推公式 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] else min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + 1
3. 初始化 dp[i][0] = i dp[0][j] = j
4. 双层for循环
5. dp数组如下
word1 = "horse"
word2 = "ros"
[
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[1, 1, 2, 3],
[2, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 2, 2, 2],
[4, 3, 3, 2],
[5, 4, 4, 3]
]
"""
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
"""
:type word1: str
:type word2: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(word2) + 1) for _ in range(len(word1) + 1)]
for i in range(len(word1) + 1):
dp[i][0] = i
for j in range(len(word2) + 1):
dp[0][j] = j
for i in range(1, len(word1) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(word2) + 1):
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + 1
print(dp)
return dp[-1][-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
word1 = "horse"
word2 = "ros"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.minDistance(word1, word2)
print(res)
10.51 回文子串
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindromic-substrings/

2. 思路1:
- 布尔类型的dp[i][j]:表示区间范围[i,j] (注意是左闭右闭)的子串是否是回文子串,如果是dp[i][j]为true,否则为false。
- 递推公式 s[i] == s[j] if j - i <= 1 or dp[i+1][j-1] 那么dp[i][j] 都为ture
- [[False] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))] 初始化
- 从下到上 从左到右
- dp数组 左下角一定是False
s = “aaa”
dp:[
[True, True, True],
[False, True, True],
[False, False, True]]
3. AC代码1:
"""
题目: 647. 回文子串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindromic-substrings/
思路:
1. 布尔类型的dp[i][j]:表示区间范围[i,j] (注意是左闭右闭)的子串是否是回文子串,如果是dp[i][j]为true,否则为false。
2. 递推公式 s[i] == s[j] if j - i <= 1 or dp[i+1][j-1] 那么dp[i][j] 都为ture
3. [[False] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))] 初始化
4. 从下到上 从左到右
5. dp数组 左下角一定是False
s = "aaa"
dp:[
[True, True, True],
[False, True, True],
[False, False, True]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def countSubstrings(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[False] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))]
res = 0
for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(i, len(s)):
if s[i] == s[j]:
if j - i <= 1 or dp[i+1][j-1]:
dp[i][j] = True
res += 1
print(f"dp:{dp}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "aaa"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.countSubstrings(s)
print(res)
2. 思路2:
- 在遍历中心点的时候,要注意中心点有两种情况。
- 一个元素可以作为中心点,两个元素也可以作为中心点。
- 三个元素就可以由一个元素左右添加元素得到,四个元素则可以由两个元素左右添加元素得到。
3. AC代码2:
# 双指针方法
"""
题目: 回文子串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindromic-substrings/
思路:
在遍历中心点的时候,要注意中心点有两种情况。
一个元素可以作为中心点,两个元素也可以作为中心点。
三个元素就可以由一个元素左右添加元素得到,四个元素则可以由两个元素左右添加元素得到。
"""
class Solution(object):
def countSubstrings(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
res = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
res += self.count(i, i, s)
res += self.count(i, i+1, s)
return res
def count(self, i, j, s):
res = 0
while i >= 0 and j < len(s) and s[i]==s[j]:
i -= 1
j += 1
res += 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "abc"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.countSubstrings(s)
print(res)
10.52 最长回文子序列
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/description/

2. 思路:
- dp[i][j]:字符串s在[i, j]范围内最长的回文子序列的长度为dp[i][j]。
- 递推公式: s[i] == s[j]: 长度小于1 dp[i][j] = j - i + 1 长度大于1 dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] + 2
不等于dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j]) - 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))]
- 从下上到 从左到右 右上方
- dp数组
s = “bbbab”
[[1, 2, 3, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 2, 3],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 3],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1]]
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 516. 最长回文子序列
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/description/
思路:
1. dp[i][j]:字符串s在[i, j]范围内最长的回文子序列的长度为dp[i][j]。
2. 递推公式: s[i] == s[j]: 长度小于1 dp[i][j] = j - i + 1 长度大于1 dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] + 2
不等于dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j])
3. 初始化: dp = [[0] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))]
4. 从下上到 从左到右 右上方
5. dp数组
s = "bbbab"
[[1, 2, 3, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 2, 3],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 3],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1]]
"""
class Solution(object):
def longestPalindromeSubseq(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[0] * (len(s)) for _ in range(len(s))]
# dp[]
for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(i, len(s)):
if s[i] == s[j]:
if j - i <= 1:
dp[i][j] = j - i + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] + 2
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j])
print(dp)
return dp[0][len(s)-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "bbbab"
s = "bbbab"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.longestPalindromeSubseq(s)
print(res)
10.53 最长回文子串
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/description/

2. 思路:
1. 遍历所有回文子串得到长度最大的即可 保留start和end
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 5. 最长回文子串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/description/
思路:
1. 遍历所有回文子串得到长度最大的即可 保留start和end
"""
class Solution(object):
def longestPalindrome(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
dp = [[False] * len(s) for _ in range(len(s))]
max_len = 0
start = 0
end = 0
for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(i, len(s)):
if s[i] == s[j]:
if j - i <= 1 or dp[i+1][j-1]:
dp[i][j] = True
current_len = j - i + 1
if current_len > max_len:
max_len = current_len
start = i
end = j + 1
print(f"dp:{dp}")
print(s[start:end])
return s[start:end]
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "babad"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.longestPalindrome(s)
print(res)
11. 单调栈

11.1 每日温度
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/

2. 思路:
利用单调栈 res数组用于存放结果数组
stack用于存放单调栈中的索引 栈顶到栈底得是升序(非降序)的
遍历得到每个元素
1.<= 入栈
2.> 循环遍历satck不为空且当前元素大于栈顶元素 利用使得stack出栈, 出栈 res[topIndex] = i - topIndex
最后i入栈
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 739. 每日温度
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/
思路:
利用单调栈
res数组用于存放结果数组
stack用于存放单调栈中的索引 栈顶到栈底得是升序(非降序)的
遍历得到每个元素
1. <= 入栈
2. > 循环遍历satck不为空且当前元素大于栈顶元素 利用使得stack出栈, 出栈 res[topIndex] = i - topIndex
最后i入栈
"""
class Solution(object):
def dailyTemperatures(self, temperatures):
"""
:type temperatures: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = [0] * len(temperatures)
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(temperatures)):
# 当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 直接入栈
if temperatures[i] < temperatures[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack[-1]
res[topIndex] = i - topIndex # 注意这里不能拿写成res[stack[-1] ] = i - stack.pop() 会数组越界, 因为先执行的是右边, stack空了之后再次执行stack[-1] 就会报错
stack.pop()
stack.append(i)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.dailyTemperatures(temperatures)
print(res)
11.2 下一个更大元素 I
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-greater-element-i

2. 思路:
1. 利用单调栈
2. res 得到比i大的元素的下一个元素的值
3. 然后遍历nums1得到每个num在nums2的索引通过res就可以得到他的值放入到ans列表中
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 496. 下一个更大元素 I
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-greater-element-i
思路:
利用单调栈
res 得到比i大的元素的下一个元素的值
然后遍历nums1得到每个num在nums2的索引通过res就可以得到他的值放入到ans列表中
"""
class Solution(object):
def nextGreaterElement(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = [-1] * len(nums2)
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(nums2)):
if nums2[i] <= nums2[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and nums2[i] > nums2[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack.pop()
res[topIndex] = nums2[i]
stack.append(i)
ans = []
for num in nums1:
ans.append(res[nums2.index(num)])
# print(res)
# print(ans)
# print(stack)
return ans
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [4, 1, 2]
nums2 = [1, 3, 4, 2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.nextGreaterElement(nums1, nums2)
print(res)
11.3 下一个更大元素 II

-
思路:
- 相对上一个问题, 由于nums是循环的 所以只需要遍历两遍即可
-
AC代码:
"""
题目: 503. 下一个更大元素 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-greater-element-ii/
思路:
相对上一个问题, 由于nums是循环的 所以只需要遍历两遍即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = [-1] * len(nums)
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] <= nums[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and nums[i] > nums[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack.pop()
res[topIndex] = nums[i]
# print(nums2[i])
stack.append(i)
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] <= nums[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and nums[i] > nums[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack.pop()
res[topIndex] = nums[i]
# print(nums2[i])
stack.append(i)
# print(stack)
print(res)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.nextGreaterElements(nums1)
print(res)
11.4 接雨水
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water

2. 思路1:
- 利用单调栈
我们先找到数组的最大值max_value, 数组两端像最大值逼近从而求雨水
nextGreater_dict key:value 当前索引:比当前索引值大的下一个索引值
进行跳跃切片, 然后对每段切片进行单独求雨水
3. AC代码1:
"""
题目: 42. 接雨水
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water
思路:
利用单调栈
我们先找到数组的最大值max_value, 数组两端像最大值逼近从而求雨水
nextGreater_dict key:value 当前索引:比当前索引值大的下一个索引值
进行跳跃切片, 然后对每段切片进行单独求雨水
"""
class Solution(object):
def trap(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
nextGreater_dict = {key: -1 for key in range(len(height))}
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(height)):
if height[i] < height[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and height[i] >= height[stack[-1]]:
nextGreater_dict[stack.pop()] = i
stack.append(i)
key = 0
res = 0
while key < len(height) - 1:
if nextGreater_dict[key] != -1:
l = key
r = nextGreater_dict[key]
res += self.singletrap(height[l:r+1])
else:
l = key
r = len(height)-1
right = height[l:r+1]
right.reverse()
res += self.trap(right)
break
key = nextGreater_dict[key]
return res
def singletrap(self, arr):
if len(arr) <= 2:
return 0
res = 0
borderlow = min(arr[0], arr[-1])
for i in range(1, len(arr)-1):
if borderlow > arr[i]:
res += borderlow - arr[i]
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
height = [0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 5, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2]
print(height)
# height = [4, 3, 2]
# height = [4, 4, 4]
height_dict = {key:height[key] for key in range(len(height))}
print(height_dict)
solution = Solution()
res = solution.trap(height)
print(res)
2. 思路2:
- 利用单调栈
- right 存放右边第一个大于自己的元素下标 left 存放左边第一个大于等于自己的元素下标 然后遍历每个元素
- 高等于当前元素 min(height[right[i]], height[left[i]]) - height[i] 宽等于
- right[i] - left[i] - 1 res 雨水总和, 每次增加 然后最终进行返回
3. AC代码2:
"""
题目: 42. 接雨水
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water
思路:
利用单调栈
right 存放右边第一个大于自己的元素下标
left 存放左边第一个大于等于自己的元素下标
然后遍历每个元素
高等于当前元素 min(height[right[i]], height[left[i]]) - height[i]
宽等于 right[i] - left[i] - 1
res 雨水总和, 每次增加 然后最终进行返回
"""
class Solution(object):
def trap(self, height):
right = [-1] * len(height)
left = [-1] * len(height)
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(height)):
if height[i] <= height[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and height[i] > height[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack[-1]
right[topIndex] = i
if len(stack) > 1:
left[topIndex] = stack[-2]
else:
left[topIndex] = -1
stack.pop()
stack.append(i)
while len(stack) > 1:
topIndex = stack[-1]
left[topIndex] = stack[-2]
stack.pop()
res = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
if left[i] != -1 and right[i] != -1:
rain = (min(height[right[i]], height[left[i]]) - height[i]) * (right[i] - left[i] - 1)
res += rain
print(f"right: {right}")
print(f"left : {left}")
print(f"stack: {stack}")
print(f"res : {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
# height = [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
height = [6, 2, 2, 1, 3]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.trap(height)
print(f"res: {res}")
11.5 柱状图中最大的矩形
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/description/

2. 思路:
- 利用单调栈
- right 存放右边第一个小于自己的元素下标 ,left 存放左边第一个小于等于自己的元素下标
- 然后遍历每个元素, 高等于当前元素 height[i] 宽等于 right[i] - left[i] - 1
- 初始化max_area为最大的结果用于保存, 每次进行比较 然后最终进行返回
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 84柱状图中最大的矩形
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/description/
思路:
利用单调栈
right 存放右边第一个小于自己的元素下标
left 存放左边第一个小于等于自己的元素下标
然后遍历每个元素
高等于当前元素 height[i] 宽等于 right[i] - left[i] - 1
初始化max_area为最大的结果用于保存, 每次进行比较 然后最终进行返回
"""
class Solution(object):
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights):
right = [len(heights)] * len(heights)
left = [-1] * len(heights)
stack = [0]
for i in range(1, len(heights)):
if heights[i] >= heights[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
else:
while stack != [] and heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]]:
topIndex = stack[-1]
right[topIndex] = i
if len(stack) > 1:
left[topIndex] = stack[-2]
stack.pop()
stack.append(i)
while len(stack) > 1:
topIndex = stack[-1]
left[topIndex] = stack[-2]
stack.pop()
max_area = 0
for i in range(len(heights)):
h = heights[i]
w = right[i] - left[i] - 1
current_area = h * w
max_area = max(max_area, current_area)
print(current_area)
print(f"right: {right}")
print(f"left: {left}")
print(max_area)
return max_area
if __name__ == '__main__':
heights = [2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.largestRectangleArea(heights)
print(res)
11.1 每日温度
1. 刷题链接:
2. 思路:
3. AC代码:


























 1067
1067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








