一、准备对象的配置文件-----beans.xml,保存路径为(E:\beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beams>
<bean id="g1" className="_10内省.Girl">
<id>1</id>
<name>刘诗诗</name>
<age>30</age>
</bean>
<bean id="gg" className="_10内省.Girl">
<id>3</id>
<name>迪丽热巴</name>
<age>28</age>
</bean>
<bean id="g2" className="_10内省.Girl">
<id>2</id>
<name>杨幂</name>
<age>33</age>
</bean>
<bean id="b1" className="_10内省.Boy">
<name>小赵</name>
</bean>
</beams>
二、要准备要生成的对象的类
Boy类
package _10内省;
public class Boy {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Boy{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Girl类
package _10内省;
public class Girl {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Girl{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
三、根据配置文件生成对应的对象类-------MyPersonSpring.java
- 将根据配置文件生成的对象保存在map集合中,生成一个map集合
/通过配置文件生成的对象保存在集合
Map<String,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
- 向外面提供获取对应对应的方法,根据传入的id值
//根据对象的id,返回对象,在获取时,要强制转换成对应的对象类型
public Object get(String id){
return map.get(id);
}
//带泛型的获得对象,在获取其对应对象时,传入对象类型,不用再调用时,进行强制类型转换
public <T> T get(String id,T t){
return (T)map.get(id);
}
- 创建一个有参构造器,传入的参数是xml文件对象,再创建该对象时,就根据配置文件beans.xml创建对应的对象
public MyPersonSpring(File xml){
}
- 根据配置文件,获得每个对象的配置信息,先获得配置文件对象
//获得配置文件,根据配置文件获得对应的字节码对象和相关属性值的配置
//1.获得 创建工厂对象
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//2.创建Document对象
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
//3.根据配置文件,获得对应的文档对象
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(xml);
- 更具配置文件对象,获得要生成的对应对象,即<bean></bean>标签包含的对象配置内容,就是要生成的对象
//4.获得跟节点
Element element = document.getDocumentElement();
//5.获得bean节点的相关配置信息
NodeList bean = element.getElementsByTagName("bean");
//6.遍历bean节点的,根据字节点的数据,创建对应的对象
for (int i = 0;i < bean.getLength();i++){
//获得每个bean节点
Element item = (Element)bean.item(i);
//根据标签节点,获得对应的对象id和类名
String id = item.getAttribute("id");
String className = item.getAttribute("className");
}
- 可以根据<bean id=“g1” className="_10内省.Girl">标签的属性className的值,通过类名获得其对象的字节码,根据字节码对象可以获得其对象实例。通过反射技术,可以获得其字节码对应里面的属性和方法
//根据类名获得字节码对象
Class aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获得 该类的对象
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
//通过字节码对象的内省技术,去获得xml文件对象的对应属性值
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(aClass, Object.class);
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
//获得对应属性的写方法
//获得属性名,去xml配置文件,根据其属性名获得其属性值
String name = propertyDescriptor.getName();
//获得对应属性的值的类型,方便后面进行写入值
Class propertyType = propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType();
//使用内省的技术,获得其对应属性的写入方法
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
}
- 通过字节码对象,反射获得对应类的对应属性名,再根据这个属性名去xml文件获得对应<bean></bean>标签下的,与该属性名对应的标签,根据其保存的内容,赋值给对应对象的属性,接着第6的for循环里面
//去xml文件获取对应属性的属性值
String value = item.getElementsByTagName(name).item(0).getTextContent();
//根据字节码的属性类型,进行xml配置文件读取的值进行转换
if(propertyType == int.class){
writeMethod.invoke(o,Integer.parseInt(value));
}else{
writeMethod.invoke(o,value);
}
- 将生成的对象保存再map集合
//将每个bean配置的对象存储在集合里面
map.put(id,o);
总代码汇总
package _10内省;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MyPersonSpring {
//通过配置文件生成的对象保存在集合
Map<String,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
//根据配置文件,生成对应的对象
public MyPersonSpring(File xml) throws ParserConfigurationException, IOException, SAXException, ClassNotFoundException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//获得配置文件,根据配置文件获得对应的字节码对象和相关属性值的配置
//1.获得 创建工厂对象
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//2.创建Document对象
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
//3.根据配置文件,获得对应的文档对象
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(xml);
//4.获得跟节点
Element element = document.getDocumentElement();
//5.获得bean节点的相关配置信息
NodeList bean = element.getElementsByTagName("bean");
//6.遍历bean节点的,根据字节点的数据,创建对应的对象
for (int i = 0;i < bean.getLength();i++){
//获得每个bean节点
Element item = (Element)bean.item(i);
//根据标签节点,获得对应的对象id和类名
String id = item.getAttribute("id");
String className = item.getAttribute("className");
//根据类名获得字节码对象
Class aClass = Class.forName(className);
//获得 该类的对象
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
//通过字节码对象的内省技术,去获得xml文件对象的对应属性值
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(aClass, Object.class);
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
//遍历
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
//获得对应属性的写方法
//获得属性名,去xml配置文件,根据其属性名获得其属性值
String name = propertyDescriptor.getName();
Class propertyType = propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType();
//去xml文件获取对应属性的属性值
String value = item.getElementsByTagName(name).item(0).getTextContent();
//使用内省的技术,写入属性值
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//根据字节码的属性类型,进行xml配置文件读取的值进行转换
if(propertyType == int.class){
writeMethod.invoke(o,Integer.parseInt(value));
}else{
writeMethod.invoke(o,value);
}
}
//将每个bean配置的对象存储在集合里面
map.put(id,o);
}
}
//根据对象的id,返回对象
public Object get(String id){
return map.get(id);
}
//带泛型的获得对象
public <T> T get(String id,T t){
return (T)map.get(id);
}
}
测试代码----PersonMain.java
package _10内省;
import java.io.File;
public class PersonMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyPersonSpring BeanObjet = new MyPersonSpring(new File("E:\\学习资料\\08_网络编程\\src\\beans.xml"));
Girl g1 = BeanObjet.get("g1", new Girl());
System.out.println(g1);
Girl g2 = BeanObjet.get("g2", new Girl());
System.out.println(g2);
Girl gg = BeanObjet.get("gg", new Girl());
System.out.println(gg);
Boy b1 = BeanObjet.get("b1", new Boy());
System.out.println(b1);
}
}
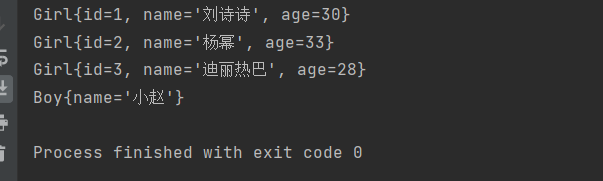
- 结果;
总结
- 对应xml配置文件,其bean下的标签数是不确定的。因此可以通过其className类名,获得其字节码对象,反射获得对象属性名,再去xml配置文件读取对应的属性值,为其写入
- 将对象保存在map集合,是因为其与id作为key保存,则可以根据id接口获得其对应的对象






















 521
521

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








