1.写一个函数找到两个数中的最大值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Max(int a,int b){
if (a>b){
return a;
}
return b;
}
int main(){
int ret = Max(10,20);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

函数的调用:
函数调用就会进入到函数体内部执行,遇到return语句,函数就结束了,回到函数调用的位置继续执行.(函数值回来的位置就是函数调用的位置)
拓展:利用三目运算符进行计算
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Max(int a,int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
int main(){
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
int ret=Max(x,y);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.写一个函数交换两个数的内容.(传指针)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Swap(int* x,int* y){ //
int tep;
tep = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tep;
}
int main(){
int a= 10;
int b= 20;
printf("交换之前的数:a=%d b=%d\n",a,b);
Swap(&a,&b);
printf("交换之后的数:a=%d b=%d\n",a,b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

总结: 形参是实参的一份拷贝.
函数的调用执行过程:函数调用就会进入到函数体内部执行,遇到return语句函数就结束了,重新回到调用位置的下一行开始执行.
3.写一个函数,判定一个数是不是素数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Isprime(int num){
if (num == 1){
return 0;
}
if (num == 0){
return 0;
}
for (int i = 2; i < num; i++){
if (num%i == 0){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
int n;
printf("请输入要判定的数: \n");
scanf("%d",&n);
int ret = Isprime(n);
printf("1代表是素数 0 代表不是素数\n");
printf("输出的数字是: %d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

4.写一个函数,判定是不是闰年
闰年分为普通闰年和世纪闰年,具体区别如下:
1、普通闰:能被4整除但不能被100整除的年份为普通闰年。(如2004年就是闰年,1900年不是闰年)。
2、世纪闰年:能被400整除的为世纪闰年。(如2000年是世纪闰年,1900年不是世纪闰年)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Leapyear(int year){
if ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){
printf("%d是闰年\n", year);
}
else{
printf("%d不是闰年\n", year);
}
}
int main(){
int Year;
printf("请输入要判定的年份: \n");
scanf("%d",&Year);
Leapyear(Year);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

5.在一个数组中找一个数字,并且返回下标
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void FindNumber(int arr[], int size, int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++){
if (arr[i] == toFind ){
printf("找到了,下标是: %d\n",i);
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr[] = { 9, 5, 2, 7 };
int toFind = 2;
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// 数组的大小
FindNumber(arr, size, toFind);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

拓展.写一个函数,在一个有序数组中找一个数字,找到返回下标.找不到返回-1.(二分查找)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int FindNumber(int arr[], int size, int toFind){
int left = 0;
int right = size - 1;// 数组的大小
//[left,right] 数组下标大小的区间范围
int mid;
while (left <= right){
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[mid] > toFind){
right = mid - 1;
}
else if (arr[mid] < toFind){
left = mid + 1;
}
else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int toFind = 5;
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//[left,right] 数组下标大小的区间范围
int ret = FindNumber(arr,size,toFind);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
6.写一个函数,每调用一次num加1;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Func(int* x){
*x += 1;
}
int main(){
int num=0 ;
Func(&num);
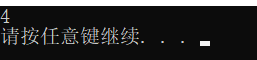
printf("%d\n",num);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

函数的声明和定义
7.返回两个数中的最大值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Max(int a,int b){
if (a>b){
return a;
}
else{
return b;
}
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n",Max(10,20));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
**函数调用: **调用函数必须写在主函数的上面,如果调用函数写在主函数的下面.必须在前面先进行声明.
函数递归
函数递归:函数调用自身的过程
1.接收一个整型值(无符号),按照它的顺序打印每一位.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void PrintNumber(int num){
if (num>9){
PrintNumber(num/10);
}
printf("%d ", num % 10);
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int n = 1234;
PrintNumber(n);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.字符串的长度
法1.利用strlen函数进行直接求解
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
char arr[] = "abcd";
int ret;
ret = strlen(arr);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
对于利用strlen函数求字符串的长度.strlen是遇到\0立马停止计算,字符串恰好 是以\0 结尾的
法2.函数调用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int Strlen(char arr[]){
int i = 0;
while (arr[i] != '\0'){ // 以字符串是以\0结尾的 所以限制条件当处于\0的时候结束计算字符串的长度
i++;
}
return i;
}
int main(){
char arr1[] = "abcd";
printf("%d\n",Strlen(arr1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法3.递归
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Strlen(char arr[]){
if (arr[0] == '\0'){
return 0;
}
return 1 + Strlen(arr + 1);
}
int main(){
char arr1[] = "abcd";
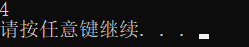
printf("%d\n",Strlen(arr1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3.求n的阶乘(n统一取5)
法1.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
int n;
int i;
int result = 1;
printf("请输入要求几的阶乘: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for (i = 1; i <= n;i++){
result *= i;
}
printf("%d\n",result);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法2.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int Factor(int n){
int i;
int result = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n;i++){
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
int main(){
int n;
int i;
printf("请输入要求几的阶乘: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", Factor(n));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法3.递归
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int Factor(int n){
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if (n == 0){
return 1;
}
return n*Factor(n - 1);
}
int main(){
int num;
int i;
printf("请输入要求几的阶乘: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("%d\n", Factor(num));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

4.斐波那契数
**法1.递归 **
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Fib(int n){
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if (n == 2){
return 1;
}
return Fib( n-2) + Fib(n-1);
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n", Fib(3));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法2.非递归
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Fib(int n){
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if (n == 2){
return 1;
}
int cur;
int last1 = 1;
int last2 = 1;
for (int i = 3; i<= n;i++){
cur = last1 + last2;
last2 = last1;
last1 = cur;
}
return cur;
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n", Fib(3));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

递归整理总结:
递归的连个必要条件;1.一定要有递归结束的限制条件.2.每一次递归之后越来越接近这个限制条件.
递归求解思路:将问题进行拆分处理.
5.青蛙跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
思路:列出一共跳的可能性,找到对应的规律
列出部分情况:
如果n = 1,只有一种跳法,那就是1
如果n = 2,那么有两种跳法,2,[1, 1]
如果n = 3,那么有三种跳法,[1, 1, 1], , [1, 2], [2, 1]
如果n = 4,那么有五种跳法,[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [2, 1, 1], [2, 2]
如果n = 5,那么有八种跳法,[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 2], [1, 1, 2, 1], [1, 2, 1, 1], [2, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1], [2, 1, 2], [1, 2, 2]
…
由规律可以很明显的看到:当前跳的总数始终等于前一项和前两项之和
法1.递归
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Jump(int n){
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if (n == 2){
return 2;
}
return Jump(n-1) + Jump(n-2);
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n", Jump(4));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法2.非递归
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Jump(int num){
int cur;
int last1 = 1;
int last2 = 2;
if (num == 1){
return 1;
}
if (num == 2){
return 2;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= num;i++){
cur = last1 + last2;
last1 = last2;
last2 = cur;
}
return cur;
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n", Jump(4));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:






















 786
786











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








