目录
作业
1.编写一个程序,开启3个 线程,这3个线程的ID分别为ABC,每个线程将自己的ID在屏幕上打印10 遍,要求输出结果必须按ABC的顺序显示,如ABCABC……依次递推;
提示:A
只能叫醒
B
,
B
只能唤醒
C
,
C
只能唤醒
A
;
2.
定义一个全局变量,
char str[] = "123456"
,要求定义两个线程:线程
A
, 线程
B
1). 要求
A
线程循环打印全局字符串
str
;
2). 要求
B
线程循环倒置全局字符串
str
:将
str
中的内容倒置为
"654321"
,再倒置为
"123456"....
注意:是倒置不是倒着打印
3). 要求
A
线程打印出的
str
字符串内容为:
123456
或者
654321
。
不允许出现乱序,例如:623451 653451,,,
4). 要求打印一次倒置一次
一、按顺序打印
1.1 函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int flag=0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
void* A(void *arg)
{
int i=0;
while(i<10)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(0 != flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}else
{
flag=1;
printf("A");
i++;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* B(void* arg)
{
int i=0;
while(i<10)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(1 != flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}else
{
flag=2;
printf("B");
i++;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* C(void* arg)
{
int i=0;
while(i<10)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(2 !=flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}else
{
flag=0;
printf("C\n");
i++;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL) !=0)
{
perror("pthread_mutex_init");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_cond_init");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,A,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,B,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,C,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}//今天裂开了,不想写注释了,。。。。。。
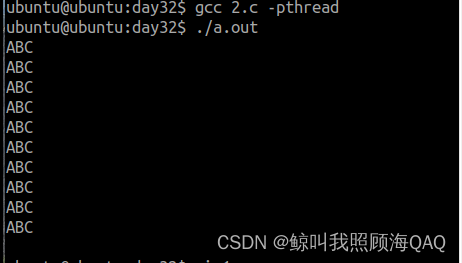
2.2 执行结果
二、倒置字符串
2.1 函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char str[]="123456";
int flag=0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
void* dayin(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(1 != flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}
int len=strlen(str);
char temp;
for(int i=0;i<len/2;i++)
{
temp=str[i];
str[i]=str[len-1-i];
str[len-1-i]=temp;
}
flag=0;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* daizhi(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(0 != flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}
printf("%s\n",str);
flag=1;
sleep(1);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL) !=0)
{
perror("pthread_mutex_init");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_cond_init");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,dayin,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,daizhi,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
2.2 执行结果























 59
59











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








