from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):
"""生成 y=Xw+b+噪声。"""
w=torch.tensor(w) #这步在沐神的代码里没有,但是在pycharm中报错说w类型是list,不是tensor.
X=torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w))) #生成X,均值为0,方差为1,大小:n个样本,列数是w的长度。shape=1000*2
y=torch.matmul(X,w)+b #torch.matmul是tensor的乘法,输入可以是高维的。
#print(y.shape) torch.Size([1000])
y+=torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape) #为了让问题复杂,加入随机噪音。
return X,y.reshape(-1,1)
#构造人造数据集的好处,知道真实的w,b
true_w=[2,-3.4]
true_b=4.2
features,labels=synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,1000)
plt.scatter(features[:,1],labels,1)
plt.show()
print(features[0])
print(labels[0])scatter()用法:scatter
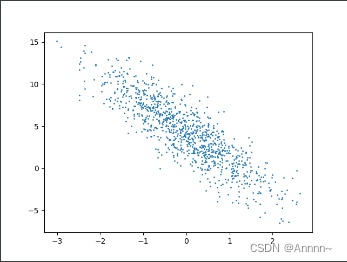
以上是随机数据生成部分。
生成数据后开始分批读取:
#批量读取数据集,为啥子呢?
#在训练模型时,我们需要遍历数据集并不断读取小批量数据样本。
#这里定义一个函数,每次返回batch_size(批量大小)个随机样本的特征和标签。
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples=len(features)
#print(num_examples) num_examples=1000
indices=list(range(num_examples))
#这些样本是随机读取的,没有特定的顺序
random.shuffle(indices) #下标打乱
#每一次从0开始,到最后num_examples,每次跳batch_size个大小。
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
#每次从i开始,每次拿到i+batch_size,每次拿bitch_size个index出来,最后不够的话,取num_examples
batch_indices=torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
#yield:python 的iteration,返回一个X,一个y,不断调用函数,不断返回。
batch_size=10
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
print(X,'\n',y)yield的用法:yield
list(range())的用法:list(range())
indices[:]数组切片
import random
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):
"""生成 y=Xw+b+噪声。"""
w=torch.tensor(w) #这步在沐神的代码里没有,但是在pycharm中报错说w类型是list,不是tensor.
X=torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w))) #生成X,均值为0,方差为1,大小:n个样本,列数是w的长度。X.shape=1000*2
y=torch.matmul(X,w)+b #torch.matmul是tensor的乘法,输入可以是高维的。y.shape=[]1000*2*[]2*1=[]1000*1
#print(y.shape) torch.Size([1000])
y+=torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape) #为了让问题复杂,加入随机噪音。y.shape=[]1000*1
return X,y.reshape(-1,1) #(reshape(-1, m)即列数固定,行数需要计算)此处该方法可省略。
#构造人造数据集的好处,知道真实的w,b
true_w=[2,-3.4]
true_b=4.2
features,labels=synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,1000)
plt.scatter(features[:,1],labels,1)
#plt.show()
#批量读取数据集,为啥子呢?
#在训练模型时,我们需要遍历数据集并不断读取小批量数据样本。
#这里定义一个函数,每次返回batch_size(批量大小)个随机样本的特征和标签。
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples=len(features)
#print(num_examples) num_examples=1000
indices=list(range(num_examples))
#这些样本是随机读取的,没有特定的顺序
random.shuffle(indices) #下标打乱
#每一次从0开始,到最后num_examples,每次跳batch_size个大小。
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
#每次从i开始,每次拿到i+batch_size,每次拿bitch_size个index出来,最后不够的话,取num_examples
batch_indices=torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
#yield:python 的iteration,返回一个X,一个y,不断调用函数,不断返回。
batch_size=10
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
print(X,'\n',y)
#数据定义好后,定义模型。
#模型,输入维度是2,随机初始化成均值为0,方差为1的正态分布。
#需要计算梯度
#偏差=0
w=torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(2,1),requires_grad=True)
b=torch.zeros(1,requires_grad=True)
def linreg(X,w,b):
"""线性回归模型"""
return torch.matmul(X,w)+b
def squared_loss(y_hat,y):
"""均方损失"""
return (y_hat-y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2/2
#参数:params-参数:一个list,包括w,b
#lr:学习率
#batch-size
def sgd(params,lr,batch_size):
"""小批量梯度下降"""
#不需要计算梯度,更新的时候不需要进行梯度计算:no_grad
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param-=lr*param.grad/batch_size
#梯度会存在.grad里面,之前的损失函数没有求均值,这里求均值
param.grad.zero_()#梯度设成0
lr=0.03
num_epochs=3 #整个数据扫三遍
net=linreg #模型
loss=squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs): #每次对数据扫一遍
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels): #每次拿出批量大小的X,y
l=loss(net(X,w,b),y) #把X,w,b放进network里面,做预测。把预测的y和真实的y做损失。
l.sum().backward() #求和之后算梯度
sgd([w,b],lr,batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
train_l=loss(net(features,w,b),labels)
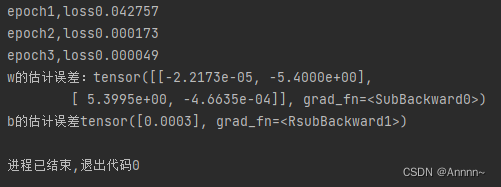
print(f'epoch{epoch+1},loss{float(train_l.mean()):f}')
print(f'w的估计误差:{torch.tensor(true_w)-w}')
print(f'b的估计误差{true_b-b}')附上完整版代码。
结果:
























 2400
2400











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








