内存回收LMKD
一、lmkd介绍
1.LMKD与Lowmemorykiller
从Android9.版本开始,系统放弃了传统的Lowmemorykiller改用LMKD(Low Memory Killer Daemon)进行低内存查杀。
从Android10版本开始,lmkd的监测内存模式从vmpressure变为了PSI方式。
LowMemoryKiller的概述
LowMemoryKiller是Android内存管理的重要组件。它的主要任务是在系统内存低于一定阈值时,选择性地杀死一些后台进程,以释放内存。这一机制能够确保用户正在使用的应用程序能够获得足够的内存,从而避免系统变得 sluggish 或出现崩溃。
LowMemoryKiller的工作流程
LMK的工作流程相对简单。首先,它会监控系统内存的使用情况。当内存使用达到特定阈值(称为“压缩阈值”)时,LMK就会被触发。接着,LMK会根据预设的优先级选择要杀死的进程。
lmkd的角色
lmkd(Low Memory Killer Daemon)是LowMemoryKiller的守护进程,负责与LMK进行协作。它通过提供更高级的内存管理功能,优化进程的选择和终止。lmkd根据系统的状态和资源分配策略,动态调整内存管理策略,在适当的时候做出响应。
lmkd的工作流程
lmkd通常以后台守护进程的形式运行,负责以下任务:
- 监控系统内存状态。
- 根据内存使用情况生成杀死进程的候选列表。
- 调用LMK来执行具体的进程杀死操作。
二、lmkd实现原理
2.1 工作原理图
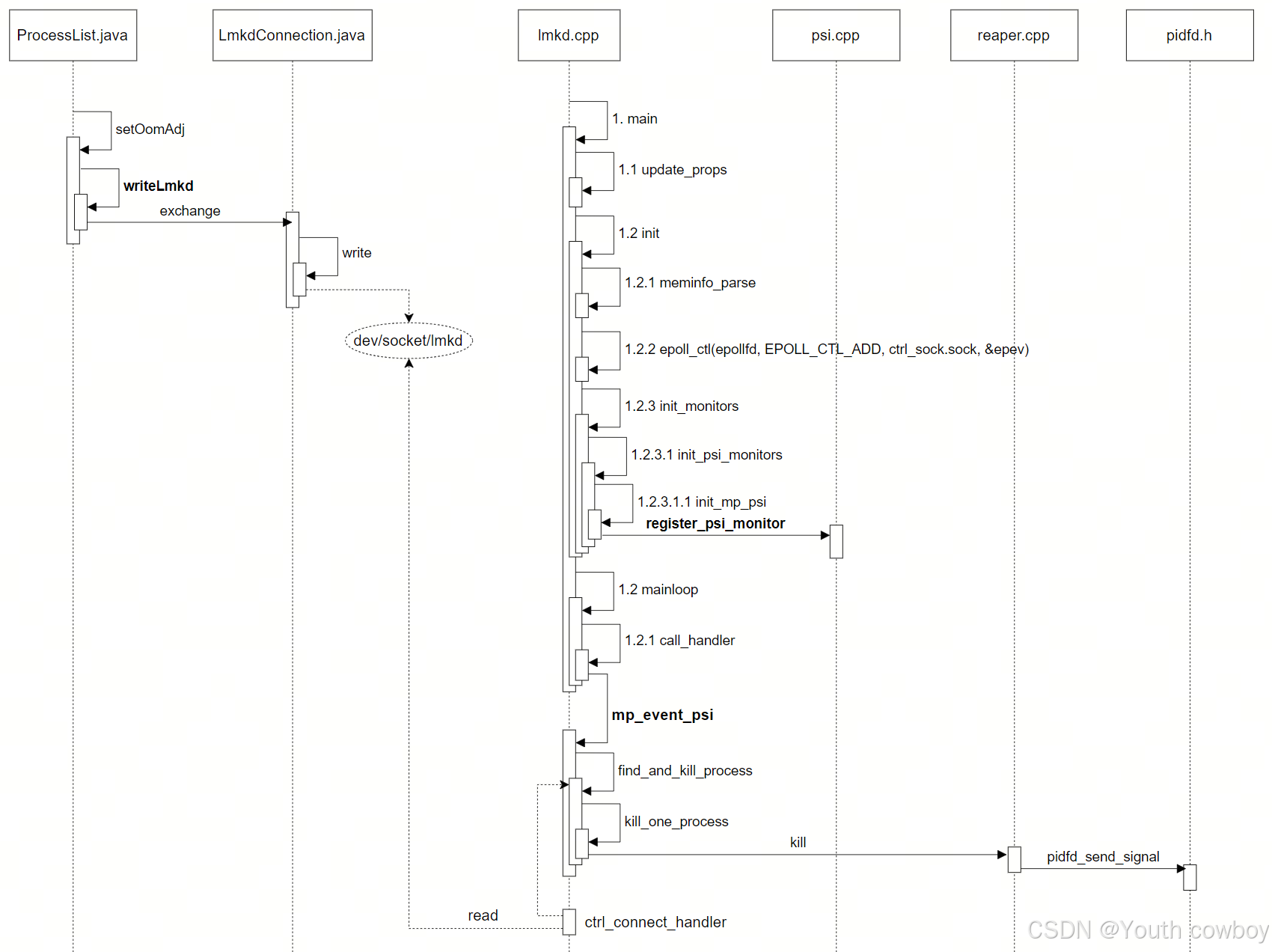
工作原理主要分为3部分:
1)app启动时,AMS将oom_adj并通过socket发送给lmkd进程,并由lmkd存起来
2)lmkd进程进入循环监听kernel psi事件
3)当发生psi事件时,根据lmkd策略进行进程查杀
2.2 lmkd启动
system/memory/lmkd/lmkd.rc
//lmkd是进程的名字,/system/bin/lmkd 代表当init进程fork lmkd成功后,需要执行的可执行文件
service lmkd /system/bin/lmkd
class core //核心进程 class_start core init.rc中 onboot
user lmkd
group lmkd system readproc
capabilities DAC_OVERRIDE KILL IPC_LOCK SYS_NICE SYS_RESOURCE
critical // 4min之内crash4次,则重启bootloader
socket lmkd seqpacket 0660 system system // 设置socket
task_profiles ServiceCapacityLow
省略其他信息......
critical的具体代码参考 system/core/init/service.cpp
/system/core/rootdir/init.rc,下面的内容是该文件的其中一部分
//on init:代表init触发器触发的时候会执行下面的各种命令
on init
省略其他命令......
# Start logd before any other services run to ensure we capture all of their logs.
start logd
# Start lmkd before any other services run so that it can register them
write /proc/sys/vm/watermark_boost_factor 0
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
//start lmkd:start命令会创建进程,lmkd与上面lmkd.rc中service后面的lmkd一致
start lmkd
当init把lmkd创建成功后,会执行下面的方法
main
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if ((argc > 1) && argv[1]) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "--reinit")) {
if (property_set(LMKD_REINIT_PROP, "")) {
ALOGE("Failed to reset " LMKD_REINIT_PROP " property");
}
return issue_reinit();
} else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "--boot_completed")) {
return on_boot_completed();
}
}
if (!update_props()) {
ALOGE("Failed to initialize props, exiting.");
return -1;
}
ctx = create_android_logger(KILLINFO_LOG_TAG);
//init方法成功返回0,从而进入下面的逻辑
if (!init()) {
if (!use_inkernel_interface) {
/*
* MCL_ONFAULT pins pages as they fault instead of loading
* everything immediately all at once. (Which would be bad,
* because as of this writing, we have a lot of mapped pages we
* never use.) Old kernels will see MCL_ONFAULT and fail with
* EINVAL; we ignore this failure.
*
* N.B. read the man page for mlockall. MCL_CURRENT | MCL_ONFAULT
* pins ⊆ MCL_CURRENT, converging to just MCL_CURRENT as we fault
* in pages.
*/
// 锁住该实时进程在物理内存上全部地址空间。这将阻止Linux将这个内存页调度到交换空间(swap space),
// 即使该进程已有一段时间没有访问这段空间。
/* CAP_IPC_LOCK required */
if (mlockall(MCL_CURRENT | MCL_FUTURE | MCL_ONFAULT) && (errno != EINVAL)) {
ALOGW("mlockall failed %s", strerror(errno));
}
/* CAP_NICE required */
struct sched_param param = {
.sched_priority = 1,
};
if (sched_setscheduler(0, SCHED_FIFO, ¶m)) { //实时调度
ALOGW("set SCHED_FIFO failed %s", strerror(errno));
}
}
//初始化reaper,创建杀进程的异步线程
if (init_reaper()) {
ALOGI("Process reaper initialized with %d threads in the pool",
reaper.thread_cnt());
}
//watchdog用来监听lmkd的主线程是否有耗时,有耗时的话,watchdog会来尝试杀进程
if (!watchdog.init()) {
ALOGE("Failed to initialize the watchdog");
}
// 循环处理事件 接收socket
mainloop();
}
android_log_destroy(&ctx);
ALOGI("exiting");
return 0;
}
LMKD init()
lmkd通过试探进入内核lmk模块路径(/sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree)的方式判断当前系统是否含义lmk模块。如果存在内核lmk模块,并且用户配置了enable_userspace_lmk为false,直接使用内核lmk。否则使用用户空间lmkd。
在lmkd启动时,会进行初始化。主要做了两个事:
1)启动 lmkd socket,进入监听,等待client端连接
2)初始化psi monitor
system/memory/lmkd/lmkd.cpp
static int init(void) {
static struct event_handler_info kernel_poll_hinfo = { 0, kernel_event_handler };
struct reread_data file_data = {
.filename = ZONEINFO_PATH,
.fd = -1,
};
struct epoll_event epev;
int pidfd;
int i;
int ret;
// Initialize page size
pagesize = getpagesize();
page_k = pagesize / 1024;
epollfd = epoll_create(MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS); //创建全局epoll文件句柄
if (epollfd == -1) {
ALOGE("epoll_create failed (errno=%d)", errno);
return -1;
}
// mark data connections as not connected
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA_CONN; i++) {
data_sock[i].sock = -1;
}
// 设置并监听 lmkd 控制套接字,以便处理来自客户端的连接请求
ctrl_sock.sock = android_get_control_socket("lmkd");
if (ctrl_sock.sock < 0) {
ALOGE("get lmkd control socket failed");
return -1;
}
ret = listen(ctrl_sock.sock, MAX_DATA_CONN);
if (ret < 0) {
ALOGE("lmkd control socket listen failed (errno=%d)", errno);
return -1;
}
epev.events = EPOLLIN;
// epoll事件处理函数,lmkd的socket连接时回调这里 这里打印"lmkd data connection established"
ctrl_sock.handler_info.handler = ctrl_connect_handler;
epev.data.ptr = (void *)&(ctrl_sock.handler_info);
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, ctrl_sock.sock, &epev) == -1) {
ALOGE("epoll_ctl for lmkd control socket failed (errno=%d)", errno);
return -1;
}
maxevents++;
//"/sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree"
has_inkernel_module = !access(INKERNEL_MINFREE_PATH, W_OK);
use_inkernel_interface = has_inkernel_module;
//在高版本use_inkernel_interface这值为false,也就是不会使用lowmemorykiller这个功能
if (use_inkernel_interface) {
ALOGI("Using in-kernel low memory killer interface");
if (init_poll_kernel()) {
epev.events = EPOLLIN;
epev.data.ptr = (void*)&kernel_poll_hinfo;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, kpoll_fd, &epev) != 0) {
ALOGE("epoll_ctl for lmk events failed (errno=%d)", errno);
close(kpoll_fd);
kpoll_fd = -1;
} else {
maxevents++;
/* let the others know it does support reporting kills */
property_set("sys.lmk.reportkills", "1");
}
}
} else {
// Do not register monitors until boot completed for devices configured
// for delaying monitors. This is done to save CPU cycles for low
// resource devices during boot up.
if (!delay_monitors_until_boot || property_get_bool("sys.boot_completed", false)) {
//初始化监听器(psi monitor)
if (!init_monitors()) {
return -1;
}
}
/* let the others know it does support reporting kills */
property_set("sys.lmk.reportkills", "1");
}
for (i = 0; i <= ADJTOSLOT(OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX); i++) {
procadjslot_list[i].next = &procadjslot_list[i];
procadjslot_list[i].prev = &procadjslot_list[i];
}
memset(killcnt_idx, KILLCNT_INVALID_IDX, sizeof(killcnt_idx));
/*
* Read zoneinfo as the biggest file we read to create and size the initial
* read buffer and avoid memory re-allocations during memory pressure
*/
if (reread_file(&file_data) == NULL) {
ALOGE("Failed to read %s: %s", file_data.filename, strerror(errno));
}
/* check if kernel supports pidfd_open syscall */
pidfd = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(pidfd_open(getpid(), 0));
if (pidfd < 0) {
pidfd_supported = (errno != ENOSYS);
} else {
pidfd_supported = true;
close(pidfd);
}
ALOGI("Process polling is %s", pidfd_supported ? "supported" : "not supported" );
if (!lmkd_init_hook()) {
ALOGE("Failed to initialize LMKD hooks.");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
具体看如何进行psi poll监听及注册回调函数:
init_monitors
static bool init_monitors() {
//use_psi_monitors为true代表使用PSI来实现资源紧张监控,在高版本为true, 如果 use_psi为true,代表使用PSI则使用init_psi_monitors()来初始化PSI
/* Try to use psi monitor first if kernel has it */
use_psi_monitors = GET_LMK_PROPERTY(bool, "use_psi", true) &&
init_psi_monitors();
//use_psi_monitors不可用的时候,使用vmpressure实现监控
/* Fall back to vmpressure */
if (!use_psi_monitors &&
(!init_mp_common(VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW) ||
!init_mp_common(VMPRESS_LEVEL_MEDIUM) ||
!init_mp_common(VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL))) {
ALOGE("Kernel does not support memory pressure events or in-kernel low memory killer");
return false;
}
if (use_psi_monitors) {
ALOGI("Using psi monitors for memory pressure detection");
} else {
ALOGI("Using vmpressure for memory pressure detection");
}
monitors_initialized = true;
return true;
}
init_psi_monitors
这里主要通过下面两个配置,进行不同的kill策略
ro.config.low_ram配置设备为低内存ro.lmk.use_minfree_levels与内核中的 LMK 驱动程序相同的kill策略(即可用内存和文件缓存阈值(file cache thresholds))做出终止决策。
//初始化PSI监听器
static bool init_psi_monitors() {
/*
* When PSI is used on low-ram devices or on high-end devices without memfree levels
* use new kill strategy based on zone watermarks, free swap and thrashing stats.
* Also use the new strategy if memcg has not been mounted in the v1 cgroups hiearchy since
* the old strategy relies on memcg attributes that are available only in the v1 cgroups
* hiearchy.
*/
bool use_new_strategy =
GET_LMK_PROPERTY(bool, "use_new_strategy", low_ram_device || !use_minfree_levels);
if (!use_new_strategy && memcg_version() != MemcgVersion::kV1) {
ALOGE("Old kill strategy can only be used with v1 cgroup hierarchy");
return false;
}
/* In default PSI mode override stall amounts using system properties */
if (use_new_strategy) {
/* Do not use low pressure level */
psi_thresholds[VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW].threshold_ms = 0;
psi_thresholds[VMPRESS_LEVEL_MEDIUM].threshold_ms = psi_partial_stall_ms;
psi_thresholds[VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL].threshold_ms = psi_complete_stall_ms;
}
// 初始化低中高级别
if (!init_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW, use_new_strategy)) {
return false;
}
if (!init_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_MEDIUM, use_new_strategy)) {
destroy_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW);
return false;
}
if (!init_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL, use_new_strategy)) {
destroy_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_MEDIUM);
destroy_mp_psi(VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW);
return false;
}
return true;
}
/* memory pressure levels */
enum vmpressure_level {
VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW = 0,
VMPRESS_LEVEL_MEDIUM,
VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL,
VMPRESS_LEVEL_COUNT
};
static struct psi_threshold psi_thresholds[VMPRESS_LEVEL_COUNT] = {
{ PSI_SOME, 70 }, /* 70ms out of 1sec for partial stall */
{ PSI_SOME, 100 }, /* 100ms out of 1sec for partial stall */
{ PSI_FULL, 70 }, /* 70ms out of 1sec for complete stall */
};
init_mp_psi
- 只有当设备不是低内存设备,同时使用minfree级别时,不使用新策略。
static bool init_mp_psi(enum vmpressure_level level, bool use_new_strategy) {
int fd;
/* Do not register a handler if threshold_ms is not set */
if (!psi_thresholds[level].threshold_ms) {
return true;
}
// 初始化psi,往"/proc/pressure/memory"节点中写入初始值
fd = init_psi_monitor(psi_thresholds[level].stall_type,
psi_thresholds[level].threshold_ms * US_PER_MS,
PSI_WINDOW_SIZE_MS * US_PER_MS);
// 监听函数---mp_event_psi
if (fd < 0) {
return false;
}
// 当有资源紧张的通知时,会调用mp_event_psi或者mp_event_common方法
vmpressure_hinfo[level].handler = use_new_strategy ? mp_event_psi : mp_event_common;
vmpressure_hinfo[level].data = level; // 注册poll事件的监听回调函数
// 使用epoll机制来监听fd上的通知,有资源紧张的通知会在fd上有数据写入
if (register_psi_monitor(epollfd, fd, &vmpressure_hinfo[level]) < 0) {
destroy_psi_monitor(fd);
return false;
}
maxevents++;
mpevfd[level] = fd;
return true;
}
基于以上的代码,当出现资源紧张的时候,mp_event_psi或者mp_event_common方法是会被调用的,被调用的时候也就是开始杀进程的时机了。
psi主要监控了proc/pressure下 io memory cpu三项指标。
2.4 LMKD接收SystemServer socket消息
1)lmkd进程的客户端是ActivityManager,通过socket(dev/socket/lmkd)跟 lmkd 进行通信, 当有客户连接时,就会回调ctrl_connect_handler函数 > ctrl_data_handler > ctrl_command_handler
这里我们直接看ctrl_command_handler
ctrl_command_handler
static void ctrl_command_handler(int dsock_idx) {
LMKD_CTRL_PACKET packet;
struct ucred cred;
int len;
enum lmk_cmd cmd;
int nargs;
int targets;
int kill_cnt;
int result;
len = ctrl_data_read(dsock_idx, (char *)packet, CTRL_PACKET_MAX_SIZE, &cred);
if (len <= 0)
return;
if (len < (int)sizeof(int)) {
ALOGE("Wrong control socket read length len=%d", len);
return;
}
cmd = lmkd_pack_get_cmd(packet);
nargs = len / sizeof(int) - 1;
if (nargs < 0)
goto wronglen;
switch(cmd) {
case LMK_TARGET:
// 解析socket packet里面传过来的数据,写入lowmem_minfree和lowmem_adj两个数组中,
// 用于控制low memory的行为;
// 设置sys.lmk.minfree_levels,比如属性值:
// [sys.lmk.minfree_levels]: [18432:0,23040:100,27648:200,85000:250,191250:900,241920:950]
targets = nargs / 2;
if (nargs & 0x1 || targets > (int)lowmem_adj.size()) {
goto wronglen;
}
cmd_target(targets, packet);
break;
// AMS客户端会往lmkd socket中写入LMK_PROCPRIO及进程信息(pid、oom_adj)
case LMK_PROCPRIO:
// 设置进程的oomadj,把oomadj写入对应的节点(/proc/pid/oom_score_adj)中;
// 将oomadj保存在一个哈希表中。
// 哈希表 pidhash 是以 pid 做 key,proc_slot 则是把 struct proc 插入到以 oomadj 为 key 的哈希表 procadjslot_list 里面
/* process type field is optional for backward compatibility */
if (nargs < 3 || nargs > 4)
goto wronglen;
cmd_procprio(packet, nargs, &cred);
break;
case LMK_PROCREMOVE:
// 解析socket传过来进程的pid,
// 通过pid_remove 把这个 pid 对应的 struct proc 从 pidhash 和 procadjslot_list 里移除
if (nargs != 1)
goto wronglen;
cmd_procremove(packet, &cred);
break;
case LMK_PROCPURGE:
if (nargs != 0)
goto wronglen;
cmd_procpurge(&cred);
break;
case LMK_GETKILLCNT:
if (nargs != 2)
goto wronglen;
kill_cnt = cmd_getkillcnt(packet);
len = lmkd_pack_set_getkillcnt_repl(packet, kill_cnt);
if (ctrl_data_write(dsock_idx, (char *)packet, len) != len)
return;
break;
case LMK_SUBSCRIBE:
if (nargs != 1)
goto wronglen;
cmd_subscribe(dsock_idx, packet);
break;
case LMK_PROCKILL:
/* This command code is NOT expected at all */
ALOGE("Received unexpected command code %d", cmd);
break;
case LMK_UPDATE_PROPS:
if (nargs != 0)
goto wronglen;
result = -1;
if (update_props()) {
if (!use_inkernel_interface && monitors_initialized) {
/* Reinitialize monitors to apply new settings */
destroy_monitors();
if (init_monitors()) {
result = 0;
}
} else {
result = 0;
}
if (direct_reclaim_threshold_ms > 0 && !memevent_listener) {
ALOGW("Kernel support for direct_reclaim_threshold_ms is not found");
direct_reclaim_threshold_ms = 0;
}
}
len = lmkd_pack_set_update_props_repl(packet, result);
if (ctrl_data_write(dsock_idx, (char *)packet, len) != len) {
ALOGE("Failed to report operation results");
}
if (!result) {
ALOGI("Properties reinitilized");
} else {
/* New settings can't be supported, crash to be restarted */
ALOGE("New configuration is not supported. Exiting...");
exit(1);
}
break;
case LMK_START_MONITORING:
if (nargs != 0)
goto wronglen;
// Registration is needed only if it was skipped earlier.
if (monitors_initialized)
return;
if (!property_get_bool("sys.boot_completed", false)) {
ALOGE("LMK_START_MONITORING cannot be handled before boot completed");
return;
}
if (!init_monitors()) {
/* Failure to start psi monitoring, crash to be restarted */
ALOGE("Failure to initialize monitoring. Exiting...");
exit(1);
}
ALOGI("Initialized monitors after boot completed.");
break;
case LMK_BOOT_COMPLETED:
if (nargs != 0) goto wronglen;
if (boot_completed_handled) {
/* Notify we have already handled post boot-up operations */
result = 1;
} else if (!property_get_bool("sys.boot_completed", false)) {
ALOGE("LMK_BOOT_COMPLETED cannot be handled before boot completed");
result = -1;
} else {
/*
* Initialize the memevent listener after boot is completed to prevent
* waiting, during boot-up, for BPF programs to be loaded.
*/
if (init_memevent_listener_monitoring()) {
ALOGI("Using memevents for direct reclaim and kswapd detection");
} else {
ALOGI("Using vmstats for direct reclaim and kswapd detection");
if (direct_reclaim_threshold_ms > 0) {
ALOGW("Kernel support for direct_reclaim_threshold_ms is not found");
direct_reclaim_threshold_ms = 0;
}
}
result = 0;
boot_completed_handled = true;
}
len = lmkd_pack_set_boot_completed_notif_repl(packet, result);
if (ctrl_data_write(dsock_idx, (char*)packet, len) != len) {
ALOGE("Failed to report boot-completed operation results");
}
break;
case LMK_PROCS_PRIO:
cmd_procs_prio(packet, nargs, &cred);
break;
default:
ALOGE("Received unknown command code %d", cmd);
return;
}
return;
wronglen:
ALOGE("Wrong control socket read length cmd=%d len=%d", cmd, len);
}
| 命令 | 功能 | 方法 |
|---|---|---|
| LMK_TARGET | 初始化 oom_adj | ProcessList::setOomAdj() |
| LMK_PROCPRIO | 更新 oom_adj | ProcessList::updateOomLevels() |
| LMK_PROCREMOVE | 移除进程(暂时无用) | ProcessList::remove() |
当监听到系统内存压力过大时,会通过/proc/pressure/memory上报内存压力,由于配置的是some 60、some 100、full70,当一秒内内存占用70ms\100ms时会上报内存压力,上报压力后,会判断use_new_strategy触发不同的事件。
3)触发lmkd socket的epoll事件,服务端接收数据,并执行处理函数,将进程及oom_adj信息存入adjslot_list结构体数组
cmd_procprio
static void cmd_procprio(LMKD_CTRL_PACKET packet, int field_count, struct ucred* cred) {
struct lmk_procprio proc_prio;
lmkd_pack_get_procprio(packet, field_count, &proc_prio);
apply_proc_prio(proc_prio, cred);
}
// Should be modified only from the main thread.
static void proc_slot(struct proc *procp) {
int adjslot = ADJTOSLOT(procp->oomadj);
std::scoped_lock lock(adjslot_list_lock);
adjslot_insert(&procadjslot_list[adjslot], &procp->asl);
}
static void adjslot_insert(struct adjslot_list *head, struct adjslot_list *new_element)
{
struct adjslot_list *next = head->next;
new_element->prev = head;
new_element->next = next;
next->prev = new_element;
head->next = new_element;
}
AMS代码
2)AMS客户端写入数据到lmkd socket
setOomAdj
/**
* Set the out-of-memory badness adjustment for a process.
* If {@code pid <= 0}, this method will be a no-op.
*
* @param pid The process identifier to set.
* @param uid The uid of the app
* @param amt Adjustment value -- lmkd allows -1000 to +1000
*
* {@hide}
*/
public static void setOomAdj(int pid, int uid, int amt) {
// This indicates that the process is not started yet and so no need to proceed further.
if (pid <= 0) {
return;
}
if (amt == UNKNOWN_ADJ)
return;
long start = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 * 4);
buf.putInt(LMK_PROCPRIO);
buf.putInt(pid);
buf.putInt(uid);
buf.putInt(amt);
writeLmkd(buf, null);
long now = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if ((now-start) > 250) {
Slog.w("ActivityManager", "SLOW OOM ADJ: " + (now-start) + "ms for pid " + pid
+ " = " + amt);
}
}
3. mp_event_psi和mp_event_common不同kill策略
3.1 mp_event_psi流程
mp_event_psi 使用zone_watermark监测。当设备为低内存或者不使用旧模式minfree时,均如下处理方式。
static void mp_event_psi(int data, uint32_t events, struct polling_params *poll_params) {
enum reclaim_state {
NO_RECLAIM = 0,
KSWAPD_RECLAIM,
DIRECT_RECLAIM,
};
static int64_t init_ws_refault;
static int64_t prev_workingset_refault;
static int64_t base_file_lru;
static int64_t init_pgscan_kswapd;
static int64_t init_pgscan_direct;
static int64_t init_pgrefill;
static bool killing;
static int thrashing_limit = thrashing_limit_pct;
static struct zone_watermarks watermarks;
static struct timespec wmark_update_tm;
static struct wakeup_info wi;
static struct timespec thrashing_reset_tm;
static int64_t prev_thrash_growth = 0;
static bool check_filecache = false;
static int max_thrashing = 0;
union meminfo mi;
union vmstat vs;
struct psi_data psi_data;
struct timespec curr_tm;
int64_t thrashing = 0;
bool swap_is_low = false;
enum vmpressure_level level = (enum vmpressure_level)data;
enum kill_reasons kill_reason = NONE;
bool cycle_after_kill = false;
enum reclaim_state reclaim = NO_RECLAIM;
enum zone_watermark wmark = WMARK_NONE;
char kill_desc[LINE_MAX];
bool cut_thrashing_limit = false;
int min_score_adj = 0;
int swap_util = 0;
int64_t swap_low_threshold;
long since_thrashing_reset_ms;
int64_t workingset_refault_file;
bool critical_stall = false;
bool in_direct_reclaim;
long direct_reclaim_duration_ms;
bool in_kswapd_reclaim;
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, &curr_tm) != 0) {
ALOGE("Failed to get current time");
return;
}
record_wakeup_time(&curr_tm, events ? Event : Polling, &wi);
bool kill_pending = is_kill_pending(); // 判断last_kill_pid_or_fd节点是否存在,存在则为true
if (kill_pending && (kill_timeout_ms == 0 ||
get_time_diff_ms(&last_kill_tm, &curr_tm) < static_cast<long>(kill_timeout_ms))) {
/* Skip while still killing a process */
wi.skipped_wakeups++;
goto no_kill;
}
/*
* Process is dead or kill timeout is over, stop waiting. This has no effect if pidfds are
* supported and death notification already caused waiting to stop.
*/
//进程已死或杀死超时结束,停止等待。 如果支持pidfds,并且死亡通知已经导致等待停止,
stop_wait_for_proc_kill(!kill_pending);
if (vmstat_parse(&vs) < 0) { // 解析/proc/vmstat
ALOGE("Failed to parse vmstat!");
return;
}
/* Starting 5.9 kernel workingset_refault vmstat field was renamed workingset_refault_file */
workingset_refault_file = vs.field.workingset_refault ? : vs.field.workingset_refault_file;
if (meminfo_parse(&mi) < 0) { // 解析/proc/meminfo并匹配各个字段的信息,获取可用内存页信息:
ALOGE("Failed to parse meminfo!");
return;
}
/* Reset states after process got killed */
if (killing) {
killing = false;
cycle_after_kill = true;
/* Reset file-backed pagecache size and refault amounts after a kill */
base_file_lru = vs.field.nr_inactive_file + vs.field.nr_active_file;
init_ws_refault = workingset_refault_file;
thrashing_reset_tm = curr_tm;
prev_thrash_growth = 0;
}
/* Check free swap levels */
if (swap_free_low_percentage) { //ro.lmk.swap_free_low_percentage 默认为10
swap_low_threshold = mi.field.total_swap * swap_free_low_percentage / 100;
//当swap可用空间低于ro.lmk.swap_free_low_percentage属性定义的百分比时,设置swap_is_low = true
swap_is_low = get_free_swap(&mi) < swap_low_threshold; // meminfo
} else {
swap_low_threshold = 0;
}
if (memevent_listener) {
in_direct_reclaim =
direct_reclaim_start_tm.tv_sec != 0 || direct_reclaim_start_tm.tv_nsec != 0;
in_kswapd_reclaim = kswapd_start_tm.tv_sec != 0 || kswapd_start_tm.tv_nsec != 0;
} else {
in_direct_reclaim = vs.field.pgscan_direct != init_pgscan_direct;
in_kswapd_reclaim = (vs.field.pgscan_kswapd != init_pgscan_kswapd) ||
(vs.field.pgrefill != init_pgrefill);
}
/* Identify reclaim state */
if (in_direct_reclaim) {
init_pgscan_direct = vs.field.pgscan_direct;
init_pgscan_kswapd = vs.field.pgscan_kswapd;
init_pgrefill = vs.field.pgrefill;
direct_reclaim_duration_ms = get_time_diff_ms(&direct_reclaim_start_tm, &curr_tm);
reclaim = DIRECT_RECLAIM;
} else if (in_kswapd_reclaim) {
init_pgscan_kswapd = vs.field.pgscan_kswapd;
init_pgrefill = vs.field.pgrefill;
reclaim = KSWAPD_RECLAIM;
} else if (workingset_refault_file == prev_workingset_refault) {
/*
* Device is not thrashing and not reclaiming, bail out early until we see these stats
* changing
*/
goto no_kill;
}
prev_workingset_refault = workingset_refault_file;
/*
* It's possible we fail to find an eligible process to kill (ex. no process is
* above oom_adj_min). When this happens, we should retry to find a new process
* for a kill whenever a new eligible process is available. This is especially
* important for a slow growing refault case. While retrying, we should keep
* monitoring new thrashing counter as someone could release the memory to mitigate
* the thrashing. Thus, when thrashing reset window comes, we decay the prev thrashing
* counter by window counts. If the counter is still greater than thrashing limit,
* we preserve the current prev_thrash counter so we will retry kill again. Otherwise,
* we reset the prev_thrash counter so we will stop retrying.
*/
/*
* 有可能找不到合适的进程进行杀进程(例如没有进程高于oom_adj_min)。 在这种情况下,
* 每当有新的合格进程可用时,我们应重试找到新的进程进行杀进程,这对于缓慢增长的
* 回页错误情况尤其重要。 在重试期间,我们应继续监控新的抖动计数器,因为有人可能释放
* 内存来缓解抖动。 因此,当抖动重置窗口来临时,我们通过窗口计数递减前一个抖动计数器。
* 如果计数器仍大于抖动限制,我们保留当前的前一个抖动计数器,这样我们将再次尝试杀死。
* 否则,我们重置prev_thrash计数器,这样我们就停止重试了。
*/
//更新trashing,trashing过高说明内存存在压力,过低说明内存空闲
since_thrashing_reset_ms = get_time_diff_ms(&thrashing_reset_tm, &curr_tm);
if (since_thrashing_reset_ms > THRASHING_RESET_INTERVAL_MS) {
long windows_passed;
/* Calculate prev_thrash_growth if we crossed THRASHING_RESET_INTERVAL_MS */
prev_thrash_growth = (workingset_refault_file - init_ws_refault) * 100
/ (base_file_lru + 1);
windows_passed = (since_thrashing_reset_ms / THRASHING_RESET_INTERVAL_MS);
/*
* Decay prev_thrashing unless over-the-limit thrashing was registered in the window we
* just crossed, which means there were no eligible processes to kill. We preserve the
* counter in that case to ensure a kill if a new eligible process appears.
*/
if (windows_passed > 1 || prev_thrash_growth < thrashing_limit) {
prev_thrash_growth >>= windows_passed;
}
/* Record file-backed pagecache size when crossing THRASHING_RESET_INTERVAL_MS */
base_file_lru = vs.field.nr_inactive_file + vs.field.nr_active_file;
init_ws_refault = workingset_refault_file;
thrashing_reset_tm = curr_tm;
thrashing_limit = thrashing_limit_pct;
} else {
/* Calculate what % of the file-backed pagecache refaulted so far */
thrashing = (workingset_refault_file - init_ws_refault) * 100 / (base_file_lru + 1);
}
/* Add previous cycle's decayed thrashing amount */
thrashing += prev_thrash_growth;
if (max_thrashing < thrashing) {
max_thrashing = thrashing;
}
update_watermarks:
/*
* Refresh watermarks once per min in case user updated one of the margins.
* TODO: b/140521024 replace this periodic update with an API for AMS to notify LMKD
* that zone watermarks were changed by the system software.
*/
//更新水位线
if (watermarks.high_wmark == 0 || get_time_diff_ms(&wmark_update_tm, &curr_tm) > 60000) {
struct zoneinfo zi;
// 解析/proc/zoneinfo并匹配相应字段信息,
// 获取保留页的大小:zi->field.totalreserve_pages += zi->field.high;(获取可用内存)
//并计算min/low/hight水位线,
if (zoneinfo_parse(&zi) < 0) {
ALOGE("Failed to parse zoneinfo!");
return;
}
calc_zone_watermarks(&zi, &watermarks);
wmark_update_tm = curr_tm;
}
/* Find out which watermark is breached if any */
wmark = get_lowest_watermark(&mi, &watermarks); //zmi->nr_free_pages - zmi->cma_free和watermarks比较
if (!psi_parse_mem(&psi_data)) {
critical_stall = psi_data.mem_stats[PSI_FULL].avg10 > (float)stall_limit_critical;
}
/*
* TODO: move this logic into a separate function
* Decide if killing a process is necessary and record the reason
*/
//根据水位线、thrashing值、压力值、swap_low值、内存回收模式等进行多种场景判断,并添加不同的kill原因
if (cycle_after_kill && wmark < WMARK_LOW) {
/*
* Prevent kills not freeing enough memory which might lead to OOM kill.
* This might happen when a process is consuming memory faster than reclaim can
* free even after a kill. Mostly happens when running memory stress tests.
*/
/*防止杀死进程时无法释放足够的内存,可能导致 OOM 杀死进程。
当一个进程消耗内存的速度比回收能够释放的速度更快时,即使进行杀死操作后,仍然可能发生这种情况。
这通常发生在运行内存压力测试时。
*/
min_score_adj = pressure_after_kill_min_score;
kill_reason = PRESSURE_AFTER_KILL;
strncpy(kill_desc, "min watermark is breached even after kill", sizeof(kill_desc));
} else if (level == VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL && events != 0) {
/*
* Device is too busy reclaiming memory which might lead to ANR.
* Critical level is triggered when PSI complete stall (all tasks are blocked because
* of the memory congestion) breaches the configured threshold.
*/
/*设备正在繁忙地回收内存,这可能导致 ANR。
当 PSI 完全停滞(所有任务因内存拥塞而被阻塞)超过配置的阈值时,就会触发关键级别。
*/
kill_reason = NOT_RESPONDING;
strncpy(kill_desc, "device is not responding", sizeof(kill_desc));
} else if (swap_is_low && thrashing > thrashing_limit_pct) { //ro.lmk.thrashing_limit 30 or 100
/* Page cache is thrashing while swap is low */
kill_reason = LOW_SWAP_AND_THRASHING;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "device is low on swap (%" PRId64
"kB < %" PRId64 "kB) and thrashing (%" PRId64 "%%)",
get_free_swap(&mi) * page_k, swap_low_threshold * page_k, thrashing);
/* Do not kill perceptible apps unless below min watermark or heavily thrashing */
if (wmark > WMARK_MIN && thrashing < thrashing_critical_pct) { //WMARK_MIN = 0 thrashing_limit_pct * 2 上面的
min_score_adj = PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ + 1; //200
}
check_filecache = true;
} else if (swap_is_low && wmark < WMARK_HIGH) { //对应上边的百分比
/* Both free memory and swap are low */
kill_reason = LOW_MEM_AND_SWAP;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "%s watermark is breached and swap is low (%"
PRId64 "kB < %" PRId64 "kB)", wmark < WMARK_LOW ? "min" : "low",
get_free_swap(&mi) * page_k, swap_low_threshold * page_k);
/* Do not kill perceptible apps unless below min watermark or heavily thrashing */
if (wmark > WMARK_MIN && thrashing < thrashing_critical_pct) {
min_score_adj = PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ + 1; //200
}
} else if (wmark < WMARK_HIGH && swap_util_max < 100 &&
(swap_util = calc_swap_utilization(&mi)) > swap_util_max) {
/*
* Too much anon memory is swapped out but swap is not low.
* Non-swappable allocations created memory pressure.
*/
kill_reason = LOW_MEM_AND_SWAP_UTIL;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "%s watermark is breached and swap utilization"
" is high (%d%% > %d%%)", wmark < WMARK_LOW ? "min" : "low",
swap_util, swap_util_max);
} else if (wmark < WMARK_HIGH && thrashing > thrashing_limit) {
/* Page cache is thrashing while memory is low */
kill_reason = LOW_MEM_AND_THRASHING;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "%s watermark is breached and thrashing (%"
PRId64 "%%)", wmark < WMARK_LOW ? "min" : "low", thrashing);
cut_thrashing_limit = true;
/* Do not kill perceptible apps unless thrashing at critical levels */
if (thrashing < thrashing_critical_pct) {
min_score_adj = PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ + 1;
}
check_filecache = true;
} else if (reclaim == DIRECT_RECLAIM && thrashing > thrashing_limit) {
/* Page cache is thrashing while in direct reclaim (mostly happens on lowram devices) */
kill_reason = DIRECT_RECL_AND_THRASHING;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "device is in direct reclaim and thrashing (%"
PRId64 "%%)", thrashing);
cut_thrashing_limit = true;
/* Do not kill perceptible apps unless thrashing at critical levels */
if (thrashing < thrashing_critical_pct) {
min_score_adj = PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ + 1;
}
check_filecache = true;
} else if (reclaim == DIRECT_RECLAIM && direct_reclaim_threshold_ms > 0 &&
direct_reclaim_duration_ms > direct_reclaim_threshold_ms) {
kill_reason = DIRECT_RECL_STUCK;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "device is stuck in direct reclaim (%ldms > %dms)",
direct_reclaim_duration_ms, direct_reclaim_threshold_ms);
} else if (check_filecache) {
int64_t file_lru_kb = (vs.field.nr_inactive_file + vs.field.nr_active_file) * page_k;
if (file_lru_kb < filecache_min_kb) {
/* File cache is too low after thrashing, keep killing background processes */
kill_reason = LOW_FILECACHE_AFTER_THRASHING;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc),
"filecache is low (%" PRId64 "kB < %" PRId64 "kB) after thrashing",
file_lru_kb, filecache_min_kb);
min_score_adj = PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ + 1;
} else {
/* File cache is big enough, stop checking */
check_filecache = false;
}
}
/* Check if a cached app should be killed */
if (kill_reason == NONE && wmark < WMARK_HIGH) {
kill_reason = LOW_MEM;
snprintf(kill_desc, sizeof(kill_desc), "%s watermark is breached",
wmark < WMARK_LOW ? "min" : "low");
min_score_adj = lowmem_min_oom_score;
}
/* Kill a process if necessary */
if (kill_reason != NONE) {
struct kill_info ki = {
.kill_reason = kill_reason,
.kill_desc = kill_desc,
.thrashing = (int)thrashing,
.max_thrashing = max_thrashing,
};
static bool first_kill = true;
/* Make sure watermarks are correct before the first kill */
if (first_kill) {
first_kill = false;
watermarks.high_wmark = 0; // force recomputation
goto update_watermarks;
}
/* Allow killing perceptible apps if the system is stalled */
if (critical_stall) {
min_score_adj = 0;
}
psi_parse_io(&psi_data);
psi_parse_cpu(&psi_data);
//最终kill的走向
int pages_freed = find_and_kill_process(min_score_adj, &ki, &mi, &wi, &curr_tm, &psi_data);
if (pages_freed > 0) {
killing = true;
max_thrashing = 0;
if (cut_thrashing_limit) {
/*
* Cut thrasing limit by thrashing_limit_decay_pct percentage of the current
* thrashing limit until the system stops thrashing.
*/
thrashing_limit = (thrashing_limit * (100 - thrashing_limit_decay_pct)) / 100;
}
}
}
no_kill:
/* Do not poll if kernel supports pidfd waiting */
if (is_waiting_for_kill()) {
/* Pause polling if we are waiting for process death notification
如果正在等待进程死亡通知,则暂停轮询
*/
poll_params->update = POLLING_PAUSE;
return;
}
/*
* Start polling after initial PSI event;
* extend polling while device is in direct reclaim or process is being killed;
* do not extend when kswapd reclaims because that might go on for a long time
* without causing memory pressure
*/
/*初始 PSI 事件后开始轮询;
在设备处于直接回收内存或进程被杀死时,延长轮询时间;
当 kswapd 回收内存时不延长轮询时间,因为这可能会持续很长时间而不会引起内存压力。
*/
if (events || killing || reclaim == DIRECT_RECLAIM) {
poll_params->update = POLLING_START;
}
/* Decide the polling interval */
if (swap_is_low || killing) {
/* Fast polling during and after a kill or when swap is low */
poll_params->polling_interval_ms = PSI_POLL_PERIOD_SHORT_MS; //10ms
} else {
/* By default use long intervals */
poll_params->polling_interval_ms = PSI_POLL_PERIOD_LONG_MS; //100ms
}
}
这段代码的主要逻辑是:
- 检查是否有需要kill的进程,如果有正在kill的进程则跳过本次循环
- 解析/proc/vmstat和/proc/meminfo获取内存状态信息
- 根据内存水位线、thrashing值、swap使用情况等判断是否需要kill进程
- 如果刚kill完进程但内存使用依然过高,则再次kill
- 如果设备长时间无响应,则kill进程试图让设备响应
- 如果swap使用过高且thrashing过高,则kill进程
- 如果内存使用过高且swap空间不足,则kill进程
- 如果内存使用过高且thrashing过高,则kill进程
- 等等
- 如果确定需要kill进程,则调用find_and_kill_process函数找到进程kill
- 根据内存状况决定PSI事件的轮询间隔,如果内存压力大则增大轮询频率
- 如果正在等待已kill进程退出,则暂停轮询
进程查杀的原因:
| 查杀原因 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PRESSURE_AFTER_KILL | 执行了一次 kill 操作后&内存水位低于低水位标记 |
| CRITICAL_KILL | 内存压力达到了CRITICAL临界值 |
| NOT_RESPONDING | 内存压力达到了超级临界级别&当前内存水位低于或等于高水位标记&触发PSI事件 |
| LOW_SWAP_AND_THRASHING | 当前抖动程度超过了抖动阈值 |
| LOW_MEM_AND_SWAP | swap空间不足&内存水位低于高水位标记 |
| LOW_MEM_AND_SWAP_UTIL | 内存水位低于高水位标记&交换空间利用率最大值小于100 &交换空间利用率超过了利用率最大值 |
| LOW_MEM_AND_THRASHING | 内存水位低于或等于高水位标记&当前抖动程度超过了抖动阈值 |
| DIRECT_RECL_AND_THRASHING | 内核直接从用户空间进程回收内存&当前抖动程度超过了抖动阈值 |
| LOW_FILECACHE_AFTER_THRASHING | 计算得到的文件缓存大小 file_lru_kb 小于预设的最小文件缓存大小 filecache_min_kb,即文件缓存过低 |
| DIRECT_RECL_AND_LOW_MEM | 内核直接从用户空间进程回收内存&内存水位低于高水位标记 |
| COMPACTION | 当前正在进行内存压缩&内存水位低于高水位标记 |
3.2 mp_event_common流程
非低内存设备并且使用iuse_minfree_levels
// The implementation of this function relies on memcg statistics that are only available in the
// v1 cgroup hierarchy.
static void mp_event_common(int data, uint32_t events, struct polling_params *poll_params) {
unsigned long long evcount;
int64_t mem_usage, memsw_usage;
int64_t mem_pressure;
union meminfo mi;
struct zoneinfo zi;
struct timespec curr_tm;
static unsigned long kill_skip_count = 0;
enum vmpressure_level level = (enum vmpressure_level)data;
long other_free = 0, other_file = 0;
int min_score_adj;
int minfree = 0;
static const std::string mem_usage_path = GetCgroupAttributePath("MemUsage");
static struct reread_data mem_usage_file_data = {
.filename = mem_usage_path.c_str(),
.fd = -1,
};
static const std::string memsw_usage_path = GetCgroupAttributePath("MemAndSwapUsage");
static struct reread_data memsw_usage_file_data = {
.filename = memsw_usage_path.c_str(),
.fd = -1,
};
static struct wakeup_info wi;
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("%s memory pressure event is triggered", level_name[level]);
}
if (!use_psi_monitors) {
/*
* Check all event counters from low to critical
* and upgrade to the highest priority one. By reading
* eventfd we also reset the event counters.
*/
for (int lvl = VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW; lvl < VMPRESS_LEVEL_COUNT; lvl++) {
if (mpevfd[lvl] != -1 &&
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(mpevfd[lvl],
&evcount, sizeof(evcount))) > 0 &&
evcount > 0 && lvl > level) {
level = static_cast<vmpressure_level>(lvl);
}
}
}
/* Start polling after initial PSI event */
if (use_psi_monitors && events) {
/* Override polling params only if current event is more critical */
if (!poll_params->poll_handler || data > poll_params->poll_handler->data) {
poll_params->polling_interval_ms = PSI_POLL_PERIOD_SHORT_MS;
poll_params->update = POLLING_START;
}
}
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, &curr_tm) != 0) {
ALOGE("Failed to get current time");
return;
}
record_wakeup_time(&curr_tm, events ? Event : Polling, &wi);
if (kill_timeout_ms &&
get_time_diff_ms(&last_kill_tm, &curr_tm) < static_cast<long>(kill_timeout_ms)) {
/*
* If we're within the no-kill timeout, see if there's pending reclaim work
* from the last killed process. If so, skip killing for now.
*/
if (is_kill_pending()) {
kill_skip_count++;
wi.skipped_wakeups++;
return;
}
/*
* Process is dead, stop waiting. This has no effect if pidfds are supported and
* death notification already caused waiting to stop.
*/
stop_wait_for_proc_kill(true);
} else {
/*
* Killing took longer than no-kill timeout. Stop waiting for the last process
* to die because we are ready to kill again.
*/
stop_wait_for_proc_kill(false);
}
if (kill_skip_count > 0) {
ALOGI("%lu memory pressure events were skipped after a kill!",
kill_skip_count);
kill_skip_count = 0;
}
if (meminfo_parse(&mi) < 0 || zoneinfo_parse(&zi) < 0) { //读取meminfo 和zoneinfo
ALOGE("Failed to get free memory!");
return;
}
if (use_minfree_levels) { //走到这都是true
int i;
//other_free 表示系统可用的内存页的数目,MemFree - high
// nr_free_pages为proc/meminfo中MemFree,当前系统的空闲内存大小,是完全没有被使用的内存
// totalreserve_pages为proc/zoneinfo中max_protection+high,其中max_protection在android中为0
other_free = mi.field.nr_free_pages - zi.totalreserve_pages;
//nr_file_pages = cached + swap_cached + buffers;有时还会有多余的页(other_file就是多余的),需要减去
if (mi.field.nr_file_pages > (mi.field.shmem + mi.field.unevictable + mi.field.swap_cached)) {
//other_file 基本就等于除 tmpfs 和 unevictable 外的缓存在内存的文件所占用的 page 数
other_file = (mi.field.nr_file_pages - mi.field.shmem -
mi.field.unevictable - mi.field.swap_cached);
} else {
other_file = 0;
}
//到这里计算出other_free 、other_file
min_score_adj = OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX + 1;
//遍历oomadj和minfree数组 根据lowmem_minfree 的值来确定 min_score_adj,oomadj小于 min_score_adj 的进程在这次回收过程中不会被杀死
for (i = 0; i < lowmem_targets_size; i++) {
minfree = lowmem_minfree[i];
if (other_free < minfree && other_file < minfree) {
min_score_adj = lowmem_adj[i];
break;
}
}
if (min_score_adj == OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX + 1) { //adj没变化不做任何处理
if (debug_process_killing && lowmem_targets_size) {
ALOGI("Ignore %s memory pressure event "
"(free memory=%ldkB, cache=%ldkB, limit=%ldkB)",
level_name[level], other_free * page_k, other_file * page_k,
(long)lowmem_minfree[lowmem_targets_size - 1] * page_k);
}
return;
}
goto do_kill;
}
//对于没有配置use_minfree_levels的情况,内存压力low时会调用record_low_pressure_levels,记录low等级时,
if (level == VMPRESS_LEVEL_LOW) {
record_low_pressure_levels(&mi); //这里主要是赋值low_pressure_mem.min_nr_free_pages low_pressure_mem.max_nr_free_pages
}
if (level_oomadj[level] > OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX) { //大于1000不考虑
/* Do not monitor this pressure level */
return;
}
// 当前memory使用情况,不含swap
if ((mem_usage = get_memory_usage(&mem_usage_file_data)) < 0) { //"/dev/memcg/memory.usage_in_bytes"
goto do_kill;
}
// 当前memory使用情况,含swap
if ((memsw_usage = get_memory_usage(&memsw_usage_file_data)) < 0) { //"/dev/memcg/memory.memsw.usage_in_bytes"
goto do_kill;
}
// Calculate percent for swappinness.
// 这个指标类似于swapness,值越大,swap使用越少,剩余swap空间越大
mem_pressure = (mem_usage * 100) / memsw_usage;
if (enable_pressure_upgrade && level != VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL) { //ro.lmk.critical_upgrade
// We are swapping too much.
// 指标偏小说明swap使用很厉害,但仍然内存压力很大
// 提高level,杀得更激进
if (mem_pressure < upgrade_pressure) { //ro.lmk.upgrade_pressure 代码default100
level = upgrade_level(level); //升级vmpressure level
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("Event upgraded to %s", level_name[level]);
}
}
}
// If we still have enough swap space available, check if we want to
// ignore/downgrade pressure events.
// swap_free_low_percentage为swap低阈值 此时swap空间还没到低阈值,有可操作空间
if (get_free_swap(&mi) >=
mi.field.total_swap * swap_free_low_percentage / 100) { //ro.lmk.swap_free_low_percentage 10或者15
// If the pressure is larger than downgrade_pressure lmk will not
// kill any process, since enough memory is available.
if (mem_pressure > downgrade_pressure) { // 虽然有内存压力警报,但是swap还是足够的,不杀进程
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("Ignore %s memory pressure", level_name[level]);
}
return;
} else if (level == VMPRESS_LEVEL_CRITICAL && mem_pressure > upgrade_pressure) {
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("Downgrade critical memory pressure");
} //swap空间足够的话,只有mem_pressure压力足够大,才会杀得更激进
// Downgrade event, since enough memory available.
level = downgrade_level(level);
}
}
do_kill:
if (low_ram_device) { //如果是低内存设备
/* For Go devices kill only one task */
if (find_and_kill_process(use_minfree_levels ? min_score_adj : level_oomadj[level],
NULL, &mi, &wi, &curr_tm, NULL) == 0) {
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("Nothing to kill");
}
}
} else {
int pages_freed;
static struct timespec last_report_tm;
static unsigned long report_skip_count = 0;
if (!use_minfree_levels) { //高版本设备一般不会走到这,只有用vmpressure策略并且不用use_minfree_levels
/* Free up enough memory to downgrate the memory pressure to low level */
if (mi.field.nr_free_pages >= low_pressure_mem.max_nr_free_pages) {
if (debug_process_killing) {
ALOGI("Ignoring pressure since more memory is "
"available (%" PRId64 ") than watermark (%" PRId64 ")",
mi.field.nr_free_pages, low_pressure_mem.max_nr_free_pages);
}
return;
}
min_score_adj = level_oomadj[level];
}
//最终进程被杀
pages_freed = find_and_kill_process(min_score_adj, NULL, &mi, &wi, &curr_tm, NULL);
if (pages_freed == 0 && min_score_adj == 0) {
lmkd_no_kill_candidates_hook();
}
if (pages_freed == 0) {
/* Rate limit kill reports when nothing was reclaimed */
if (get_time_diff_ms(&last_report_tm, &curr_tm) < FAIL_REPORT_RLIMIT_MS) {
report_skip_count++;
return;
}
}
/* Log whenever we kill or when report rate limit allows */
if (use_minfree_levels) {
ALOGI("Reclaimed %ldkB, cache(%ldkB) and free(%" PRId64 "kB)-reserved(%" PRId64 "kB) "
"below min(%ldkB) for oom_score_adj %d",
pages_freed * page_k,
other_file * page_k, mi.field.nr_free_pages * page_k,
zi.totalreserve_pages * page_k,
minfree * page_k, min_score_adj);
} else {
ALOGI("Reclaimed %ldkB at oom_score_adj %d", pages_freed * page_k, min_score_adj);
}
if (report_skip_count > 0) {
ALOGI("Suppressed %lu failed kill reports", report_skip_count);
report_skip_count = 0;
}
last_report_tm = curr_tm;
}
if (is_waiting_for_kill()) {
/* pause polling if we are waiting for process death notification */
poll_params->update = POLLING_PAUSE;
}
}
低内存设备(low-memory device)和高性能设备(high-performance device)的kill策略有所不同:
- 对于内存不足的设备,一般情况下,系统会选择承受较大的内存压力。
- 对于高性能设备,如果出现内存压力,则会视为异常情况,应及时修复,以免影响整体性能。
-
解析/proc/meminfo和/proc/zoneinfo获取内存状态
-
如果配置了use_minfree_levels,则根据lowmem_minfree数组计算合适的min_score_adj
逐个比较other_free和other_file是否低于minfree,是则使用对应的oomadj作为min_score_adj
-
如果没有配置use_minfree_levels,则根据vmpressure等级计算min_score_adj
对低内存压力级别,记录当时的内存使用情况
根据级别对应表获取oomadj1
如果swap空间充足,检查是否需要降级内存压力级别
-
使用计算出的min_score_adj找到进程并kill
3.3 mp_event_psi和mp_event_common的不同之处
- mp_event_psi主要基于zoneinfo的水位线方式判断内存状态,mp_event_common主要检测meminfo中的free memory大小。
- mp_event_psi会计算thrashing和swap使用情况,mp_event_common主要检测vmpressure级别。
- mp_event_psi有定期轮询逻辑, mp_event_common仅在收到事件时触发。
- mp_event_psi会更细致地判断不同内存压力场景,mp_event_common较简单直接。
- mp_event_psi自身就可以完成整个判断和杀进程流程,mp_event_common仅完成内存判断后交给上层管理杀进程。
- mp_event_psi可以动态调整轮询间隔,mp_event_common没有这方面逻辑。
- mp_event_psi记录更多调试统计信息。
3.4 find_and_kill_process 杀进程
在系统中找到并杀死一个符合给定 oom_score_adj 级别的进程,以释放内存。该函数通过循环查找并选择合适的进程,如下:
这里针对adj<200的情况,默认会杀最重的进程。
/*
* Find one process to kill at or above the given oom_score_adj level.
* Returns size of the killed process.
*/
//查找需要杀掉的进程, min_score_adj代表查找到最小分数截止
static int find_and_kill_process(int min_score_adj, struct kill_info *ki, union meminfo *mi,
struct wakeup_info *wi, struct timespec *tm,
struct psi_data *pd) {
int i;
int killed_size = 0;
bool choose_heaviest_task = kill_heaviest_task;
//OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX:代表最大分数它的值是1000,从最大分数开始查找
for (i = OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MAX; i >= min_score_adj; i--) { //遍历adj
struct proc *procp;
//choose_heaviest_task代表是否杀掉任务繁重的进程,PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ的值是200
if (!choose_heaviest_task && i <= PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ) { // 可感的应用程序
/*
* If we have to choose a perceptible process, choose the heaviest one to
* hopefully minimize the number of victims.
*/
choose_heaviest_task = true; // 可以理解成adj < 200 杀最重的进程
}
// 如果是杀繁重任务的进程,则调用proc_get_heaviest(i)方法找到繁重任务进程;否则调用proc_adj_tail(i)去查找
while (true) {
//分数i对应的索引处的循环双向链表的尾节点的进程
procp = choose_heaviest_task ? //根据adj200 判断杀最重或者根据lru杀
proc_get_heaviest(i) : proc_adj_tail(i);
if (!procp)
break;
//调用kill_one_process方法开始杀进程,killed_size代表释放的空间
killed_size = kill_one_process(procp, min_score_adj, ki, mi, wi, tm, pd);
//若释放的空间大于等于0,则跳出循环
if (killed_size >= 0) {
break;
}
}
//若释放空间不为0,则跳出查杀进程循环逻辑
if (killed_size) {
break;
}
}
return killed_size;
}
proc_get_heaviest
从给定的 oomadj 级别中选择内存占用最多的进程
// Can be called only from the main thread.
static struct proc *proc_get_heaviest(int oomadj) {
struct adjslot_list *head = &procadjslot_list[ADJTOSLOT(oomadj)];
struct adjslot_list *curr = head->next;
struct proc *maxprocp = NULL;
int maxsize = 0;
// 循环遍历进程链表,对比各进程占用的内存大小,找到内存占用最多的那个进程
while (curr != head) {
int pid = ((struct proc *)curr)->pid;
// 从"/proc/%d/statm"节点中获取rss的信息
int tasksize = proc_get_size(pid);
if (tasksize < 0) {
struct adjslot_list *next = curr->next;
pid_remove(pid);
curr = next;
} else {
if (tasksize > maxsize) {
maxsize = tasksize;
maxprocp = (struct proc *)curr;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
}
return maxprocp;
}
proc_adj_tail
从procadjslot_list列表的队尾找到目标进程
// When called from a non-main thread, adjslot_list_lock read lock should be taken.
static struct proc *proc_adj_tail(int oomadj) {
return (struct proc *)adjslot_tail(&procadjslot_list[ADJTOSLOT(oomadj)]);
}
static struct adjslot_list *adjslot_tail(struct adjslot_list *head) {
struct adjslot_list *asl = head->prev;
return asl == head ? NULL : asl;
}
// procadjslot_list should be modified only from the main thread while exclusively holding
// adjslot_list_lock. Readers from non-main threads should hold adjslot_list_lock shared lock.
static struct adjslot_list procadjslot_list[ADJTOSLOT_COUNT];
3.5 kill_one_process
主线程将进程pid、uid先存入queue队列,异步线程从queue中取出pid、uid进行杀进程。
/* Kill one process specified by procp. Returns the size (in pages) of the process killed */
static int kill_one_process(struct proc* procp, int min_oom_score, struct kill_info *ki,
union meminfo *mi, struct wakeup_info *wi, struct timespec *tm,
struct psi_data *pd) {
int pid = procp->pid;
int pidfd = procp->pidfd;
uid_t uid = procp->uid;
char *taskname;
int kill_result;
int result = -1;
struct memory_stat *mem_st;
struct kill_stat kill_st;
int64_t tgid;
int64_t rss_kb;
int64_t swap_kb;
char buf[pagesize];
char desc[LINE_MAX];
if (!procp->valid || !read_proc_status(pid, buf, sizeof(buf))) {
goto out;
}
if (!parse_status_tag(buf, PROC_STATUS_TGID_FIELD, &tgid)) {
ALOGE("Unable to parse tgid from /proc/%d/status", pid);
goto out;
}
if (tgid != pid) {
ALOGE("Possible pid reuse detected (pid %d, tgid %" PRId64 ")!", pid, tgid);
goto out;
}
// Zombie processes will not have RSS / Swap fields.
if (!parse_status_tag(buf, PROC_STATUS_RSS_FIELD, &rss_kb)) {
goto out;
}
if (!parse_status_tag(buf, PROC_STATUS_SWAP_FIELD, &swap_kb)) {
goto out;
}
taskname = proc_get_name(pid, buf, sizeof(buf));
// taskname will point inside buf, do not reuse buf onwards.
if (!taskname) {
goto out;
}
mem_st = stats_read_memory_stat(per_app_memcg, pid, uid, rss_kb * 1024, swap_kb * 1024);
snprintf(desc, sizeof(desc), "lmk,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d", pid, ki ? (int)ki->kill_reason : -1,
procp->oomadj, min_oom_score, ki ? ki->max_thrashing : -1);
result = lmkd_free_memory_before_kill_hook(procp, rss_kb / page_k, procp->oomadj,
ki ? (int)ki->kill_reason : -1);
if (result > 0) {
/*
* Memory was freed elsewhere; no need to kill. Note: intentionally do not
* pid_remove(pid) since it was not killed.
*/
ALOGI("Skipping kill; %ld kB freed elsewhere.", result * page_k);
return result;
}
trace_kill_start(desc);
//来等待该进程被杀死。这个函数会启动一个新的线程或进程,在其中轮询该进程是否被杀死,并在该进程被杀死后返回。
start_wait_for_proc_kill(pidfd < 0 ? pid : pidfd);
// 最后一个参数为false,放入队列等待 repaer 线程处理
kill_result = reaper.kill({ pidfd, pid, uid }, false); // 成功return 0,失败-1
trace_kill_end();
if (kill_result) {
stop_wait_for_proc_kill(false);
ALOGE("kill(%d): errno=%d", pid, errno);
/* Delete process record even when we fail to kill so that we don't get stuck on it */
goto out;
}
last_kill_tm = *tm;
inc_killcnt(procp->oomadj);
if (ki) {
kill_st.kill_reason = ki->kill_reason;
kill_st.thrashing = ki->thrashing;
kill_st.max_thrashing = ki->max_thrashing;
ALOGI("Kill '%s' (%d), uid %d, oom_score_adj %d to free %" PRId64 "kB rss, %" PRId64
"kB swap; reason: %s", taskname, pid, uid, procp->oomadj, rss_kb, swap_kb,
ki->kill_desc);
} else {
kill_st.kill_reason = NONE;
kill_st.thrashing = 0;
kill_st.max_thrashing = 0;
ALOGI("Kill '%s' (%d), uid %d, oom_score_adj %d to free %" PRId64 "kB rss, %" PRId64
"kb swap", taskname, pid, uid, procp->oomadj, rss_kb, swap_kb);
}
killinfo_log(procp, min_oom_score, rss_kb, swap_kb, ki, mi, wi, tm, pd);
kill_st.uid = static_cast<int32_t>(uid);
kill_st.taskname = taskname;
kill_st.oom_score = procp->oomadj;
kill_st.min_oom_score = min_oom_score;
kill_st.free_mem_kb = mi->field.nr_free_pages * page_k;
kill_st.free_swap_kb = get_free_swap(mi) * page_k;
stats_write_lmk_kill_occurred(&kill_st, mem_st);
ctrl_data_write_lmk_kill_occurred((pid_t)pid, uid, rss_kb);
result = rss_kb / page_k;
out:
/*
* WARNING: After pid_remove() procp is freed and can't be used!
警告:pid_remove()后procp被释放,不能使用!
* Therefore placed at the end of the function.
因此放在函数的末尾。
*/
pid_remove(pid);
return result;
}
reaper.kill
system/memory/lmkd/reaper.cpp
主线程将进程pid、uid先存入queue队列,异步线程从queue中取出pid、uid进行杀进程。
主线程将进程pid、uid先存入queue队列,如下:
int Reaper::kill(const struct target_proc& target, bool synchronous) {
/* CAP_KILL required */
if (target.pidfd < 0) {
return ::kill(target.pid, SIGKILL);
}
// 异步方式查杀进程
if (!synchronous && async_kill(target)) {
// we assume the kill will be successful and if it fails we will be notified
return 0;
}
// SIGKILL 9 发送给一个进程来导致它立即终止的信号
int result = pidfd_send_signal(target.pidfd, SIGKILL, NULL, 0);
if (result) {
return result;
}
return 0;
}
// 目标进程的pid、uid放入queue_队列,唤醒reaper thread线程
bool Reaper::async_kill(const struct target_proc& target) {
if (target.pidfd == -1) {
return false;
}
if (!thread_cnt_) {
return false;
}
mutex_.lock();
if (active_requests_ >= thread_cnt_) {
mutex_.unlock();
return false;
}
active_requests_++;
// Duplicate pidfd instead of reusing the original one to avoid synchronization and refcounting
// when both reaper and main threads are using or closing the pidfd
queue_.push_back({ dup(target.pidfd), target.pid, target.uid });
// Wake up a reaper thread
//唤醒dequeue_request
cond_.notify_one();
mutex_.unlock();
return true;
}
Reaper::init
在init初始化阶段创建子线程,监控queue队列是否为空。如果为空,进入wait,当主线程往queue中push进程数据时,唤醒该子线程。子线程从queue中取出pid、uid进行杀进程,如下:
bool Reaper::init(int comm_fd) {
char name[16];
struct sched_param param = {
.sched_priority = 0,
};
if (thread_cnt_ > 0) {
// init should not be called multiple times
return false;
}
thread_pool_ = new pthread_t[THREAD_POOL_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_POOL_SIZE; i++) {
if (pthread_create(&thread_pool_[thread_cnt_], NULL, reaper_main, this)) { //继续
ALOGE("pthread_create failed: %s", strerror(errno));
continue;
}
// set normal scheduling policy for the reaper thread
if (pthread_setschedparam(thread_pool_[thread_cnt_], SCHED_OTHER, ¶m)) {
ALOGW("set SCHED_FIFO failed %s", strerror(errno));
}
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "lmkd_reaper%d", thread_cnt_);
if (pthread_setname_np(thread_pool_[thread_cnt_], name)) {
ALOGW("pthread_setname_np failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
thread_cnt_++;
}
if (!thread_cnt_) {
delete[] thread_pool_;
return false;
}
queue_.reserve(thread_cnt_);
comm_fd_ = comm_fd;
return true;
}
reaper_main
static void* reaper_main(void* param) {
Reaper *reaper = static_cast<Reaper*>(param);
struct timespec start_tm, end_tm;
struct Reaper::target_proc target;
pid_t tid = gettid();
// Ensure the thread does not use little cores
if (!SetTaskProfiles(tid, {"CPUSET_SP_FOREGROUND"}, true)) {
ALOGE("Failed to assign cpuset to the reaper thread");
}
if (setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, tid, ANDROID_PRIORITY_HIGHEST)) {
ALOGW("Unable to raise priority of the reaper thread (%d): errno=%d", tid, errno);
}
for (;;) {
// 从队列中取出pid
target = reaper->dequeue_request();
if (reaper->debug_enabled()) {
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, &start_tm);
}
// 给目标进程发送SIGKILL信号,强制终止该进程的执行
if (pidfd_send_signal(target.pidfd, SIGKILL, NULL, 0)) {
// Inform the main thread about failure to kill
reaper->notify_kill_failure(target.pid);
goto done;
}
set_process_group_and_prio(target.uid, target.pid,
{"CPUSET_SP_FOREGROUND", "SCHED_SP_FOREGROUND"},
ANDROID_PRIORITY_NORMAL);
if (process_mrelease(target.pidfd, 0)) {
ALOGE("process_mrelease %d failed: %s", target.pid, strerror(errno));
goto done;
}
if (reaper->debug_enabled()) {
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, &end_tm);
ALOGI("Process %d was reaped in %ldms", target.pid,
get_time_diff_ms(&start_tm, &end_tm));
}
done:
close(target.pidfd);
reaper->request_complete();
}
return NULL;
}
...
Reaper::target_proc Reaper::dequeue_request() {
struct target_proc target;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
// queue队列为空时,进入休眠。否则,从队列中取出uid、pid
while (queue_.empty()) {
cond_.wait(lock);
}
target = queue_.back();
queue_.pop_back();
return target;
}
三、核心数据结构
// epoll event结构体
/** The type representing an epoll() event. */
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events;
epoll_data_t data;
}
// 内存回收的水位
enum zone_watermark {
WMARK_MIN = 0,
WMARK_LOW,
WMARK_HIGH,
WMARK_NONE
};
// 用于存放进程信息
struct proc {
struct adjslot_list asl;
int pid;
int pidfd;
uid_t uid;
int oomadj;
pid_t reg_pid; /* PID of the process that registered this record */
bool valid;
struct proc *pidhash_next;
};
// 存放struct proc的结构体
struct adjslot_list {
struct adjslot_list *next;
struct adjslot_list *prev;
};
// 用于设置lmkd socket的epoll监听的sock信息封装
/* data required to handle socket events */
struct sock_event_handler_info {
int sock;
pid_t pid;
uint32_t async_event_mask;
struct event_handler_info handler_info;
};
四、代码时序
代码时序包括三部分:
1)AMS客户端将进程信息(pid、oom_adj)写入lmkd socket
2)lmkd初始化,包括设置lmkd socket的epoll监听与注册回调函数、psi epoll监听及注册回调函数
3)进入loop循环监听psi epoll,事件发生时,回调执行注册函数,选取目标进程&查杀

五.内存指标
5.1 zoneinfo
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| nr_free_pages | 该zone空闲页数目 |
| nr_file_pages | 该zone文件页大小 |
| nr_shmem | 该zone中shmem/tmpfs占用内存大小 |
| nr_unevictable | 该zone不可回收页个数 |
| high | 该zone的高水位线 |
| protection | 该zone的保留内存 |
lmkd中zoneinfo_field_names保存了需要从zoneinfo中解析的字段,union zoneinfo则用来保存解析出来的数据。
解析中使用了小技巧,zoneinfo为union,因此可以通过遍历zoneinfo_field_names的同时遍历zoneinfo的attr,实现快速解析。在使用时,又可以通过zone的field快速访问。
zoneinfo中多计算了个totalreserve_pages,该值时根据high水线和protection保护页面数量(防止过度借出页面)共同计算得来(high水线 + protection选取最大保留页)。
lmkd中计算出来的zoneinfo为总大小,并未区分各个zone
5.2 meminfo
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| MemFree | 系统尚未使用的内存 |
| Cached | 文件页缓存,其中包括tmpfs中文件(未发生swap-out) |
| SwapCached | 匿名页或者shmem/tmpfs,被swapout过,当前swapin后未改变,如果改变会从SwapCached删除 |
| Buffers | io设备占用的缓存页,也统计在file lru |
| Mapped | 正在与用户进程关联的文件页 |
/proc/meminfo信息打印的地方在[kernel/msm-5.4/fs/proc/meminfo.c]的meminfo_proc_show函数当中;其中主要是调用show_val_kb()函数将字符串和具体的数值凑成一个字符串,然后把这些字符串打印出来。
shmem比较特殊,基于文件系统所以不算匿名页,但又不能pageout,因此在内存中被统计进了Cached (pagecache)和Mapped(shmem被attached),但lru里是放在anon lru,因为可能会被swap out。
lmkd的meminfo中也多计算了一个字段nr_file_pages,该值包括cached + swap_cached + buffers。可以理解为能够被drop的文件页。
5.3 memcg
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| memory.usage_in_bytes | 该memcg的内存(不含swap)使用情况 |
| memory.memsw.usage_in_bytes | 该memcg的内存(含swap)使用情况 |
进程信息
进程rss信息获取:“/proc/pid/statm”
统计的数据依次为:虚拟地址空间大小,rss,共享页数,代码段大小,库文件大小,数据段大小,和脏页大小(单位为page)。
进程状态信息: “/proc/pid/status”
进程统计信息: “/proc/pid/stat”
lmkd比较关心第10位pgfault,12位pgmajfault,22位进程开始时间,rss大小(单位page)。
参考:
Android启动系列之进程杀手–lmkd_android lmkd-CSDN博客
Android进程管理3——内存回收LMKDAndroid进程管理3——内存回收LMKD 关于android内存的调节一 - 掘金
【安卓基础】一文总结oomadj、lmkd、kernel-psi之间的关系_kernel psi-CSDN博客
Android中的LowMemoryKiller机制_android lowmemorykiller-CSDN博客
Android进程管理3——内存回收LMKDAndroid进程管理3——内存回收LMKD 关于android内存的调节一 - 掘金
 Android内存回收LMKD机制详解
Android内存回收LMKD机制详解




















 3145
3145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








