Spring AOP介绍与使用
- AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程
- OOP:Object Oriented Programming 面向对象编程
面向切面编程:基于OOP基础之上新的编程思想,OOP面向的主要对象是类,而AOP面向的主要对象是切面,在处理日志、安全管理、事务管理等方面有非常重要的作用。AOP是Spring中重要的核心点,虽然IOC容器没有依赖AOP,但是AOP提供了非常强大的功能,用来对IOC做补充。通俗点说的话就是在程序运行期间,将某段代码动态切入到指定方法的指定位置进行运行的这种编程方式。
一、AOP的概念
为什么要引入AOP?
Calculator.java
package com.mashibing.inter;
public interface Calculator {
public int add(int i,int j);
public int sub(int i,int j);
public int mult(int i,int j);
public int div(int i,int j);
}
MyCalculator.java
package com.mashibing.inter;
public class MyCalculator implements Calculator {
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
public int mult(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}
MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyCalculator myCalculator = new MyCalculator();
System.out.println(myCalculator.add(1, 2));
}
}
此代码非常简单,就是基础的javase的代码实现,此时如果需要添加日志功能应该怎么做呢,只能在每个方法中添加日志输出,同时如果需要修改的话会变得非常麻烦。
MyCalculator.java
package com.mashibing.inter;
public class MyCalculator implements Calculator {
public int add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("add 方法开始执行,参数为:"+i+","+j);
int result = i + j;
System.outprintln("add 方法开始完成结果为:"+result);
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("sub 方法开始执行,参数为:"+i+","+j);
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("add 方法开始完成结果为:"+result);
return result;
}
public int mult(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("mult 方法开始执行,参数为:"+i+","+j);
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("add 方法开始完成结果为:"+result);
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("div 方法开始执行,参数为:"+i+","+j);
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("add 方法开始完成结果为:"+result);
return result;
}
}
可以考虑将日志的处理抽象出来,变成工具类来进行实现:
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class LogUtil {
public static void start(Object ... objects){
System.out.println("XXX方法开始执行,使用的参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
}
public static void stop(Object ... objects){
System.out.println("XXX方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
}
}
MyCalculator.java
package com.mashibing.inter;
import com.mashibing.util.LogUtil;
public class MyCalculator implements Calculator {
public int add(int i, int j) {
LogUtil.start(i,j);
int result = i + j;
LogUtil.stop(result);
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
LogUtil.start(i,j);
int result = i - j;
LogUtil.stop(result);
return result;
}
public int mult(int i, int j) {
LogUtil.start(i,j);
int result = i * j;
LogUtil.stop(result);
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
LogUtil.start(i,j);
int result = i / j;
LogUtil.stop(result);
return result;
}
}
按照上述方式抽象之后,代码确实简单很多,但是大家应该已经发现在输出的信息中并不包含具体的方法名称,我们更多的是想要在程序运行过程中动态的获取方法的名称及参数、结果等相关信息,此时可以通过使用动态代理的方式来进行实现。
CalculatorProxy.java
package com.mashibing.proxy;
import com.mashibing.inter.Calculator;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 帮助Calculator生成代理对象的类
*/
public class CalculatorProxy {
/**
*
* 为传入的参数对象创建一个动态代理对象
* @param calculator 被代理对象
* @return
*/
public static Calculator getProxy(final Calculator calculator){
//被代理对象的类加载器
ClassLoader loader = calculator.getClass().getClassLoader();
//被代理对象的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = calculator.getClass().getInterfaces();
//方法执行器,执行被代理对象的目标方法
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 执行目标方法
* @param proxy 代理对象,给jdk使用,任何时候都不要操作此对象
* @param method 当前将要执行的目标对象的方法
* @param args 这个方法调用时外界传入的参数值
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//利用反射执行目标方法,目标方法执行后的返回值
// System.out.println("这是动态代理执行的方法");
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
result = method.invoke(calculator, args);
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+ result);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法出现异常:"+ e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......");
}
//将结果返回回去
return result;
}
};
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return (Calculator) proxy;
}
}
我们可以看到这种方式更加灵活,而且不需要在业务方法中添加额外的代码,这才是常用的方式。如果想追求完美的话,还可以使用上述的日志工具类来完善。
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class LogUtil {
public static void start(Method method, Object ... objects){
// System.out.println("XXX方法开始执行,使用的参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
}
public static void stop(Method method,Object ... objects){
// System.out.println("XXX方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
}
public static void logException(Method method,Exception e){
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法出现异常:"+ e.getMessage());
}
public static void end(Method method){
System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......");
}
}
CalculatorProxy.java
package com.mashibing.proxy;
import com.mashibing.inter.Calculator;
import com.mashibing.util.LogUtil;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 帮助Calculator生成代理对象的类
*/
public class CalculatorProxy {
/**
*
* 为传入的参数对象创建一个动态代理对象
* @param calculator 被代理对象
* @return
*/
public static Calculator getProxy(final Calculator calculator){
//被代理对象的类加载器
ClassLoader loader = calculator.getClass().getClassLoader();
//被代理对象的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = calculator.getClass().getInterfaces();
//方法执行器,执行被代理对象的目标方法
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 执行目标方法
* @param proxy 代理对象,给jdk使用,任何时候都不要操作此对象
* @param method 当前将要执行的目标对象的方法
* @param args 这个方法调用时外界传入的参数值
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//利用反射执行目标方法,目标方法执行后的返回值
// System.out.println("这是动态代理执行的方法");
Object result = null;
try {
LogUtil.start(method,args);
result = method.invoke(calculator, args);
LogUtil.stop(method,args);
} catch (Exception e) {
LogUtil.logException(method,e);
} finally {
LogUtil.end(method);
}
//将结果返回回去
return result;
}
};
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return (Calculator) proxy;
}
}
看到上述代码之后可能感觉已经非常完美了,但是要说明的是,这种动态代理的实现方式调用的是jdk的基本实现,如果需要代理的目标对象没有实现任何接口,那么是无法为他创建代理对象的,这也是致命的缺陷。而在Spring中我们可以不编写上述如此复杂的代码,只需要利用AOP,就能够轻轻松松实现上述功能,当然,Spring AOP的底层实现也依赖的是动态代理。
基于JDK实现动态代理
实现步骤
- 通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口创建自己的调用处理器
- 通过为 Proxy 类指定 ClassLoader 对象和一组 interface 来创建动态代理类
- 通过反射机制获得动态代理类的构造函数(jdk自带,不需手动处理)
- 通过构造函数创建动态代理类实例,构造时调用处理器对象作为参数被传入(jdk自带,不需手动处理)
AOP的核心概念及术语
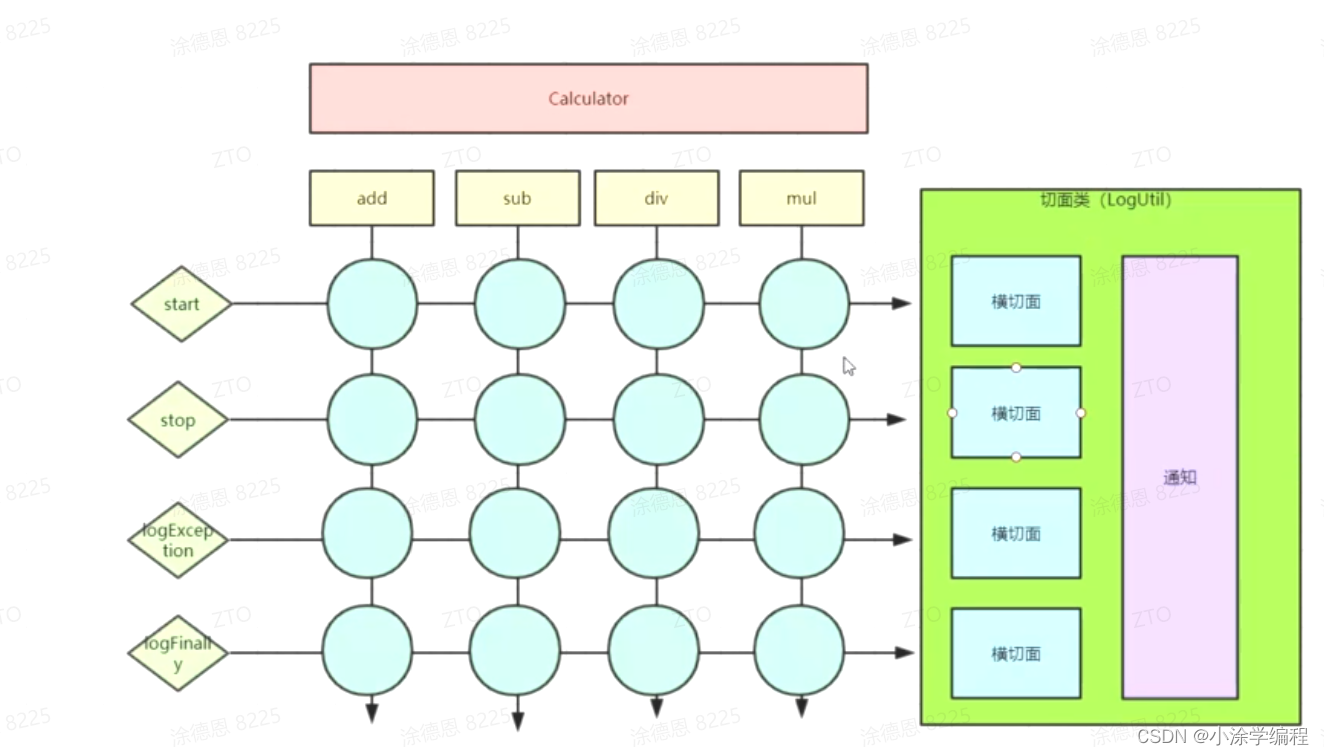
-
切面(Aspect): 指关注点模块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象。事务管理是企业级Java应用中有关横切关注点的例子。 在Spring AOP中,切面可以使用通用类基于模式的方式(schema-based approach)或者在普通类中以@Aspect注解(@AspectJ 注解方式)来实现。(不管完成事务还是日志等等,最终还是把往里面嵌入的代码或者核心功能抽象成一个单独的类,这个类可以称之为切面,例如LogUtil 方法封装成一个对象叫切面) -
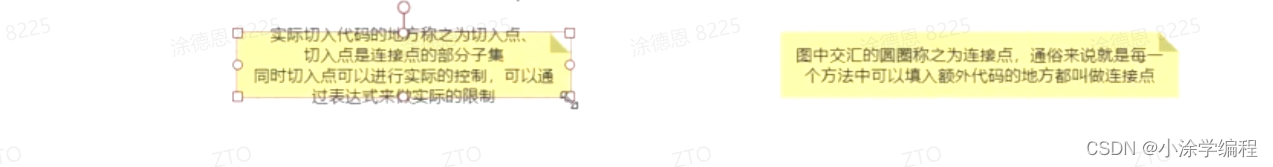
连接点(Join point): 在程序执行过程中某个特定的点,例如某个方法调用的时间点或者处理异常的时间点。在Spring AOP中,一个连接点总是代表一个方法的执行。(LogUtil.stop(method,result); ) -
通知(Advice):在切面的某个特定的连接点上执行的动作。通知有多种类型,包括“around”, “before” and “after”等等。许多AOP框架,包括Spring在内,都是以拦截器做通知模型的,并维护着一个以连接点为中心的拦截器链。 -
切入点(Pointcut): 匹配连接点的断言。通知和切点表达式相关联,并在满足这个切点的连接点上运行(例如,当执行某个特定名称的方法时)。切点表达式如何和连接点匹配是AOP的核心:Spring默认使用AspectJ切点语义。 -
引入(Introduction): 声明额外的方法或者某个类型的字段。Spring允许引入新的接口(以及一个对应的实现)到任何被通知的对象上。例如,可以使用引入来使bean实现IsModified接口, 以便简化缓存机制(在AspectJ社区,引入也被称为内部类型声明(inter))。 -
目标对象(Target object): 被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。也被称作被通知(advised)对象。既然Spring AOP是通过运行时代理实现的,那么这个对象永远是一个被代理(proxied)的对象。(实际要操作的类MyCalculator) -
AOP代理(AOP proxy):AOP框架创建的对象,用来实现切面契约(aspect contract)(包括通知方法执行等功能)。在Spring中,AOP代理可以是JDK动态代理或CGLIB代理。(代理对象CalculatorProxy) -
织入(Weaving): 把切面连接到其它的应用程序类型或者对象上,并创建一个被通知的对象的**过程**。这个过程可以在编译时(例如使用AspectJ编译器)、类加载时或运行时中完成。 Spring和其他纯Java AOP框架一样,是在运行时完成织入的。
public Integer add(Integer i, Integer j)
AOP的通知类型
前置通知(Before advice): 在连接点之前运行但无法阻止执行流程进入连接点的通知(除非它引发异常)。后置返回通知(After returning advice):在连接点正常完成后执行的通知(例如,当方法没有抛出任何异常并正常返回时)。后置异常通知(After throwing advice): 在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。后置通知(总会执行)(After (finally) advice): 当连接点退出的时候执行的通知(无论是正常返回还是异常退出)。环绕通知(Around Advice):环绕连接点的通知,例如方法调用。这是最强大的一种通知类型,。环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为。它可以选择是否继续执行连接点或直接返回自定义的返回值又或抛出异常将执行结束。
AOP的应用场景
- 日志管理
- 权限认证
- 安全检查
- 事务控制
二、Spring AOP的简单配置
在上述代码中我们是通过动态代理的方式实现日志功能的,但是比较麻烦,现在我们将要使用spring aop的功能实现此需求,其实通俗点说的话,就是把LogUtil的工具类换成另外一种实现方式。
1.添加pom依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/cglib/cglib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/aopalliance/aopalliance -->
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliance</groupId>
<artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-aspects -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2. 编写配置
-
将目标类和切面类加入到IOC容器中,在对应的类上添加组件注解
-
给LogUtil添加@Component注解
-
给MyCalculator添加@Service注解
-
添加自动扫描的配置
<!--别忘了添加context命名空间--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mashibing"></context:component-scan>
-
-
设置程序中的切面类
- 在LogUtil.java中添加@Aspect注解
-
设置切面类中的方法是什么时候在哪里执行
package com.mashibing.util; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; @Component @Aspect public class LogUtil { /* 设置下面方法在什么时候运行 @Before:在目标方法之前运行:前置通知 @After:在目标方法之后运行:后置通知 @AfterReturning:在目标方法正常返回之后:返回通知 @AfterThrowing:在目标方法抛出异常后开始运行:异常通知 @Around:环绕:环绕通知 当编写完注解之后还需要设置在哪些方法上执行,使用表达式 execution(访问修饰符 返回值类型 方法全称) */ @Before("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))") public static void start(){ // System.out.println("XXX方法开始执行,使用的参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects)); // System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects)); System.out.println("方法开始执行,参数是:"); } @AfterReturning("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))") public static void stop(){ // System.out.println("XXX方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects)); // System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects)); System.out.println("方法执行完成,结果是:"); } @AfterThrowing("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))") public static void logException(){ // System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法出现异常:"+ e.getMessage()); System.out.println("方法出现异常:"); } @After("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))") public static void end(){ // System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......"); System.out.println("方法执行结束了......"); } } -
开启基于注解的aop的功能
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd "> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mashibing"></context:component-scan> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
3. 测试
MyTest.java
import com.mashibing.inter.Calculator;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
Calculator bean = context.getBean(Calculator.class);
bean.add(1,1);
}
}
spring AOP的动态代理方式是jdk自带的方式,容器中保存的组件是代理对象com.sun.proxy.$Proxy对象
4. 通过cglib来创建代理对象
MyCalculator.java
package com.mashibing.inter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyCalculator {
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
public int mult(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}
MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
MyCalculator bean = context.getBean(MyCalculator.class);
bean.add(1,1);
System.out.println(bean);
System.out.println(bean.getClass());
}
}
可以通过cglib的方式来创建代理对象,此时不需要实现任何接口,代理对象是
class com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator E n h a n c e r B y S p r i n g C G L I B EnhancerBySpringCGLIB EnhancerBySpringCGLIB1f93b605类型
综上所述:在spring容器中,如果有接口,那么会使用jdk自带的动态代理,如果没有接口,那么会使用cglib的动态代理。动态代理的实现原理,后续会详细讲。 那种效率比较高?,早起的时候cglib效率比较高,但是jdk一直在更新迭代,现在的话差不多
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect //声明切面
@Component
@Order(200)
public class LogUtil {
/**
* 通知注解有以下几种类型:
*
* @Before:前置通知,在方法执行之前完成
* @After:后置通知,在方法执行完成之后执行
* @AfterReturing:返回通知:在返回结果之后运行
* @AfterThrowing:异常通知:出现异常的时候使用
* @Around:环绕通知
*
* 在方法的参数列表中不要随便添加参数值,会有异常信息
*
* 切入点表达式:
* 最精确的匹配方式:
* public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.add(Integer,Integer)
* 在实际的生产环境中,更多的时候使用通配符的方式
* *:
* 1、可以用来匹配一个或者多个字符
* execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,Integer)
* 2、匹配任意类型的参数,只能匹配一个
* execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*))
* 3、*在进行匹配的时候只能匹配一层路径,不能匹配多层
* execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator*.*(Integer,*))
* MyCalculator1、MyCalculator2、MyCalculator3.....这种不支持,只属于一层目录
* 4、*不能够匹配访问修饰符,如果不确定访问修饰符是什么,可以直接省略不写
* execution( * Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*)) 不支持
* execution( Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*)) 不写* 支持
* 5、返回值可以使用*来代替
* ..:
* 1、可以匹配多个参数,任意类型
* execution(* com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..))
* 2、可以匹配多层路径
* execution(* com.mashibing..MyCalculator*.*(..))
* 最偷懒的方式:
* execution(* *(..))
* execution(* com..*(..))
* 如果表达式是以*开头,那么可以代替所有
*
* 在使用表达式的时候还支持逻辑运算
* &&:多个条件必须同时满足
* execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..)) && execution(* *(..))
* ||:多个条件只要满足其中一个即可
* execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..)) || execution(* *(..))
* !:取反,除了这种情况的其他都满足
* !execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.add(Integer,Integer))
*
* 使用通配符的时候不是越简洁越好,更多的是要选择符合要求或者符合规则的匹配方式,
* 此时就要求在定义标识符的时候必须要遵循项目规范
*
* 通知的正常执行顺序:
* 如果正常执行:@Before--》@After----》@AfterReturning
* 如果异常结束:@Before--》@After----》@AfterThrowing
*
*
* 如果想要在方法中获取对应的参数或者方法名称等信息的时候,必须要使用JoinPoint对象,并且此参数必须是第一个
* getSignature()
* getArgs()
* 如果方法中有返回值,那么必须要在注解中添加 Returing="result" ,这个result必须要和参数列表中的参数名称保持一致
* 如果需要添加异常信息,那么在注解中要添加Throwing="e" 这个e的名称必须跟参数列表中的名称保持一致
* 如果想要添加其他参数,必须要添加args(参数列表),ArgNames(参数列表)
* @Before(value = "execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,Integer)) && args(joinPoint,k)",argNames = "joinPoint,k")
*
*
* 通知方法在定义的时候有没有什么特殊的要求?
* 通知方法在定义的时候对于访问修饰符、返回值类型都没有明确的要求,
* 但是要注意,参数不能随便添加
*
* 如果有多个匹配的表达式相同,能否做抽象?
* 定义一个没有返回值的空方法,给该方法添加@PointCut注解,后续在使用的时候可以直接调用方法名称
* 此处的方法只是起一个声明的作用,能够供内部的其他通知方法进行调用
*
*
* 环绕通知:
* 环绕通知在执行的时候是优先于普通通知的
* 如果是正常结束,那么执行顺序是:
* 环绕前置通知--》@Before--》环绕后置通知--》环绕返回通知--》@After--》@AfterReturning
* 如果是异常结束,那么执行顺序是:
* 环绕前置通知--》@Before--》环绕异常通知--》环绕返回通知--》@After--》@AfterReturing
* 如果出现异常的时候,在环绕通知中解决了,那么普通通知是接受不到的,如果想让普通通知接收到需要进行抛出 throw throwable
* 执行顺序改为:
* 环绕前置通知--》@Before--》环绕异常通知--》环绕返回通知--》@After--》@AfterThrowing
*
* 当应用程序中包含多个切面类的时候,具体的执行顺序是什么样?
* 按照切面类的名称的首字母进行排序操作,按照字典序
* 如果需要认为的规定顺序,可以在切面类上添加@Order注解同时可以添加具体的值
* 值越小,越优先
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,Integer))")
public void myPointCut(){}
@Pointcut("execution(* *(..))")
public void myPointCut1(){}
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
private int start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
//获取参数信息
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法开始执行:参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
return 100;
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()",throwing = "e")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法抛出异常:"+e.getMessage());
}
@After("myPointCut()")
public static void logFinally(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("log---"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束。。。。。over");
}
@Around("myPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("log---环绕通知start:"+signature.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数为:"+Arrays.asList(args));
//通过反射的方式调用目标的方法,相当于执行method.invoke(),可以自己修改结果值
result = pjp.proceed(args);
// result=100;
System.out.println("log---环绕通知stop"+signature.getName()+"方法执行结束");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("log---环绕异常通知:"+signature.getName()+"出现异常");
throw throwable;
}finally {
System.out.println("log---环绕返回通知:"+signature.getName()+"方法返回结果是:"+result);
}
return result;
}
}
注意:
1. 切入点表达式
在使用表达式的时候,除了之前的写法之外,还可以使用通配符的方式:
- 最精确的匹配方式:
public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.add(Integer,Integer)
- *
- 匹配一个参数或者多个字符 :
execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,Integer)
- 匹配任意一个参数 :
execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*))
- 只能匹配一层路径,如果项目路径下有多层目录,那么*只能匹配一层路径
execution( public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator*.*(Integer,*))
- *不能够匹配访问修饰符,如果不确定访问修饰符是什么,可以直接省略不写
execution( * Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*)) 不支持
execution( Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(Integer,*)) 不写* 支持
-
返回值可以使用*来代替
-
…
-
匹配多个参数,任意类型参数 :
execution(* com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..))
- 匹配任意多层路径 :
execution(* com.mashibing..MyCalculator*.*(..))
- 在写表达式的时候,可以有N多种写法,但是有一种最偷懒和最精确的方式:
- 最偷懒的方式:
如果表达式是以*开头,那么可以代替所有
- 最偷懒的方式:
execution(* *(..))
execution(* com..*(..))
- 在使用表达式的时候还支持逻辑运算
- &&:多个条件必须同时满足
execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..)) && execution(* *(..))
- ||:多个条件只要满足其中一个即可
execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.*(..)) || execution(* *(..))
- !:取反,除了这种情况的其他都满足
!execution(public Integer com.mashibing.service.MyCalculator.add(Integer,Integer))
- 使用通配符的时候不是越简洁越好,更多的是要选择符合要求或者符合规则的匹配方式,此时就要求在定义标识符的时候必须要遵循项目规范
2. 通知方法的执行顺序
在之前的代码中大家一直对通知的执行顺序有疑问,其实执行的结果并没有错,大家需要注意:
- 正常执行:@Before—>@After—>@AfterReturning
- 异常执行:@Before—>@After—>@AfterThrowing
3. 获取方法的详细信息
在上面的案例中,我们并没有获取Method的详细信息,例如方法名、参数列表等信息,想要获取的话其实非常简单,只需要添加JoinPoint参数即可。
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Before("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:");
}
@After("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行结束了......");
}
}
刚刚只是获取了方法的信息,但是如果需要获取结果,还需要添加另外一个方法参数,并且告诉spring使用哪个参数来进行结果接收
LogUtil.java
@AfterReturning(value = "execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
也可以通过相同的方式来获取异常的信息
LogUtil.java
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:"+exception);
}
4. spring对通过方法的要求
spring对于通知方法的要求并不是很高,你可以任意改变方法的返回值和方法的访问修饰符,但是唯一不能修改的就是方法的参数,会出现参数绑定的错误,原因在于通知方法是spring利用反射调用的,每次方法调用得确定这个方法的参数的值。
LogUtil.java
@After("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint,String aa){
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......");
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
5. 表达式的抽取
如果在实际使用过程中,多个方法的表达式是一致的话,那么可以考虑将切入点表达式抽取出来:
a. 随便声明一个没有实现的返回void的空方法
b. 给方法上标注@Potintcut注解
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
}
6. 环绕通知的使用
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke(),该方法底层使用反射
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
总结:环绕通知的执行顺序是优于普通通知的,具体的执行顺序如下:
但是需要注意的是,如果出现了异常,那么环绕通知会处理或者捕获异常,普通异常通知是接收不到的,因此最好的方式是在环绕异常通知中向外抛出异常。
7.多切面运行的顺序
如果有多个切面要进行执行,那么顺序是什么样的呢?
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
// System.out.println("XXX方法开始执行,使用的参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
// System.out.println("XXX方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法出现异常:"+ e.getMessage());
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......");
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
//@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke()
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
SecurityAspect.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class SecurityAspect {
@Before("com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
//@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke()
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
在spring中,默认是按照切面名称的字典顺序进行执行的,但是如果想自己改变具体的执行顺序的话,可以使用@Order注解来解决,数值越小,优先级越高。
LogUtil.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
// System.out.println("XXX方法开始执行,使用的参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
// System.out.println("XXX方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束,结果是:"+ Arrays.asList(objects));
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法出现异常:"+ e.getMessage());
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
// System.out.println(method.getName()+"方法执行结束了......");
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Log:"+name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
//@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke()
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
SecurityAspect.java
package com.mashibing.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class SecurityAspect {
@Before("com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("com.mashibing.util.LogUtil.myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Security:"+name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
//@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke()
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
如果需要添加环绕通知呢,具体的执行顺序又会是什么顺序呢?
因为环绕通知在进行添加的时候,是在切面层引入的,所以在哪个切面添加环绕通知,那么就会在哪个切面执行。
三、基于配置的AOP配置
之前我们讲解了基于注解的AOP配置方式,下面我们开始讲一下基于xml的配置方式,虽然在现在的企业级开发中使用注解的方式比较多,但是你不能不会,因此需要简单的进行配置,注解配置快速简单,配置的方式共呢个完善。
-
将所有的注解都进行删除
-
添加配置文件
aop.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mashibing"></context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean id="logUtil" class="com.mashibing.util.LogUtil2"></bean>
<bean id="securityAspect" class="com.mashibing.util.SecurityAspect"></bean>
<bean id="myCalculator" class="com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="globalPoint" expression="execution(public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<aop:pointcut id="mypoint" expression="execution(public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="end" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="mypoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="mypoint" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="securityAspect">
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="end" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="globalPoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="globalPoint" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
<aop:pointcut id="globalPoint" expression="execution(public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<aop:pointcut id="mypoint" expression="execution(public int com.mashibing.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="end" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="mypoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="mypoint" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="securityAspect">
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="end" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="globalPoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="globalPoint" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>






















 246
246











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








