C语言
快排
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int change(int arr[],int low,int high){
int key=arr[low];
while(low<high){
while(low<high && arr[high]>=key) high--;
if(low<high) arr[low++]=arr[high];
while(low<high && arr[low]<=key) low++;
if(low<high) arr[high--]=arr[low];
}
arr[low]=key;
return low;
}
void Qsort(int arr[],int low,int high){
if(low<high){
int pos=change(arr,low,high);
Qsort(arr,low,pos-1);
Qsort(arr,pos+1,high);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int buf[100];
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&buf[i]);
}
Qsort(buf,0,n-1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
printf("%d ",buf[i]);
}
}
}
C语言计算无穷级数(设置精度即可 1e-6 与1e-9 结果一样)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<math.h>
unsigned long n;
int main()
{
double x;
scanf("%lf",&x);
double sum=0.0;
for(int i=0;;i++){
double temp=pow(-1,i)*pow(x,i+2)/(9*i+3);
if(temp<1e-9){
break;
}
sum+=temp;
}
printf("%d",sum);
return 0;
}
C语言 整型转字符串
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int num ;
scanf("%d",&num);
char str[10];
char digit[10];
sprintf(str, "%d", num);
sprintf(str,"%d",num)
int len = strlen(str);
int flag=0;
for (int i = 0; i < len/2; i++) {
if(str[i]==str[len-1-i]){
flag++;
}
}
if(len/2==flag) {
printf("%d 是回文数",num);
}
else printf("%d 不是回文数",num);
return 0;
}
C语言的行列式求值 注意二维数组的传参
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int caculate(double matrix[][10],int n)
{
double det=0.0;
double temp[10][10];
int sign=1;
if(n==1) return matrix[0][0];
else if(n==2){
return matrix[0][0]*matrix[1][1]-matrix[0][1]*matrix[1][0];
}
else{
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(j!=k){
temp[i-1][j<k?j:j-1]=matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
det+=sign*matrix[0][k]*caculate(temp,n-1);
sign=-sign;
}
return det;
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
double matrix[10][10];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
scanf("%lf",&matrix[i][j]);
}
}
double det=caculate(matrix,n);
printf("%lf",det);
}
C语言 最大公约数与公倍数
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
int lcm(int a,int b){
return a*b/gcd(a,b);
}
C字符串处理
输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其他字符的个数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char c;
int zimu=0;
int shuzi=0;
int kongge=0;
int other=0;
while((c=getchar())!='\n'){
if(c>='a'&&c<='z' || c>='A'&&c<='Z') zimu++;
else if(c==' ') kongge++;
else if(c>='0'&&c<='9') shuzi++;
else other++;
}
printf("字母:%d,数字=%d,空格=%d\n",zimu,shuzi,kongge);
}
单词首字母大写 有多个空格
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char c;
int flag=1;
while((c=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(flag==1){
flag=0;
if(c>='a'&&c<='z') c-=32;
}
if(c==' '){
flag=1;
}
putchar(c);
}
}
查找strcspn()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[] = "hello world, how are you?";
int first_index = strcspn(str, " ");
int second_index = strcspn(str + first_index + 1, " ") + first_index + 1;
printf("第二个空格字符在字符串中的位置是:%d\n", second_index);
return 0;
}
多行输入
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_LEN 100
int main() {
char str[MAX_LEN];
printf("请输入字符串,按Ctrl + D结束输入:\n");
while (fgets(str, MAX_LEN, stdin) != NULL) {
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0';
printf("您输入的字符串是:%s\n", str);
}
return 0;
}
A变E ,Z变D 注意非字符字母不变
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MaxSize 100
int main()
{
char c;
while((c=getchar())!='\n'){
if(c>='A'&&c<='Z' || c>='a'&&c<='z'){
c=c+4;
}
if(c>'Z'&&c<='Z'+4 || c>'z'&&c<='z'+4){
c=c-26;
}
printf("%c\n",c);
}
}
16进制转10
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
char str[100];
scanf("%s",&str);
int num=0;
int n=strlen(str);
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
if(str[i]>='0'&&str[i]<='9'){
num+=(str[i]-'0')*pow(16,n-1-i);
}
else if(str[i]>='A'&&str[i]<='F'){
num+=(str[i]-'A'+10)*pow(16,n-1-i);
}
else if(str[i]>='a'&&str[i]<='f'){
num+=(str[i]-'a'+10)*pow(16,n-1-i);
}
}
printf("%d\n",num);
}
打印菱形
#include <math.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
int n,len;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
if(n%2==0) {
printf("请输入奇数\n");
continue;
}
int x=n/2+1;
int a=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i<=x){
int b=x-i;
for(int j=1;j<=b;j++){
printf(" ");
}
for(int k=1;k<=a;k++)
{
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
if(i<x) a=a+2;
}
else{
a=a-2;
int b=i-x;
for(int j=1;j<=b;j++){
printf(" ");
}
for(int k=1;k<=a;k++)
{
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
最大字符平台(有)多个
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char str[100];
scanf("%s",&str);
int len=strlen(str);
int max_len=0;
int start[100],end[100];
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
int j=i;
while(j<len && str[j]==str[i]) j++;
int cur_len=j-i;
if(cur_len>max_len){
max_len=cur_len;
cnt=0;
start[cnt]=i;
end[cnt]=j-1;
cnt++;
}
else if(cur_len==max_len){
start[cnt]=i;
end[cnt]=j-1;
cnt++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
for(int j=start[i];j<=end[i];j++){
printf("%c",str[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
输入一个字符串,内有数字和非数字字符,打印字符串中所有连续的数字所组成的整数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<string.h>
int check(char c)
{
if(c>='0'&&c<='9') return 1;
else return 0;
}
int main()
{
char str[100];
scanf("%s",&str);
int len=strlen(str);
int cnt=0;
int cur_len=-1;
int start[100],end[100];
int i=0;
while(i<len){
int j=i+1;
if(check(str[i])){
while(j<len && check(str[j])) j++;
cur_len=j-i;
start[cnt]=i;
end[cnt]=j-1;
cnt++;
i=j+1;
}
else i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
for(int j=start[i];j<=end[i];j++)
{
printf("%c",str[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
C语言结构体
注意结构体的定义 打印学生成绩
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef struct{
int id;
char name[20];
int grade1,grade2,grade3;
}student;
student print(student stu[]){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
double x=0.0;
x=(stu[i].grade1+stu[i].grade2+stu[i].grade3)/3;
printf("%s,%lf\n",stu[i].name,x);
}
}
int main()
{
student stu[6];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
scanf("%d %s %d %d %d",&stu[i].id,&stu[i].name,&stu[i].grade1,&stu[i].grade2,&stu[i].grade3);
}
print(stu);
}
C语言链表
头插 尾插
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct student{
char name[20];
int age;
int grade;
struct student* next;
}student;
int n;
student* create(){
student* head=(student*)malloc(sizeof(student));
head->next=NULL;
student* tail=head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
student* node=(student*)malloc(sizeof(student));
printf("第%d个学生信息:",i+1);
scanf("%s %d %d",&node->name,&node->age,&node->grade);
node->next=NULL;
tail->next=node;
tail=node;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
student* head=create();
student* node=head->next;
while(node!=NULL){
printf("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,成绩:%d\n",node->name,node->age,node->grade);
node=node->next;
}
}
循环链表 报数问题 13 报3
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node{
int num;
struct Node* next;
}node;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);
node* head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
head->num=1;
head->next=head;
node* tail=head;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
node* lnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
lnode->num=i;
lnode->next=head;
tail->next=lnode;
tail=lnode;
}
int count=n;
int i=1;
while(count>1){
if(head->num==0){
head=head->next;
continue;
}
if(i==m){
printf("第%d个人退出\n",head->num);
head->num=0;
count--;
}
head=head->next;
i++;
if(i>m) i=1;
}
while (head->num == 0)
{
head = head->next;
if (head->num != 0)
{
printf("没有退出的人为:%d\n", head->num);
break;
}
}
}
链表二进制数加法
#include <math.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node* next;
}Node,*List;
Node* create()
{
char c;
Node* head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next=NULL;
Node* tail=head;
while(1){
scanf("%c",&c);
if(c=='\n') break;
Node* node=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data=c-'0';
node->next=NULL;
tail->next=node;
tail=node;
}
return head;
}
int main(){
Node* head=create();
Node* p=head->next;
Node* q=head->next;
while(p!=NULL){
if(p->data==0) q=p;
p=p->next;
}
if(q!=NULL){
q->data=1;
q=q->next;
while(q!=NULL){
q->data=0;
q=q->next;
}
}
else{
Node* node=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data=1;
node->next=head->next;
head->next=node;
p=head->next->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
p->data=0;
p=p->next;
}
}
p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
C语言树问题
二叉排序树建树,从大到小输出并计算结点个数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct Node* left,*right;
}Node,*BiTree;
void Preorder(BiTree T){
}
void insert(Node **root, char data) {
if(*root==NULL){
*root=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
(*root)->data=data;
(*root)->left=NULL;
(*root)->right=NULL;
}
else if(data<(*root)->data){
insert(&(*root)->left,data);
}
else insert(&(*root)->right,data);
}
void printTree(Node *root)
{
if(root!=NULL){
printTree(root->right);
printf("%c ",root->data);
printTree(root->left);
}
}
int count1(Node* T){
int n1,n2;
if(T==NULL) return 0;
else{
n1=count1(T->left);
n2=count1(T->right);
return n1+n2+1;
}
}
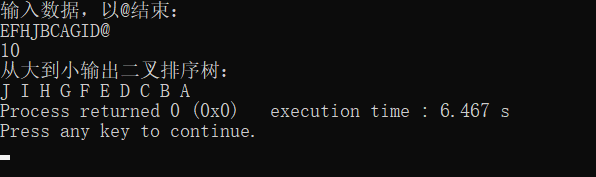
int main()
{
char c;
Node *root = NULL;
printf("输入数据,以@结束:\n");
while((c=getchar())!='@'){
insert(&root,c);
}
printf("%d\n",count1(root));
printf("从大到小输出二叉排序树:\n");
printTree(root);
}
(1)前序建树,中序输出(2)交换左右子树,中序输出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct TreeNode{
char weight;
struct TreeNode* left,*right;
}TreeNode;
TreeNode* createTree(){
TreeNode* root=NULL;
char weight;
scanf("%c",&weight);
if(weight=='#') return NULL;
root=(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->weight=weight;
root->left=createTree();
root->right=createTree();
return root;
}
void inorder(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return;
inorder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->weight);
inorder(root->right);
}
void swapTree(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return;
TreeNode* temp=root->left;
root->left=root->right;
root->right=temp;
swapTree(root->left);
swapTree(root->right);
}
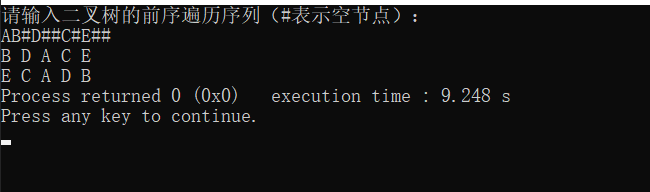
int main()
{
printf("请输入二叉树的前序遍历序列(#表示空节点):\n");
TreeNode* root=createTree();
inorder(root);
printf("\n");
swapTree(root);
inorder(root);
}
哈夫曼树另一种解法:从大到小排序,每次排序取最小的加入排序因为WPL也 = 哈夫曼树中所有非叶子结点的权值之和
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int cmp(const void* a,const void* b){
return *(int*)b-*(int*)a;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int num[1000];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
}
qsort(num,n,sizeof(num[0]),cmp);
int sum=0,i;
for(i=n-1;i>0;i--){
int a=num[i];
int b=num[i-1];
num[i-1]=a+b;
sum+=num[i-1];
qsort(num,i,sizeof(num[0]),cmp);
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return 0;
}
打印树
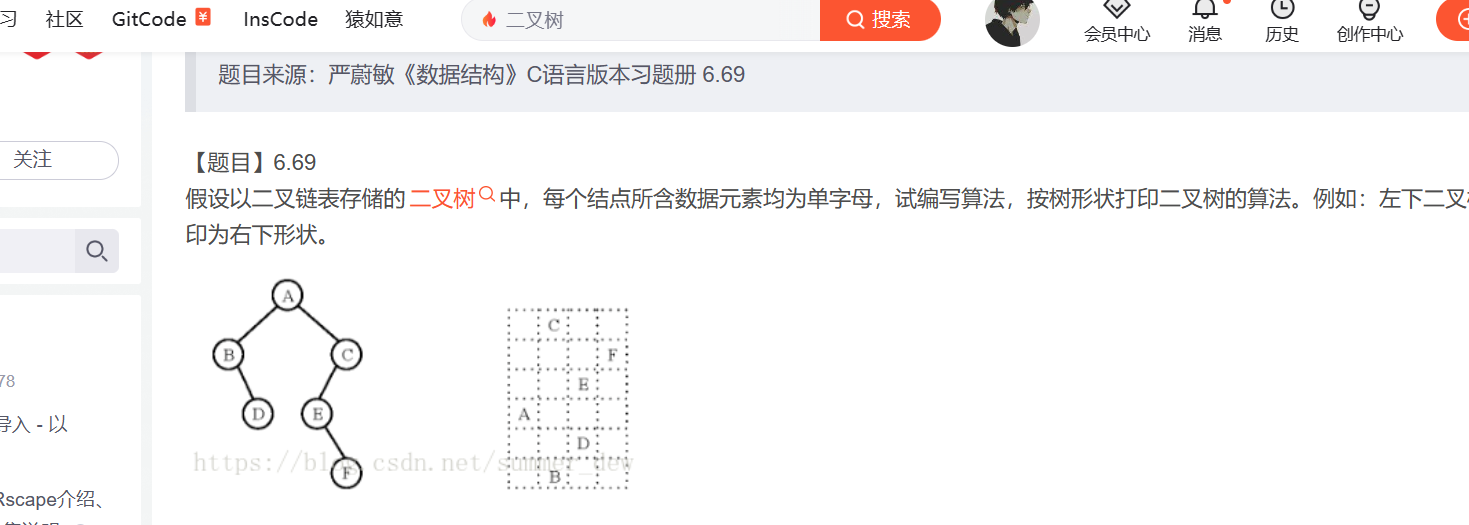
#include <math.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node{
char data;
struct node* left,*right;
}Node;
Node* preCreate(){
Node* root=NULL;
char data;
scanf("%c",&data);
if(data=='#') return NULL;
root=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
root->data=data;
root->left=preCreate();
root->right=preCreate();
return root;
}
void inOrder(Node* root){
if(root==NULL) return;
inOrder(root->left);
printf("%c",root->data);
inOrder(root->right);
}
void PrintTree(Node* root,int i){
if(root){
PrintTree(root->right,i+1);
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) printf("@");
printf("%c\n",root->data);
PrintTree(root->left,i+1);
}
}
int main(){
Node* root=preCreate();
inOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PrintTree(root,0);
}
根到叶子,叶子到树
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct TreeNode{
char weight;
struct TreeNode* left,*right;
}TreeNode;
TreeNode* createTree(){
TreeNode* root=NULL;
char weight;
scanf("%c",&weight);
if(weight=='#') return NULL;
root=(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->weight=weight;
root->left=createTree();
root->right=createTree();
return root;
}
void inorder(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return;
inorder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->weight);
inorder(root->right);
}
void swapTree(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return;
TreeNode* temp=root->left;
root->left=root->right;
root->right=temp;
swapTree(root->left);
swapTree(root->right);
}
void leaf_root(TreeNode* T,int *path,int len)
{
if(T)
{
if(T->left==NULL&&T->right==NULL)
{
for(int i=0;i<=len-1;i++)
{
printf("%c->",path[i]);
}
printf("%c",T->weight);
printf("\n");
}
else
{
path[len++]=T->weight;
leaf_root(T->left,path,len);
leaf_root(T->right,path,len);
}
}
}
int main()
{
printf("请输入二叉树的前序遍历序列(#表示空节点):\n");
TreeNode* root=createTree();
inorder(root);
printf("\n");
int path[20]={0};
int len=0;
leaf_root(root,path,len);
}













 本文展示了C语言在排序算法(如快速排序)、数学计算(如无限级数、行列式求值)、字符串操作(如整型转字符串、回文数检测)以及数据结构(如链表、二叉树)等方面的应用。通过实例代码,涵盖了基础算法和数据结构处理方法。
本文展示了C语言在排序算法(如快速排序)、数学计算(如无限级数、行列式求值)、字符串操作(如整型转字符串、回文数检测)以及数据结构(如链表、二叉树)等方面的应用。通过实例代码,涵盖了基础算法和数据结构处理方法。

















 2517
2517

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










