目录
一、WaterFlow简介
WaterFlow是HarmonyOS中的瀑布流容器组件,由"行"和"列"分割的单元格所组成,通过容器自身的排列规则,将不同大小的"项目"自上而下,如瀑布般紧密布局。这种布局方式特别适合展示图片画廊、商品列表等内容不规则的场景。
二、基础用法
2.1 创建简单的双列瀑布流
最基本的瀑布流创建方式如下:
WaterFlow() {
ForEach(this.dataArray, (item) => {
FlowItem() {
Column() {
Image(item.imageUrl)
.width('100%')
.borderRadius(8)
Text(item.title)
.fontSize(14)
}
}
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr') // 创建两列布局
.columnsGap(10) // 设置列间距
.rowsGap(10) // 设置行间距2.2 自动计算列数
可以使用repeat(auto-fill, size)实现根据容器宽度自动计算列数:
WaterFlow() {
// 瀑布流内容
}
.columnsTemplate('repeat(auto-fill, 120)') // 每列120vp宽度,自动计算列数三、数据源管理
3.1 创建数据源类
推荐使用实现IDataSource接口的数据源类与LazyForEach结合使用:
export class WaterFlowDataSource implements IDataSource {
private dataArray: any[] = [];
private listeners: DataChangeListener[] = [];
constructor() {
// 初始化数据
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
this.dataArray.push({
id: i,
title: `标题${i}`,
height: 100 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
});
}
}
// 获取索引对应的数据
public getData(index: number): any {
return this.dataArray[index];
}
// 获取数据总数
public totalCount(): number {
return this.dataArray.length;
}
// 注册数据变化监听器
registerDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
if (this.listeners.indexOf(listener) < 0) {
this.listeners.push(listener);
}
}
// 取消注册数据变化监听器
unregisterDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
const pos = this.listeners.indexOf(listener);
if (pos >= 0) {
this.listeners.splice(pos, 1);
}
}
// 通知数据添加
notifyDataAdd(index: number): void {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener.onDataAdd(index);
})
}
// 添加数据方法
public addLastItem(): void {
const index = this.dataArray.length;
this.dataArray.push({
id: index,
title: `标题${index}`,
height: 100 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
});
this.notifyDataAdd(index);
}
}3.2 使用LazyForEach加载数据
@Component
struct WaterFlowExample {
dataSource: WaterFlowDataSource = new WaterFlowDataSource();
build() {
WaterFlow() {
LazyForEach(this.dataSource, (item) => {
FlowItem() {
// 内容组件
}
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
}, item => item.id.toString())
}
}
}四、高级功能
4.1 底部加载更多
使用footer参数和onReachEnd事件实现触底加载:
@Component
struct WaterFlowExample {
@State isLoading: boolean = false;
@State isEnd: boolean = false;
@Builder
footerBuilder() {
Column() {
if (this.isLoading) {
Row({ space: 5 }) {
LoadingProgress().width(20).height(20)
Text('加载中...').fontSize(14)
}
.height(40)
} else if (this.isEnd) {
Text('已经到底了').fontSize(14)
.height(40)
}
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
build() {
WaterFlow({ footer: this.footerBuilder() }) {
// 瀑布流内容
}
.onReachEnd(() => {
if (this.isEnd) return;
this.isLoading = true;
// 模拟网络请求
setTimeout(() => {
// 添加更多数据
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
this.dataSource.addLastItem();
}
// 判断是否加载完毕
if (this.dataSource.totalCount() > 200) {
this.isEnd = true;
}
this.isLoading = false;
}, 1000);
})
}
}4.2 分组布局
使用sections参数实现不同列数的混合布局:
@Component
struct WaterFlowSectionsExample {
@State sections: WaterFlowSections = new WaterFlowSections();
aboutToAppear() {
// 初始化分组
this.sections.splice(0, 0, [
{
itemsCount: 3, // 第一组包含3个项目
crossCount: 1, // 单列布局
margin: { top: 10, bottom: 10 },
columnsGap: 0,
rowsGap: 8
},
{
itemsCount: 6, // 第二组包含6个项目
crossCount: 2, // 双列布局
margin: { top: 0, bottom: 10 },
columnsGap: 8,
rowsGap: 8
},
{
itemsCount: 12, // 第三组包含12个项目
crossCount: 3, // 三列布局
margin: { top: 0, bottom: 10 }
}
]);
}
build() {
WaterFlow({ sections: this.sections }) {
LazyForEach(this.dataSource, (item, index) => {
FlowItem() {
// 内容组件,可根据索引判断显示不同样式
}
})
}
}
}4.3 性能优化
使用onGetItemMainSizeByIndex提前计算项目尺寸提高性能:
{
itemsCount: 20,
crossCount: 2,
onGetItemMainSizeByIndex: (index: number) => {
// 提前计算高度,避免布局计算开销
return this.itemHeightArray[index % this.itemHeightArray.length];
}
}4.4 滑动窗口模式
使用layoutMode选择更高效的布局模式:
- ALWAYS_TOP_DOWN:默认模式,滚动位置依赖所有上方项目的布局
- SLIDING_WINDOW:移动窗口式布局,仅考虑视窗内的布局,对大数据集性能更好
WaterFlow()
.layoutMode(WaterFlowLayoutMode.SLIDING_WINDOW)4.5 边缘渐隐效果
设置边缘渐隐效果增强视觉体验:
WaterFlow()
.fadingEdge(true, {fadingEdgeLength: LengthMetrics.vp(80)})五、交互与控制
5.1 设置滚动控制器
使用Scroller控制瀑布流滚动:
@Component
struct WaterFlowExample {
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
build() {
Column() {
// 添加控制按钮
Row({ space: 10 }) {
Button('滚动到顶部')
.onClick(() => {
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(0);
})
Button('滚动到中间')
.onClick(() => {
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(50);
})
}
WaterFlow({ scroller: this.scroller }) {
// 瀑布流内容
}
}
}
}5.2 监听滚动事件
WaterFlow()
.onScrollIndex((first: number, last: number) => {
console.log(`当前显示范围: ${first} - ${last}`);
})
.onScrollStart(() => {
console.log('开始滚动');
})
.onScrollStop(() => {
console.log('停止滚动');
})六、实战案例:图片瀑布流
下面是一个完整的图片瀑布流示例:
@Entry
@Component
struct ImageWaterFlow {
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
dataSource: WaterFlowDataSource = new WaterFlowDataSource();
@State isLoading: boolean = false;
@State isEnd: boolean = false;
aboutToAppear() {
// 初始化数据
this.loadImages();
}
loadImages() {
this.isLoading = true;
// 模拟网络请求
setTimeout(() => {
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
this.dataSource.addImageItem();
}
this.isLoading = false;
}, 1000);
}
@Builder
footerBuilder() {
Column() {
if (this.isLoading) {
Row({ space: 10 }) {
LoadingProgress().width(24).height(24)
Text('正在加载更多图片...').fontSize(14)
}
.height(50)
} else if (this.isEnd) {
Text('已经没有更多图片了').fontSize(14)
.height(50)
}
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Text('图片瀑布流').fontSize(20).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.height(56)
WaterFlow({ footer: this.footerBuilder(), scroller: this.scroller }) {
LazyForEach(this.dataSource, (item: ImageItem) => {
FlowItem() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Image(item.imageUrl)
.width('100%')
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius({ topLeft: 8, topRight: 8 })
if (item.isNew) {
Text('New')
.fontSize(12)
.backgroundColor('#FF3B30')
.fontColor(Color.White)
.borderRadius(4)
.padding(4)
.position({ x: 8, y: 8 })
}
}
Column({ space: 4 }) {
Text(item.title)
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.maxLines(2)
Row() {
Row({ space: 4 }) {
Image('/assets/user_avatar.png')
.width(16)
.height(16)
.borderRadius(8)
Text(item.author)
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#666')
}
Row({ space: 4 }) {
Image('/assets/like_icon.png')
.width(14)
.height(14)
Text(item.likes.toString())
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#666')
}
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
}
.padding(8)
}
.borderRadius(8)
.backgroundColor(Color.White)
.width('100%')
}
.width('100%')
.height(item.height)
})
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(12)
.rowsGap(12)
.padding(16)
.layoutWeight(1)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.onReachEnd(() => {
if (this.isLoading || this.isEnd) return;
if (this.dataSource.totalCount() > 100) {
this.isEnd = true;
} else {
this.loadImages();
}
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
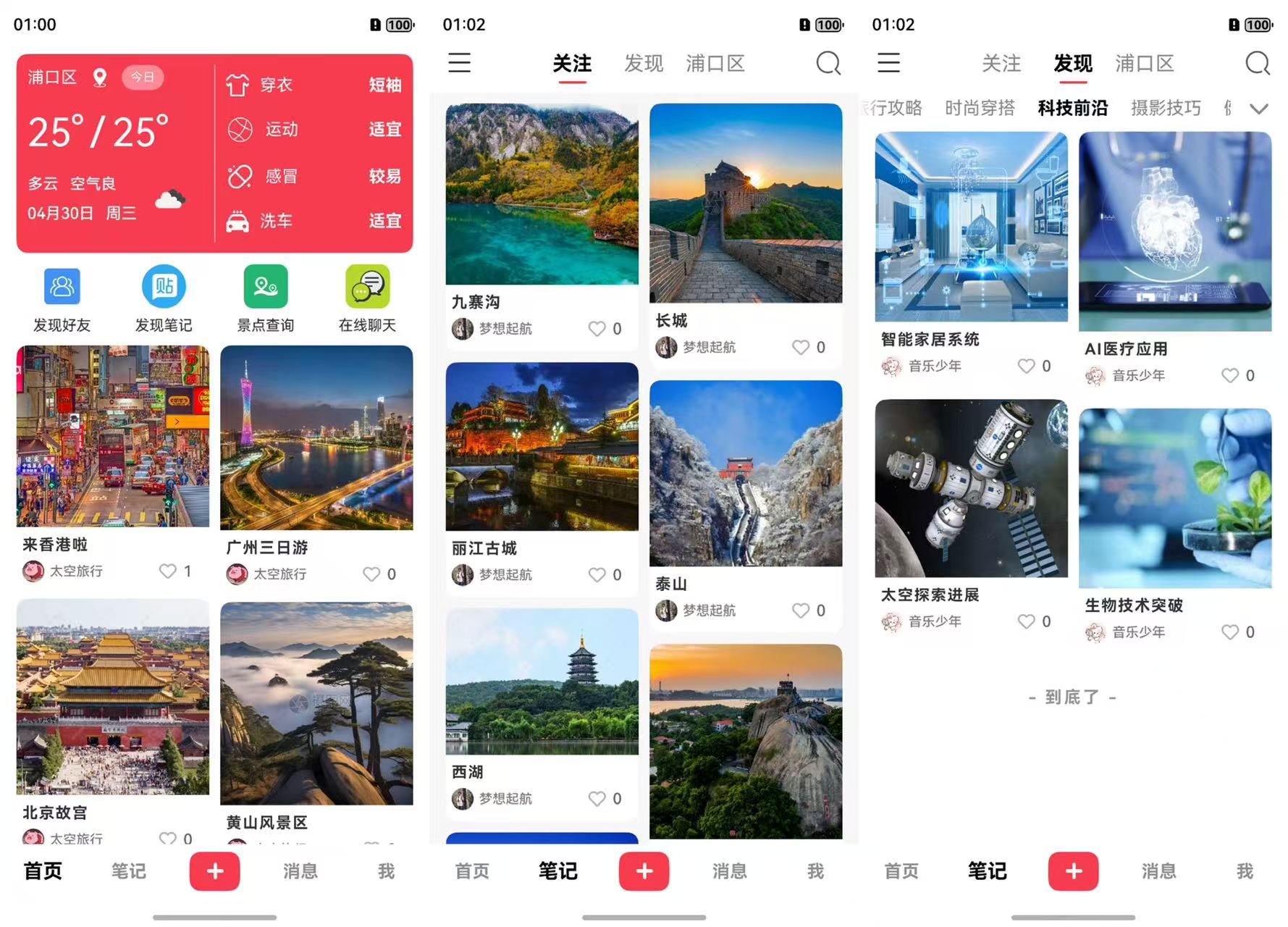
// 数据源实现省略笔记列表呈现瀑布流实际效果图:
七、注意事项
- WaterFlow组件仅支持FlowItem子组件
- 使用分组布局时会忽略columnsTemplate和rowsTemplate属性
- 如果同时设置itemConstraintSize和FlowItem的constraintSize,则取两者之间的适当值
- 滑动窗口模式不支持使用滚动条,但性能更好
- 使用onGetItemMainSizeByIndex会覆盖FlowItem设置的主轴长度
- 分组布局中务必保证所有分组子节点总数与实际子节点数一致
八、最佳实践
- 对于大数据集,优先使用滑动窗口布局模式
- 提前计算并缓存元素尺寸,使用onGetItemMainSizeByIndex提高性能
- 实现组件复用机制,减少内存占用
- 图片加载使用懒加载方式,避免一次性加载过多图片
- 当数据量大时使用分页加载机制,避免一次性加载全部数据
通过本教程,您已经掌握了HarmonyOS中WaterFlow瀑布流组件的各种用法和技巧。这个组件为开发复杂的内容展示界面提供了强大而灵活的布局方案,希望能帮助您更好地开发HarmonyOS应用!























 1019
1019

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








