39. 组合总和
回溯三步曲
1.回溯参数 backtrack(candidates, target, cursum, index,path,res) 无返回值
2.终止条件 :cursum>target,return cursum=target ,存起来
3.单层回溯逻辑:
本题还需要startIndex来控制for循环的起始位置,对于组合问题,什么时候需要startIndex呢?
如果是一个集合来求组合的话,就需要startIndex;如果是多个集合取组合,各个集合之间相互不影响,那么就不用startIndex
class Solution:
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, path, result):
if total == target:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if total + candidates[i] > target: #排序+剪枝
continue
total += candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i, path, result)
total -= candidates[i]
path.pop()
def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
result = []
candidates.sort() # 需要排序
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, [], result)
return result
不设置cursum,进来一个数,就减掉target,只要判断target == 0
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result =[]
candidates.sort()
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, [], result)
return result
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, startIndex, path, result):
if target == 0:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if target - candidates[i] < 0:
break
path.append(candidates[i])
self.backtracking(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, path, result)
path.pop()
40.组合总和II
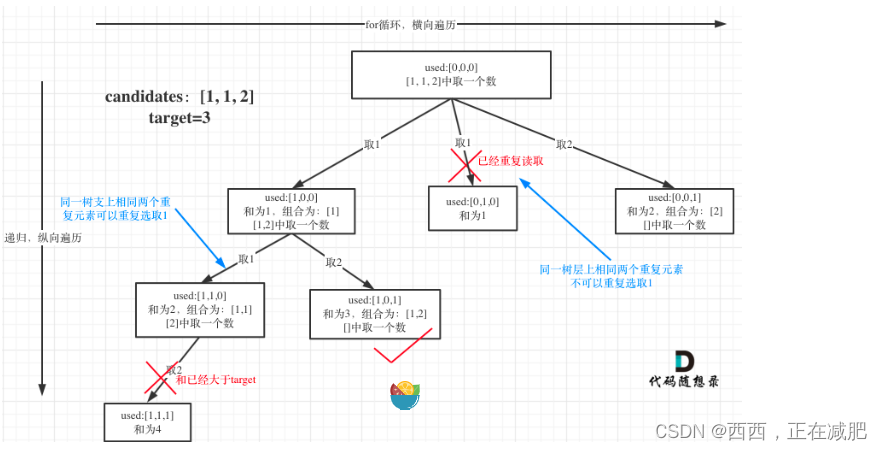
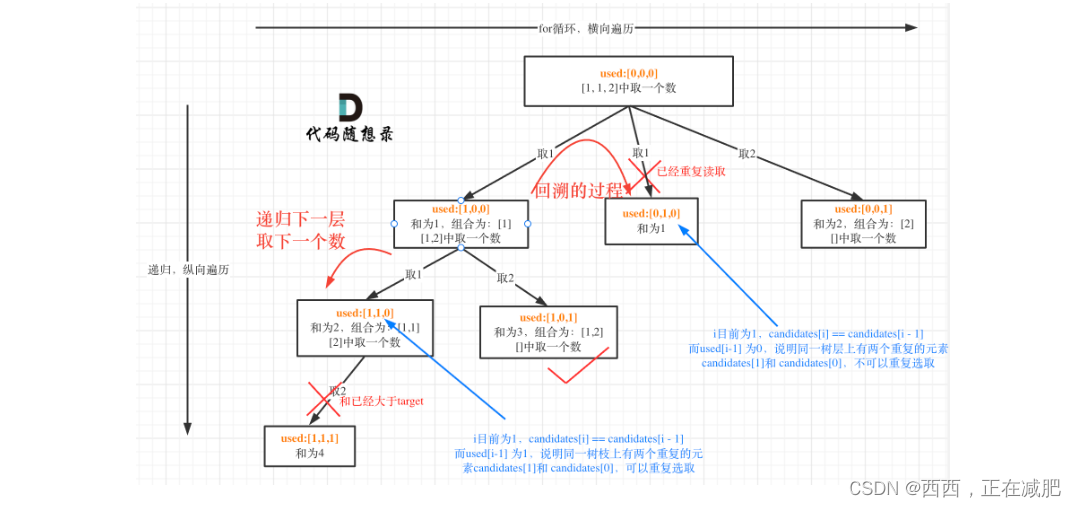
本题的难点在于区别2中:集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合。
组合问题可以抽象为树形结构,那么“使用过”在这个树形结构上是有两个维度的,一个维度是同一树枝上使用过,一个维度是同一树层上使用过。
显然,本题是要在同一树层上去重。强调一下,树层去重的话,需要对数组 排序!
回溯三步曲
1.回溯参数和返回值:backtract(candidate, target , cursum, startindex,used)
2.终止条件:cursum >= target , 当前遍历的在used里面
3.单层逻辑:
class Solution:
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, path, result):
if total == target:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]: #对同一层树层去重,要先排序
continue
if total + candidates[i] > target:
break
total += candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i + 1, path, result)
total -= candidates[i]
path.pop()
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
result = []
candidates.sort()
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, [], result)
return result
class Solution:
def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, used, path, result):
if total == target:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
# 对于相同的数字,只选择第一个未被使用的数字,跳过其他相同数字
if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]: #前一个节点没用过
continue
if total + candidates[i] > target:
break
total += candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
used[i] = True
self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i + 1, used, path, result)
used[i] = False
total -= candidates[i]
path.pop()
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
used = [False] * len(candidates)
result = []
candidates.sort()
self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, used, [], result)
return result
131.分割回文串
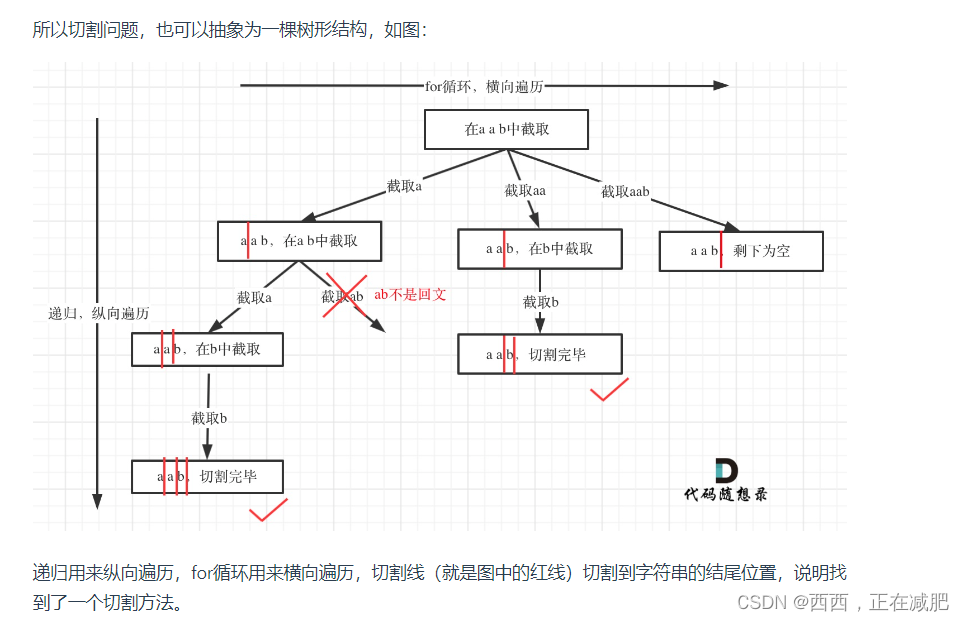
本题这涉及到两个关键问题:1.切割问题,有不同的切割方式 2.判断回文
回溯三步曲
1.回溯参数 backtrack(s, startindex, path ,res) 无返回值
2.终止条件 :startindex == len(s)收集结果
3.单层回溯逻辑:判断回文,如果是就加入path
class Solution:
def partition(self, s: str) -> List[List[str]]:
result = []
self.backtracking(s, 0, [], result)
return result
def backtracking(self, s, start_index, path, result ):
# Base Case
if start_index == len(s):
result.append(path[:])
return
# 单层递归逻辑
for i in range(start_index, len(s)):
# 若反序和正序相同,意味着这是回文串
if s[start_index: i + 1] == s[start_index: i + 1][::-1]:
path.append(s[start_index:i+1])
self.backtracking(s, i+1, path, result) # 递归纵向遍历:从下一处进行切割,判断其余是否仍为回文串
path.pop() # 回溯



























 33
33











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








