图的广度优先搜索
描述:
图的广度优先搜索类似于树的按层次遍历,即从某个结点开始,先访问该结点,然后访问该结点的所有邻接点,再依次访问各邻接点的邻接点。如此进行下去,直到所有的结点都访问为止。在该题中,假定所有的结点以“A”–“Z”中的若干字符表示,且要求结点的访问顺序要求根据由“A”至“Z”的字典顺序进行访问。例如有如下图:
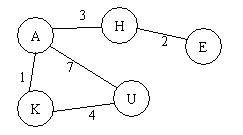
如果要求从H开始进行广度优先搜索,则搜索结果为:H->A->E->K->U.
输入:
输入只包含一个测试用例,第一行为一个自然数n,表示顶点的个数,第二行为n个大写字母构成的字符串,表示顶点,接下来是为一个n*n大小的矩阵,表示图的邻接关系。数字为0表示不邻接,否则为相应的边的长度。
最后一行为一个字符,表示要求进行广度优先搜索的起始顶点。
输出:
用一行输出广度优先搜索结果,起始点为给定的顶点,各顶点之间用一个空格隔开。要求同一顶点的邻接点的访问顺序按“A”—“Z”的字典顺序。
样例输入:
5
HUEAK
0 0 2 3 0
0 0 0 7 4
2 0 0 0 0
3 7 0 0 1
0 4 0 1 0
H
样例输出:
H A E K U
参考:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String name = sc.next();
int[][] mp = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
mp[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
String be = sc.next();
int begin = name.indexOf(be);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(begin);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int fr = q.poll();
System.out.print(name.charAt(fr) + " ");
vis[fr] = true;
ArrayList<Character> al = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (mp[fr][i] != 0 && !vis[i]) {
al.add(name.charAt(i));
vis[i] = true;
}
}
Collections.sort(al);
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
q.add(name.indexOf(al.get(i)));
}
}
}
}


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










