目录
该文章是算法设计与分析(第二版)中各章的课后习题 主编 : 李春葆
在本文中,主要是对该书第五章-回溯法章节中的上机实验题以及在线编程题进行代码解答。
代码运行环境是:DEVc++
上机实验题
问题一:求解填字游戏问题

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//素数,计算过程中可能用到的素数
int a1[] = {2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23};
vector<int> a(a1,a1+10);
int result[4][4];
// coun 用于记录满足要求的方阵个数
int coun = 0;
int tag[11] = {0};
bool panduan(int x, int y, int t) //判断 t 是否为素数
{
// tag[t] 判断 数字 t是否被使用
if(tag[t] == 1){
return false;
}
if(x - 1 >= 0)
{
if(find(a.begin(),a.end(),t+result[x-1][y]) == a.end())
return false;
}
if(y - 1 >= 0)
{
if(find(a.begin(),a.end(),t+result[x][y-1]) == a.end())
return false;
}
return true;
}
void pushin(int x,int y){
if(x == 3){
coun++;
cout<<"coun = "<<coun<<endl;
//可以输出查看结果
for(int i = 0;i <= 2;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j <= 2;j++)
{
cout << result[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//system("pause");
return;
}else{
//递归
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
if(panduan(x,y,i)){
result[x][y] = i; // 标记
tag[i] = 1; //将已经用过的数标记为置1
if(y != 2){
pushin(x,y+1);
}else{
//x+1换行
pushin(x+1,0);
}
result[x][y] = 0;
tag[i] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
pushin(0,0);
return 0;
}
运行部分截图:

问题二:求解组合问题

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void dfs(int n,int r,int i,vector<int> &a){
if(a.size() == r){
for(int j = 0 ; j < r ;j++){
cout<<a[j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}else{
for(int k = i;k <= n;k++){
a.push_back(k);
dfs(n,r,k+1,a);
a.pop_back();
}
}
}
int main(){
int n,r;
cin>>n>>r;
while(n<r){
cout<<"r 必须小于 n,请重新输入"<<endl;
cin>>n>>r;
}
vector<int> a;
dfs(n,r,1,a);
return 0;
}
运行截图:
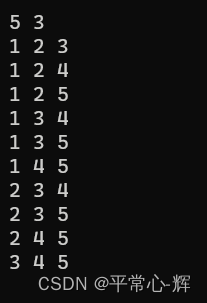
问题三:求解满足方程解问题(该题无解)
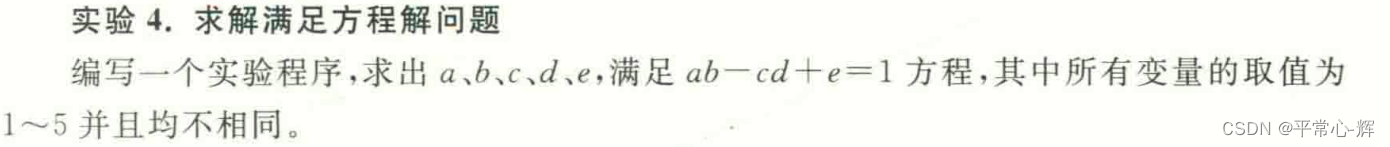
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//这题貌似没有正确的结果,真实老六。
int coun = 0;
void dfs(int i,int a[]){
if(i >= 5){
if((a[1]*a[2]) - (a[3]*a[4]) + a[5] == 1){
coun++;
for(int p = 1;p <= 5;p++){
cout<<a[p]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return;
}else{
for(int j = i;j <= 5 ;j++){
swap(a[i],a[j]);
dfs(i+1,a);
swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
}
}
int main(){
int a[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5};
dfs(1,a);
cout<<"该方程解的个数为:"<<coun<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

在线编程题
问题一:求解会议安排问题

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 20
int n;
int ans, temp, counter;
struct classroom
{
int start;
int end;
};
/*
4
1 2
3 5
1 4
4 5
*/
void dfs(classroom a[], int i)
{
counter = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[j].start >= a[i].end)
{
int t=(a[j].end - a[j].start);
temp += t;
dfs(a, j);
temp -=t; //回溯
counter++;
}
}
if (counter == 0){
if (temp>ans){
ans = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
classroom a[MAX];
a[0].end = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i].start >> a[i].end;
dfs(a, 0);
cout <<"所有活动占用的最大时间为: "<< ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

问题二:求解最小机器重量设计问题1


#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int w[100][100];//w[i][j]为第i个零件在第j个供应商的重量
int c[100][100];//c[i][j]为第i个零件在第j个供应商的价格
int bestx[100];//bestx[i]表示一次搜索到底后的最优解,用来存放第i个零件的供应商,
int x[100];//x[i]临时存放第i个零件的供应商
int cw = 0, cc = 0, bestw = 10000;
int cost;//限定价格
int n;//部件数
int m;//供应商数
/*
3 3 7
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 3 2
1 2 3
5 4 2
2 1 2
*/
void Backtrack(int t)
{
int j;
if (t > n)//搜索到叶子结点,一个搜索结束,所有零件已经找完
{
bestw = cw;//当前最小重量
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++){
//拷贝对应的供货商
bestx[j] = x[j];
}
}
else
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (cc + c[t][j] <= cost && cw + w[t][j] < bestw)
{
x[t] = j;
cc += c[t][j];
cw += w[t][j];
Backtrack(t + 1);
cc -= c[t][j];
cw -= w[t][j];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
cin >> n;
cin >> m;
cin >> cost;
// 请输入各部件的在不同供应商的重量:
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> w[i][j];
}
}
//cout << "请输入各部件的在不同供应商的价格:" << endl;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> c[i][j];
}
}
Backtrack(1);
cout << "每个部件的供应商为:" << endl;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << bestx[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
cout<<"最小重量为:" << bestw;
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行截图:

问题三:求解最小机器重量设计问题2

#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int w[100][100];//w[i][j]为第i个零件在第j个供应商的重量
int c[100][100];//c[i][j]为第i个零件在第j个供应商的价格
int bestx[100];//bestx[i]表示一次搜索到底后的最优解,用来存放第i个零件的供应商,
int x[100];//x[i]临时存放第i个零件的供应商
int cw = 0, cc = 0, bestw = 10000;
int cost;//限定价格
int n;//部件数
int m;//供应商数
/*
3 3 7
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 3 2
1 2 3
5 4 2
2 1 2
*/
void Backtrack(int t)
{
int j;
if (t > n)//搜索到叶子结点,一个搜索结束,所有零件已经找完
{
bestw = cw;//当前最小重量
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
bestx[j] = x[j];
}
else
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
int temp = 0; //用于判断该供应商是否被选取
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i++){
if(x[i] == j){
temp = 1;
}
}
if(temp != 1){ //当还没有在该供货商处购物时
if (cc + c[t][j] <= cost && cw + w[t][j] < bestw)
{
x[t] = j;
cc += c[t][j];
cw += w[t][j];
Backtrack(t + 1);
cc -= c[t][j];
cw -= w[t][j];
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
cin >> n;
cin >> m;
cin >> cost;
//请输入各部件的在不同供应商的重量:
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> w[i][j];
}
}
//cout << "请输入各部件的在不同供应商的价格:" << endl;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> c[i][j];
}
}
Backtrack(1);
cout << "每个部件的供应商:" << endl;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << bestx[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
cout <<"最小重量为:"<< bestw;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行截图:

问题四:求解密码问题

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//1 ABCDEFGHIJKL
//11700519 ZAYEXIWOVU
//3072997 SOUGHT
//1234567 THEQUICKFROG
int a[6];
char result[6] = {0};
int max1 = -1;
void dfs(int i,int len,string str,int n){
if(i == 6){
if(a[1] - pow(a[2],2) + pow(a[3],3) - pow(a[4],4) + pow(a[5],5) == n){
int tmax = 0;
for(int k = 1;k < 6;k++){
char cc = a[k] +'A'-1;
if(a[k] +'A'-1 < result[k]){
break;
}else if(a[k] +'A'-1 == result[k]){
continue;
}else{
tmax = 1;
break;
}
}
if(tmax == 1){
for(int k = 1;k < 6;k++){
max1 = 1;
char ch = a[k] + 'A' - 1;
result[k] = ch;
}
}
}
return ;
}else{
for(int j = len-1;j >= 0 ;j--){
//判断字母是否重复
int chongfu = 0;
for(int k = 1;k < i;k++){
if(a[k] == str[j] - 'A' + 1){
chongfu = 1;
break;
}
}
if(chongfu != 1){
a[i] = str[j] - 'A' + 1;
dfs(i+1,len,str,n);
a[i] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
for(int k = 1 ; k < 6 ;k++){
result[k] = 'A';
}
int n;
string str = "";
cin>>n>>str;
int len = str.length();
dfs(1,len,str,n);
//输出结果
if(max1 == -1){
cout<<"no solution";
}else{
cout<<"答案为:"<<endl;
for(int k = 1 ; k < 6 ;k++){
cout<<result[k]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<"对应的数字为:"<<endl;
for(int k = 1 ; k < 6 ;k++){
cout<<result[k] - 'A' + 1<<" ";
}
}
return 0;
}
运行截图:

问题五:求解马走棋问题

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 4 4
int sum = 0;
void dfs(int x,int y,int m,int n){
if(x == m && y == n){
sum++;
return;
}else{
if(x+2 <= m && y+1 <= n){
dfs(x+2,y+1,m,n);
}
if(x+1 <= m && y+2 <= n){
dfs(x+1,y+2,m,n);
}
}
}
int main(){
int m , n;
cin>>m>>n;
dfs(1,1,m,n);
cout<<"总共的方案数为:"<<sum;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

问题六:求解幸运的袋子问题

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,num = 1;
int sum = 0,mul = 1,result = 0;
vector<int> res;
vector<vector<int>> quchong;
//3 1 1 1
//4 1 1 2 3
//问题7 求解幸运的袋子问题
void dfs(int i,vector<int>& a){
if(i > n){
if(sum > mul){
//去重
if(find(quchong.begin(),quchong.end(),res) == quchong.end()){
//输出满足条件的结果
cout<<"方案 "<<num++<<endl;
for(auto h:res){
cout<<h<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//加入结果数组中
quchong.push_back(res);
result++;
}
}
return;
}else{
res.push_back(a[i]);
sum += a[i];
mul *= a[i];
dfs(i+1,a);
//回溯
res.pop_back();
sum -= a[i];
mul /= a[i];
dfs(i+1,a);
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
dfs(1,a);
cout<<"幸运袋子的总个数为: "<<result<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图;























 1105
1105

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








