多进程输入,非阻塞输出
- 各个进程使用父子进程,分别完成读写
缺点
应用程序中同时处理多路输入输出流,若设置多进程,分别处理一条数据通路,将新产生进程间的同步与通信问题, 使程序变得更加复杂;
比较好的方法是使用I/O多路复用 如此操作
多进程处理多路输入输出
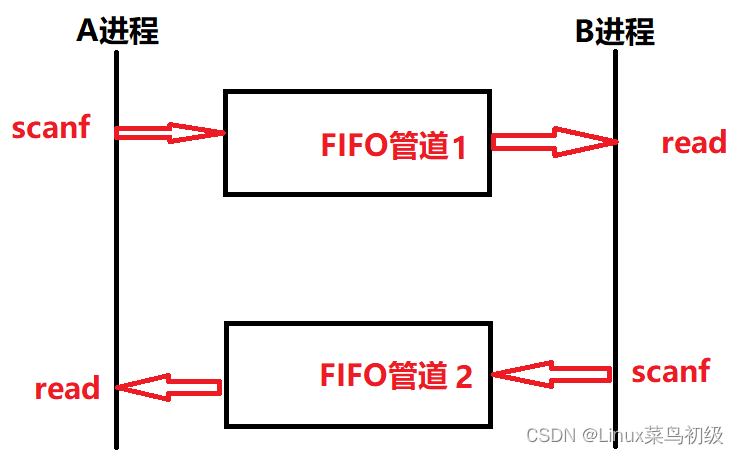
代码实现
a.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
/*fork*/
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
// 1.创建文件mkfifo fifo1 fifo2
// 2.打开文件
int fd1 = open("fifo1", O_WRONLY);//写
int fd2 = open("fifo2", O_RDONLY);//读
char write_buff[32] = {0};
char read_buff[32] = {0};
//创建子进程
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
while (1)
{
scanf("%s", write_buff);
write(fd1, write_buff, 32);
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
while (1)
{
read(fd2, read_buff, 32);
printf("A收到: %s\n", read_buff);
}
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
return 0;
}
b.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
/*fork*/
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
// 1.创建文件mkfifo fifo1 fifo2
// 2.打开文件
int fd1 = open("fifo1", O_RDONLY);//读
int fd2 = open("fifo2", O_WRONLY);//写
char write_buff[32] = {0};
char read_buff[32] = {0};
//创建子进程
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
while (1)
{
scanf("%s", write_buff);
write(fd2, write_buff, 32);
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
while (1)
{
read(fd1, read_buff, 32);
printf("B收到: %s\n", read_buff);
}
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
return 0;
}
执行结果
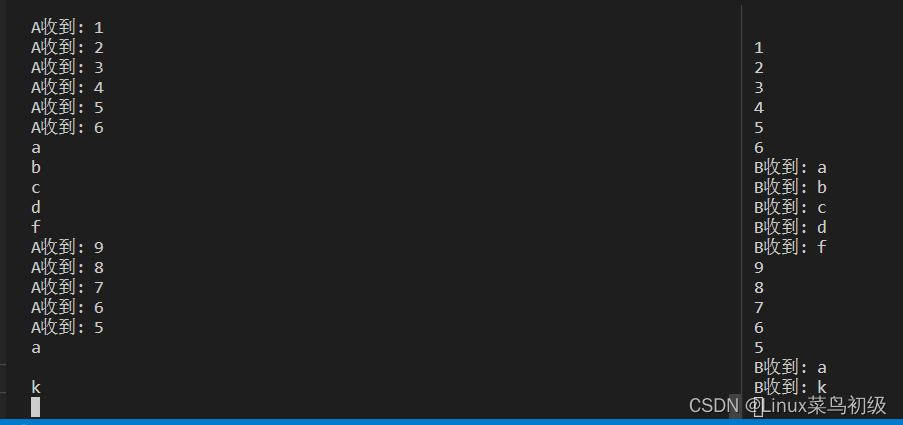






















 1360
1360











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








