目录
前言:
基本数据类型访问:直接根据变量名去访问
复杂数据类型:下标去访问
tuple的用法:
count:(self, value, /)
Return number of occurrences of value. (返回出现value的次数)
index:(self, value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)
Return first index of value. (返回value出现的第一个索引)
tuple编写程序练习:
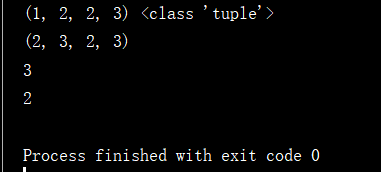
tuple_data1 = (1, 2)
tuple_data2 = (2, 3)
tuple_data3 = tuple_data1 + tuple_data2
print(tuple_data3, type(tuple_data3))
tuple_data4 = 2 * tuple_data2
print(tuple_data4)
tuple_data5 = (1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 4)
print(tuple_data5.count(3))
print(tuple_data5.index(3))
输出结果为:
list的用法:
append(self, object, /)
Append object to the end of the list. (将object追加到列表末尾)
clear(self, /)
Remove all items from list. (从列表中移除所有的条目)
扩展和清除列表程序编写:








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 368
368











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








