文章目录
1. 柔性数组
1.1 定义
数组大小声明为0,或者不给出大小,称之为柔性数组。
注意:全局数组和局部数据不能这样定义
柔性数组是一种数组大小待定的数组。在c语言中,可以使用结构体产生柔性数组,结构体的最后一个元素可以是大小未知的数组。
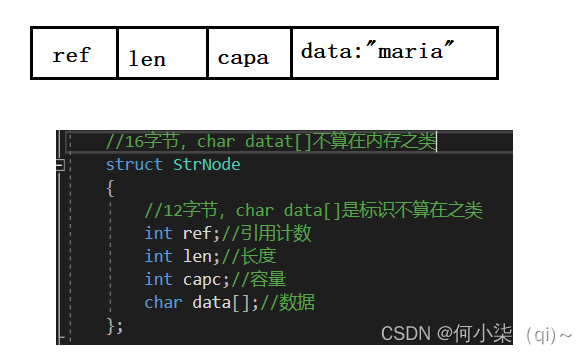
data是标识符,不占用存储空间。
//柔性数组
struct StrNode
{
int ref;//引用个数
int len;//字符串长度
int size;//字符串空间大小
char data[];
//char data[0];
};
1.2 用途
长度为0的数组主要是为了满足长度可变的结构体,只能在结构体最后声明。
1.3 用法
在一个结构体的最后,声明一个长度为0的数组。就可以使得这个结构体是可变长的。对于编译器来说。此时长度为О的数组并不占用空间,因为数组名本身不占空间,它只是一个偏移量,数组名这个符号本身代表了一个不可修改的地址常量。但对于这个数组的大小,我们可以进行动态分配。
注意︰如果结构体是通过calloc、malloc或 realloc等动态分配方式生成,在不需要时要释放相应的空间。优点︰比起在结构体中声明一个指针变量、再进行动态分配的办法,这种方法效率要高。因为简单。
1.4 缺点
在结构体中,数组为О的数组必须在最后声明,在设计结构体类型有一定限制。
2. 写时拷贝
2.1 定义
写时拷贝就是在写的时候(即改变字符串的时候)才会真正的开辟空间拷贝(深拷贝),如果只是对数据的读时,只会对数据进行浅拷贝。
2.2 特点和实现
-
写时拷贝:引用计数器的浅拷贝,又称延时拷贝
-
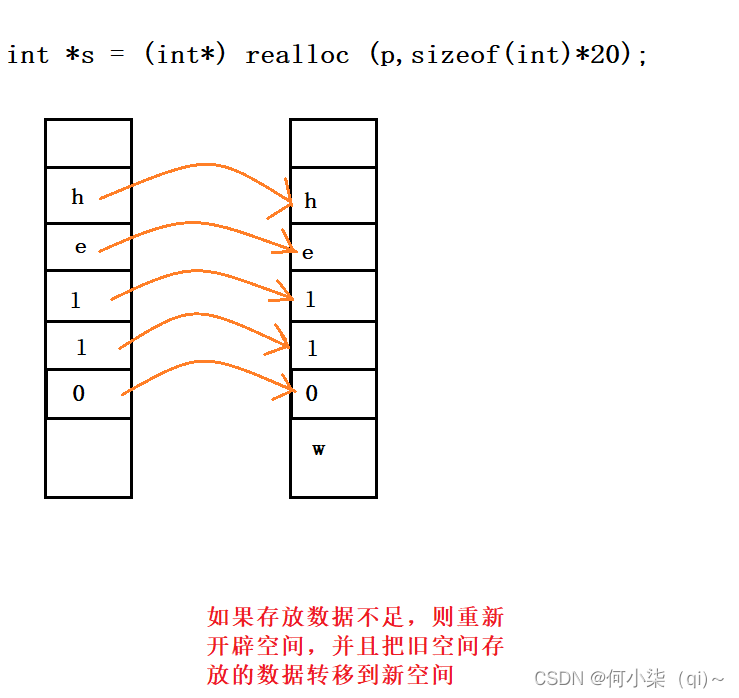
写时拷贝技术是通过"引用计数"实现的,在分配空间的时候多分配4个字节,用来记录有多少个指针指向块空间,当有新的指针指向这块空间时,引用计数加一,当要释放这块空间时,引用计数减一(假装释放),直到引用计数减为0时才真的释放掉这块空间。当有的指针要改变这块空间的值时,再为这个指针分配自己的空间(注意这时引用计数的变化,旧的空间的引用计数减一,新分配的空间引用计数加一。
3. MyString
3.1 内存释放产生失效指针
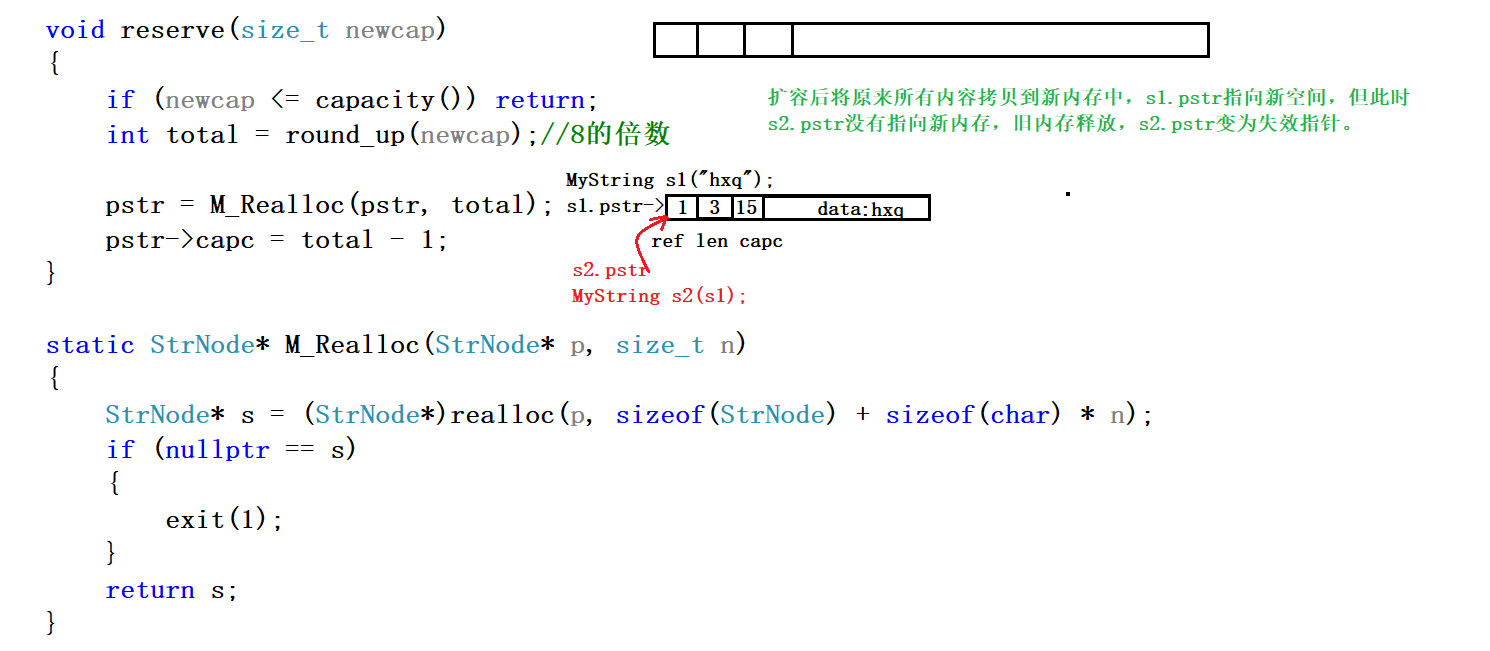
3.2 代码优化
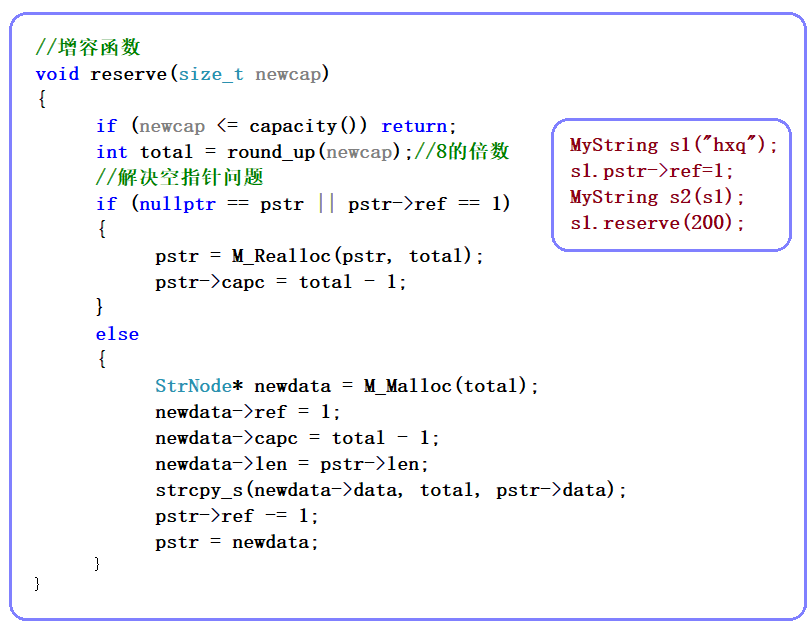
优化前
void reserve(size_t newcap)
{
if (newcap <= capacity()) return;
int total = round_up(newcap);//8的倍数
//解决空指针问题
if (nullptr == pstr || pstr->ref == 1)
{
int n = size();
if (nullptr == pstr)
{
pstr = M_Realloc(pstr, total);
pstr->data[0] = '\0';
}
else
{
pstr = M_Realloc(pstr, total);
}
pstr = M_Realloc(pstr, total);
pstr->capc = total - 1;
}
else
{
StrNode* newdata = M_Malloc(total);
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->capc = total - 1;
newdata->len = pstr->len;
strcpy_s(newdata->data, total, pstr->data);
pstr->ref -= 1;
pstr = newdata;//指向新空间
}
}
优化后
//增容函数(对象共享字符串可以增容)
void reserve(size_t newcap)
{
if (newcap <= capacity()) return;
int total = round_up(newcap);//8的倍数
//解决空指针问题
if (nullptr == pstr || pstr->ref == 1)
{
StrNode* newdata = M_Realloc(pstr, total);
if (nullptr == pstr)
{
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->len = 0;
newdata->data[0] = '\0';
}
newdata->capc = total - 1;
pstr = newdata;
}
else
{
StrNode* newdata = M_Malloc(total);
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->capc = total - 1;
newdata->len = pstr->len;
strcpy_s(newdata->data, total, pstr->data);
pstr->ref -= 1;
pstr = newdata;//指向新空间
}
}
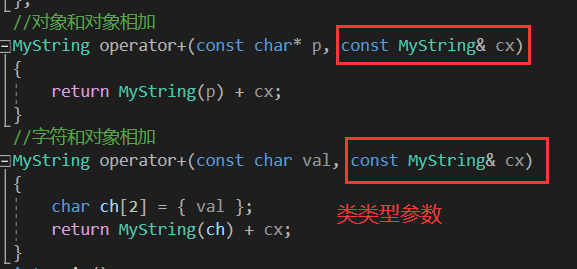
3.3 重载运算符
重载运算符时候,其中一个参数必须为类类型
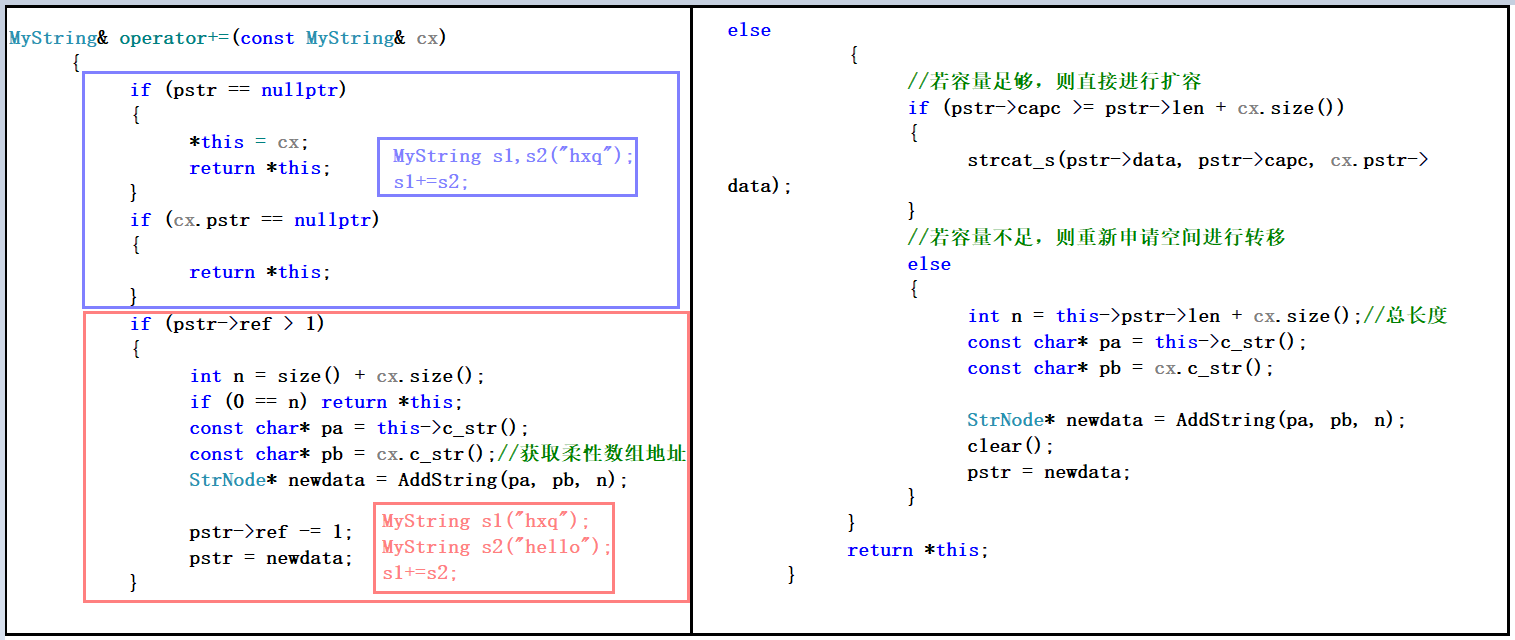
3.4 +=运算符重载代码详解
优化前
MyString& operator+=(const MyString& cx)
{
if (pstr == nullptr)
{
*this = cx;
return *this;
}
if (cx.pstr == nullptr)
{
return *this;
}
if (pstr->ref > 1)
{
int n = size() + cx.size();
if (0 == n) return *this;
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = cx.c_str();//获取柔性数组地址
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
pstr->ref -= 1;
pstr = newdata;
}
else
{
//若容量足够,则直接进行扩容
if (pstr->capc >= pstr->len + cx.size())
{
strcat_s(pstr->data, pstr->capc, cx.pstr->data);
}
//若容量不足,则重新申请空间进行转移
else
{
int n = this->pstr->len + cx.size();//总长度
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = cx.c_str();
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
clear();
pstr = newdata;
}
}
return *this;
}
优化后
MyString& operator+=(const MyString& cx)
{
if (pstr == nullptr)
{
*this = cx;
return *this;
}
if (cx.pstr == nullptr)
{
return *this;
}
if (pstr->ref == 1 && pstr->capc >= pstr->len + cx.size())
{
strcat_s(pstr->data, pstr->capc, cx.pstr->data);
}
else
{
int n = this->pstr->len + cx.size();//总长度
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = cx.c_str();
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
clear();
pstr = newdata;
}
return *this;
}
3.5 解决自赋值问题
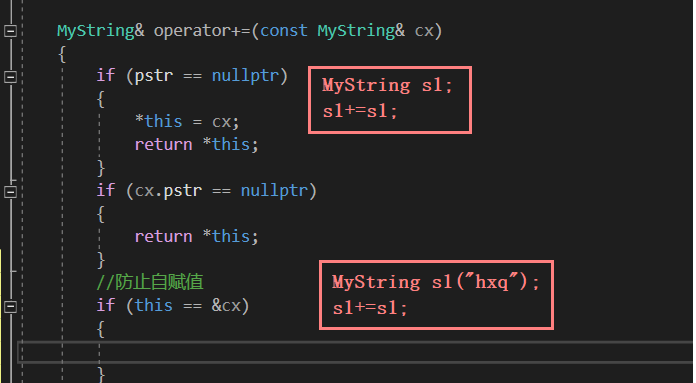
3.5.1 自链接
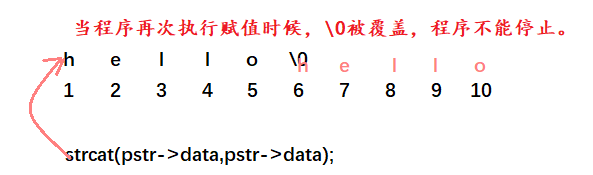
3.5.2 运行结果
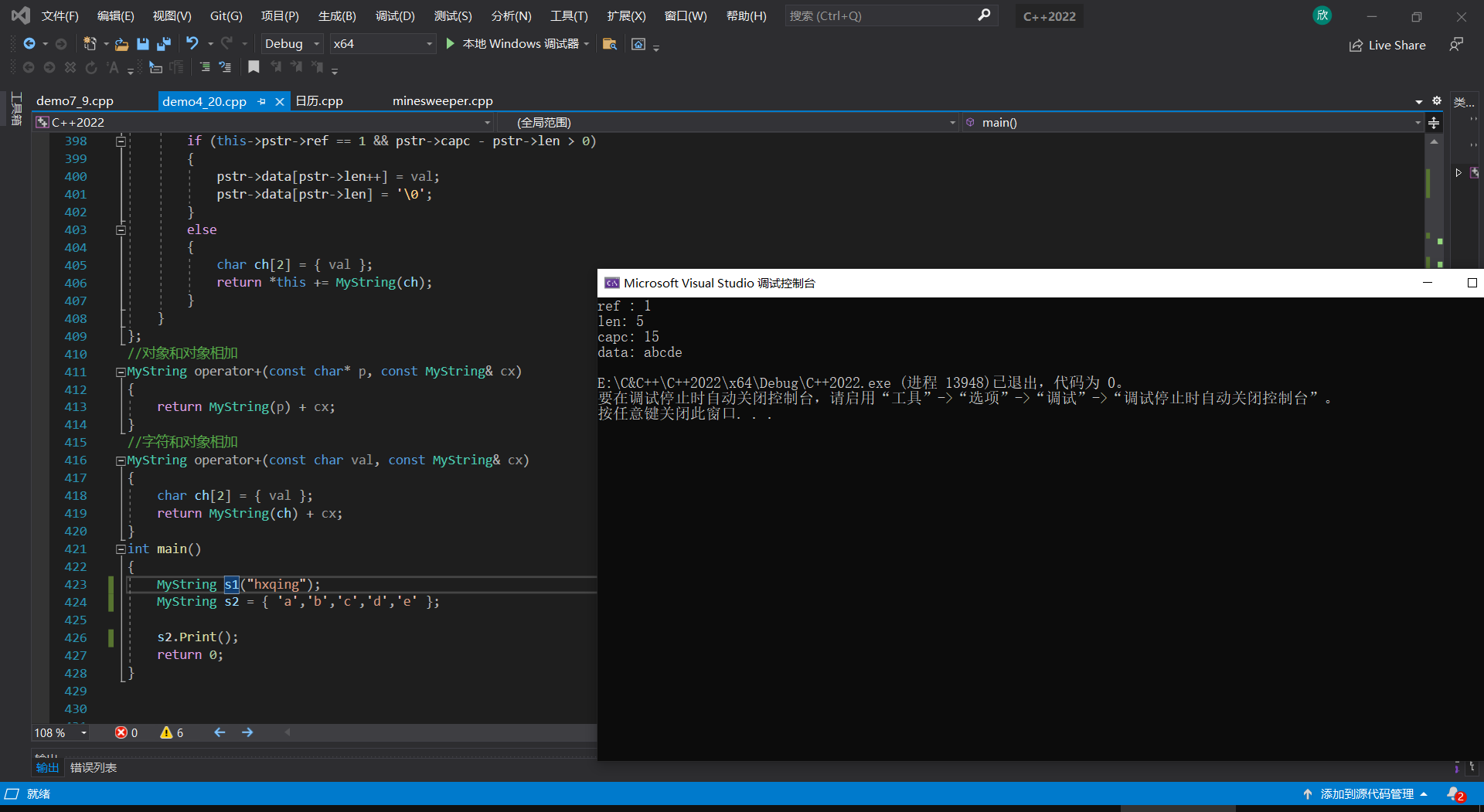
3.6 代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<cassert>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class MyString
{
private:
enum { ALIGN = 8 };
//16字节,char datat[]不算在内存之类
struct StrNode
{
//12字节,char data[]是标识不算在之类
int ref;//引用计数
int len;//长度
int capc;//容量
char data[];//字符串
};
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return (pstr != nullptr ? pstr->data : nullptr);
}
iterator end()
{
return (pstr != nullptr ? pstr->data + pstr->len : nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return (pstr != nullptr ? pstr->data : nullptr);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return (pstr != nullptr ? pstr->data + pstr->len : nullptr);
}
private:
StrNode* pstr;//指针指向结构体地址
static size_t round_up(size_t n)//上取整函数
{
return(n + ALIGN - 1) & ~(ALIGN - 1);
}
static StrNode* M_Malloc(size_t n)
{
StrNode* s = (StrNode*)malloc(sizeof(StrNode) + sizeof(char) * n);
if (nullptr == s)
{
cout << "malloc申请空间失败" << endl;
exit(1);
}
return s;
}
//扩容函数
static StrNode* M_Realloc(StrNode* p, size_t n)
{
StrNode* s = (StrNode*)realloc(p, sizeof(StrNode) + sizeof(char) * n);
if (nullptr == s)
{
cout << "realloc申请空间失败" << endl;
exit(1);
}
return s;
}
static void M_Free(StrNode* p)
{
free(p);
}
//字符串相加函数
static StrNode* AddString(const char* pa, const char* pb, int n)
{
int total = round_up(2 * n);
StrNode* newdata = M_Malloc(total);
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->len = n;
newdata->capc = total - 1;
newdata->data[0] = '\0';
if (nullptr != pa)
{
strcpy_s(newdata->data, total, pa);
}
if (nullptr != pb)
{
strcat_s(newdata->data, total, pb);
}
return newdata;
}
//克隆函数
static StrNode* cloneStrNode(StrNode* old)
{
int n = old->len;
int total = round_up(2 * n);
StrNode* newdata = M_Malloc(total);
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->len = n;
newdata->capc = old->capc;
strcpy_s(newdata->data, newdata->capc, old->data);
return newdata;
}
public:
//判断当前元素个数是否为0
size_t size() const
{
return pstr == nullptr ? 0 : pstr->len;
}
size_t length() const
{
return size();
}
//判空函数
bool empty() const
{
return size() == 0;
}
//容量函数
size_t capacity() const
{
return pstr == nullptr ? 0 : pstr->capc;
}
const char* data() const
{
return pstr == nullptr ? nullptr : pstr->data;
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return data();
}
//首元素???
char& front()
{
assert(pstr != nullptr);
return pstr->data[0];
}
const char& front() const
{
assert(pstr != nullptr);
return pstr->data[0];
}
//末尾元素???
char& back()
{
assert(pstr != nullptr);
return pstr->data[pstr->len - 1];
}
const char& back() const
{
assert(pstr != nullptr);
return pstr->data[pstr->len - 1];
}
//下标运算符
char& at(const int index)
{
assert(pstr != nullptr && index >= 0 && index < pstr->len);
return (*this)[index];
}
const char& at(const int index) const
{
assert(pstr != nullptr && index >= 0 && index < pstr->len);
return pstr->data[index];
}
char& operator[](const int index)//写时拷贝
{
assert(pstr != nullptr && index >= 0 && index < pstr->len);
if (pstr->ref > 1)//多个对象共有
{
pstr->ref -= 1;
pstr = cloneStrNode(pstr);
}
return pstr->data[index];
}
const char& operator[](const int index) const
{
assert(pstr != nullptr && index >= 0 && index < pstr->len);
return pstr->data[index];
}
//私有构造函数(加法)
MyString(StrNode* p) :pstr(p) {}
public:
//字符转换成字符串
MyString(const char val) :pstr(nullptr)
{
int total = 16;
pstr = M_Malloc(total);
pstr->ref = 1;
pstr->len = 1;
pstr->capc = total - 1;
pstr->data[0] = val;
pstr->data[1] = '\0';
}
//字符串转化为字符串对象
MyString(const char* p = nullptr) :pstr(nullptr)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
int n = strlen(p); // 6
int total = round_up(2 * n);
if (total != 0)
{
pstr = M_Malloc(total);
pstr->ref = 1;
pstr->len = n;
pstr->capc = total - 1;
strcpy_s(pstr->data, total, p);
}
}
}
//字符串列表转化为对象(初始化列表)
MyString(std::initializer_list<const char> ilist) :pstr(nullptr)
{
int n = ilist.size();
int total = round_up(2 * n);
pstr = M_Malloc(total);
pstr->ref = 1;
pstr->len = n;
pstr->capc = total - 1;
std::initializer_list<const char>::iterator it = ilist.begin();
int i = 0;
for (; it != ilist.end(); ++it)
{
pstr->data[i++] = *it;
}
pstr->data[i] = '\0';
}
//拷贝构造函数
MyString(const MyString& sx) :pstr(sx.pstr)
{
if (pstr != nullptr)
{
pstr->ref += 1;
}
}
//两个对象赋值
MyString& operator=(const MyString& sx)
{
if (this == &sx || this->pstr == sx.pstr)//防止自赋值
{
return *this;
}
clear();//引用计数减1时,释放占有的空间
this->pstr = sx.pstr;
if (this->pstr != nullptr)
{
this->pstr->ref += 1;
}
return *this;
}
~MyString()
{
clear();
}
//清空函数(取消字符串和对象关联)
void clear()
{
if (pstr != nullptr && --pstr->ref == 0)
{
M_Free(pstr);
}
pstr = nullptr;
}
//移动拷贝构造函数(资源进行转移)
MyString(MyString&& sx) :pstr(sx.pstr)
{
sx.pstr = nullptr;
}
//移动赋值函数(进行资源转移)
MyString& operator=(MyString&& sx)
{
if (this == &sx) return *this;
if (this->pstr == sx.pstr)
{
sx.clear();
return *this;
}
clear();
this->pstr = sx.pstr;
sx.pstr = nullptr;
return *this;
}
//增容函数(对象共享字符串可以增容)
void reserve(size_t newcap)
{
if (newcap <= capacity()) return;
int total = round_up(newcap);//8的倍数
//解决空指针问题
if (nullptr == pstr || pstr->ref == 1)
{
StrNode* newdata = M_Realloc(pstr, total);
if (nullptr == pstr)
{
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->len = 0;
newdata->data[0] = '\0';
}
newdata->capc = total - 1;
pstr = newdata;
}
else
{
StrNode* newdata = M_Malloc(total);
newdata->ref = 1;
newdata->capc = total - 1;
newdata->len = pstr->len;
strcpy_s(newdata->data, total, pstr->data);
pstr->ref -= 1;
pstr = newdata;//指向新空间
}
}
//对象和对象相加
MyString operator+(const MyString& cx) const
{
int n = this->size() + cx.size();//长度
if (n == 0)
{
return MyString();
}
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = cx.c_str();
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
return MyString(newdata);
}
//字符串对象和字符串相加
MyString operator+(const char* p) const
{
int n = this->size() + (p != nullptr ? strlen(p) : 0);
if (n == 0)
{
return MyString();
}
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = p;
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
return MyString(newdata);
}
//字符串对象和字符相加
MyString operator+(const char val) const
{
char ch[2] = { val };
return *this + ch;
}
void Print() const
{
if (pstr != nullptr)
{
cout << "ref : " << pstr->ref << endl;
cout << "len: " << pstr->len << endl;
cout << "capc: " << pstr->capc << endl;
cout << "data: " << pstr->data << endl;
}
}
MyString& operator+=(const MyString& cx)
{
if (pstr == nullptr)
{
*this = cx;
return *this;
}
if (cx.pstr == nullptr)
{
return *this;
}
if (pstr->ref == 1 && pstr->capc >= pstr->len + cx.size())
{
//strcat_s(pstr->data, pstr->capc, cx.pstr->data);
strncat_s(pstr->data, pstr->len, cx.pstr->data, pstr->len);
pstr->len = size() + cx.size();
}
else
{
int n = size() + cx.size();//总长度
if (0 == n) return *this;
const char* pa = this->c_str();
const char* pb = cx.c_str();
StrNode* newdata = AddString(pa, pb, n);
clear();
pstr = newdata;
}
return *this;
}
//对象和字符相加
MyString& operator+=(const char* p)
{
return *this += MyString(p);
}
MyString& operator+=(const char val)
{
//判断是否有剩余空间
if (this->pstr->ref == 1 && pstr->capc - pstr->len > 0)
{
pstr->data[pstr->len++] = val;
pstr->data[pstr->len] = '\0';
}
else
{
char ch[2] = { val };
return *this += MyString(ch);
}
}
};
//对象和对象相加
MyString operator+(const char* p, const MyString& cx)
{
return MyString(p) + cx;
}
//字符和对象相加
MyString operator+(const char val, const MyString& cx)
{
char ch[2] = { val };
return MyString(ch) + cx;
}
int main()
{
MyString s1("hxqing");
MyString s2 = { 'a','b','c','d','e' };
s2.Print();
return 0;
}
realloc函数使用
strcpy函数使用
strcat函数使用






















 4458
4458











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








