axios是一个专注于网络请求的库。 不同于jquery,功能复杂,既可以操作dom,又可以做动画,还可以发ajax请求。axios是一个专注于网络请求的库。
目录
一、基本使用
1.导入库文件
在js中导入axios的库文件后,会直接在全局挂载一个axios方法,就可以直接使用了。
<!-- 导入axios的库文件 --> <script src="lib/axios.js"></script> <script> console.log(axios); </script>
在控制台打印axios可以看到,它是一个方法,我们现在就可以直接使用了。
2.基本语法
axios({ //请求方式,'GET'或者'POST' method: 'GET', //请求地址 url: '' }).then(res => {})axios方法获取的结果是一个Promise对象,测试如下:
const res = axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks' }) console.log(res);
既然是一个Promise对象,那么就可以通过 .then的方式拿到获取成功后的结果了。
axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks' }).then(res => console.log(res))
可以看到获取成功了。到此为对基本语法的使用解释。
3.结果分析
但是,axios方法拿到的结果就是服务器请求到的结果吗?我们使用postman来测试一下。
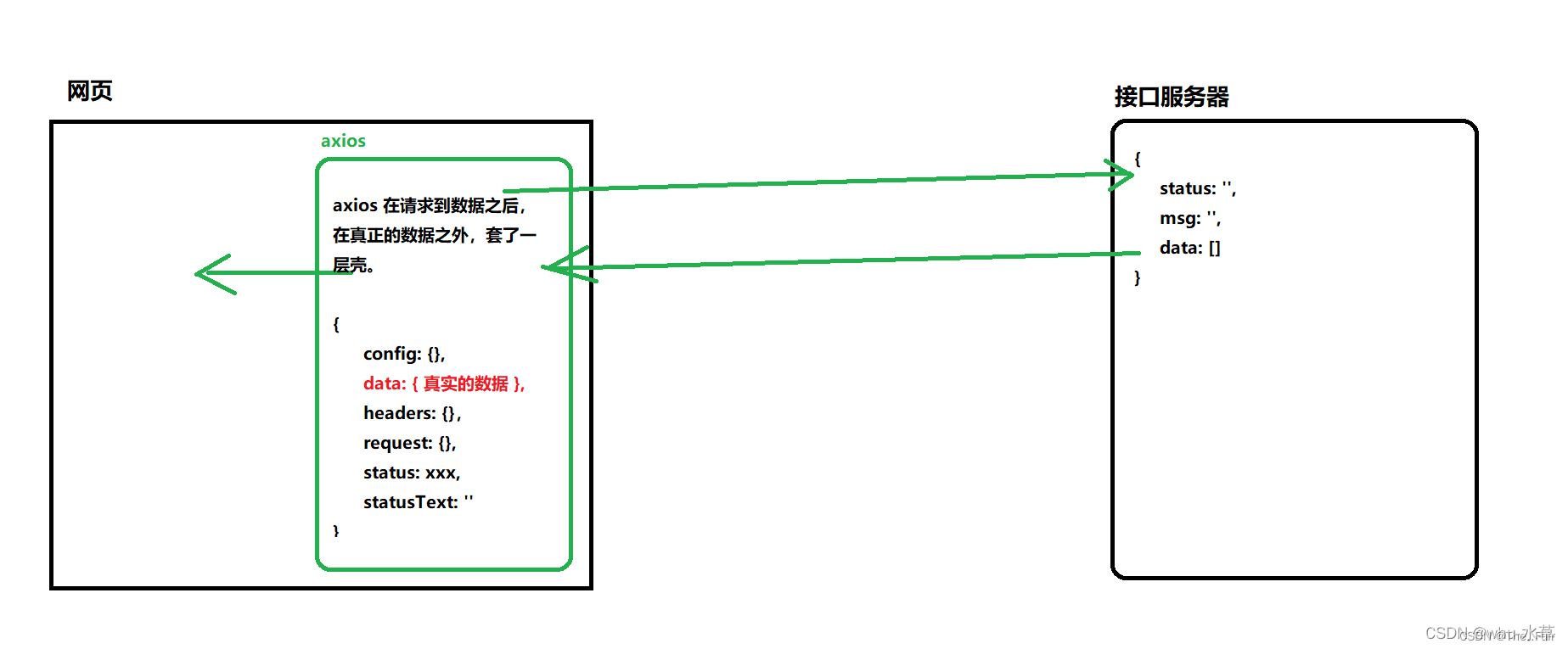
postman显示的是服务器请求后拿到的返回结果。我们可以看到,和axios拿到的结果并不一样,经过比对,我们可以发现,axios拿到的对象结果中有一个data属性,那里面放着的才是服务器请求的真正的返回结果。
到此,我们可以得到axios拿到的对象结果和服务器请求的真正的返回结果之间的关系:
要想直接拿到真实数据的格式,只需要res.data。
4.参数传递
【基本语法】 params中写GET方法的传参,data中写POST方法的传参。
axios({ //请求方式,'GET'或者'POST' method: 'GET', //请求地址 url: '', //url中的查询参数,GET方法的传参 params: {}, //请求体参数,POST方法的传参 data: {} }).then(res => {})get传参演示:
post传参演示:
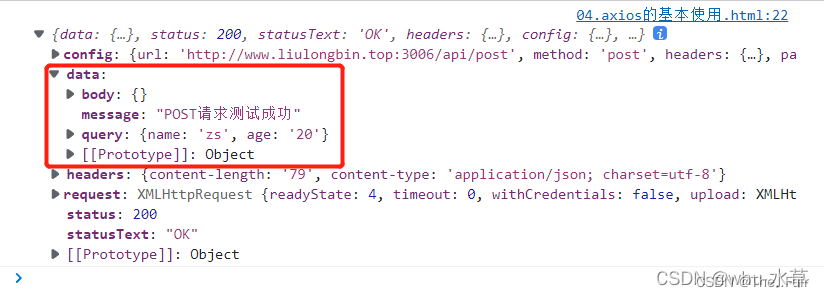
axios({ method: 'POST', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/post', data: { name: 'zs', age: 20 }, }).then(res => console.log(res))
5.方法简化
(1)通过async和await的方式直接拿到返回值
因为axios方法获取的结果是一个Promise对象,所以我们可以通过async和await的方式直接拿到返回值,不需要再通过调用.then的方式了。
给’#btnGet’按钮绑定一个点击事件,点击后发起axios请求。通过async和await的方式可以直接拿到返回值。
document.querySelector('#btnGet').addEventListener('click', async function () { const res = await axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', // params: { // id: 1 // } }) console.log(res); })
(2)解构赋值拿到服务器请求到的真正数据
由第3小节我们知道,axios拿到的对象结果在服务器请求到的真正数据外面套了一层壳子,存在它的data属性中,我们可以通过对象解构的方式直接拿到服务器请求到的真正数据。
document.querySelector('#btnGet').addEventListener('click', async function () { const {data} = await axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', }) console.log(data); })
(3)解构赋值重命名
服务器请求到的真正数据有三个属性,data,status,msg,其中data是我们最关心的,存着需要的数据项,我们只希望取到这个data数组,这个比较简单,因为解构赋值已经拿到服务器请求到的真正数据了,并存在data变量中,所以只需要访问这个变量的data属性就能拿到,即data.data,但是这样很容易混淆, 所以我们在解构赋值的时候给data换个名字 { data: res } 。
document.querySelector('#btnGet').addEventListener('click', async function () { const { data: res } = await axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', }) console.log(res.data); })
6.axios直接发起GET请求和POST请求
基本语法:
//axios直接发起GET请求 axios.get('url地址', { //GET参数 params: {} }) //axios直接发起POST请求 axios.post('url地址', { //POST参数 })示例:
document.querySelector('#btnGet').addEventListener('click', async function () { const { data: res } = await axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', { params: { id: 1 } }) console.log(res.data); }) document.querySelector('#btnPost').addEventListener('click', async function () { const { data: res } = await axios.post('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/post', { name: 'zs', gender: '女' }) console.log(res); })案例
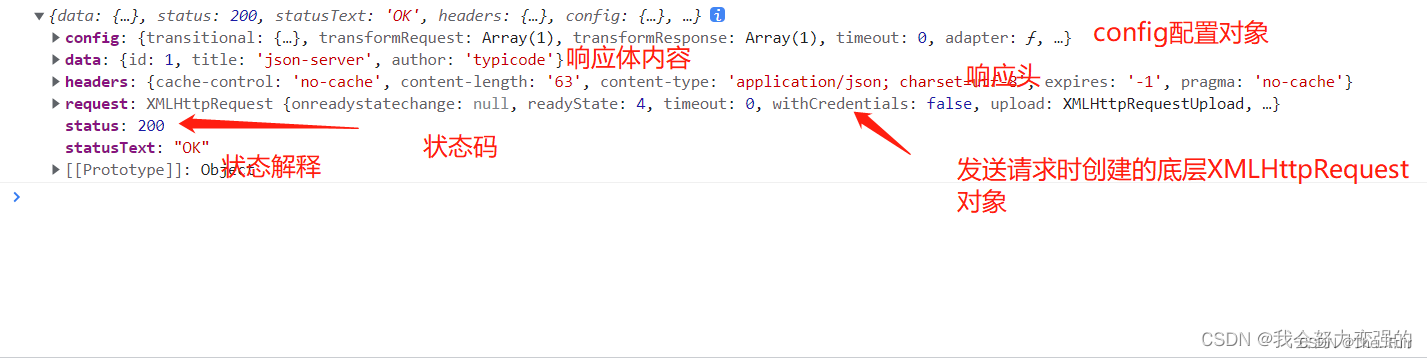
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>axios基本使用</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">发送get请求</button> <br><br> <button id="btn2">发送post请求</button><br><br> <button id="btn3">发送put请求</button><br><br> <button id="btn4">发送delete请求</button> <hr> <div>其他发送请求的api:</div><br><br> <button id="btn5">发送get请求1</button> <br><br> <button id="btn6">发送post请求1</button><br><br> <button id="btn7">发送put请求1</button><br><br> <button id="btn8">发送delete请求1</button> </body> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> //发送get document.getElementById("btn1").onclick = function(){ axios({ method:"GET", url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/1" }).then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //发送post document.getElementById("btn2").onclick = function(){ axios({ method:"POST", url:"http://localhost:3000/posts", data:{ title:"axios学习", author:"Yehaocong" } }).then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //发送put document.getElementById("btn3").onclick = function(){ axios({ method:"PUT", url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2", data:{ title:"axios学习", author:"Liaoxiaoyan" } }).then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; document.getElementById("btn4").onclick = function(){ axios({ method:"DELETE", url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2", }).then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //其他发送请求的api document.getElementById("btn5").onclick = function(){ //发送get,使用get,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时config配置对象 axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1") .then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //发送post document.getElementById("btn6").onclick = function(){ //发送post请求,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时请求体,第三个参数时config配置对象 axios.post("http://localhost:3000/posts", {title:"axios学习2", author:"Yehaocong2"}) .then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //发送put, document.getElementById("btn7").onclick = function(){ //发送put,接收三个参数,url 请求体 、 config配置对象 axios.put("http://localhost:3000/posts/2",{title:"axios学习", author:"Liaoxiaoyan"}) .then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; document.getElementById("btn8").onclick = function(){ //发送delete请求,接收2个参数, url config配置对象 axios.delete("http://localhost:3000/posts/3") .then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) }; //这个与axios({})基本相同 // axios.request({ // }) </script> </html>请求的响应结果结构分析:
配置对象常用的配置项:
{ // 路径url url: '/user', // 请求方法,默认get method: 'get', //基础url,最终请求的url是 baseURL+url拼接,所以再全局设置默认,可以使得发送请求时的url变得简洁 baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/', //设置请求头 headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'}, //设置请求url的query参数,可以使得url简洁。 //比如url是https://some-domain.com/api/user 然后params如下设置,那么最终的url是: //https://some-domain.com/api/user?ID=12345&name=Jack params: { ID: 12345, name:"Jack" }, //设置请求体 data: { firstName: 'Fred' }, //设置请求的另外一种格式,不过这个是直接设置字符串的 data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte', //请求超时,单位毫秒,默认0,不超时。 timeout: 1000, //响应数据类型,默认json responseType: 'json', //响应数据的编码规则,默认utf-8 responseEncoding: 'utf8', //响应体的最大长度 maxContentLength: 2000, // 请求体的最大长度 maxBodyLength: 2000, //设置响应状态码为多少时是成功,调用resolve,否则调用reject失败 //默认是大于等于200,小于300 validateStatus: function (status) { return status >= 200 && status < 300; },默认配置
可以设置全局默认配置,是为了避免多种重复配置在不同请求中重复,比如baseURL、timeout等,这里设置baseURL。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>默认配置</title> </head> <body> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> axios.defaults.baseURL="http://localhost:3000"; //因为上面配置了baseURL,所以我们之后的请求只需要配置url不用像之前那样的全路径 axios.get("/posts/1") .then(response=>{ console.log(response); }) </script> </body> </html>
axios拦截器
实质就是函数。
分为两种类型:1.请求拦截器:用于拦截请求,自定义做一个逻辑后再把请求发送,可以用于配置公用的逻辑,就不用每个请求都配一遍。
2. 响应拦截器:用于拦截响应,做一些处理后再出发响应回调。
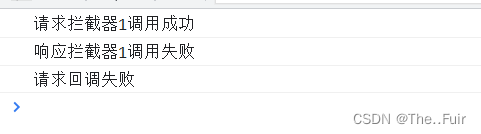
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>axios拦截器</title> </head> <body> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> //这个是设置请求拦截器的api,传入两个回调,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调。 axios.interceptors.request.use( function(config){ console.log("请求拦截器1调用成功"); return config; }, function(error){ console.log("请求拦截器1调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error) } ) //这个是设置响应拦截器的api,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调 axios.interceptors.response.use( function(response){ console.log("响应拦截器1调用成功"); return response; }, function(error){ console.log("响应拦截器1调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error); } ) axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1") .then(function(response){ // console.log("请求回调成功"); }).catch(function(error){ console.log("请求回调失败"); }) </script> </body> </html>
要理解这些个拦截器需要由一定的es6 Promise基础,出现上面效果的原因是,发送请求前,请求被请求拦截器拦截了,并且请求拦截器返回了一个非Promise实例的对象config,所以下一个拦截器是调用成功回调的,所以就打印响应拦截器成功,然后响应拦截器成功的回调返回的是非Promise实例的对象response,所以最终的请求回调是调用成功的回调,所以返回请求调用成功。
尝试以下再请求拦截器的成功回调中,返回reject状态的Promise。
出现上面效果的原因是,请求拦截器的成功回调中最后返回了reject状态的Promise实例对象,被判断为失败,到了回调链的下一回调,也就是响应拦截器的回调时,调用的时失败的回调,失败的回调中又返回了reject状态的Promise实例对象,所以到了真正请求的回调页调用了失败回调。
上面的效果与Promise如出一辙。
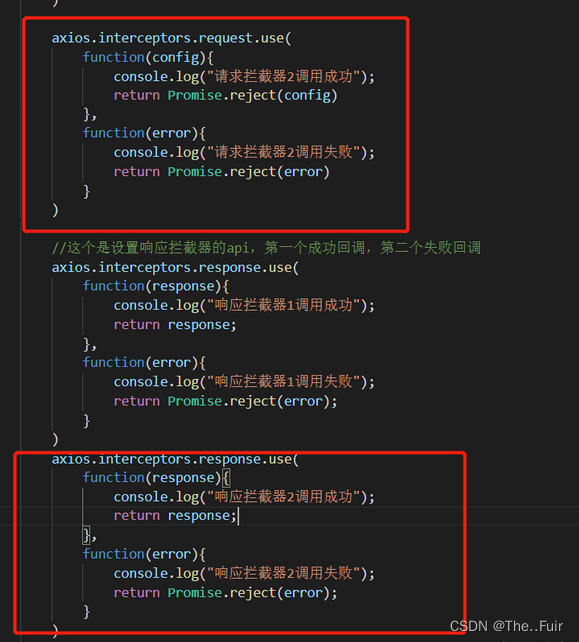
多个拦截器的效果:加了一个请求拦截器一个响应拦截器:
可以看到请求拦截器类似栈,后进先出,响应拦截器类似队列,先进先出。
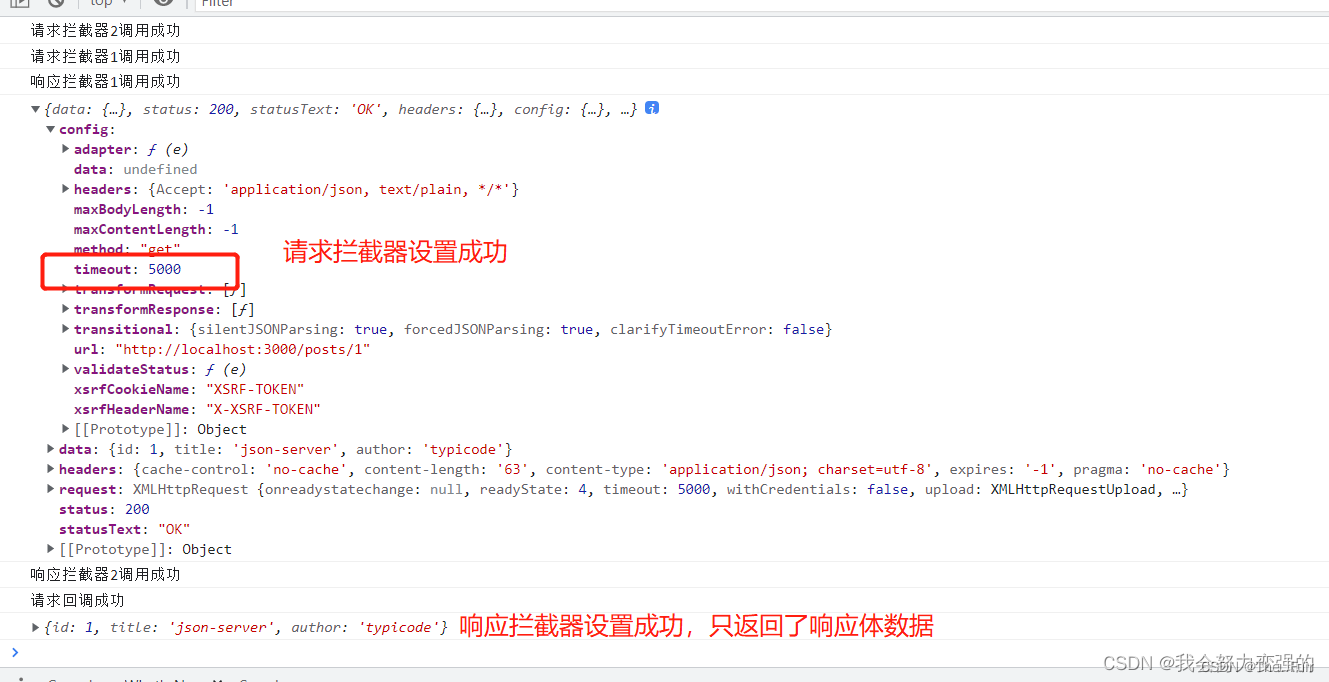
可以在请求拦截器中对config进行调整,比如添加一个超时什么的,可以在响应拦截器中对response返回值进行调整,比如我返回到回调函数中只想要响应体部分。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>axios拦截器</title> </head> <body> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> //这个是设置请求拦截器的api,传入两个回调,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调。 axios.interceptors.request.use( function(config){ console.log("请求拦截器1调用成功"); return config; }, function(error){ console.log("请求拦截器1调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error) } ) axios.interceptors.request.use( function(config){ //设置请求超时时间 config.timeout = 5000; console.log("请求拦截器2调用成功"); return config; }, function(error){ console.log("请求拦截器2调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error) } ) //这个是设置响应拦截器的api,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调 axios.interceptors.response.use( function(response){ console.log("响应拦截器1调用成功"); console.log(response); //返回到请求回调时,只要data数据 return response.data; }, function(error){ console.log("响应拦截器1调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error); } ) axios.interceptors.response.use( function(response){ console.log("响应拦截器2调用成功"); return response; }, function(error){ console.log("响应拦截器2调用失败"); return Promise.reject(error); } ) axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1") .then(function(response){ // console.log("请求回调成功"); console.log(response); }).catch(function(error){ console.log("请求回调失败"); }) </script> </body> </html>
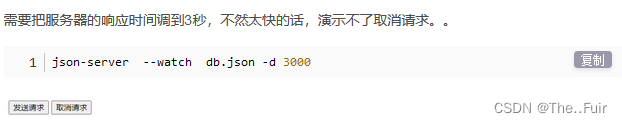
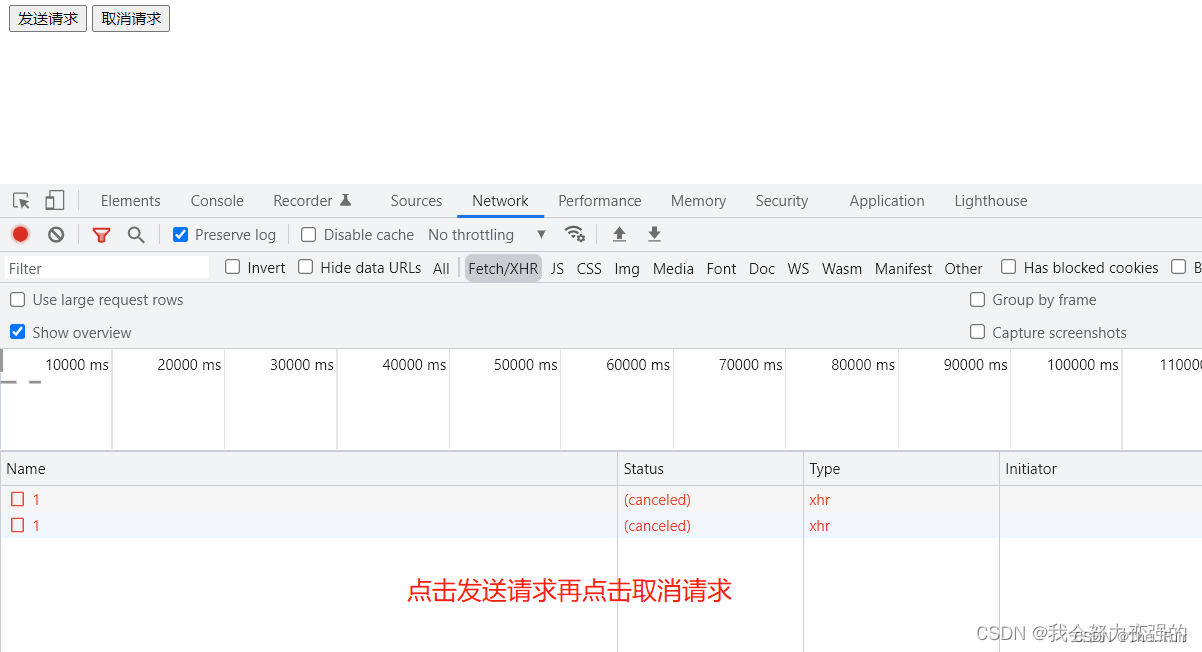
取消请求
取消请求就是发送了请求后,等待一段时间得不到回应,可以取消他。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>axios取消请求</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">发送请求</button> <button id="btn2">取消请求</button> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> //第一步:定义一个全局的cancel变量,初始值是null let cancel = null; document.getElementById("btn1").onclick = function(){ axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1", { //第二步:在请求的配置对象中,配置cancelToken属性值,并把函数的c参数赋值给全局变量cancel cancelToken:new axios.CancelToken(function(c){ cancel = c; }) }) .then(function(response){ // console.log(response); }).catch(function(error){ console.log("请求回调失败"); }) } document.getElementById("btn2").onclick = function(){ //第三步:调用cancel函数就是取消请求接收 cancel(); } </script> </body> </html>
实习打怪之路:axios的基本使用
最新推荐文章于 2024-03-26 15:38:52 发布

































 2131
2131











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








