0905
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/fu983531588/article/details/89597521
一、算法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getKthFromEnd = function (head, k) {
let p = head,
len = 0;
while (p) {
p = p.next;
len++;
}
p = head;
for (var i = 0; i < len - k; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
return p;
};
二、js
1. 什么是IIFE?如何使用?
IIFE表示立即调用函数表达式,是一个在定义时就会立即执行的js函数
(function () {
console.log(123);
})();
无需调用即可输出123
第一部分是包围在()里的一个匿名函数,这个函数拥有独立的词法作用域。可以避免外界访问IIFE中的变量,而且又不会污染全局作用域;
注意:
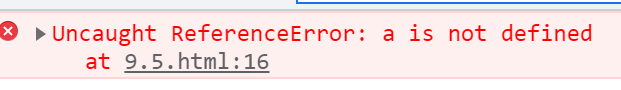
IIFE中的变量外界不能访问
(function () {
var a=12;
})();
console.log(a);
将IIFE分配给一个变量,不是存储IIFE本身,而是存储IIFE执行后返回的结果。
var result=(function () {
var a=12;
return a;
})();
console.log(result); //12
2. 什么是闭包?闭包有什么优点
闭包是包含被引用变量(函数)的对象
1 闭包可以延长局部变量的生存周期,使得函数内部的变量在函数执行完后,依然存活在内存中
2.让函数外部可以操作(读写)到函数内部的数据(变量/函数)
3. 什么是提升(变量提升/函数提升)?提升规则是什么
变量和函数在声明时会进行预解析,这个时候用关键词声明的变量会被提升。函数声明(不是用函数表达式声明)也会被提升
console.log(a);
var a = 3; //undefined
// 上述代码相当于
var a;
console.log(a);
a = 3;
提升规则:
- 变量提升
var 声明的变量,提升时只声明,不赋值,默认为undefined;不用关键字直接赋值的变量不存在提升
console.log('a=',a) //a=undefined
console.log('b=',b) // Uncaught ReferenceError: b is not defined
var a=1
b=6
变量重名,提升时不会重复定义;在执行阶段后面赋值的会覆盖上面的赋值;预解析的顺序是从上到下;
console.log('a=', a) // a=undefined
var a = 2
console.log('a=', a) //a=2
var a = 3
var a = 4
console.log('a=', a) // a=4
console.log('b=', b) //b= undefined
var b = 'b1'
- 函数提升
会连带函数体一起提升,不执行
console.log('a=',a) // a=function a() {console.log("func a()")}
function a() {
console.log("func a()")
}
函数的优先级高于变量,函数声明提前到当前作用域最顶端;
用函数表达式声明函数,会按照声明变量规则进行提升;
console.log('a=',a) // a=undefined
var a=function(){console.log('a1')}
var a=3
var a=4
var a=5
console.log(a)
var a=function(){console.log('a2')}
console.log('a=',a) // a= ƒ (){console.log('a2')}
函数执行时,函数内部的变量声明和函数声明也按照以上规则进行提升;
console.log('b=',b)
var a=3
function b(i){
console.log('a=',a)
var a=4
function a(){
console.log('fun a')
}
console.log('a=',a)
}
b()
let、const不存在提升
console.log('a=',a) //Uncaught ReferenceError: a is not defined
let a=4
--------------------
console.log('b=',b) // Uncaught ReferenceError: b is not defined
const b=5
4. delete命令的作用是什么?其局限性是什么
用于删除对象的某个属性;如果没有指向这个属性的引用,那它最终会被释放。成功删除的时候会返回 true,否则返回 false。
const classmate = {
name: 'qrs',
age: '11'
}
console.log(classmate.name);//qrs
delete classmate.name;
console.log(classmate.name);//undefined
局限:
- 如果你试图删除的属性不存在,那么delete将不会起任何作用,但仍会返回true
var Employee = {
age: 28,
name: 'abc',
designation: 'developer'
}
console.log(delete Employee.name); // returns true
console.log(delete Employee.age); // returns true
// 当试着删除一个不存在的属性时
// 同样会返回true
console.log(delete Employee.salary); // returns true
- 如果对象的原型链上有一个与待删除属性同名的属性,那么删除属性之后,对象会使用原型链上的那个属性(也就是说,delete操作只会在自身的属性上起作用)
function Foo() {
this.bar = 10;
}
Foo.prototype.bar = 42;
var foo = new Foo();
// 返回 true,因为删除的是 foo 对象的自身属性
delete foo.bar;
// foo.bar 仍然可用,因为它在原型链上可用。
console.log(foo.bar); //42
// 从原型上删除属性
delete Foo.prototype.bar; //true
// 由于已删除“ bar”属性,因此不能再从Foo继承它。
console.log(foo.bar); //undefined
- 任何使用 var 声明的属性(它被设置为不可设置)不能从全局作用域或函数的作用域中删除。
这样的话,delete操作不能删除任何在全局作用域中的函数(无论这个函数是来自于函数声明或函数表达式)
除了在全局作用域中的函数不能被删除,在对象(object)中的函数是能够用delete操作删除的。 - 任何用let或const声明的属性不能够从它被声明的作用域中删除。
var nameOther = 'XYZ';
// 通过以下方法获取全局属性:
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(window, 'nameOther');
// 输出: Object {value: "XYZ",
// writable: true,
// enumerable: true,
// configurable: false}
// 因为“nameOther”使用var关键词添加,
// 它被设置为不可设置(non-configurable)
delete nameOther; // return false
//在严格模式下,此操作会抛出异常
- 不可设置的(Non-configurable)属性不能被移除。这意味着像Math, Array, Object内置对象的属性以及使用Object.defineProperty()方法设置为不可设置的属性不能被删除。
var Employee = {};
Object.defineProperty(Employee, 'name', {configurable: false});
console.log(delete Employee.name); // returns false
- 删除一个数组元素时,数组的长度不受影响,即便删除的是数组的最后一个元素也是如此。不会那个元素还是被删除掉了的,他也不再属于这个数组。
var trees = ["redwood","bay","cedar","oak","maple"];
delete trees[3];
if (3 in trees) {
// 这里不会执行
}
5. 如何获取函数预期传入的参数个数
使用arguments可以获得
function numbers() {
console.log(arguments.length);//7
}
numbers(1,2,3,4,5,6,3);
6. eval命令的作用是什么
将传入的字符串当作js代码来执行
eval() 的参数是一个字符串。如果字符串表示的是表达式,eval() 会对表达式进行求值。如果参数表示一个或多个 JavaScript 语句,那么eval() 就会执行这些语句。
console.log(eval('2 + 2'));
// output: 4
console.log(eval(new String('2 + 2')));
// output: 2 + 2
console.log(eval('2 + 2') === eval('4'));
// output: true
console.log(eval('2 + 2') === eval(new String('2 + 2')));
// output: false
7. 遍历数组有哪些方式
map
// 一、会改变原数组
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
var newArr = arr.map(function (item, idnex) {
return item * item
})
console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
console.log(newArr) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
// 二、会改变原数组元素中对象的属性值
var arr = [{a: 1, b: 2},{a: 11, b: 12}]
let newARR = arr.map((item)=>{
item.b = 111
return item
})
console.log('arr数组',arr) // [{a: 1, b: 111},{a: 11, b: 111}]
console.log('newARR',newARR) // [{a: 1, b: 111},{a: 11, b: 111}]
// 三、不会改变原数组
var arr = [{a: 1, b: 2},{a: 11, b: 12}]
let newARR = arr.map((item)=>{
return {
...item,
b:111
}
})
console.log('arr数组',arr) // [{a: 1, b: 2},{a: 11, b: 12}]
console.log('newARR',newARR) // [{a: 1, b: 111},{a: 11, b: 111}]
// 四、使用try...catch...可以跳出循环
try {
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.map((item) => {
//跳出条件
if (item === 3) {
throw new Error("LoopTerminates");
}
console.log(item);
return item
});
} catch (e) {
if (e.message !== "LoopTerminates") throw e;
};
// 1 2
filter()
遍历数组,过滤出符合条件的元素并返回一个新数组
var arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '买笔', done: true },
{ id: 2, name: '买笔记本', done: true },
{ id: 3, name: '练字', done: false }
]
var newArr = arr.filter(function (item, index) {
return item.done
})
console.log(newArr)
// [{ id: 1, name: '买笔', done: true },{ id: 2, name: '买笔记本', done: true }]
for
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i])
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
for…in…
遍历输出的是数组下标或者对象属性名
var arr = ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '~']
for(let key in arr) {
console.log(key)
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
let obj = {
a: 11,
b: 22,
c: 33
}
for(let key in obj) {
console.log(key)
}
// a b c
for…of
var arr = ['我', '是', '谁', '我', '在', '哪']
for(var key of arr) {
console.log(key)
}
// 我 是 谁 我 在 哪
forEach()
function logArrayElements(element, index, array) {
console.log("a[" + index + "] = " + element);
}
//索引 2 被跳过了,因为在数组的这个位置没有项
[2, 5, , 9].forEach(logArrayElements);
// log :a[0]=2,a[1]=5,a[3]=9
some
遍历数组,只要有一个以上的元素满足条件就返回 true,否则返回 false
var arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '买笔', done: true },
{ id: 2, name: '买笔记本', done: true },
{ id: 3, name: '练字', done: false }
]
var bool = arr.some(function (item, index) {
return item.done
})
console.log(bool) // true
every
遍历数组,每一个元素都满足条件 则返回 true,否则返回 false
var arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '买笔', done: true },
{ id: 2, name: '买笔记本', done: true },
{ id: 3, name: '练字', done: false }
]
var bool = arr.every(function (item, index) {
return item.done
})
console.log(bool) // false
find(ES6)
遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 undefined
var arr = [1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6]
var num = arr.find(function (item, index) {
return item === 3
})
console.log(num) // 3
findIndex(ES6)
遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素的索引,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 -1
var arr = [1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6]
var num = arr.findIndex(function (item) {
return item === 3
})
console.log(num) // 4
8. forin遍历数组有什么缺点
效率很低。
9. 逗号(",")运算符的作用是什么
对它的每个操作数求值(从左到右),并返回最后一个操作数的值。
let x = 1;
x = (x++, x);
console.log(x);//2
10. 将字符串转为数字的方法有哪些
- 转换函数
js提供了parseInt()和parseFloat()两个转换函数。前者把值转换成整数,后者把值转换成浮点数。 - 强制类型转换
Boolean(value)——把给定的值转换成Boolean型;
Number(value)——把给定的值转换成数字(可以是整数或浮点数;
String(value)——把给定的值转换成字符串。
三、react
实现按钮在登录与注册之间的相互切换,且渲染不同的标题。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>0905</title>
<style>
button {
background-color: pink;
border: none;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="test"></div>
<script></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入react-dom,用于支持react操作DOM -->
<script
type="text/javascript"
src="../js/react-dom.development.js"
></script>
<!-- 引入babel,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class Change extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { isregister: false };
// 在回调中也能使用this
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState((state) => ({
isregister: !state.isregister,
}));
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.state.isregister?'注册成功 请登录':'请注册'}</h1>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
{this.state.isregister ? "登录" : "注册"}
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Change />, document.getElementById("test"));
</script>
</body>
</html>























 2650
2650











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








